| A | B |
|---|
| cell theory | all living things are made of cells, cells come from pre-existing cells, the cell is the most basic unit of life |
| Robert Hooke | 1st to observe living cells under a microscope, cork |
| Leeuwenhook | made better microscope, observed cells in more detail |
| Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow | their work developed cell theory |
| prokaryotic cells | simple, no nucleus or membrane bound organelles |
| eukaryotic cells | have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, complex |
| cytoskeleton | network of proteins that supports and shapes cells, acts as a highway for transport |
| nucleus | command center for cell, contains DNA |
| nucleolus | makes ribosomes |
| rough ER | makes and modifies secretory proteins |
| smooth ER | makes lipids, detoxifies drugs |
| Golgi apparatus | modifies, packages, and transports proteins and lipids |
| ribosomes | make proteins from amino acids |
| vesicles | divide some materials from the rest of the cell, transport |
| mitochondria | supply energy (ATP) to the cell |
| vacuole | fluid-filled sac used for storage |
| lysosome | contain enzymes and digest food and waste |
| cell wall | plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria have this layer that protects and supports the cell |
| chloroplasts | carry out photosynthesis |
| centrosomes | produce microtubules |
| centrioles | help in cell division, form cilia and flagella |
| cilia | move liquid across a cell |
| flagella | move the cell, act like a whip |
| central vacuole | in plants, stores and controls water, digests waste |
| the Protein Process involves | nucleus, ribosomes, rough ER, smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, plasma membrane |
| Protein Process includes which molecules? | 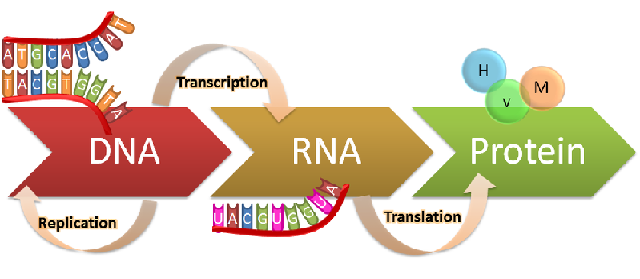 |
| the waste process involves | rough ER, smooth ER, Golgi, vesicles, lysosome, cell membrane |
| the ATP process involves | chloroplast, cytoplasm, mitochondria, cell membrane, cytoskeleton |