| A | B |
|---|
| The Parthenon | Greek temple built at the Acropolis in Athens dedicated to the goddess Athena |
| Theocracy | Where the government leader is also the religious leader |
| Pharaoh | The Title Egyptian leaders took for themselves, they were believed to be part God |
| Hinduism | Oldest religion founded in India, it features many different versions of the same god or universal spirit |
| Vedas and Upanishads | The sacred texts of Hinduism |
| Caste System | A rigid social structure in India, in which society is dicided into four seperate classes and there is no social mobility |
| Dharma | this was the duty in life that Hindus were supposed to follow if they wanted to accumulate good Karma. |
| Reincarnation | the belief in a cycle of life where one's spirit is reborn when they die into another form |
| Zoroastrianism | A religion founded in Persia that depicted life as a struggle between good and evil. It may have influenced Christianity and Judaism |
| The Four Noble Truths | The basic principles or philosophy of Buddhism. |
| The Eightfold Path | Part of the Four Noble Truths, this was what Buddhists were supposed to follow if they wanted to end their desires and reach nirvana. |
| Monotheism | Belief in one god |
| Polytheism | Belief in many gods |
| The Ten Commandments | from the Hebrews, and Moses this described moral and religious conduct |
| The Hebrews | The group who founded the first monotheisic religion |
| Jerusalem | the capital of the Kingdom of Israel constructed by David |
| The Diaspora | means "the scattering" and represents the state that the Hebrews lived in after being forced out of their homeland |
| The Aeneid | written by Virgil it is a great piece of Roman literature and is somewhat similar to the Odyssey |
| The Pantheon | Temple in Rome dedicated to all of the gods |
| Hinduism | Oldest religion founded in India, it features many different versions of the same god or universal spirit |
| Caste System | A rigid social structure in India, in which society is dicided into four seperate classes and there is no social mobility |
| Dharma | this was the duty in life that Hindus were supposed to follow if they wanted to accumulate good Karma. |
| Karma | Hindu idea that all thoughts and actions have consequences |
| Reincarnation | the belief in a cycle of life where one's spirit is reborn when they die into another form |
| The Four Noble Truths | The basic principles or philosophy of Buddhism. |
| The Eightfold Path | Part of the Four Noble Truths, this was what Buddhists were supposed to follow if they wanted to end their desires and reach nirvana. |
| The Aryans | Invaders of India wrote the Vedas and contributed to the establishment of the caste system |
| Siddhartha Guatama | Founder of Buddhism, He was the Buddha or the "enlightened" one |
| Nirvana | According to Buddhists this was the state where you would eliminate your desires and end suffering. |
| The Analects | collection of writings that describe confucianism |
| Brahman | The Universal spirit of Hinduism that takes many forms |
| Vishnu | The preserver god of hindusim |
| Shiva | the destroyer/rejuvenator god of Hindusim |
| Ganesha | the elephant headed god of overcoming obstacles |
| The Tao Te Ching | important text of Taoism |
| Shinto | The Native Religion of Japan based on worshiping "Kamis" or spirits in nature |
| Torii | Gates that symbolize entrances to Shinto shrines in Japan |
| Siddhartha Guatama | founder of Buddhism |
| Confucius | founder of philosophy based on code of politeness |
| Lao Tzu | founder of Taoism |
| The Eightfold Path | the steps in Buddhism for achieving enlightenment |
| Nirvana | the end of desires, it is the goal of Buddhism |
| Asoka | Indian Emperor responsible for spreading Buddhism to China and Japan |
| Taoism | Chinese Philsophy based on following "the way" and living a simple life |
| Confucianism | Chinese philosophy based on a code of politeness, an emphasis on education, and respect for elders |
| Buddhism | religion/philosophy based on ending desires and achieving enlightenment |
| Yin and Yang | Chinese symbol that represents a balance between opposite forces |
| Mandate of Heaven | Chinese belief that a dynasty ruled only with approval of gods |
| Abraham | Hebrew leader credited with being first to believe in one god |
| Moses | Hebrew leader, led the Exodus and contributed the Ten Commandments |
| Pantheon (image) |  |
| Buddha (image) |  |
| Caste System (image) | 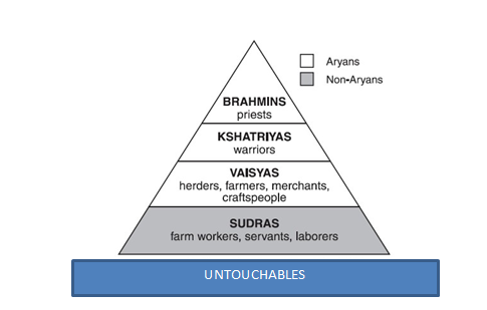 |
| Parhenon |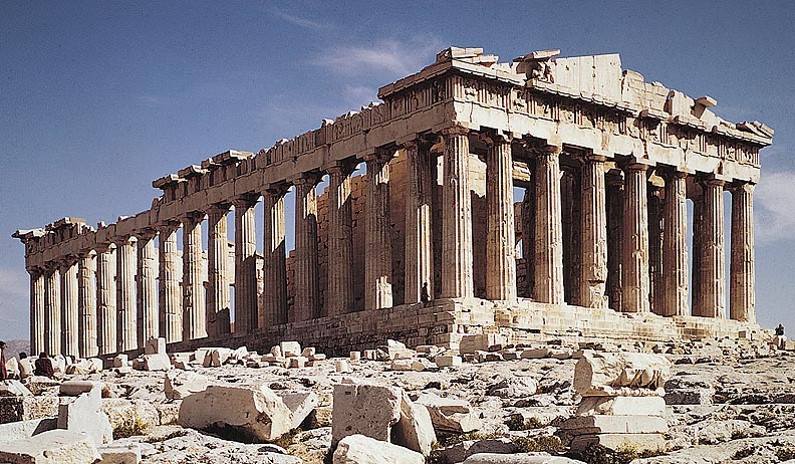  |
| Torii Gate (image) |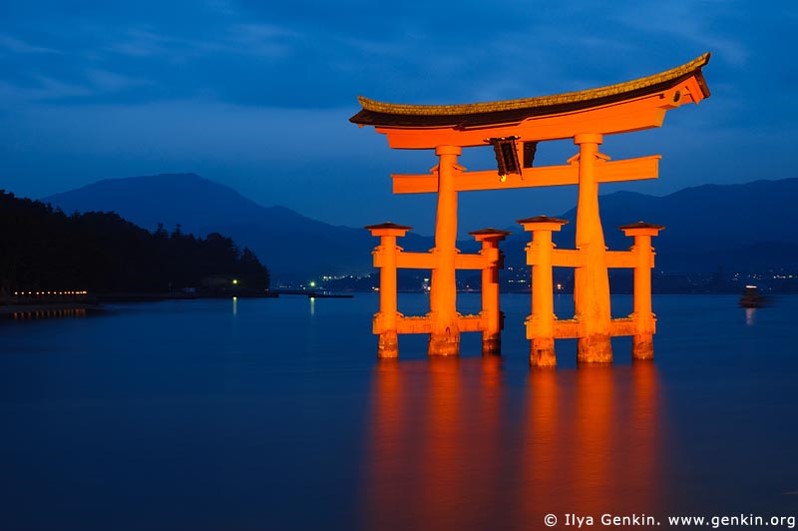  |
| Yin and Yang (image) |  |