| A | B |
|---|
| chemical energy | a form of potential energy in food |
| heat | a form of unusable energy |
| 1st law of thermodynamics | energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form |
| 2nd law of thermodynamics | energy cannot be changed from one form to another without a loss of usable energy |
| metabolism | the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur in a cell |
| reactants | substances that participate in a reaction (starting materials) |
| products | substance that are the results of a reaction |
| free energy | delta G, the energy left to do work after a chemical reaction has occurred |
| exergonic reaction | spontaneous, - delta G, release energy, products are at a lower energy state than reactants |
| endergonic reaction | require an input of energy to occur, + delta G, products higher energy state than reactants |
| ATP (adenosine triphosphate) | energy currency of the cell |
| coupled reactions | where an endergonic reaction uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to occur, or where an exergonic reaction is coupled to the synthesis of ATP from ADP |
| metabolic pathway | a series of linked reactions where the product of one enzyme becomes a reactant for the next |
| substrates | reactants in an enzyme catalyzed reaction |
| enzyme-substrate complex | an intermediate complex formed when the substrate binds during an enzyme catalyzed reaction |
| active site | the area on the enzyme where the substrate binds |
| induced fit model | the active site undergoes a slight change upon binding the substrate, allows the substrate to fit better |
| energy of activation (E-A) | the energy that must be added to allow molecules to react with one another, lowered by enzymes |
| denaturation | a factor that alters the shape of the enzyme (unfolds it) so that it cannot bind substrate |
What best describes this graph?, 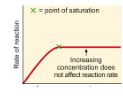 | Increasing the substrate concentration will increase the enzyme activity up until the enzyme is saturated with substrate, then further addition of substrate will not increase the enzyme activity |
What best describes this graph?, 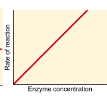 | Adding more enzyme continues to increase enzyme activity |
What best describes this graph?, 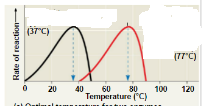 | Different enzymes have different optimum temperatures at which they work best |
What best describes this graph?, 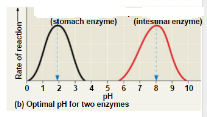 | Different enzymes have different optimum pHs in which they work best. |
| cofactors | an inorganic ion or a nonprotein organic molecule that binds to the active site and is needed for proper functioning |
| conenzymes | a nonprotein organic molecule (usually a vitamin) that binds to the active site and is necessary for proper function |
| inhibition | when an inhibitor binds to an enzyme and decreases its activity |
| noncompetitive inhibition | the inhibitor binds somewhere else on the enzyme and changes its shape so that it can no longer bind substrate |
| competitive inhibition | the inhibitor resembles the substrate and competes with the substrate for binding to the active site, lowering enzyme activity |
| redox reaction | A reaction in which one substance is oxidized and another is reduced. |
| oxidation | a loss of electrons and possibly hydrogen ions, lower energy |
| reduction | a gain in electrons and possibly hydrogens, making the molecule a higher energy state |