| A | B |
|---|
| The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane (from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration) is called ___. | osmosis |
| In a salt water solution, the salt is known as the ___. | solute |
| If a cell membrane allows glucose to pass through it, then the cell membrane is said to be ____ to glucose. | permeable, 
|
| In a salt water solution, the water is known as the ____. | solvent |
| The movement of particles across a cell membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is known as ____. | diffusion |
| The cell membrane is said to be _______ permeable to substances because it lets some pass through but not others. | selectively |
| The type of substances that can most easily diffuse across a cell membrane are ____ substances. | small non-polar substances |
| The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a(n) __________ bilayer with embedded _______. | phospholipid, proteins, 
|
| Larger molecules usually pass through _____ to get into or out of a cell. | Transport proteins (Like channel proteins and carrier proteins. Polar molecules and ions also usually need to go through transport proteins because they get attracted to and stuck to the phosphate head of the phospholipids, and therefore don't pass through the lipid bilayer even if they are small enough) |
| Cells will shrink if placed into a(n) _____ solution. | hypertonic |
| When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ is taking place. | active transport |
| Cells will grow bigger if placed in a(n) ____ solution. | hypotonic (think about big fat hippo to help you remember that "hypo"tonic solutions cause cells to try and get bigger) |
When pressure increases in plant cells, why don't the cells usually burst?, 
| Plant cells have a tough cell wall that keeps the cell from expanding enough to burst. |
| If a solution is 6% solutes, it will be ____ % water. | 94 |
| If a solution is 90% water, it will have ___ % solutes. | 10 |
| A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic |
| Active transport requires _____. | energy |
| If a substance is crossing a cell membrane due to active transport, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ____ concentration. | low, high |
| If a substance is diffusing across a cell membrane, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration. | high, low |
| The four types of proteins found in cell membranes are: | transport, receptor, marker, and pumps |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows larger molecules and ions to pass through by facilitated diffusion is called a ____ protein. | Transport protein (Can be called a channel protein if it looks like a tunnel and carrier protein if it takes something in, changes shape, and spits it out on the other side) |
| The type of protein that a hormone could attach to on the outside of a cell membrane is called a ____ protein. | receptor protein |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows your body to recognize your own cells is called a ____ protein. | marker protein |
The process pictured below is called ____., 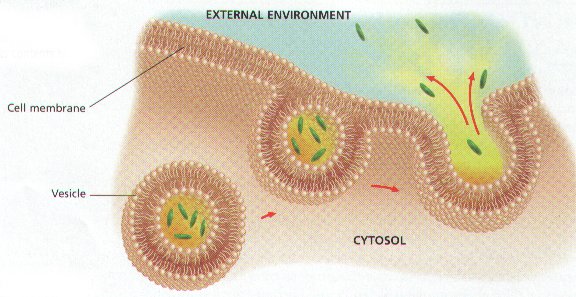 | exocytosis,  , , 
|
| A type of protein that travels through the blood stream and attaches to receptor proteins on a cell's surface in order to deliver a chemical message is known as a ____. | hormone |
The process pictured below is called ____., 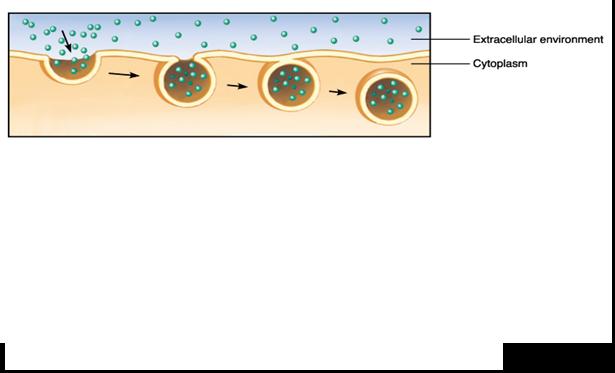 | endocytosis,  , , 
|
| When large molecules need the help of transport proteins (like channel and carrier proteins) to cross the cell membrane, the process that is occurring is called ______. | facilitated diffusion |
| Name 3 types of active transport. | protein pumps, endocytosis and exocytosis. |
| A special type of transport protein that moves molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration is called a(n) ___. | protein pump |
| True or False: "Both active and passive transport work to cause equilibrium of substances on each side of the cell membrane. | FALSE (While passive transport does do this, active transport rarely does this. Active transport usually moves substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration, making one side of the membrane have an even higher concentration while the other side gets an even lower concentration. This is the opposite of moving towards having even concentrations, a.k.a. equilibrium, on both sides of the membrane) |
| When water is the substance that is diffusing across a cell membrane, the process is referred to as ___. | osmosis |