| A | B |
|---|
| The type of inheritance where neither allele is dominant and they tend to produce a mix of the two traits such as blue + white = light blue would be _____. | incomplete dominance |
| The type of inheritance where both alleles are dominant, such as red fur + white fur = red and white fur hairs in roan cattle is known as ____. | codominance |
| The type of inheritance where there is more than two alleles for a single trait, such as A, B, and O alleles for blood type, is known as ____. | multiple alleles |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IA, what is your blood type? | type A |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,i, what is your blood type? | Type A |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,IB, what is your blood type? | Type B |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,i, what is your blood type? | type B |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IB, what is your blood type? | Type AB |
| If your genotype for blood type is ii, what is your blood type? | Type O |
| Genes that are located on the 23rd pair of chromosomes (but only on the X, not the Y chromosome) are known as ____. | sex-linked genes |
| If you have an X and a Y chromosome, what is your gender? | male |
| If you have two X chromosomes, what is your gender? | female |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring of this cross? (Change the A's to IA's, the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  | 25% type AB blood, 25% type A blood, 25% type B blood, 25% type O blood,  |
| How would you set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a heterozygous blood type A male and a heterozygous blood type B female? | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  |
In humans, colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive allele. What are the expected phenotypes of the offspring if both parents have normal vision but the mother is heterozygous?, 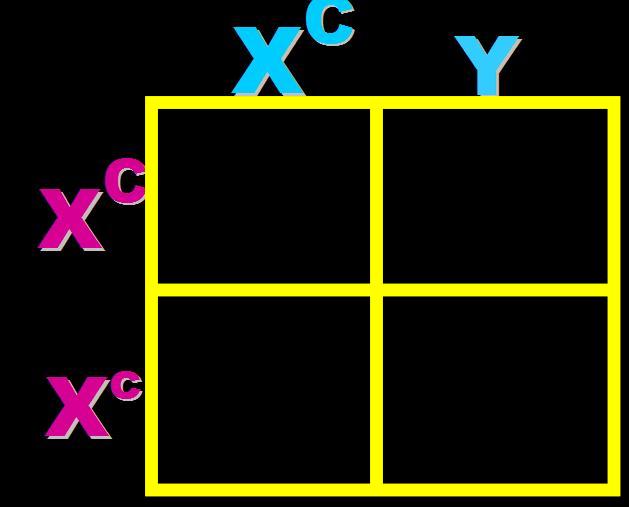 | 100% normal vision girls and 50% of the boys are expected to be colorblind., 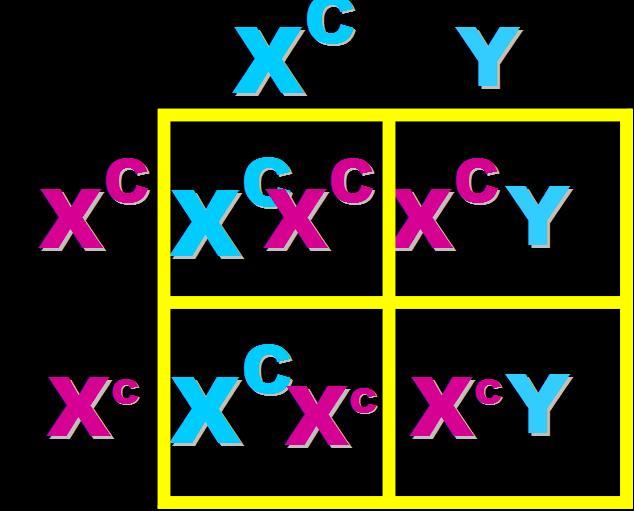 |
| How would you set up a cross between a male with type AB blood and a female with type O blood? (The A stands for IA, the B's stand for IB and the O stands for i) | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's), 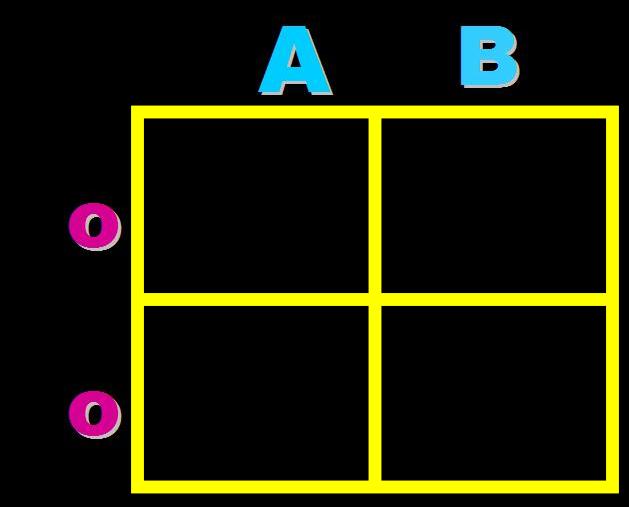 |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring and what are the odds of each? (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  | 50% of the offspring are expected to have type A blood and 50% are expected to have type B blood. All offspring will be heterozygous. Remember that the O allele is recessive.,  |
| A trait, like human skin color, that involves several different genes is called a(n) _____. | polygenic trait (remember, "poly" means many and "genic" refers to genes) |
The following diagram is an example of a(n) ___.,  | pedigree chart,  |
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles |
| New alleles for a gene are formed by _________ that survive the ________ process. | mutations, natural selection |
| Humans have ____ autosomes and ____ sex chromosomes in a normal karyotype. | 44, 2,  |
| Give an example of a disorder caused by sex-linked inheritance. | color-blindness, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy are possible answers (Remember, you only need to give one) |
| If a certain species of flower has a codominant inheritance pattern for flower color and a red flower was pollinated by a white flower, the offspring would a flower that is _____. | both red and white (Remember, with codominance, both traits, in this case red and white, show up in the heterozygous form) |
| If a certain species of flower has an incomplete inheritance pattern for flower color and a red flower was pollinated by a white flower, the offspring would a flower that is _____. | pink (Remember, the traits blend in incomplete dominance) |