 |
Java Games: Flashcards, matching, concentration, and word search. |
 |
 |
| A | B |
|---|
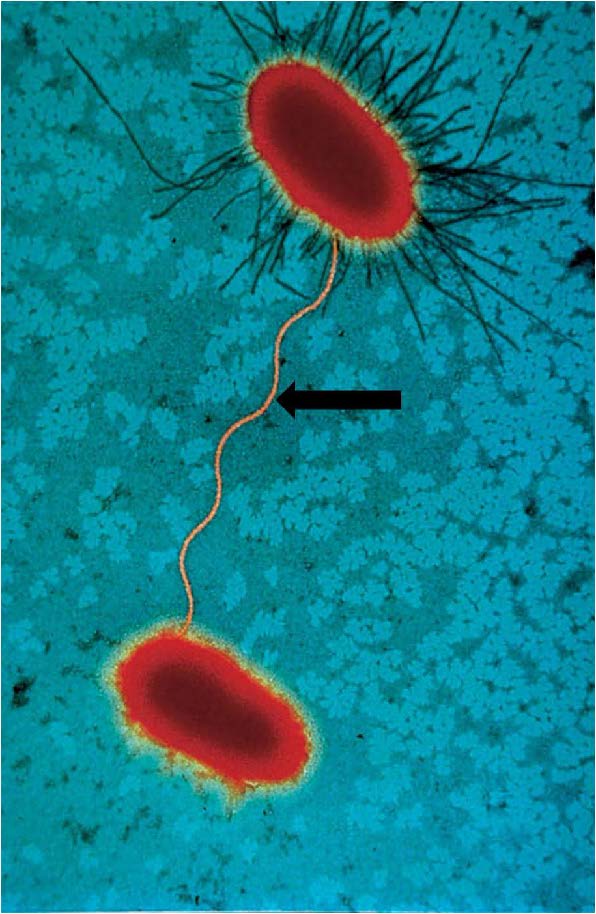 | Sex pilus - bacterial conjugation |
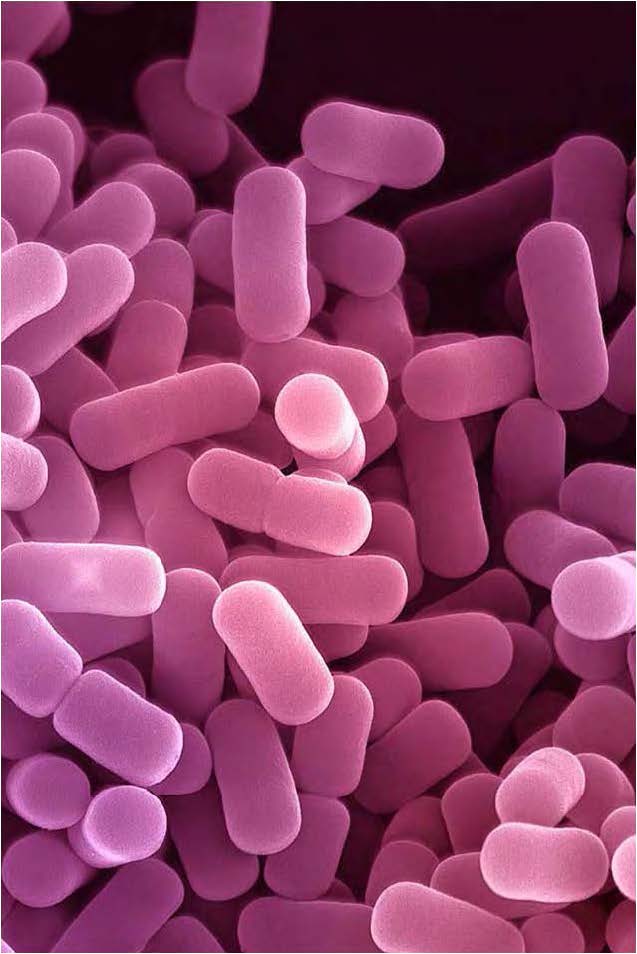 | Lactobacillus acidophilus (Rod) - domain Bacteria, a 'good' probiotic bacteria, found in yogurt |
 | Staphylococcus aureus (Cocci) - domain Bacteria, common skin bacteria |
 | Treponema pallidum (Spiral) - domain Bacteria, cause of syphilis |
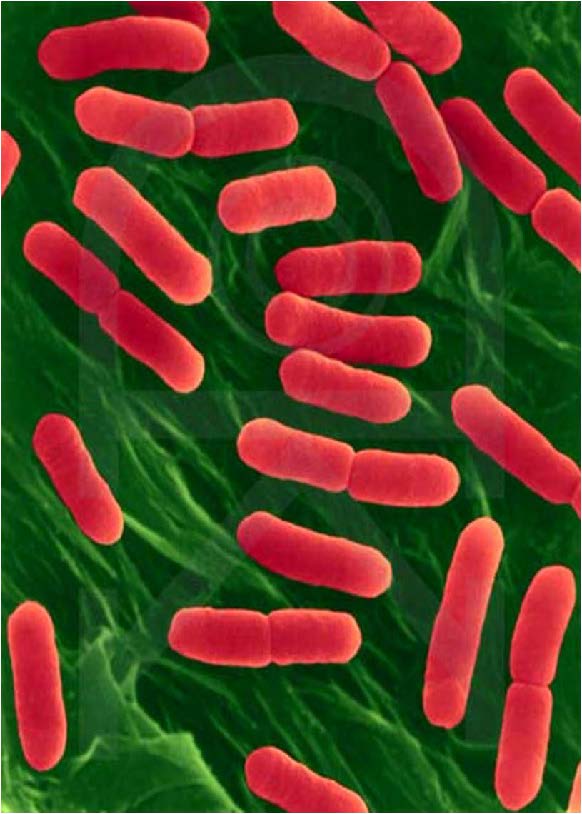 | E. coli - Gram (-), Proteobacteria, rod shaped, |
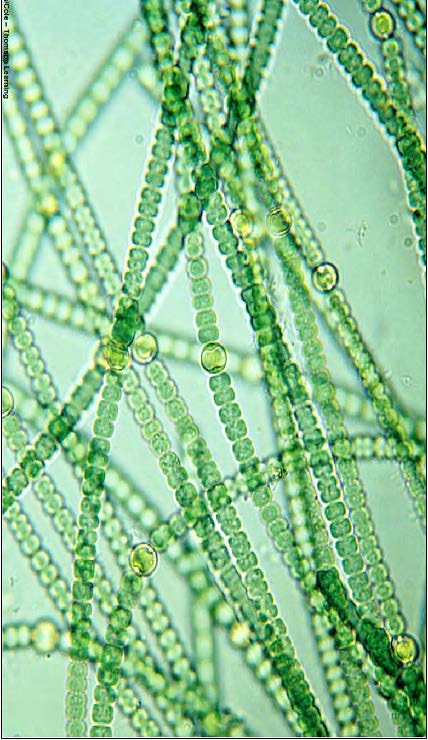 | Anabaena - domain Bacteria, phylum Cyanobacteria, have nitrogen-fixing heterocysts, like chloroplasts, produce oxygen gas |
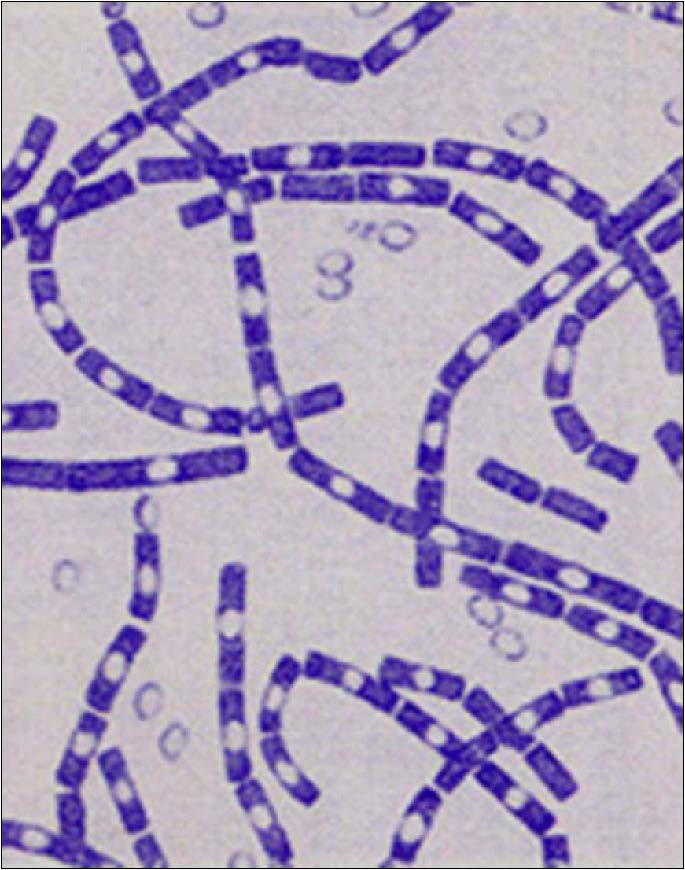 | Bacillus anthracis - domain Bacteria, phylum Eubacteria, Gram (+), causes anthrax, spore-forming |
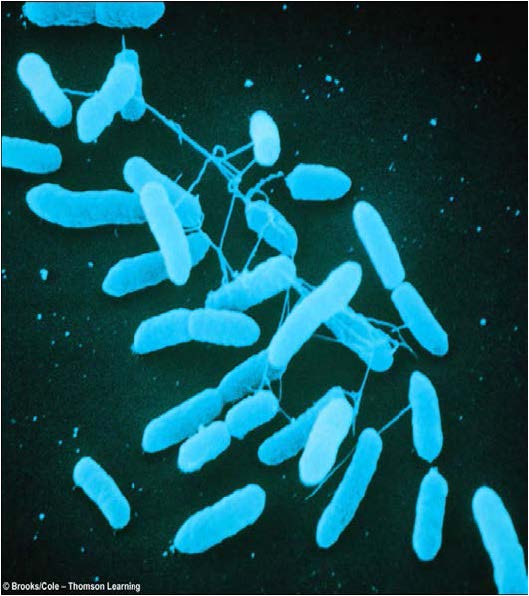 | conjugation in Serratia, exchanging genetic material via a sex pilus |
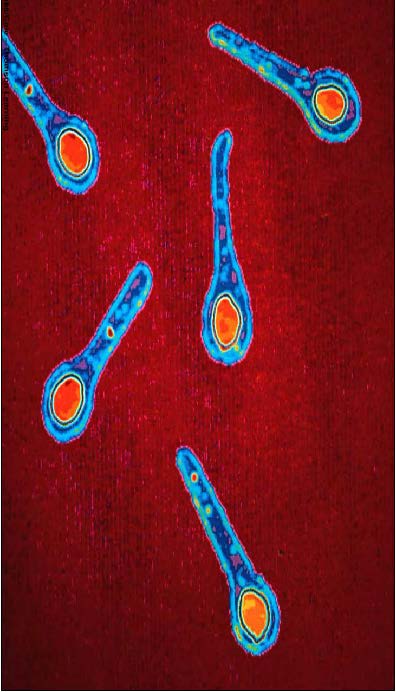 | Clostridium - domain Bacteria, Gram (+), phylum Eubacteria, have endospores that allow them to survive long periods of environmental stress, cause human disease botulism and tetanus |
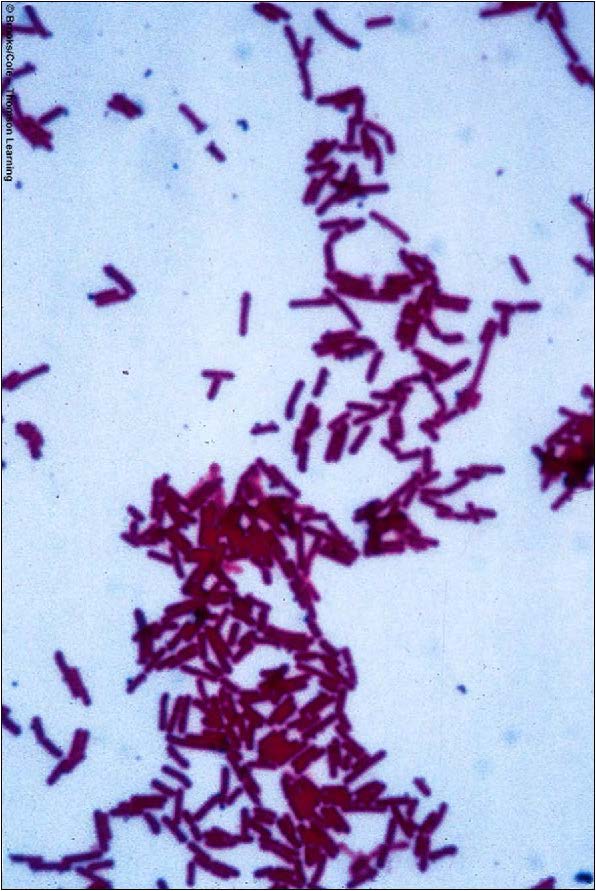 | Lactobacillus acidophilus (Rod) - domain Bacteria, a 'good' probiotic bacteria, found in yogurt |
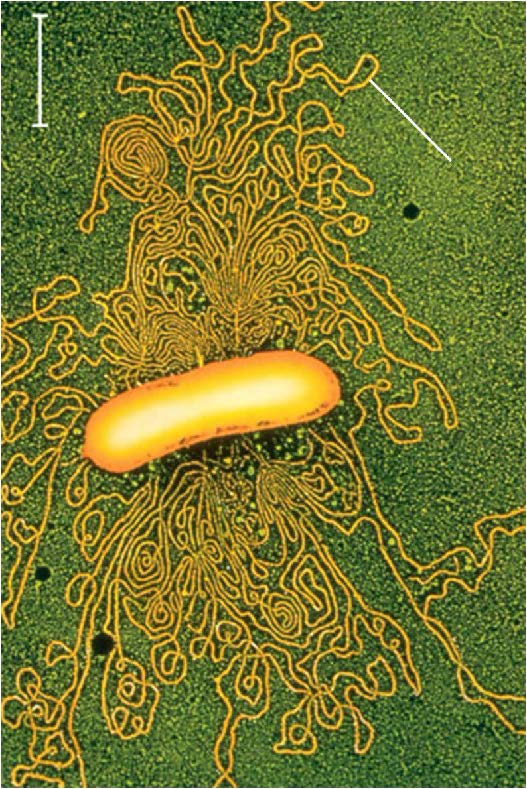 | chromosomes |
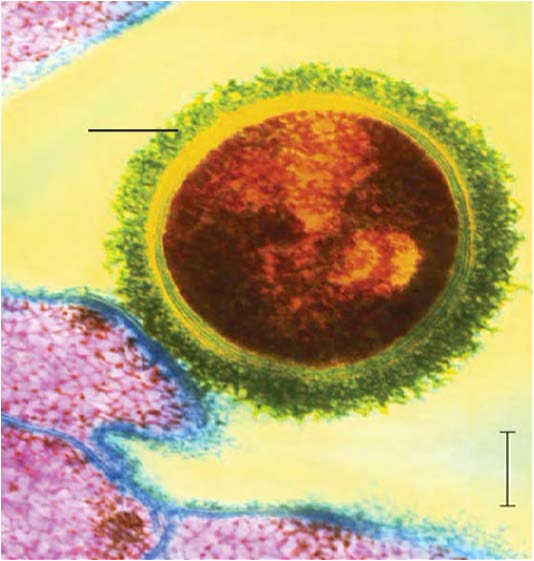 | capsule - allows the cell to evade the host's immune response |
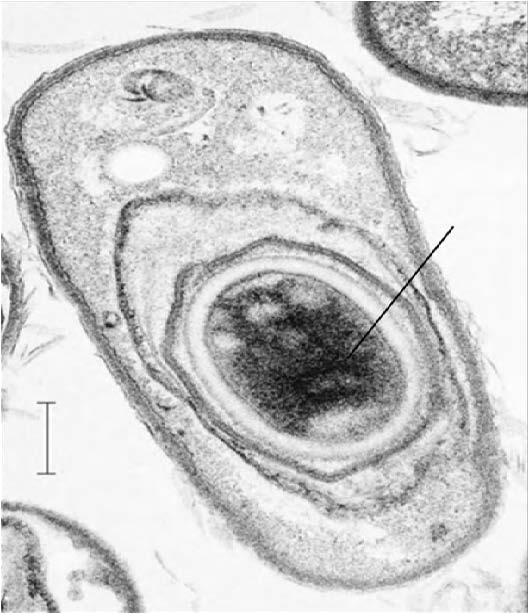 | Endospore |
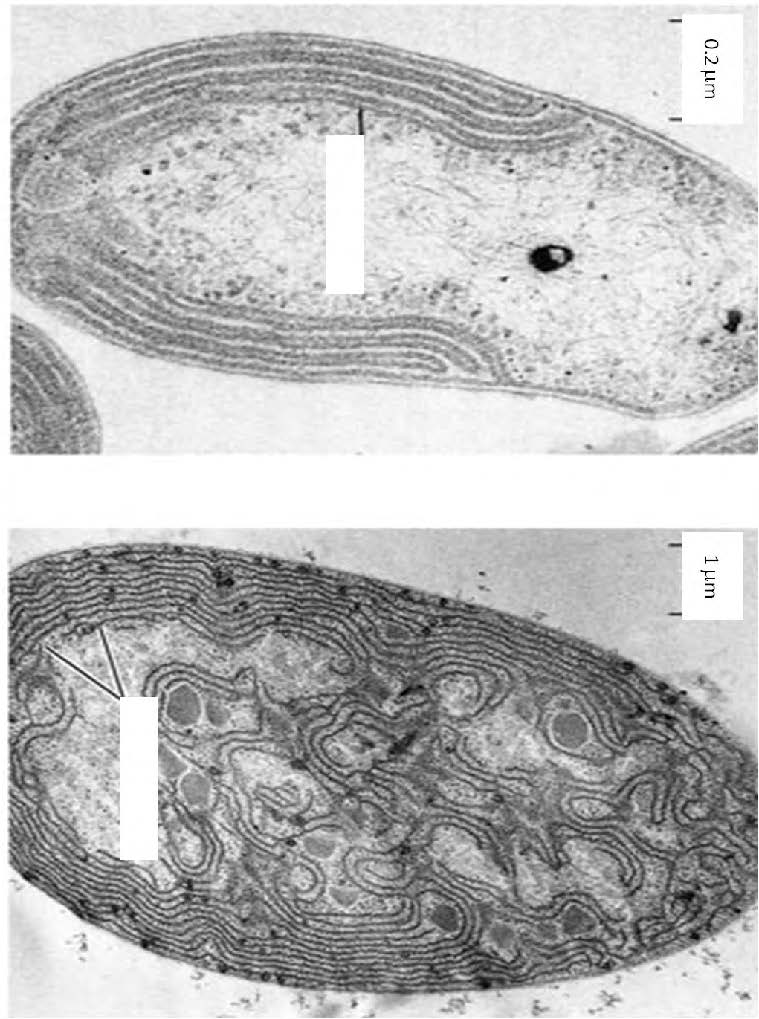 | Top: Respiratory membranes in an aerobic prokaryote, Bottom: Thylakoid membrane in photosynthetic prokaryote |
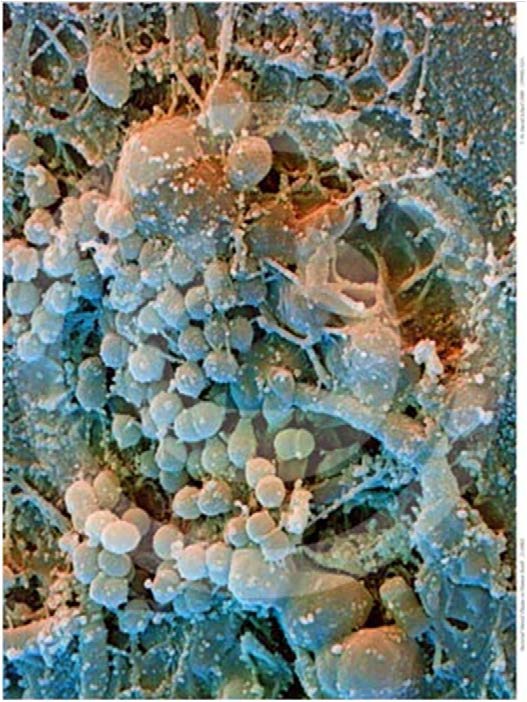 | Biofilm in dental plaque |
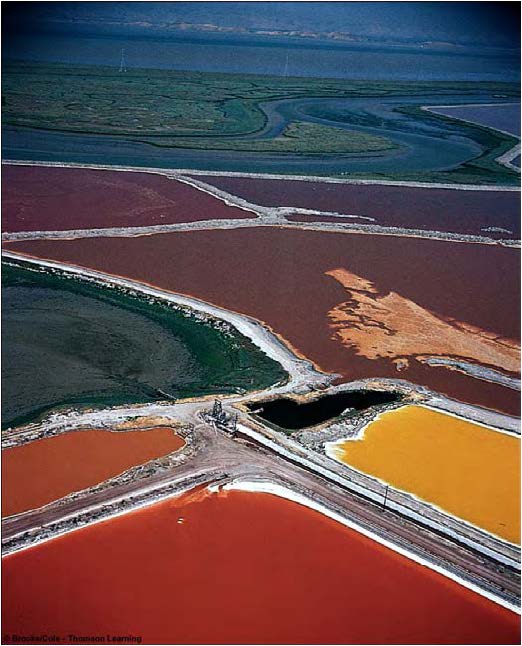 | Domain: Archaea, phylum: Extreme halophiles, "Salt-loving", colors created by different bacteriorhodopsins |
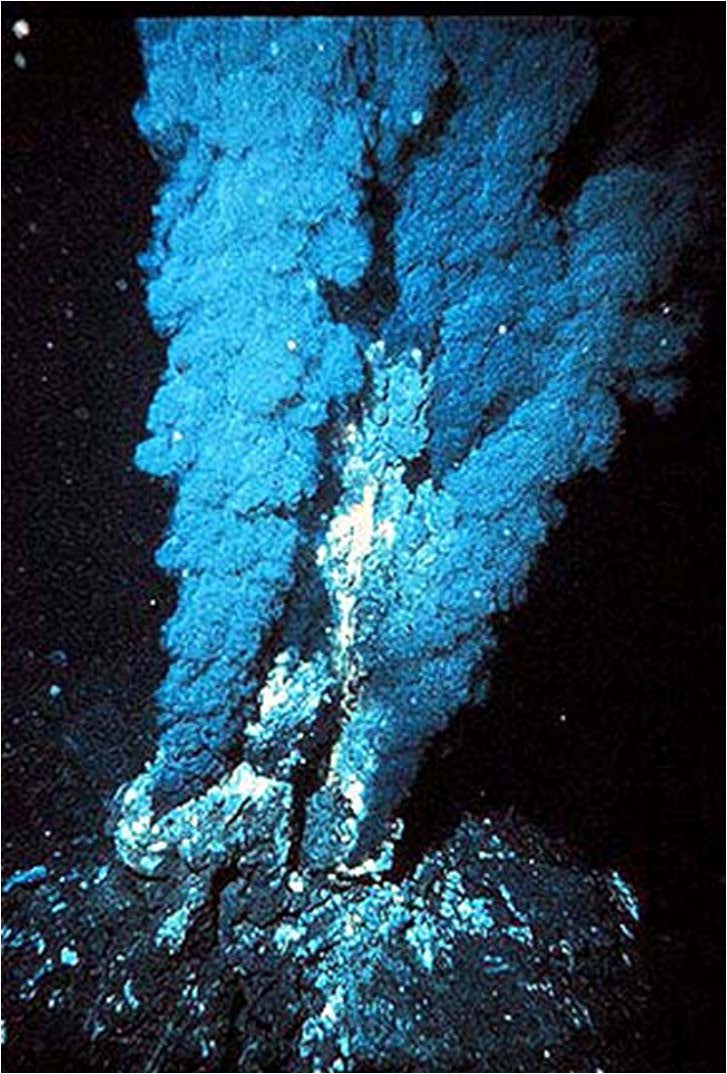 | Domain: Archaea, Phylum: Extreme Thermophile, Name: Black Smoker |
