| A | B |
|---|
| During which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replicate? | interphase |
| The ____ is a series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. | cell cycle |
| Identical sister chromatids are held together at a narrow region called the ____. | centromere |
| The centromere region is where _____ are held together. | sister chromatids |
| During which stage of mitosis do sister chromatids start to separate? | anaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis are sister chromatids lined up along the center of the cell? | metaphase (think metaphase = middle) |
| During which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes condense to become visible? | prophase |
| Centrioles help organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called ____ that help pull the chromosomes apart. | spindle fibers |
| In animal cells, ________ help organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called the spindle that help pull the chromosomes apart. | Centrioles |
| The division of the cytoplasm itself is called ___. | cytokinesis |
| During which stage of mitosis are the chromosomes divided into the two opposite ends of the cell and the nuclear membrane reforms? | telophase |
| During normal cell division, a human cell with 46 chromosomes would produce two daughter cells with ___ chromosomes each. | 46 |
During which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?,  | Prophase |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?,  | Metaphase |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?,  | Anaphase |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?,  | Telophase |
Which stage of the cell cycle is depicted in the picture below?,  | Interphase |
The structures labeled A are,  | sister chromatids,  |
The structures labeled B are,  | spindle fibers,  |
The area labeled C is called the ___.,  | centromere,  |
| Uncontrolled cell division is also known as ______. | cancer |
| When cells divide over and over again because of cancer, a lump of cells called a ____ forms. | tumor |
| Gametes are produced by the process of ___. | meiosis |
| Another word for sex cell is ___. | gamete |
| During which stage of meiosis do chromosomes form tetrads? | prophase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell? | metaphase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids separate from each other? | anaphase II |
| When does the DNA replication involved with meiosis occur? | Interphase |
| What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans? | 46 (also written as 2n=46) |
| What is the haploid number for humans? | 23 (also written as n=23) |
| _________ chromosomes are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, but are not identical. | Homologous |
| _________ are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, and are identical. | Sister chromatids |
| A _____ is a segment of DNA that has the instructions for making one protein. | gene |
| A chromosome is made of ___ DNA molecule(s) | one |
| When two homologous chromosome pairs are lined up right next to each other during meiosis, they are referred to as a ___. | tetrad |
| During which stage of meiosis might crossing over occur? | prophase I |
| When homologous chromosomes are lined up next to each other during meiosis, they might swap pieces of DNA. This phenomenon is called ___. | crossing over |
| Crossing over during meiosis is important because it increases ___. | genetic variation (= the number of different chromosomes, and therefore different combinations of traits, that offspring can inherit) |
Which diagram is mitosis?,  | Mitosis is on the left,  |
When chromosomes are lined up like this during meiosis, what are they referred to as?, 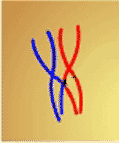 | A tetrad,  |
Which process from meiosis is shown below?, 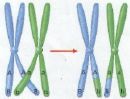 | The picture shows "crossing over" and it usually happens during prophase I.,  |
| As a cell becomes larger, its volume increases _____ than its surface area. | faster |
| As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases _____ than its volume. | slower |
| The rate at which a cell can get rid of waste is determined by its ____. | surface area |
| The amount of nutrients that a cell needs is determined by its ___. | volume |
What is the color of the curve that would represent volume in a graph of volume versus surface area as cells grow?, 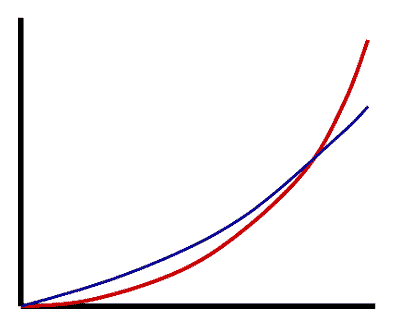 | the red curve,  |
| A student notices bubbles coming off of an aquatic plant when it is exposed to bright sunlight. These bubbles are most likely ___. | oxygen (because the plant is doing photosynthesis), 
|
What are the two main things produced by photosynthesis?, 
| oxygen and glucose (the sugars can be changed into starch, cellulose, proteins, lipids, or nucleic acids later on) |
What are two main molecules needed for photosynthesis to occur?, 
| water and carbon dioxide |
| Which type of pigment is used to capture most of the sun's energy? | chlorophyll, 
|
| Most plants appear green because chlorophyll ____ green light. | reflects |
| The region of the chloroplast that is outside of the thylakoids is called the ___. | stroma |
| Where in the chloroplast can chlorophyll be found? | In the thylakoids |
In which part of the chloroplast do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place?, 
| the thylakoid (within the membrane of the thylakoid) |
Where do the electrons that travel through the electron transport chain of photosynthesis originally come from?, 
| Water molecules (The electrons that absorb energy from the sun and then travel through the electron transport chain (ETC) must be replaced. They are replaced by stripping water molecules of their low energy electrons that then absorb energy (becoming high energy electrons) and travel through the ETC. The water molecules that lost electrons fall apart, producing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions) |
