| A | B |
|---|
| The smaller structures inside the cell which have specific functions are called __. | organelles |
| Which cell structure is located only in animal cells and helps the cell to divide and reproduce? | centriole, 
|
| Which organelle stores the DNA of a cell? | nucleus |
| The dark structure located inside the nucleus that manufactures ribosomes is called ____. | the nucleolus, 
|
| What is located just inside the cell wall of plant cells? | the cell membrane |
| The ______ doesn't allow DNA to leave the nucleus. | nuclear membrane (a.k.a. nuclear envelope) |
| Which organelle do plants use for photosynthesis? | chloroplasts, 
|
| Long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins are known as ___. | chromosomes, 
|
| Which part of the cell regulates what enters or leaves the cell? | cell membrane |
| Which pigment helps plants capture energy from the sun? | chlorophyll, 
|
| The liquid interior of the cell is called the ____. | cytoplasm, 
|
| The network of tube-like protein filaments that help give cells shape and support and also help with movement is called the ___. | cytoskeleton, 
|
| The structure that modifies, sorts and moves complex molecules made in the endoplasmic reticulum to other parts of the cell (or even to the outside of the cell) is called the ____. | golgi |
| The organelle that specializes in transferring the chemical energy in food into molecules that the cell can more easily use for energy (ATP) is called the ___. | mitochondrion (plural is mitochondria), 
|
| (True or false) Mitochondria are found only in animal cells. | False (plants need mitochondria also to break down the food they made during photosynthesis using the chloroplasts), 
|
| The organelle where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported (sent out of) the cell is called the ____. | endoplasmic reticulum, 
|
| The organelle that acts like a storage center is called a(n) ___. | vacuole |
| The small organelle that serves as the site where proteins are put together is called the ___. | ribosome, 
|
| The organelle that contains strong enzymes for breaking down food molecules and recycling old cell parts is called the __. | lysosome, 
|
The highlighted portion of this cell is called a ______.,  | cell wall |
The small green organelles in this picture are ___., 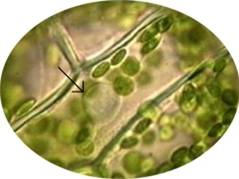 | chloroplasts, 
|
The highlighted portion of this cell is called the ______., 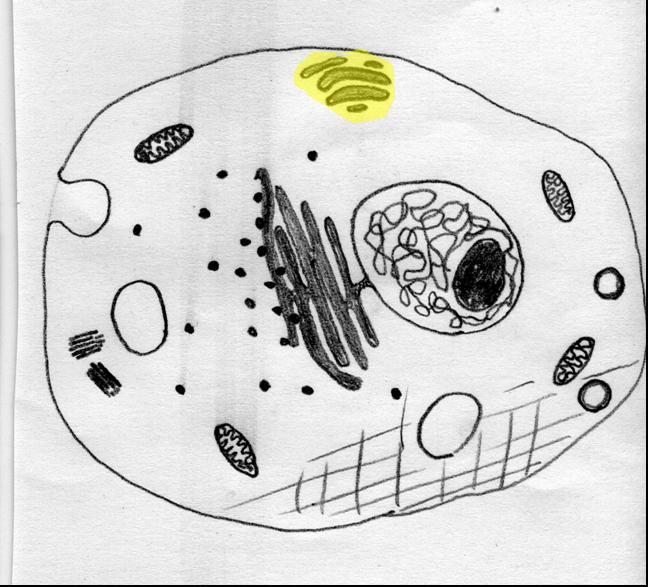 | golgi |
The short hair-like structures that help some single-celled organisms (like the one pictured below) swim, and that are also found on cells lining our throats, are called ___,  | cilia, 
|
The longer tail-like structures that help some single-celled organisms (like the one pictured below) are called ___.,  | flagella, 
|
| Cells that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles are _____ | Prokaryotic |
______ electron microscope produce 2-dimensional images like the one below.,  | transmission |
_____ electron microscopes produce 3-D images like the one below,  | scanning |
| Cells with a nucleus (and other membrane-bound organelles) are __. | eukaryotic, 
|
| The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane (from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration) is called ___. | osmosis |
| In a salt water solution, the salt is known as the ___. | solute |
| If glucose can enter a cell through the cell membrane, the ___ is said to be permeable. | cell membrane, 
|
| The movement of particles across any part of the cell membrane, from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is known as ____. | diffusion |
| _____ are arranged in a bilayer and make up most of the cell membrane | phospholipids, 
|
| Larger molecules, polar molecules, and charged particles (ions) usually pass through _____ proteins to get into or out of a cell. | transport |
| Cells will shrink if placed into a _____ solution. | hypertonic |
| When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ transport is taking place. | active |
| Cells will grow bigger or turgor pressure will increase (in plant cells) if placed in a ____ solution. | hypotonic |
| A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic |
| The type of protein that a hormone could attach to on the outside of a cell membrane is called a ____ protein. | receptor |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows your body to recognize your own cells is called a ____ protein . | marker |
The process pictured below is called ____., 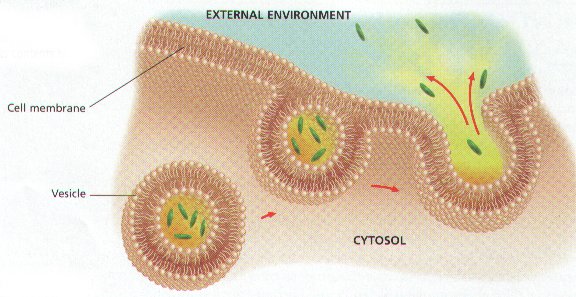 | exocytosis, 
|
The plant cells pictured below have been soaking in a ____ solution.,  | hypertonic |
| A type of protein that travels through the blood stream and attaches to receptor proteins on a cell's surface in order to deliver a chemical message is known as a ____. | hormone |
The process pictured below is called ____., 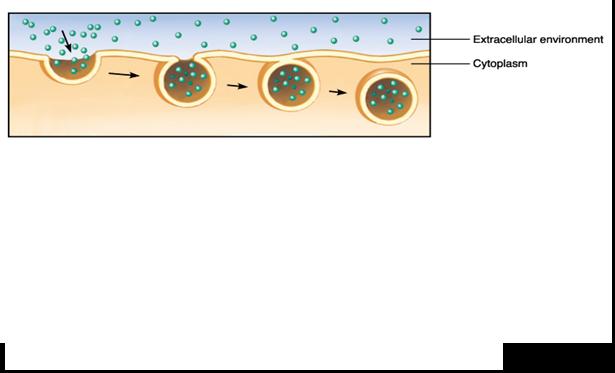 | endocytosis, 
|
| When large molecules need the help of protein channels to cross the cell membrane, the process that is occurring is called ______. | facilitated diffusion |
| The type of cell membrane protein that moves molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration is called a ___. | pump |
| Muscle, connective and nerve are types of ____ in the body. | tissues |
| Heart, lungs, pancreas, and liver are examples of ____ in the body. | organs |
| A group of similar cells that perform a particular function in the body is called ___. | a tissue |
| True or False: "Only passive transport works to cause equilibrium of substances on each side of the cell membrane. Active transport does not. | True |