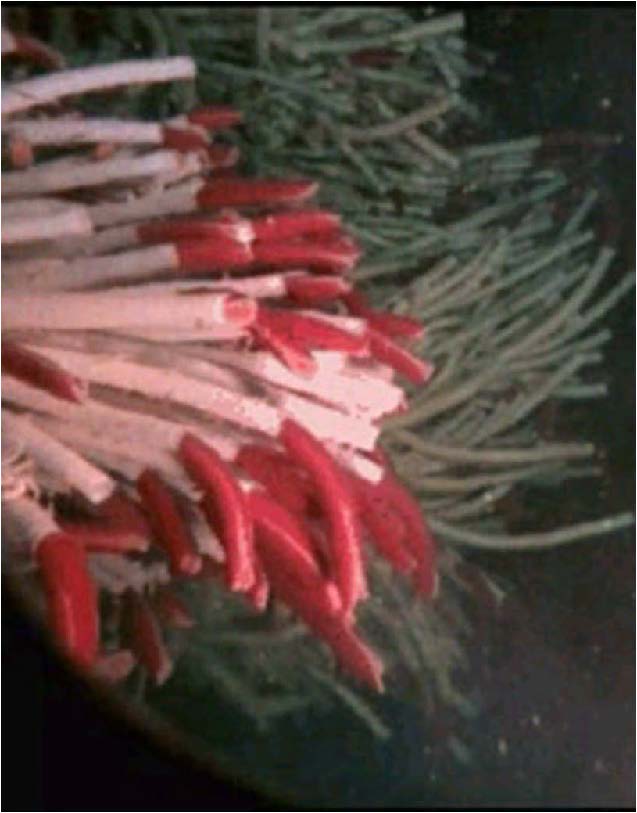 | Domain: Archaea, Phylum: Extreme Thermophile, Name: Giant tubeworm |
 | Black smoker |
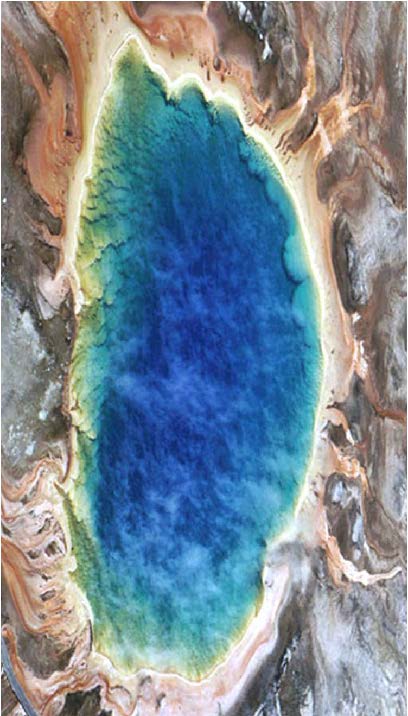 | Domain: Archaea, Phylum: Extreme Thermophile, found in hot sulfur springs at Yellowstone Park |
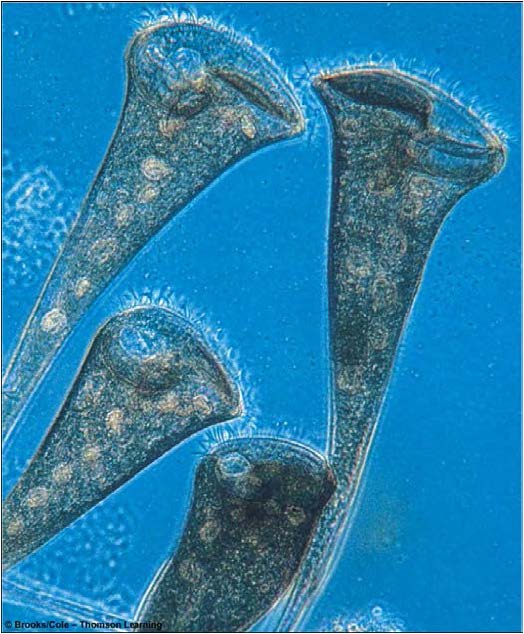 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Alveolata, Alveolates, Name: Stentor, contain membrane-bound sacs called alveoli, use cilia to move and feed |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, (Rhizarians), Clade: Cercozoa & Radiolarians, Name: Radiolarians, Thread-like pseudopodia, calcium carbonate shells or tests, ingest smaller cells by phagocytosis using their pseudopodia and cytoplasmic streaming |
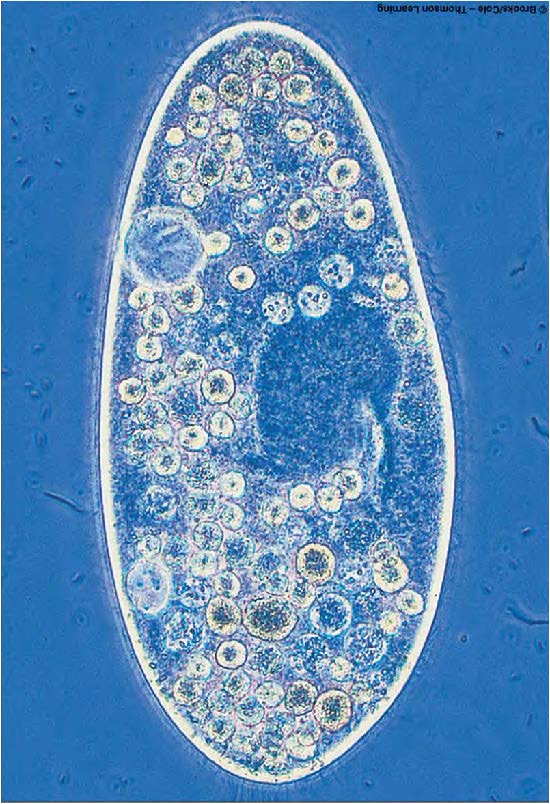 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Alveolata, Name: Paramecium caudatum, Contain membrane-bound sacs called alveoli, have cilia and oral groove |
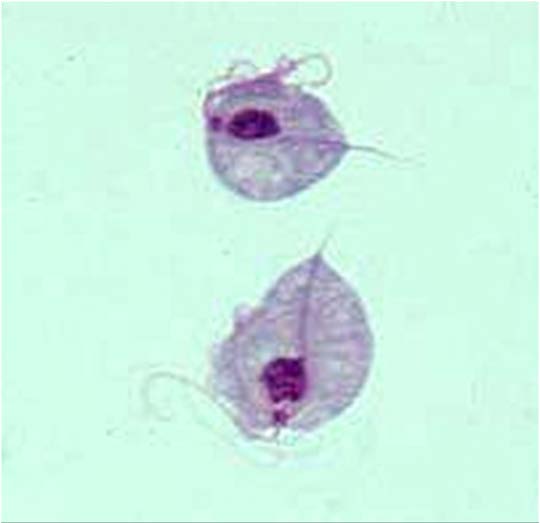 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Excavata, Name: Trichomonas vaginalis, STD, non-functional mitochondria, flagella and undulating membrane move it along mucus-coated tract |
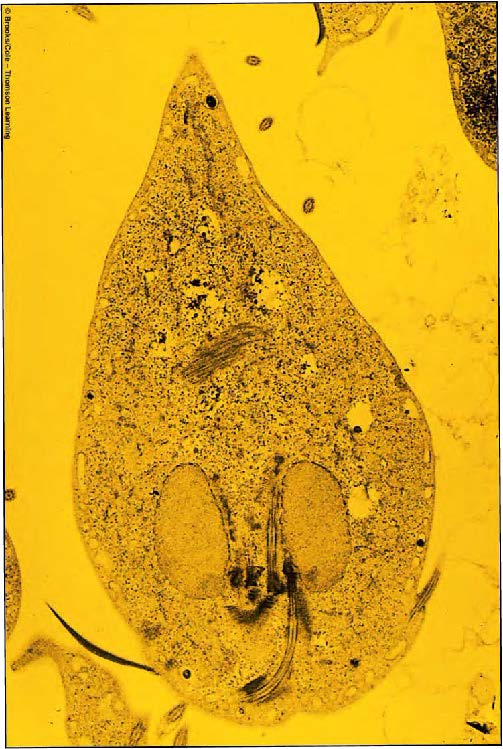 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Excavata, Order: Diplomonadida, Name: Giardia intestinalis, causes "Backpacker's Diarrhea", non-functional mitochondria, two haploid nuclei, four flagella |
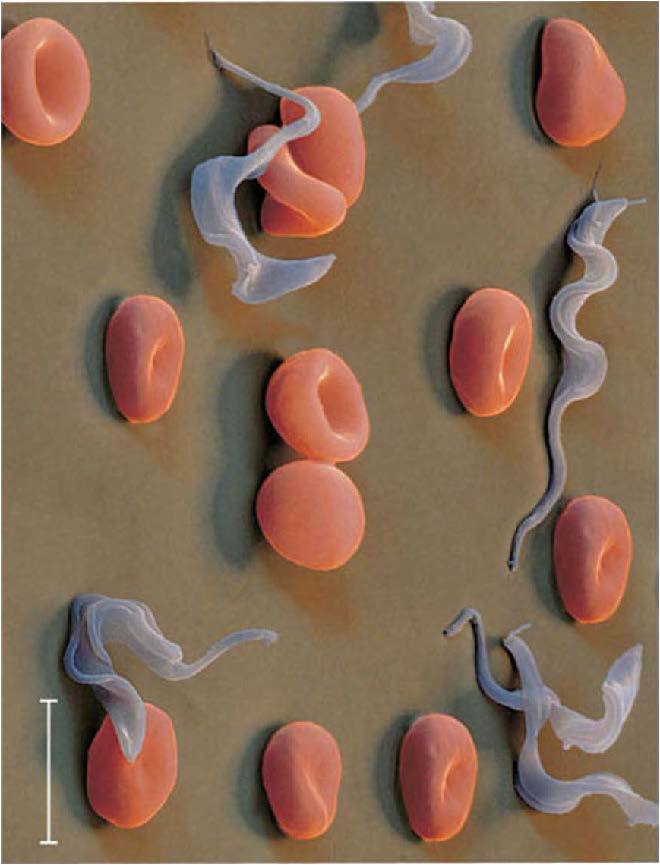 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Excavata, Clade: Euglenozoa, Class: Kinetoplastea, Name: Trypanosoma bruceii, Flagella have a unique crystalline rod of unknown function, single mitrochondrion containing a large mass of DNA called a kinetoplast, causes Chagas disease and African sleeping sickness |
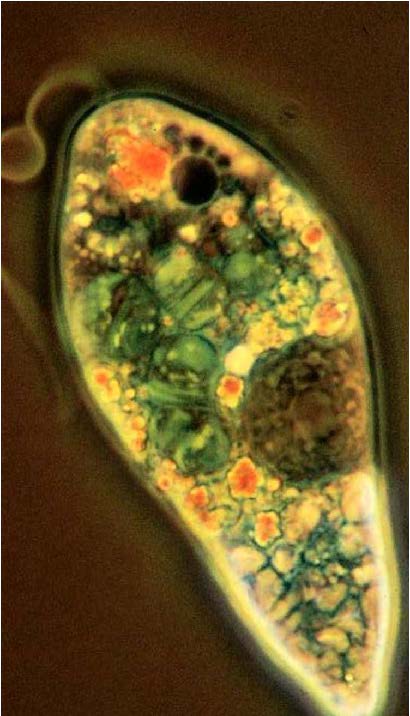 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Excavata, Clade: Eugelnozoa, Class/Order: Euglenid, Name: Euglena gracilis, Flagella have unique crystalline rod of unknown function, photosynthetic, has an eye spot |
