| A | B |
|---|
| cell (plasma) membrane | forms a boundary between a cell and the outside environment and controls the passage of materials into and out of a cell |
| phospholipid | a molecule composed of a charged phosphate group, glycerol, and two fatty acid chains |
| phospholipid head | the glycerol and phosphate--hydrophilic |
| phospholipid tails | 2 fatty acid chains--hydrophobic |
The molecules labeled C, 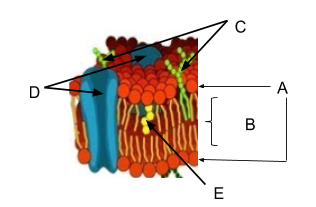 | carbohydrates |
The molecules labeled D,  | proteins |
The part of the molecules labeled A,  | phospholipid head (hydrophilic) |
The bracketed part of the membrane (B),  | fatty acid (hydrophobic) tails |
The molecule labeled E,  | cholesterol |
| cholesterol | affects the fluidity of the membrane |
| proteins | used to transport substances and as membrane receptors |
| carbohydrates | used in cell communication and identification |
| fluid mosaic model | describes the membrane as flexible rather than rigid, with a variety of patterns |
| selective permeability (semipermeable) | it allows some, but not all, materials to cross |
| passive transport | the movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy input from the cell |
| diffusion | movement of molecules of a fluid or gas from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration |
| concentration gradient | a difference int he concentration of a substance from one location to another |
| osmosis | diffusion of water molecules from high concentration of water (low solute) to low concentrations of water (high solute) |
| isotonic | when a solution has the same concentration of solute as a cell or another solution, equal amounts of water enter and leave |
| hypertonic | higher concentration of solute than a cell or another solution |
| hypotonic | lower concentration of solute than a cell or another solution |
| an animal cell in a hypertonic solution | will shrivel |
| an animal cell in a hypotonic solution | will swell and possibly burst |
| a plant cell in a hypertonic solution | will have a shriveled vacuole and organelles in the center, plasmolysis |
| a plant cell in hypotonic solution | will have a swelled vacuole and organelles pushed against the cell wall |
| facilitated diffusion | diffusion of molecules across a membrane through transport proteins down their concentration gradients |
| active transport | drives molecules (ions) across a membrane from low to high concentration and requires energy |
| endocytosis | process of taking in liquids or fairly large molecules into a cell by engulfing them into a membrane vesicle |
| exocytosis | release of large substances out of a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane |
| phagocytosis | a type of endocytosis where the cell membrane engulfs large particles--food or bacteria, "cell eating" |
| pinocytosis | a type of endocytosis where the cell engulfs a large amount of liquid, "cell drinking" |
| plasmolysis | plant cells lose water from their vacuole and the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall in a hypertonic solution |