The stage of photosynthesis during which water is needed is the ___ reactions, 
| light-dependent reactions |
The stage of photosynthesis during which carbon dioxide is needed is the ____ reactions., 
| light-independent reactions) |
The stage of photosynthesis during which oxygen is produced is the ____ reactions, 
| light-dependent reactions |
The stage of photosynthesis that the energy from ATP is used to produce high energy sugars is the ___ reactions, 
| light-independent |
| Which product of the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis is needed during the Calvin Cycle? | ATP |
The Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis is another name for the _____ reactions, 
| light-independent reactions |
| What is the product of the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis? | sugars |
| Where does the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis take place? | In the stroma of the chloroplast |
What is the name of this entire structure?,  | chloroplast,  |
What is the overall balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis? If you know it, write it down at the bottom of your paper. If you get it right, you can ask me to circle any answer. If you get it wrong, you may not use the middle square for bingo. You do not have to write the words above and below the arrow., 
| .,  |
| Where do photosynthetic organisms (like trees) get the carbon atoms that are needed to make high energy sugars? | carbon dioxide |
| The first set of reactions in photosynthesis are the _________ reactions. | light-dependent |
| The last set of reactions in photosynthesis are the _________ reactions. | light-independent |
| TRUE or FALSE: The electron transport chain is part of the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis. | TRUE |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. The term that would be found behind the number 1 would be the ____ reactions., .gif) | Light-dependent reactions, .gif) |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. Which term would be found behind the number 2?, .gif) | water, .gif) |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. Which term would be found behind the number 3?, .gif) | oxygen, .gif) |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. Which term would be found behind the number 4?, .gif) | ATP, .gif) |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. The term that would be found behind the number 5 is the _____ reactions, .gif) | Light-independent Reactions (a.k.a. - Calvin Cycle), .gif) |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. Which term would be found behind the number 7?, .gif) | sugars, .gif) |
This picture is a summary of photosynthesis. Which term would be found behind the number 8?, .gif) | carbon dioxide, .gif) |
| TRUE or FALSE: Plants don't do cellular respiration or require any oxygen because they do photosynthesis instead. | FALSE (Plants do both. They make food to store energy and produce oxygen during photosynthesis, but when they need energy, they will use cellular respiration to get the energy out of the food, just like you do) |
| How many phosphate groups does ATP have? | Three (that's why it is called adenosine tri-phosphate) |
| How many phosphate groups does ADP have? | Two (that's why it is called adenosine di-phosphate) |
| The energy in most food comes originally from ___. | sunlight |
| The formation of ADP from ATP ____ energy. | releases |
| The formation of ATP from ADP ____ energy. | requires |
| ATP --> ADP + P is an _____ reaction. | exothermic (because it releases energy that can be used for cellular processes) |
| ADP + P --> ATP is an ____ reaction. | endothermic (because it requires energy to put the 3rd phosphate back onto ADP to form ATP, but that energy is then stored in the ATP molecule and can be used again once ATP is broken back down into ADP + P) |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from the glycolysis stage? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose that goes through glycolysis. |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of glycolysis occur? | In the cytosol (cytoplasm) |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is available? | 36 (can be as much as 38 in some organisms or cell types) |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is NOT available? | Only 2 (by using fermentation to keep glycolysis going) |
| What are the two main reactants of aerobic cellular respiration? | Glucose and oxygen (these are the reactants of cellular respiration, and happen to be the products of photosynthesis. Remember, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are basically opposites of each other), 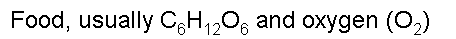 |
| What are the two main products of aerobic cellular respiration? | carbon dioxide and water (these are the products of cellular respiration, and happen to be the reactants of photosynthesis. Remember, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are basically opposites of each other),  |
| How many ATP can be generated from one molecule of glucose under anaerobic conditions? | 2 (Two ATP can be generated per molecule of glucose under anaerobic conditions using a process called fermentation that keeps glycolysis going). |
What is the name of this organelle?,  | mitochondria,  |
| What do humans produce if they are not getting enough oxygen to process their food aerobically? | Lactic acid |
| A method for getting energy out of food that produces lactic acid or alcohol when no oxygen is available. | Fermentation |
| What do yeast and bacteria usually produce when they break down food under anaerobic conditions? | alcohol (and carbon dioxide) |