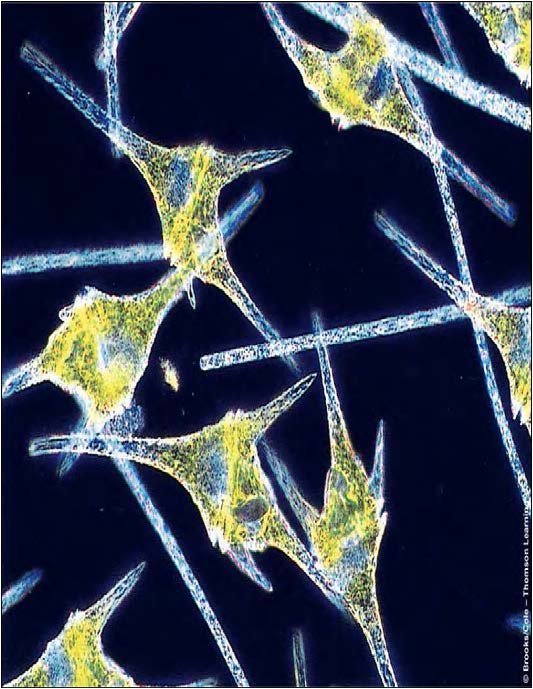 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Alveolata, Class/Order: Alveolate, Name: Dinoflagellates, Contain membrane-bound sacs called alveoli, cause "red tides" in oceans that produce neurotoxins |
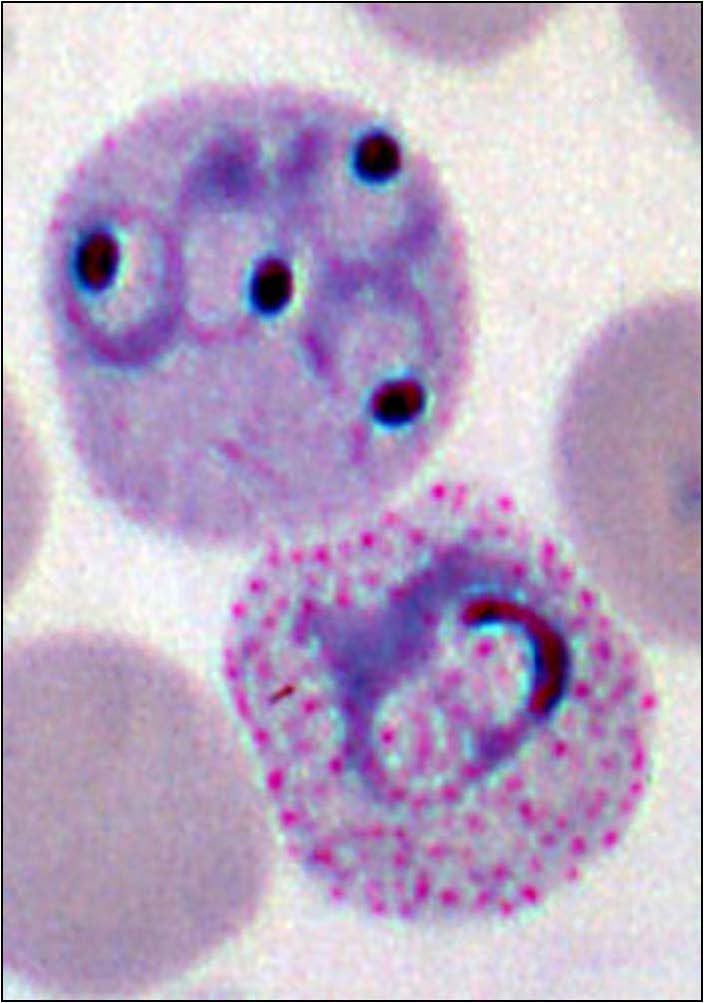 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Alveolata, Class/Order: Alveolate, Name: Plasmodium vivax, Contain membrane-bound sacs called alveoli, parasites of mammals |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Stramenopiles, Name: Brown algae |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Stramenopiles, Name: Diatoms, Have one smooth flagellum, have one tinsel flagellum, have silica shells, pillbox shape, make up diatomaceous earth |
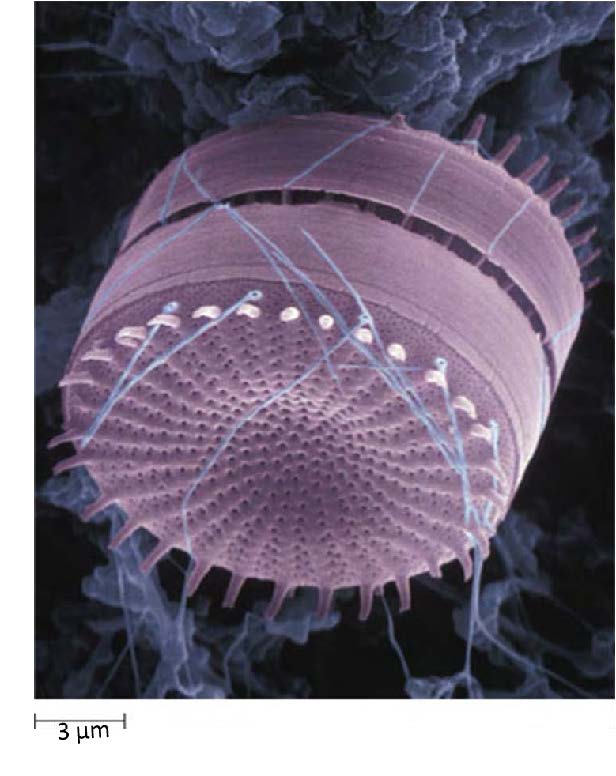 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Stramenopiles, Name: Diatoms, Have one smooth flagellum, have one tinsel flagellum, have silica shells, pillbox shape, make up diatomaceous earth |
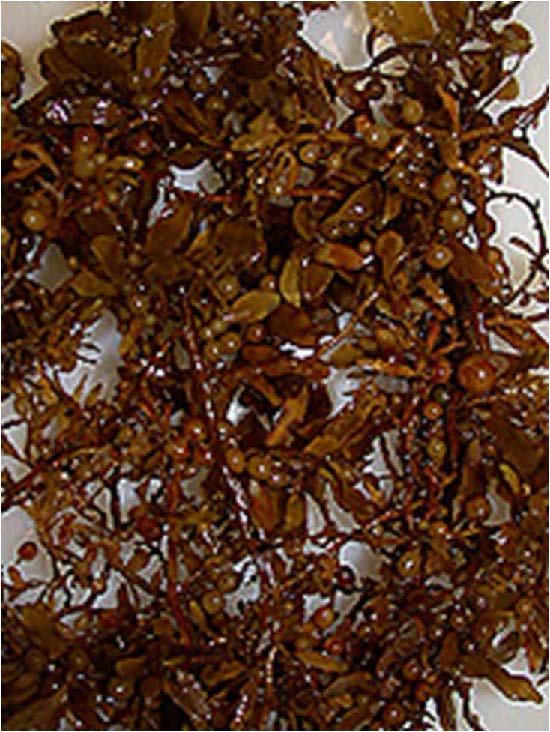 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Stramenopiles, Name: Brown algae |
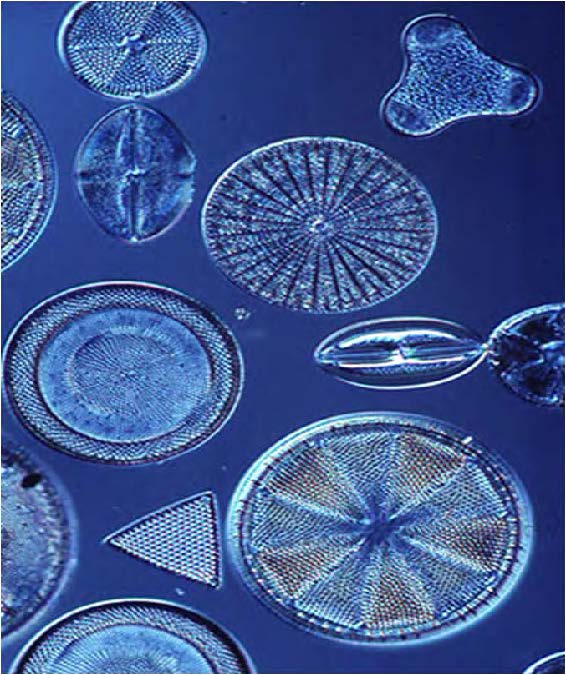 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, Clade: Stramenopiles, Name: Diatoms, Have one smooth flagellum, have one tinsel flagellum, have silica shells, pillbox shape, make up diatomaceous earth |
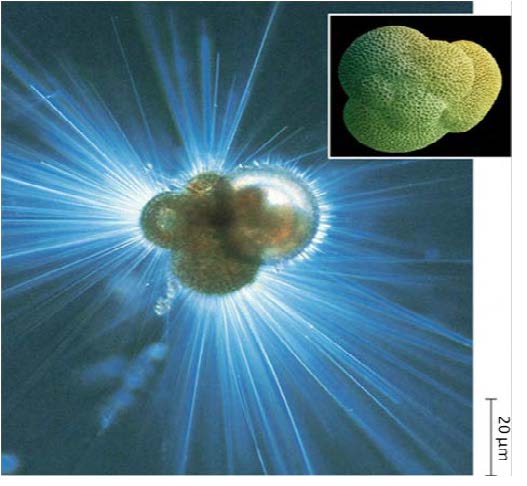 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, (Rhizarians), Clade: Cercozoa/Radiolarians, Name: Globigerina, Thread-like pseudopodia, calcium carbonate shells or tests, feed by extending pseudopodia through pores in their tests |
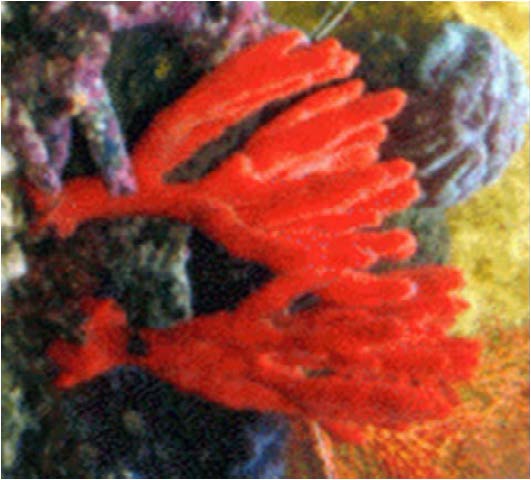
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: SAR, (Rhizarians), Clade: Cercozoa/Radiolarians, Name: Cercozoan, Trillions of Cercozoan tests make up the White Cliffs of Dover, Thread-like pseudopodia, calcium carbonate shells or tests, feed by extending pseudopodia through pores in their tests |
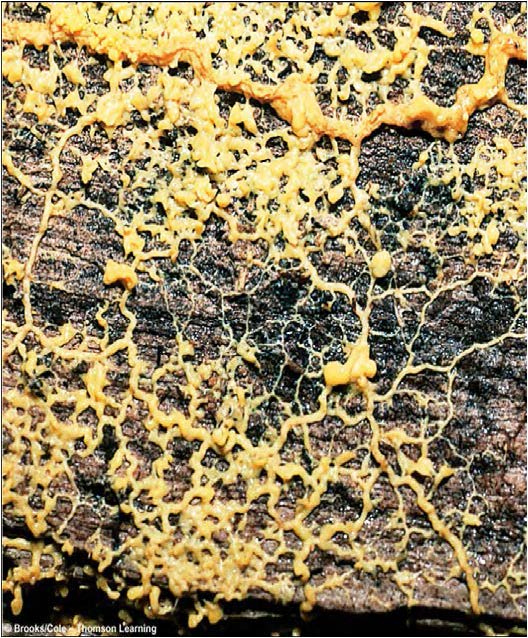 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Amoebozoa, Name: Entamoeba histolytica, Plasmodial slime molds, causes traveller's diarrhea ("Montezuma's Revenge") |
