| A | B |
|---|
| gives support, shapes and protects a plant cell | cell wall |
| chromosomes are made of this type of nucleic acid | DNA |
| found in the nucleus of a cell, contains genes | chromosomes |
| use information in DNA to synthesize proteins | ribosomes |
| proteins are made up of monomers called.. | amino acids |
| directs all cell activities | nucleus |
| the vacuoles found in plant cells function to | store wastes, food and water |
| convert chemical energy in glucose to usable energy for the cell | mitochondria |
| convert solar energy, water and carbon dioxide into chemical energy | chloroplasts |
| fluid part of cell between cell membrane and nuclear membrane | cytoplasm |
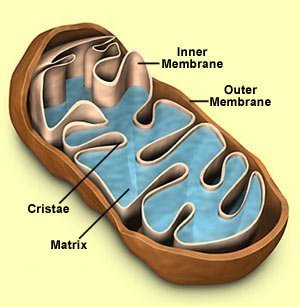 | mitochondria (picture) |
 | endoplasmic reticulum (picture) |
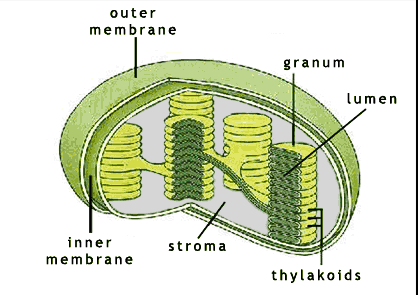 | chloroplast (picture) |
 | vacuole (picture) |
| function of the endoplasmic reticulum | assembles proteins and lipids |
| the chloroplasts contain this pigment | chlorophyll |
| cell wall is made of this carbohydrate | cellulose |
| this structure allows a sperm and some bacteria cells to move | flagella |
| paramecium move using these structures | cilia |
| structure within nucleus that helps make ribosomes | nucleolus |
| nucleus | prokaryotic organism lacks this structure |
| example of a prokaryotic organism | bacteria |
| term used to describe the process of cells getting special jobs | differentiation |
| unicellular | organism consists of only one cell |
| organelles present in animal cells but lacking in plant cells | lysosome and centrioles |
| cytoskeleton | gives shape to the cell |
| outer membrane of nucleus | nuclear envelope |
| granular material visible within nucleus that becomes chromosomes | chromatin |
| cell membrane | all cells are surrounded by this structure |
| regulates what enters and leaves the cell | cell membrane |
| specialized structures found inside of cells | organelles |
| Discovered all plants are made of cells | Matthias Schleiden |
| Discovered animal are made of cells | Theodor Schwann |
| Discovered that cells come from existing cells | Rudolph Virchow |
| one of the three parts of the cell theory | cells are the basic units of structure and function of living things |
| Looked at cork and called the compartments cells | Robert Hook |
| made microscope and saw tiny organisms in pond water | Anton van Leeuwenhoek |
| eukaryotic organisms have cells that contain this structure | nucleus |
| golgi apparatus | modifies, sorts and packages proteins and lipids |
| centrioles | organizes cell division in animal cells |
| lysosomes | contain digestive enzymes break down macromolecules |