| A | B |
|---|
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from the glycolysis stage? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose that goes through glycolysis. |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from chemical reactions in the Krebs Cycle? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose during the Krebs Cycle. |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using the high energy electrons from one molecule of glucose during the electron transport chain? | 32 (can be as high as 34 in some cases) |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of glycolysis occur? | In the cytosol (cytoplasm) |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of the Krebs Cycle occur? | In the mitochondria |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of the electron transport chain occur? | In the mitochondria |
| What is the only stage in cellular respiration that requires molecular oxygen? | The electron transport chain. |
| Why is oxygen needed during aerobic cellular respiration? | Oxygen is needed to take the electrons away after they go through the electron transport chain. (If they don't get taken away, the electron transport chain gets clogged with electrons and stops working, and then the Krebs cycle stops working too. Glycolysis can keep working to produce 2ATP per molecule of glucose by switching over to a process called fermentation) |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is available? | 36 (can be as much as 38 in some organisms or cell types) |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is NOT available? | Only 2 (by using fermentation to keep glycolysis going) |
| Which of the three stages of cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide as a waste product? | Krebs Cycle |
| Which of the three stages of cellular respiration produces water as a waste product? | The electron transport chain. |
| What is the major difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic fermentation? | Aerobic cellular respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic fermentation does not. |
| What are the two main reactants of aerobic cellular respiration? | Glucose and oxygen (these are the reactants of cellular respiration, and happen to be the products of photosynthesis. Remember, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are basically opposites of each other), 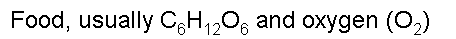 |
| What are the two main products of aerobic cellular respiration? | carbon dioxide and water (these are the products of cellular respiration, and happen to be the reactants of photosynthesis. Remember, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are basically opposites of each other),  |
| How many ATP can be generated from one molecule of glucose under anaerobic conditions? | 2 (Two ATP can be generated per molecule of glucose under anaerobic conditions using a process called fermentation that keeps glycolysis going). |
What is the name of this organelle?,  | mitochondria,  |
What is the area labeled D called?,  | The matrix,  |
What is letter A pointing to?,  | The outer membrane of the mitochondrion.,  |
What is the letter B pointing to?,  | The inner membrane of the mitochondrion,  |
What is the area labeled F called?,  | That would be the cytoplasm of the cell (it's where the reactions of glycolysis occur.),  |
Where would the proteins involved with the electron transport chain be located?,  | B,  |
Where would the Kreb's Cycle take place?,  | D,  |
Where would glycolysis take place?,  | F,  |
Which letter indicates where aerobic cellular respiration takes place?,  | B,  |
Which letter refers to where glycolysis and fermentation take place?,  | I,  |
What does letter B refer to?,  | a mitochondrion,  |
What does letter I refer to?,  | The cytoplasm,  |
| What do humans produce if they are not getting enough oxygen to process their food aerobically? | Lactic acid |
| A method for getting energy out of food that produces lactic acid or alcohol when no oxygen is available. | Fermentation |
| What do yeast and bacteria usually produce when they break down food under anaerobic conditions? | alcohol (and carbon dioxide) |
| What is the basic chemical equation for the overall process of aerobic cellular respiration? | 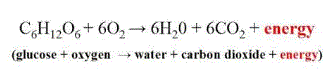 |
| The overall chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration is the exact OPPOSITE of the overall chemical equation for _____. | photosynthesis (The reactants of cellular respiration are the products of photosynthesis and visa versa). |