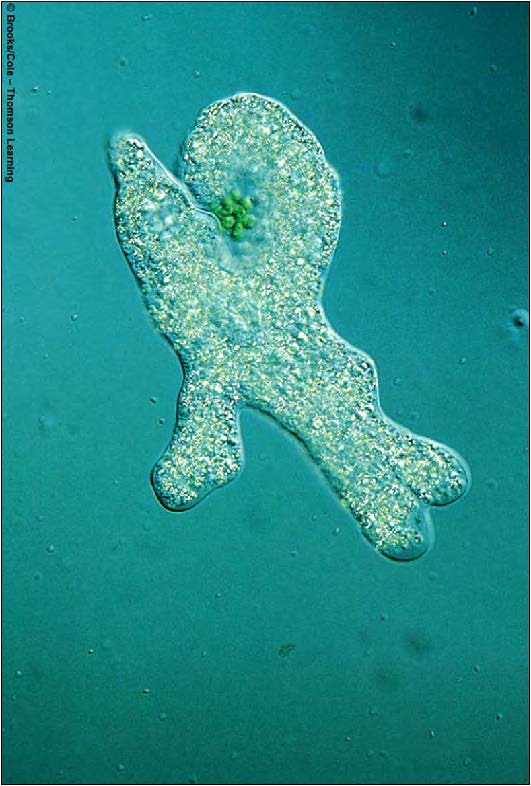 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Amoebozoa, Name: Amoeba proteus, have lobe-shaped pseudopodia or false-feet, engulf prey via pseudopodia |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokonts, Name: Choanoflagellate, have a posterior flagella, protist ancestor of fungi and animals |
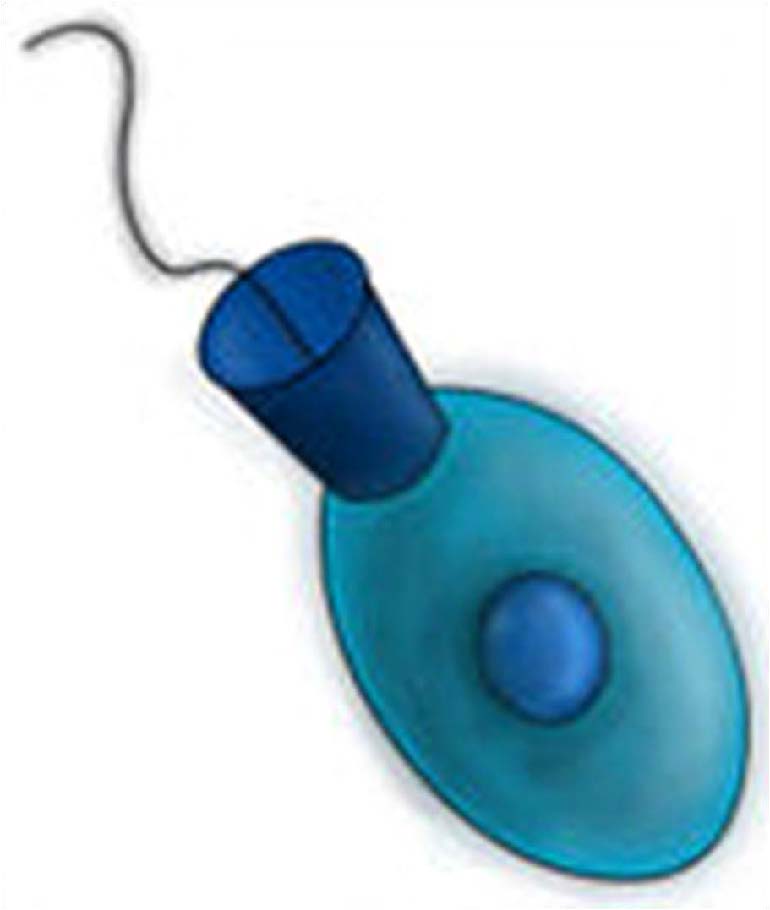 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokonts, Name: Choanoflagellum, have a posterior flagella, protist ancestor of fungi and animals |
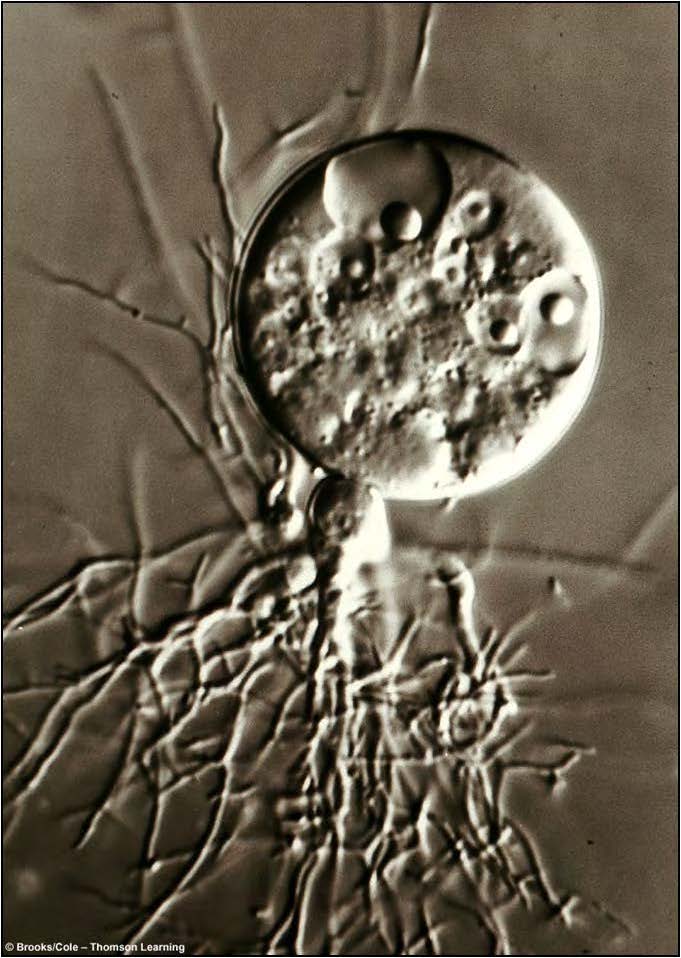 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Name: Chytriomyces hyalinus, type of Chytridiomycota fungi, earliest group, flagellated spores, parasitic, aquatic, responsible for amphibian decline worldwide |
 | <needs info> |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Clade: Viridiplantae, Name: Red algae, photosynthetic, red to blue pigments |
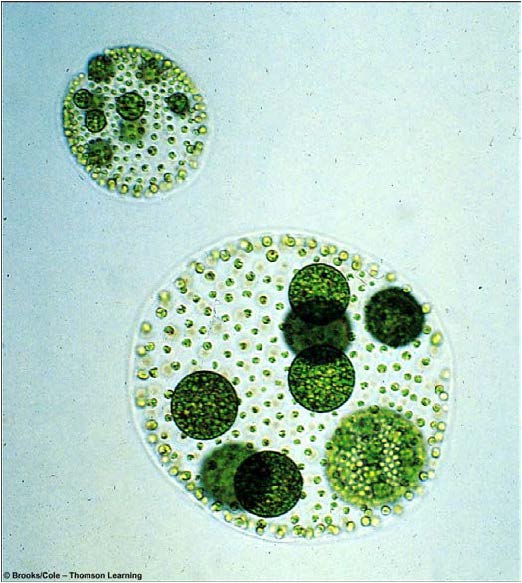 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Clade: Viridiplantae, Name: Green algae (Chlorophyta volvox), photosynthetic |
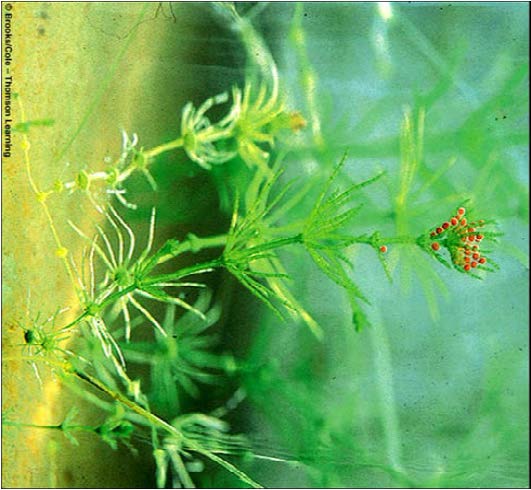 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Clade: Viridiplantae, Name: Green algae (Chlorophyta chara), photosynthetic, direct ancestor of land plants |
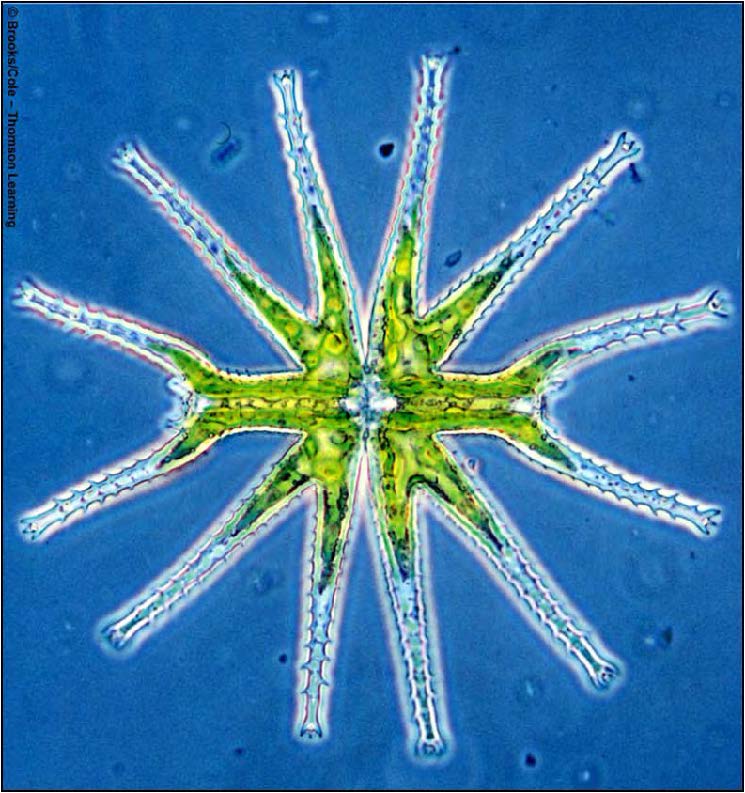 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Clade: Viridiplantae, Name: Green algae, photosynthetic |
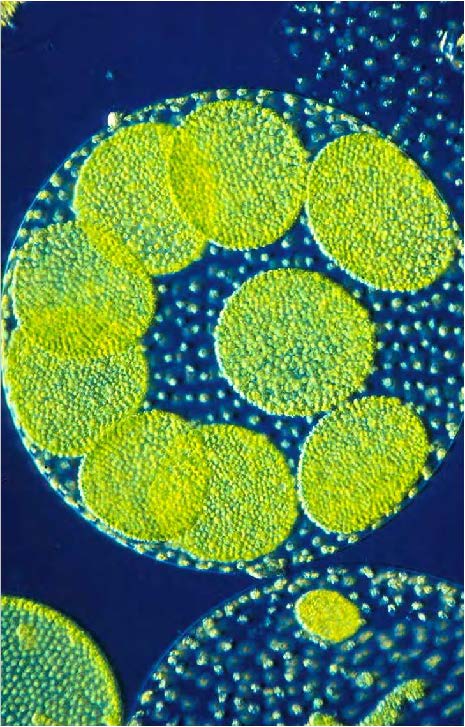 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Clade: Viridiplantae, Name: Green algae (Chlorophyta volvox), photosynthetic |
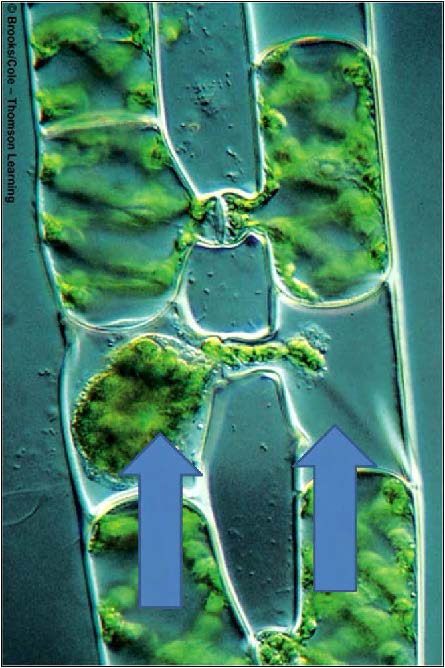 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, conjugation (sexual reproduction) in Spirogyra, left strain (+), right strain (-) |
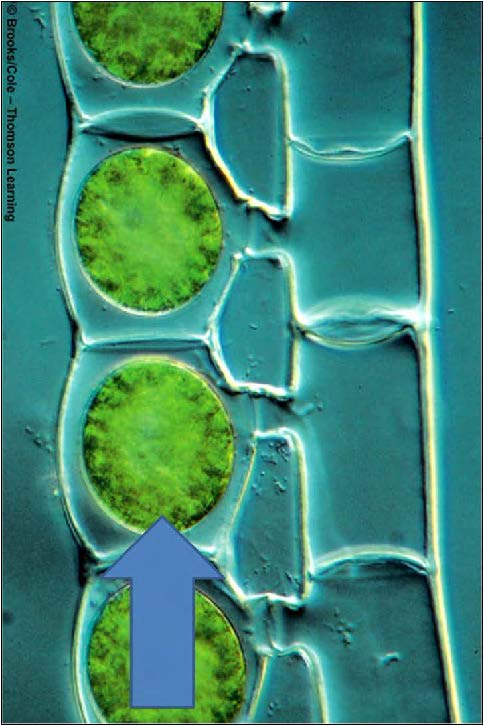 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Zygotes |
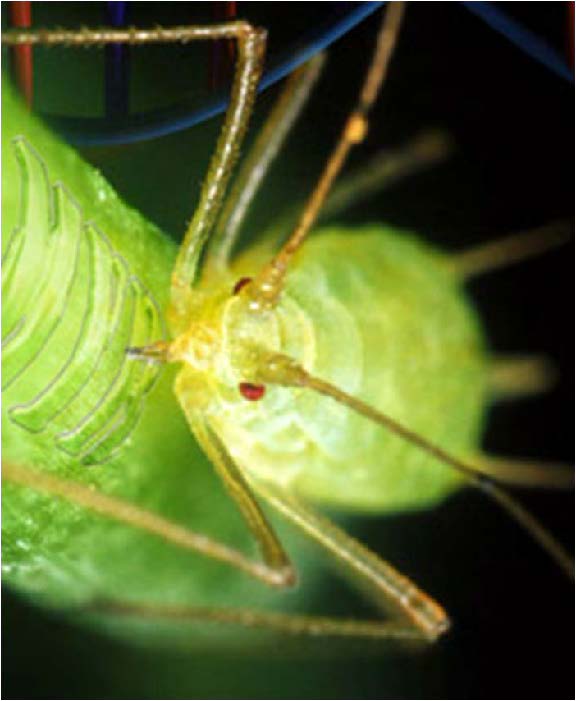 | Aphid (Homoptera), have 60-80 huge cells called bacteriocytes - filled with mutualistic bacteria, 200 million years of co-evolution, bacteria are maternally transmitted to eggs and embryos, neither bacteria or aphid can reproduce independently, each has streamlined genome and elimnated genes present in the other (bacteria may be B. aphidicola) |
 | sea slugs, endosymbiotes with algae, horizontal transfer of algal photosynthetic genes in slug genome, algal chloroplasts |
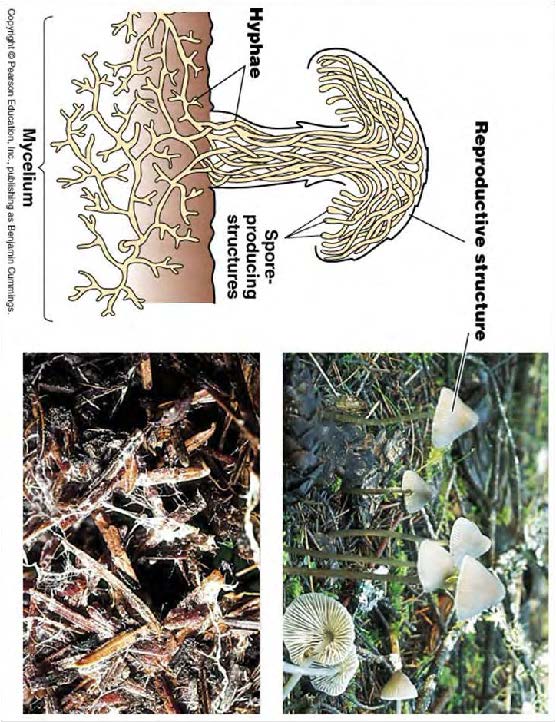 | <needs info> |
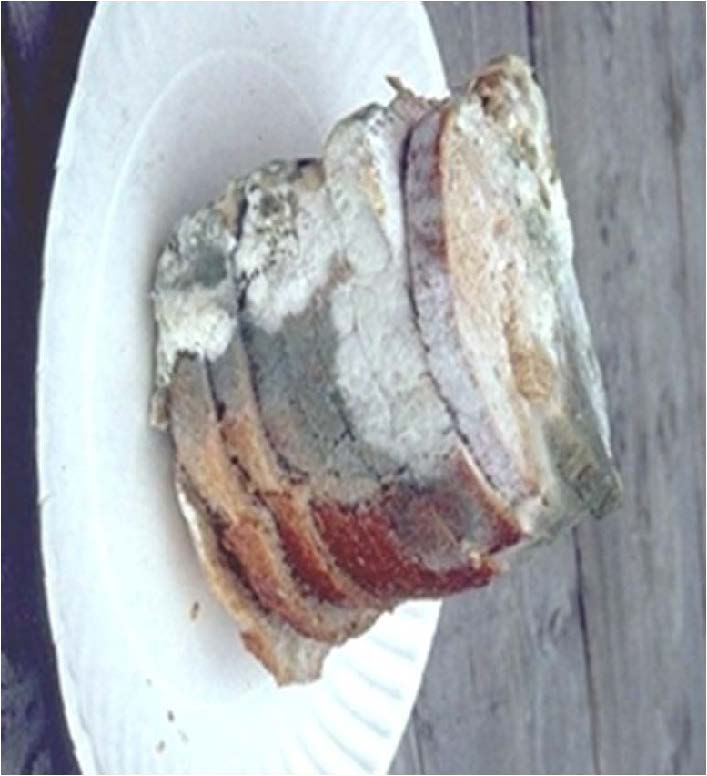 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Zygomycota |
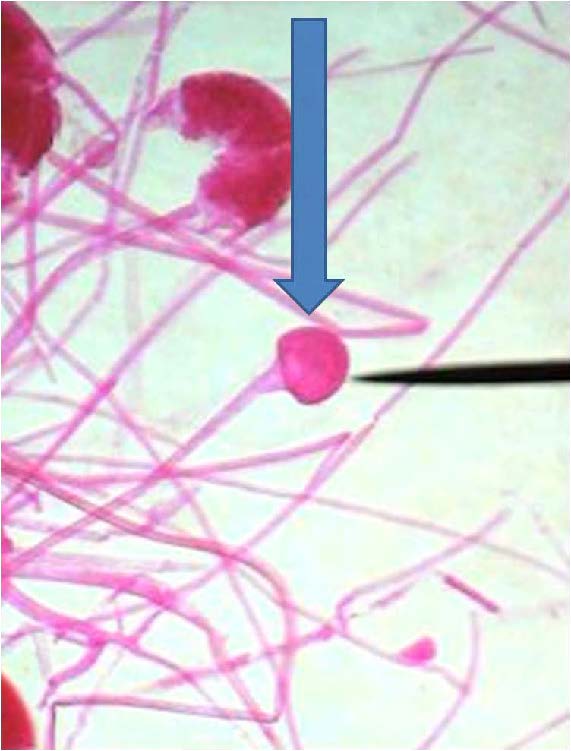 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Zygomycota, shows asexual sporangium |
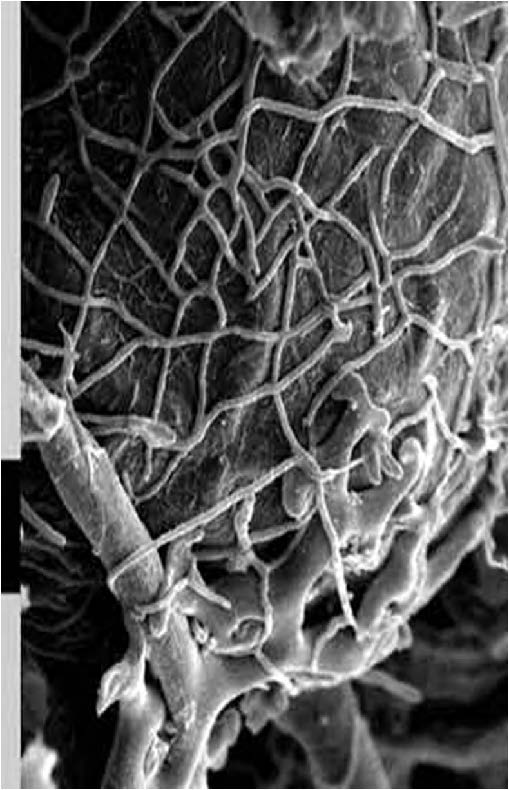 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Zygomycota, shows fungal hyphae |
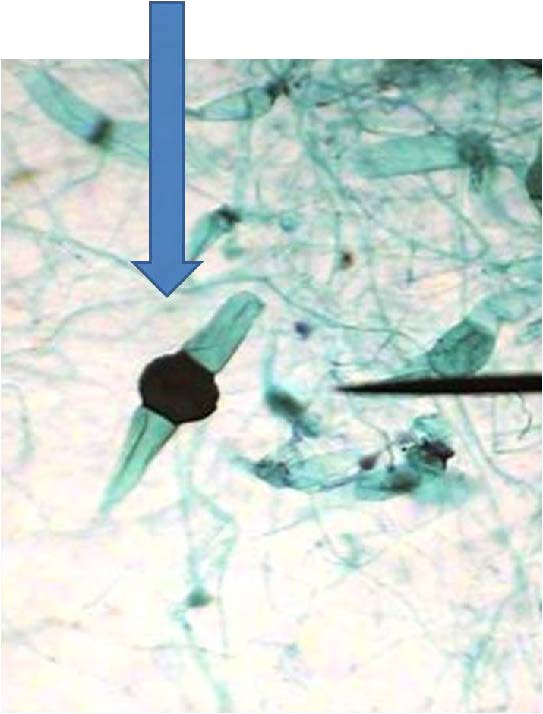 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Zygomycota, shows sexual zygospore |
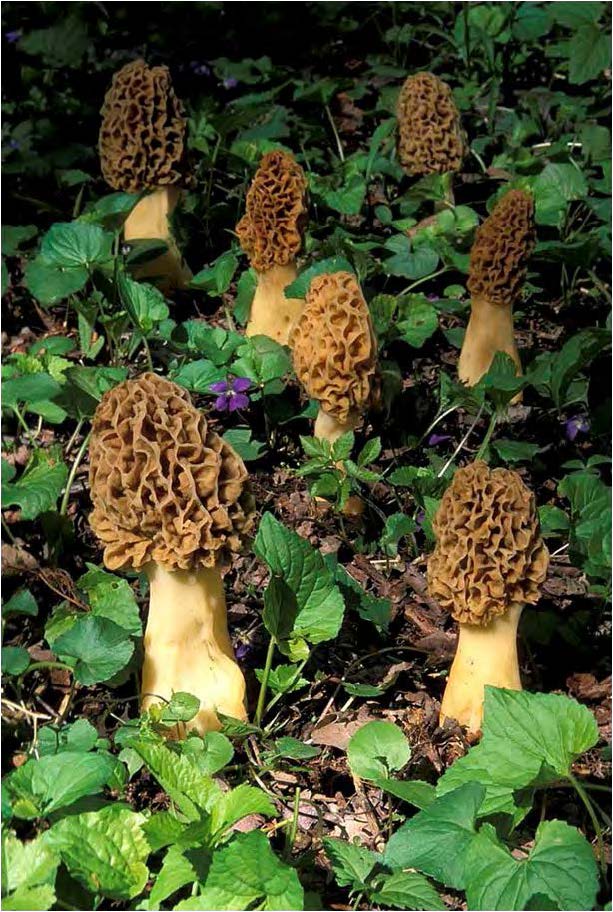 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, Name: Morel mushroom, sac/cup fungi, edible |
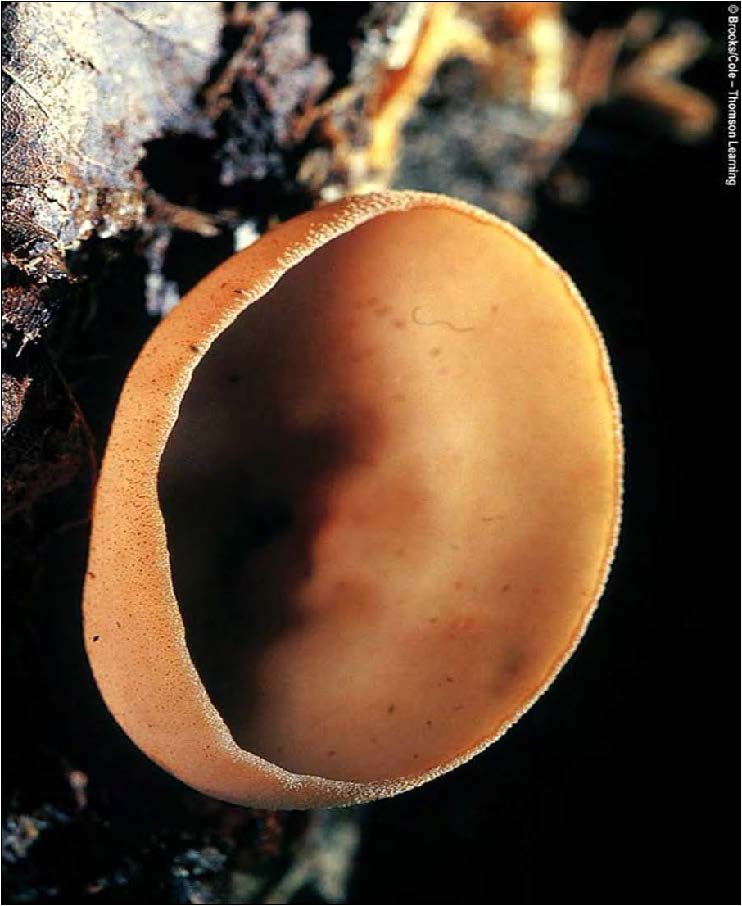 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, sac/cup fungi |
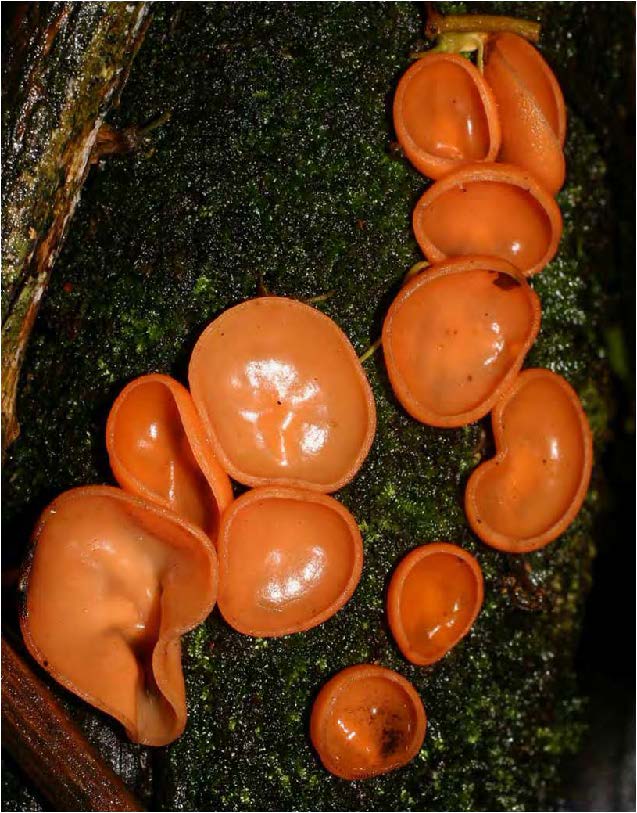 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, sac/cup fungi |
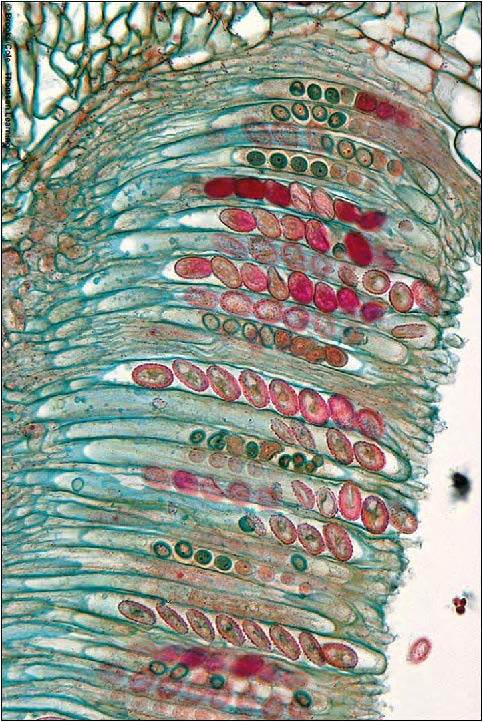 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, sac/cup fungi, shows sexual ascus and ascospores |
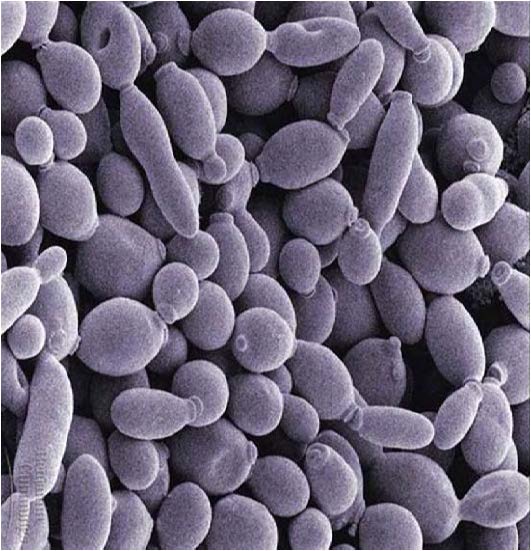 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, Name: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, shows asexual reproduction (budding) |
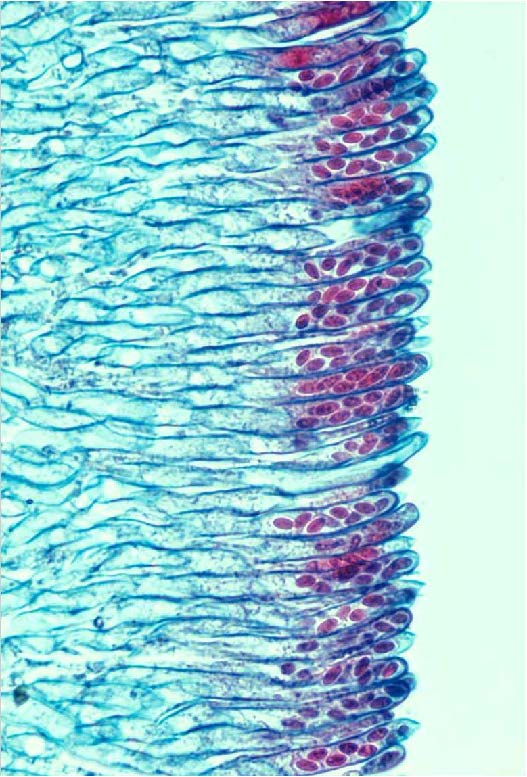 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, sac/cup fungi, shows sexual ascus and ascospores |
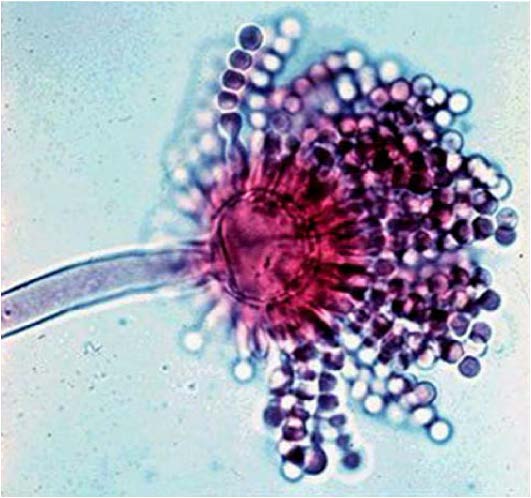 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, sac/cup fungi, shows asexual conidiophores and conidia (spores) |
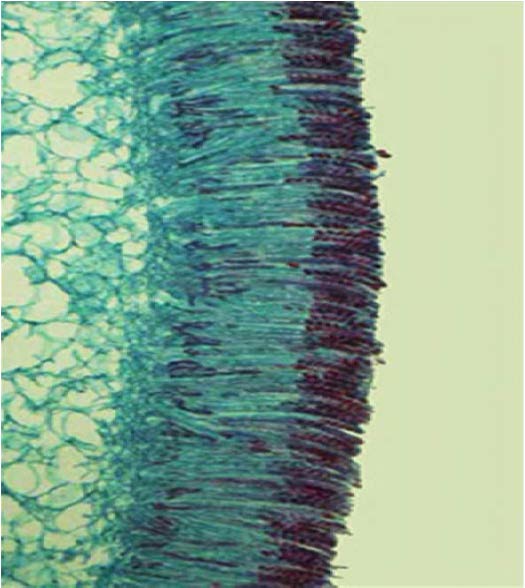 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, sac/cup fungi, Name: Peziza |
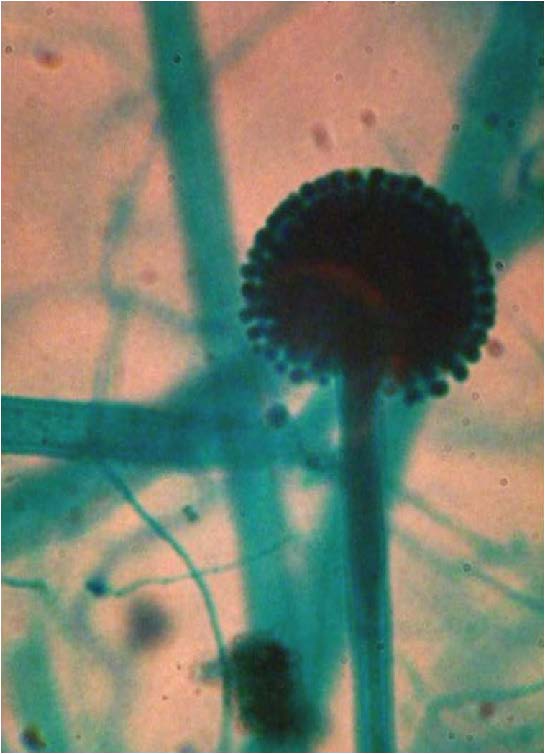 | <needs info> |
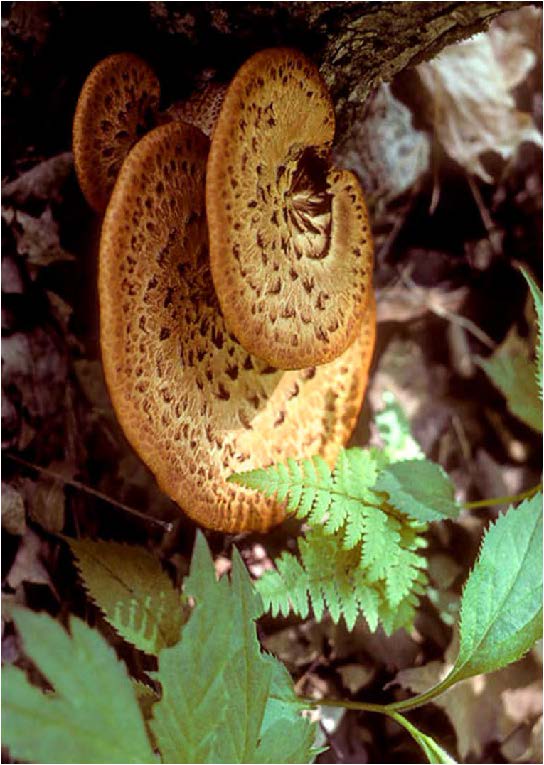 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Club fungi |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Amanita muscaria (fly agaric mushroom), club fungi |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Turkey Tall Shelf Fungus, club fungi |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Giant Puffball Mushroom, club fungi |
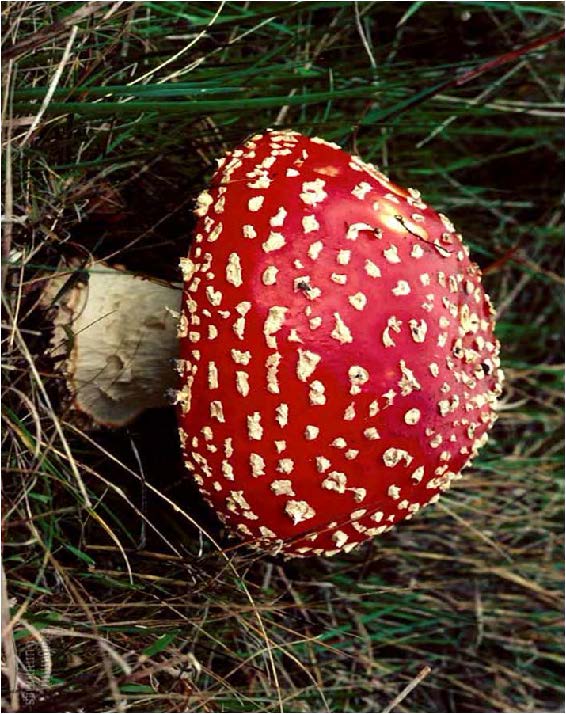 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Amanita muscarina, club fungi, poisonous, psychoactive |
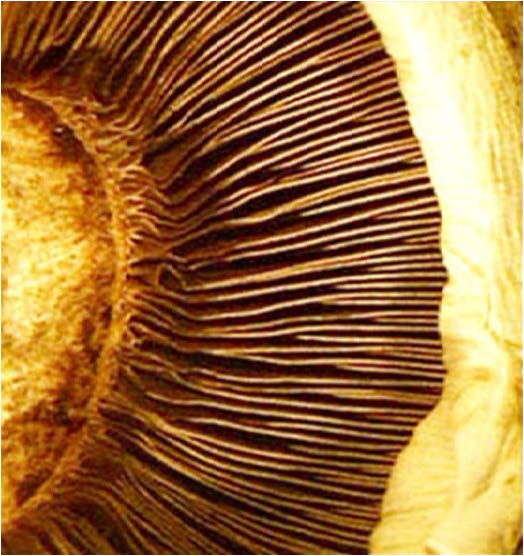 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, shows basidiospores (products of meiosis produced under the gills of a mushroom) |
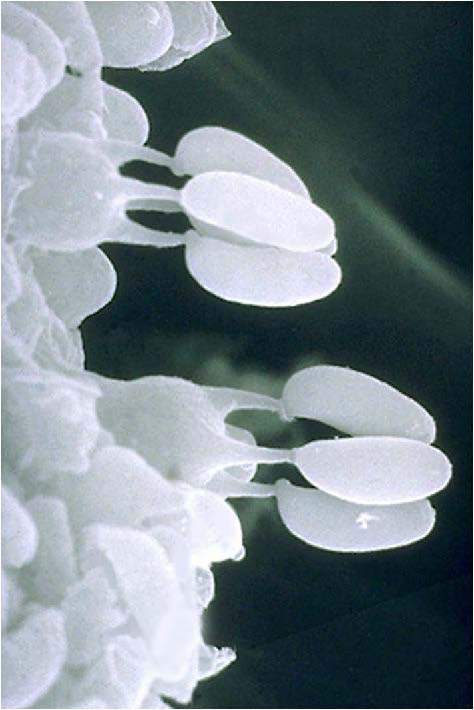 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, shows basidiospores (products of meiosis produced under the gills of a mushroom) |
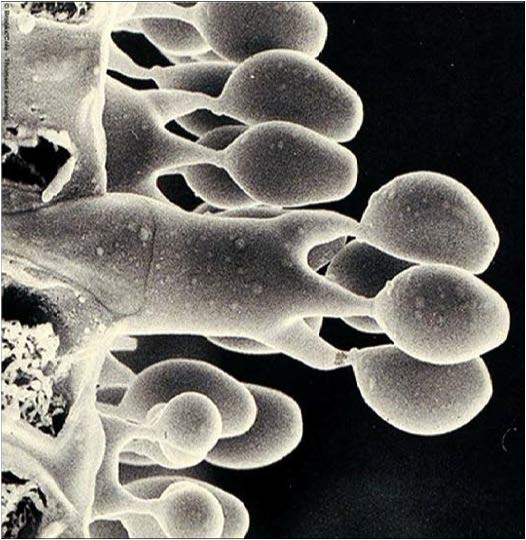 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, shows basidiospores (products of meiosis produced under the gills of a mushroom) |
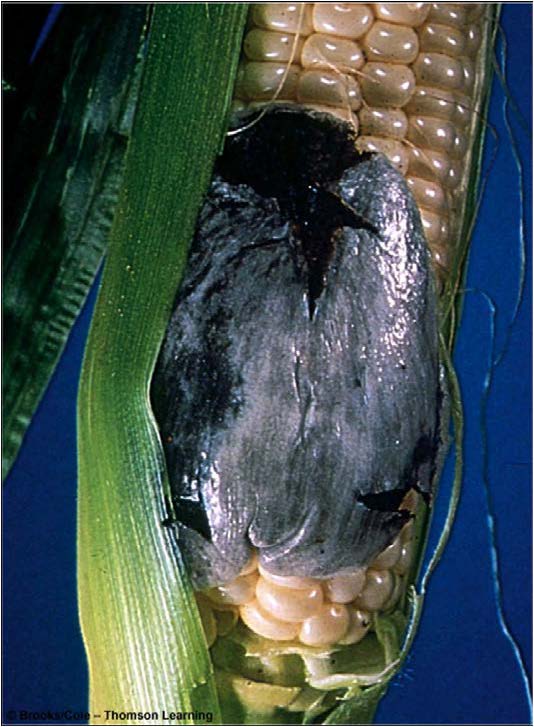 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Corn smut (Ustilago maydis), club fungi |
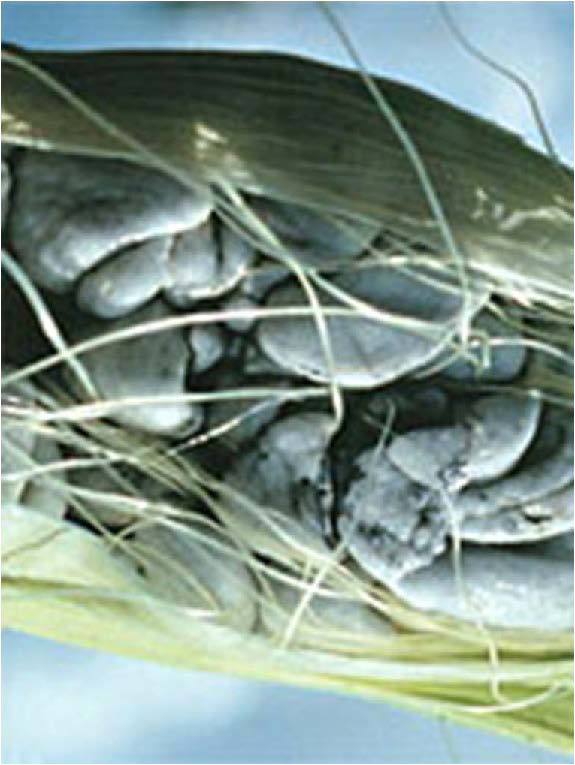 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Corn smut (Ustilago maydis), club fungi |
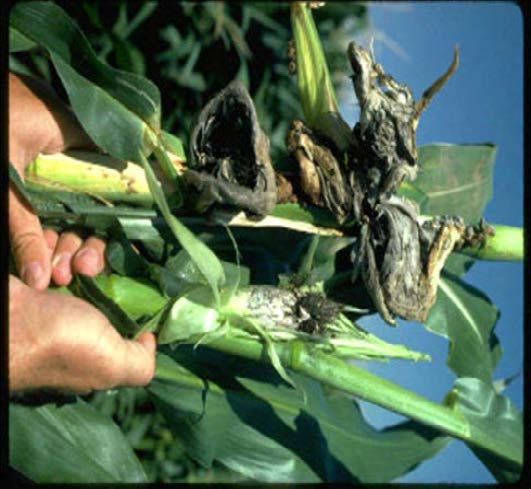 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Basidiomycota, Name: Corn smut (Ustilago maydis), club fungi |
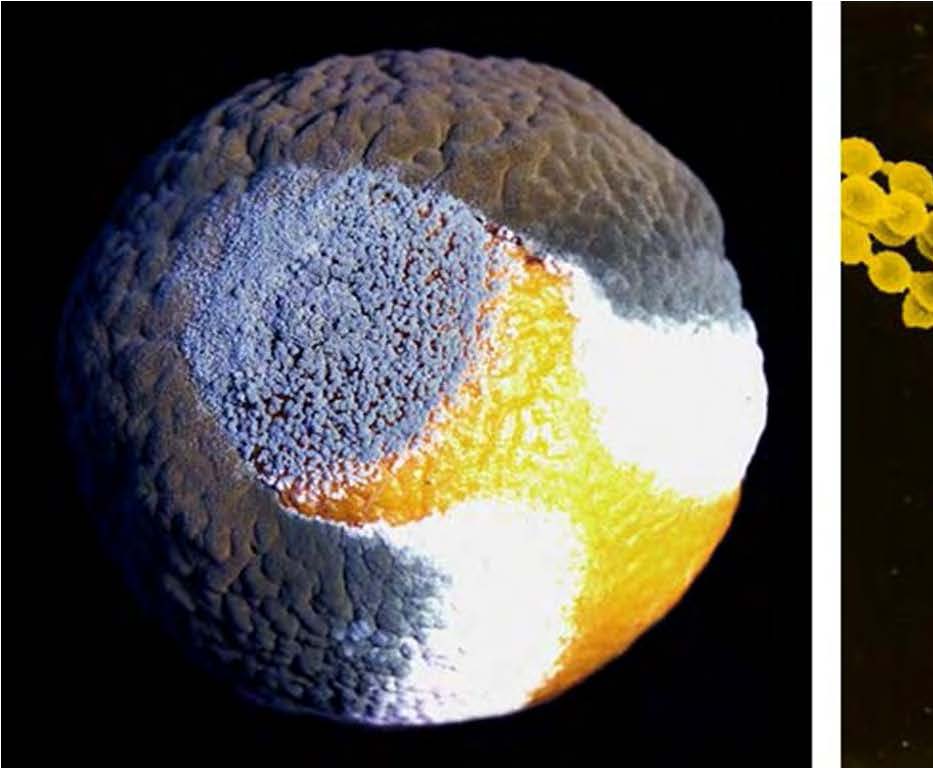 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Deuteromycota ("Imperfect Fungi"), No known sexual phase, asexual conidia only |
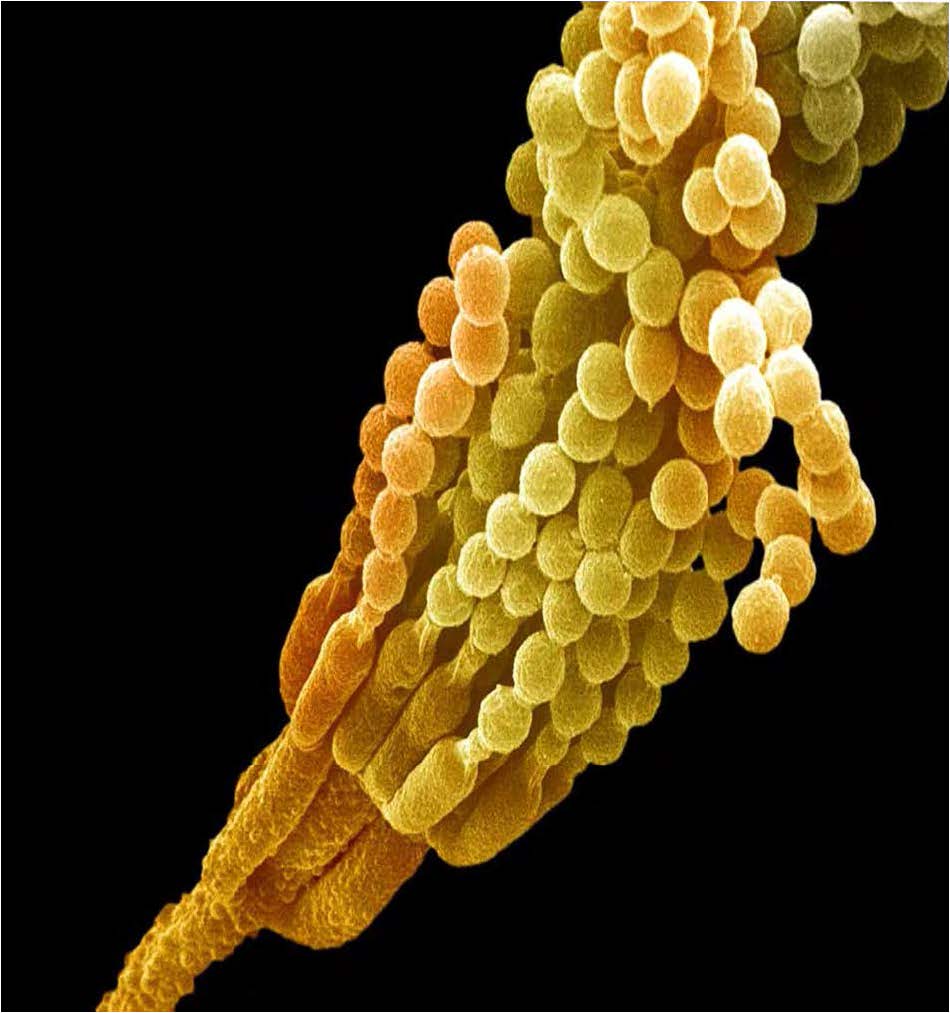 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Deuteromycota ("Imperfect Fungi"), No known sexual phase, asexual conidia only |
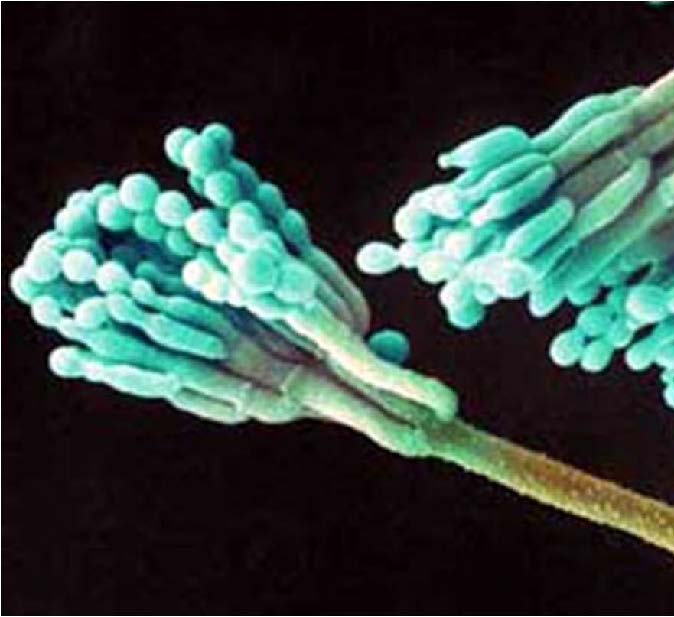 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Deuteromycota ("Imperfect Fungi"), No known sexual phase, asexual conidia only |
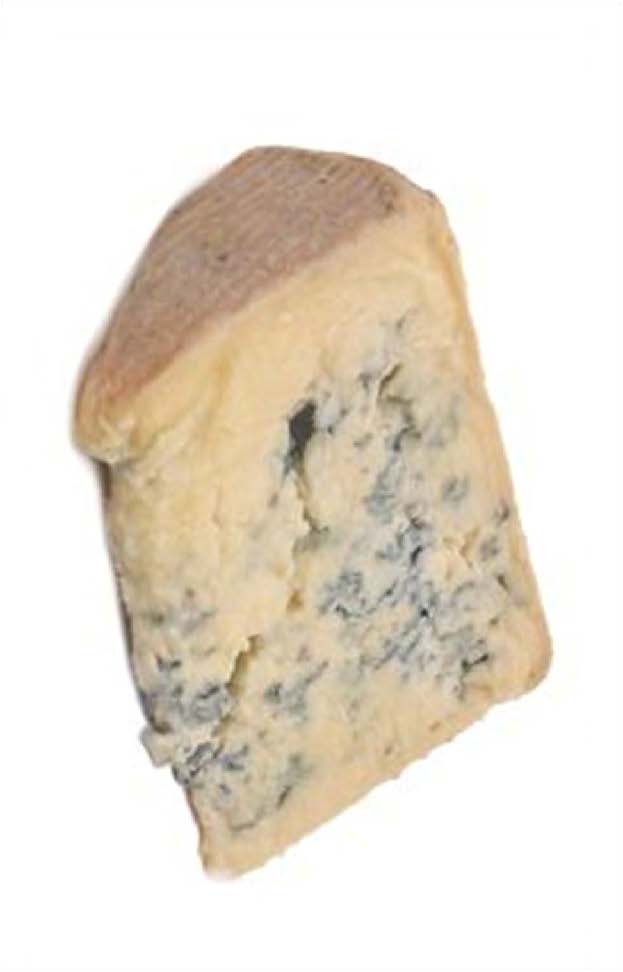 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Deuteromycota ("Imperfect Fungi"), No known sexual phase, asexual conidia only, Bleu cheese |
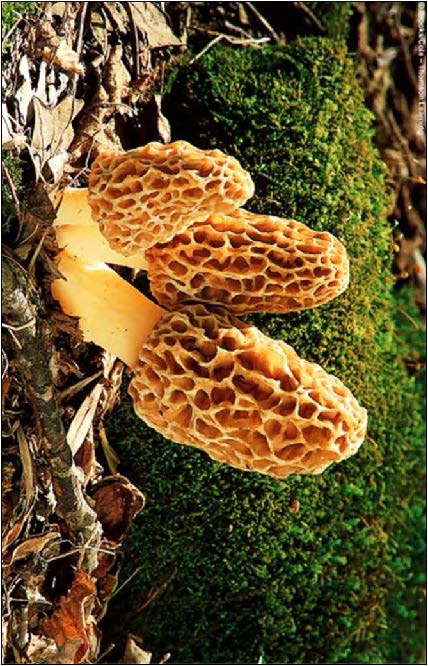 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Ascomycota, Name: Morel mushroom, sac/cup fungi, edible |
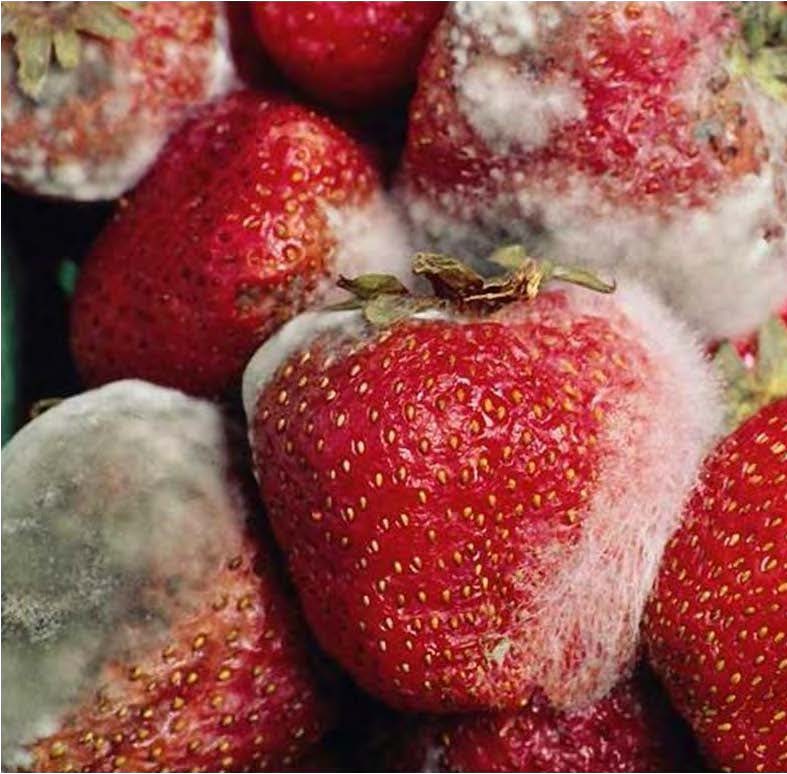 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Name: Rhizopus, causes food spoilage on stored food, such as strawberries (shown), bread, grapes, other berries, and grain |
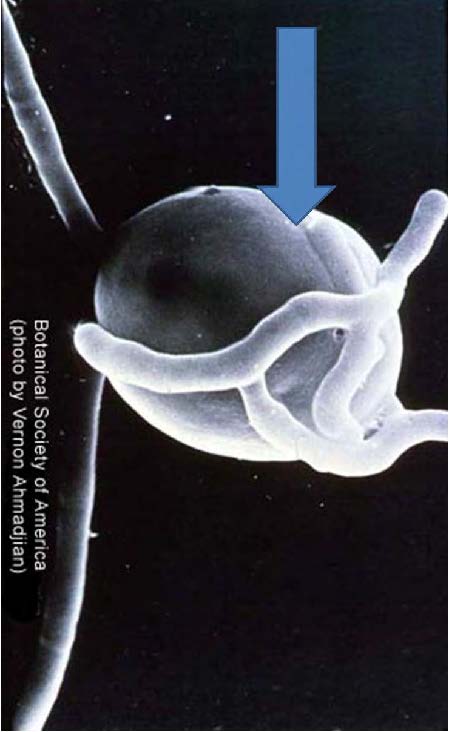 | shows Soredia which can break off and start a new lichen |
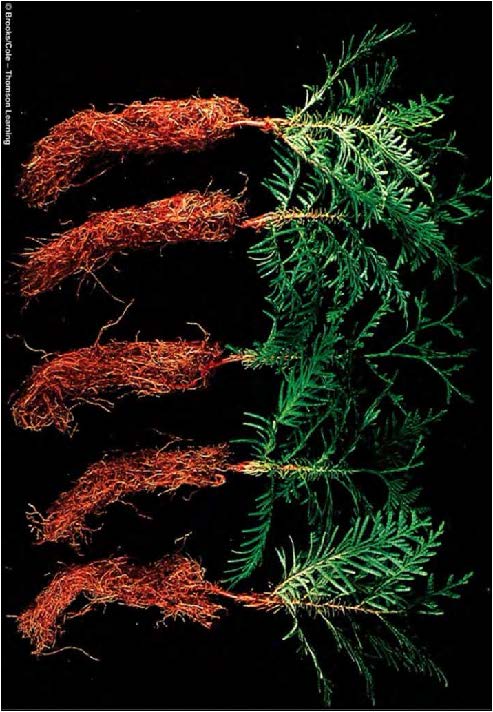 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Unikonta, Clade: Opisthokont, Phylum: Glomeromycota, Name: Mycorrhizae, friendly to roots |
 | Slime molds and fungal hyphae |
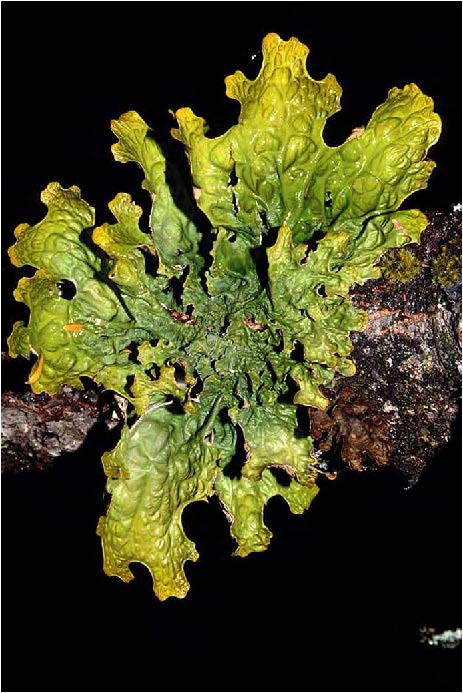 | Lichen |
 | shows lichen which is a mutualistic association of millions of photosynthetic cyanobacteria held in a mesh of fungal hyphae |
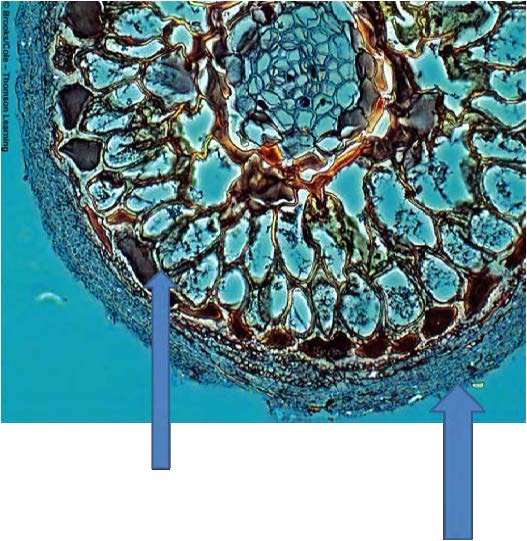 | bottom left corner: fungal hypha between plant cells, bottom right: sheath of fungal hyphae encircling root |
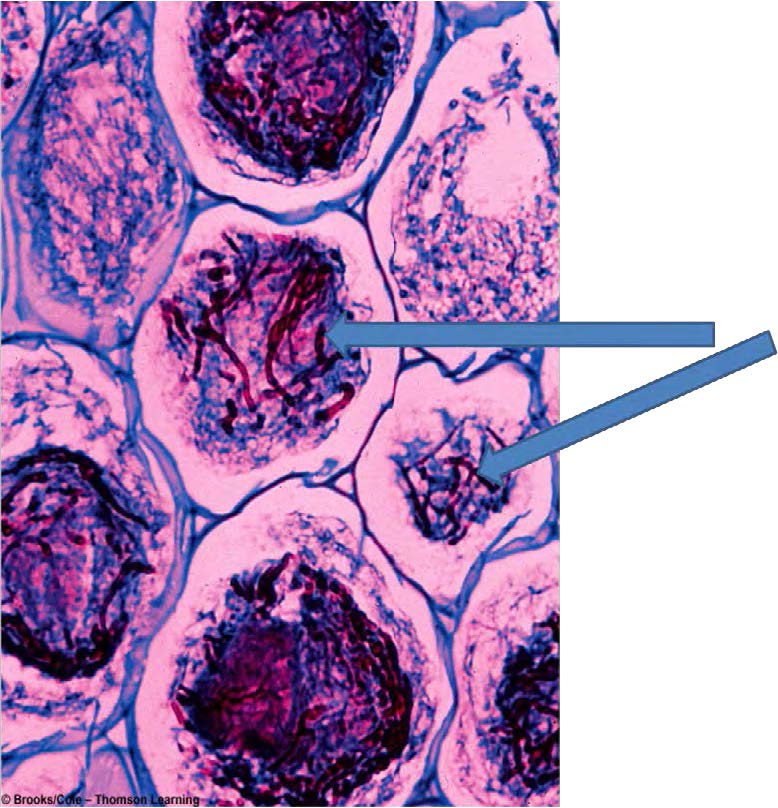 | shows fungal hyphae within plant cortical cells |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Bryophytes, Name: Mosses, hornworts, liverworts; Facts: Non-vascular, no true leaves, stems, or roots, must live near moist environment, gametophyte dominant, diploid part are tall, stalk-like sporophytes. |
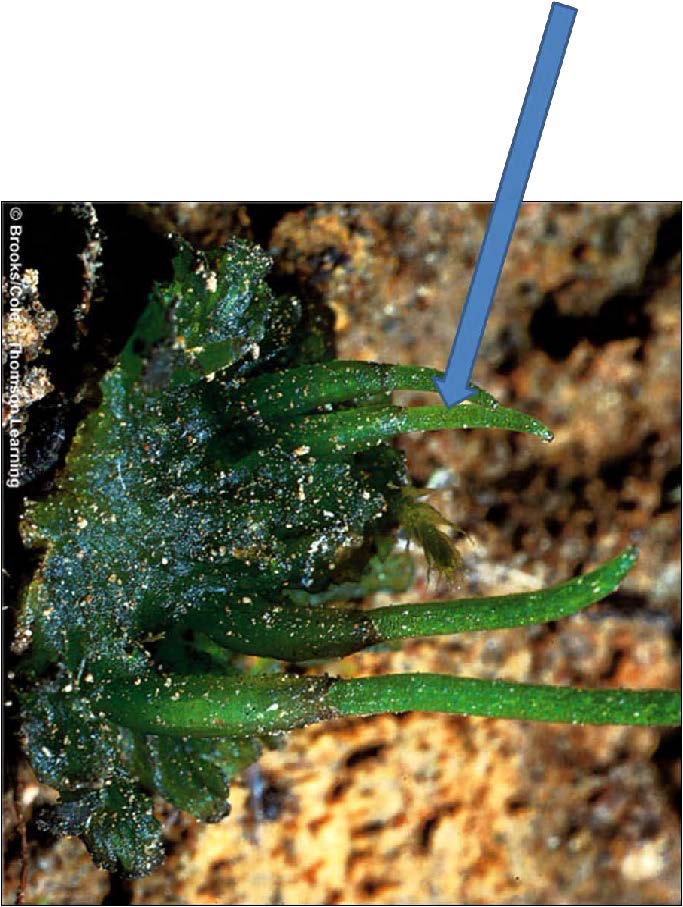 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Bryophytes, Name: Anthoceros - hornworts, Facts: Non-vascular, no true leaves, stems, or roots, must live near moist environment, gametophyte dominant, diploid part are tall, stalk-like sporophytes. |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Bryophytes, Name: Marchantia - Liverworts, Facts: Non-vascular, no true leaves, stems, or roots, must live near moist environment, gametophyte dominant, diploid part are tall, stalk-like sporophytes, reproduce by forming gemmae cups that contain gemmae that are dispersed by rain drops. |
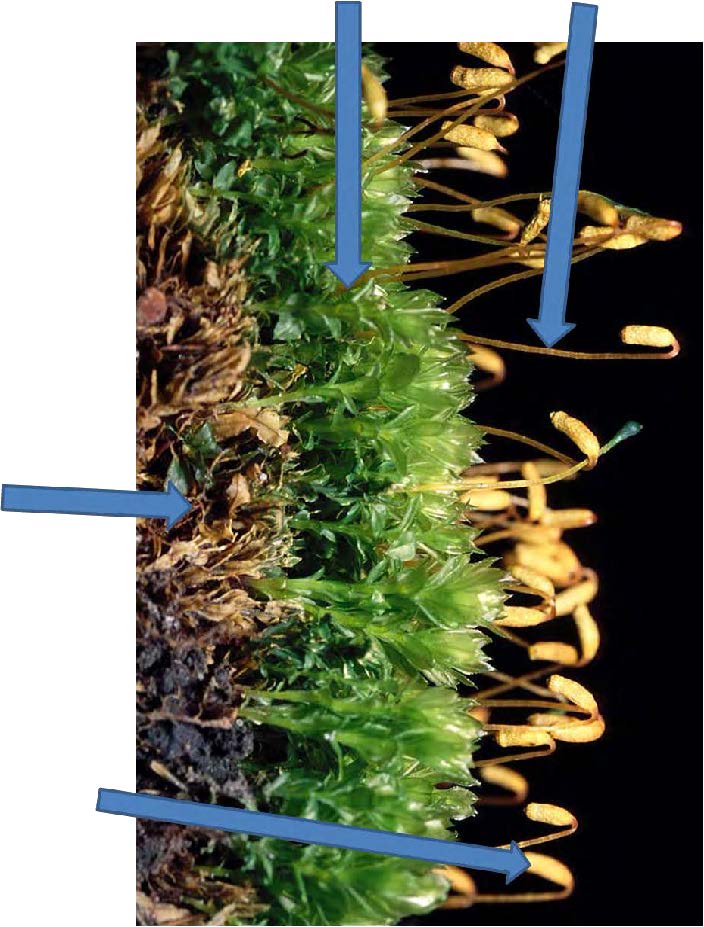 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Bryophytes, Phylum: Bryophyta (mosses), Facts: Non-vascular, no true leaves, stems, or roots, must live near moist environment, gametophyte dominant, diploid part are tall, stalk-like sporophytes., .png) |
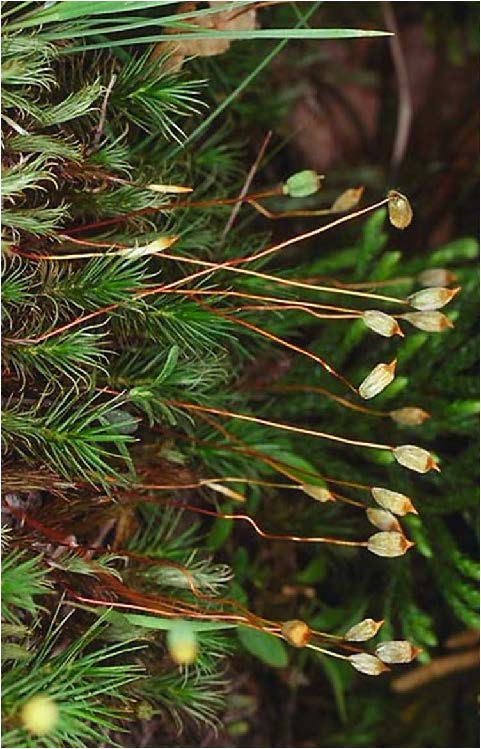 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Bryophytes, Phylum: Bryophyta (mosses), Facts: Non-vascular, no true leaves, stems, or roots, must live near moist environment, gametophyte dominant, diploid part are tall, stalk-like sporophytes. |
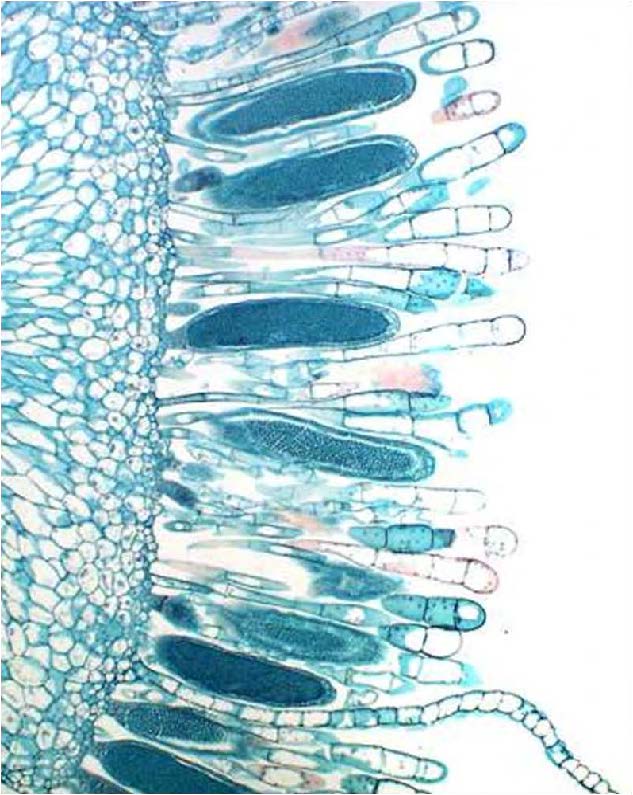 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Bryophytes, Name: Mosses, hornworts, liverworts, shows antheridia (male) that makes sperm to swim down the neck of the female archaegonia to fertilize eggs |
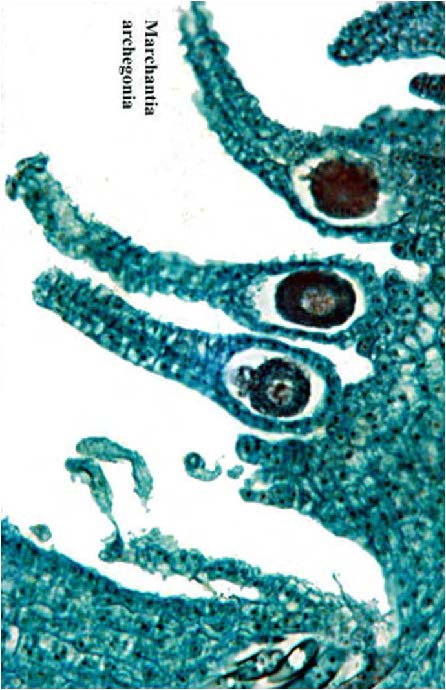 | Marchantia archegonia |
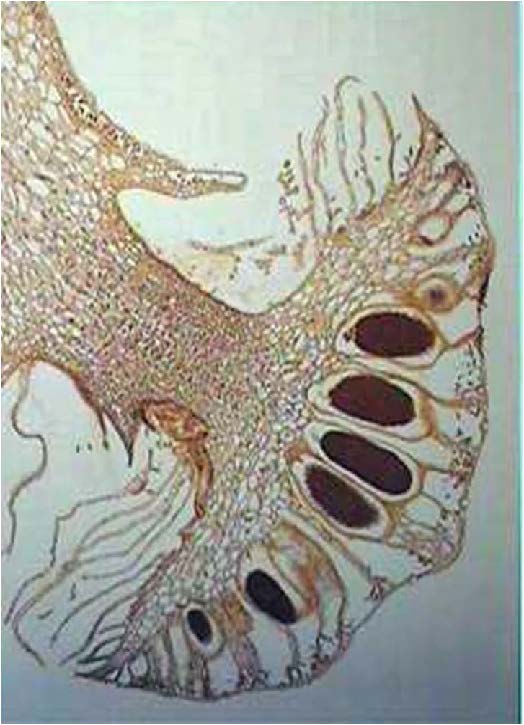 | <needs info> |
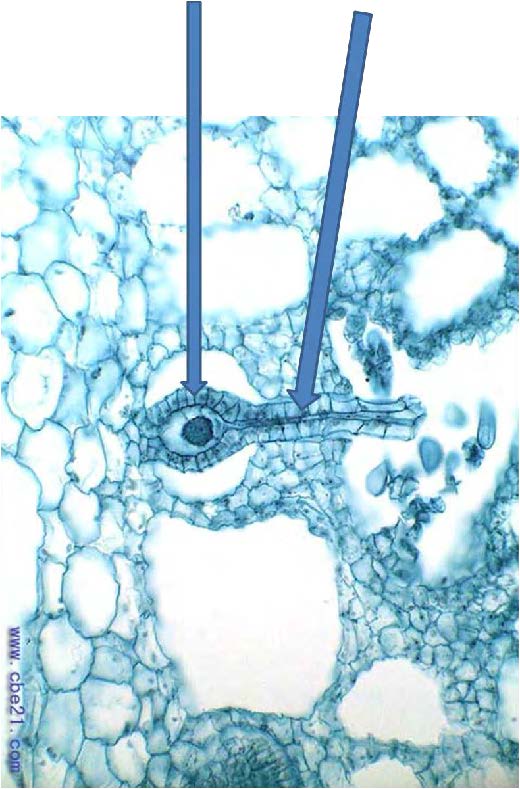 | Domain: Eukarya, Superclade: Archaeplastida, Derived homology: Bryophytes, Name: Mosses, SHOWS female archegonia that contains egg to be fertilized as sperm from male antheridia swim down neck |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Whisk fern, Facts: Seedless vascular plants, true leaves, stems, and/or roots, sporophyte dominant, leaves can be tiny microphylls with one vein or megaphylls with many veins. SHOWS sporangium of Psilotum - Whisk Fern that contains haploid spores |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Whisk Ferns (Psilotum), Facts: Seedless vascular plants, true leaves, stems, and/or roots, sporophyte dominant, leaves can be tiny microphylls with one vein or megaphylls with many veins. |
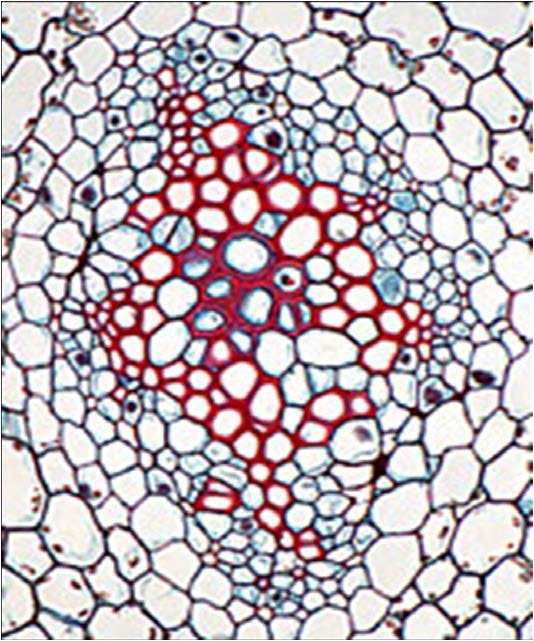 | shows vascular tissue of plants |
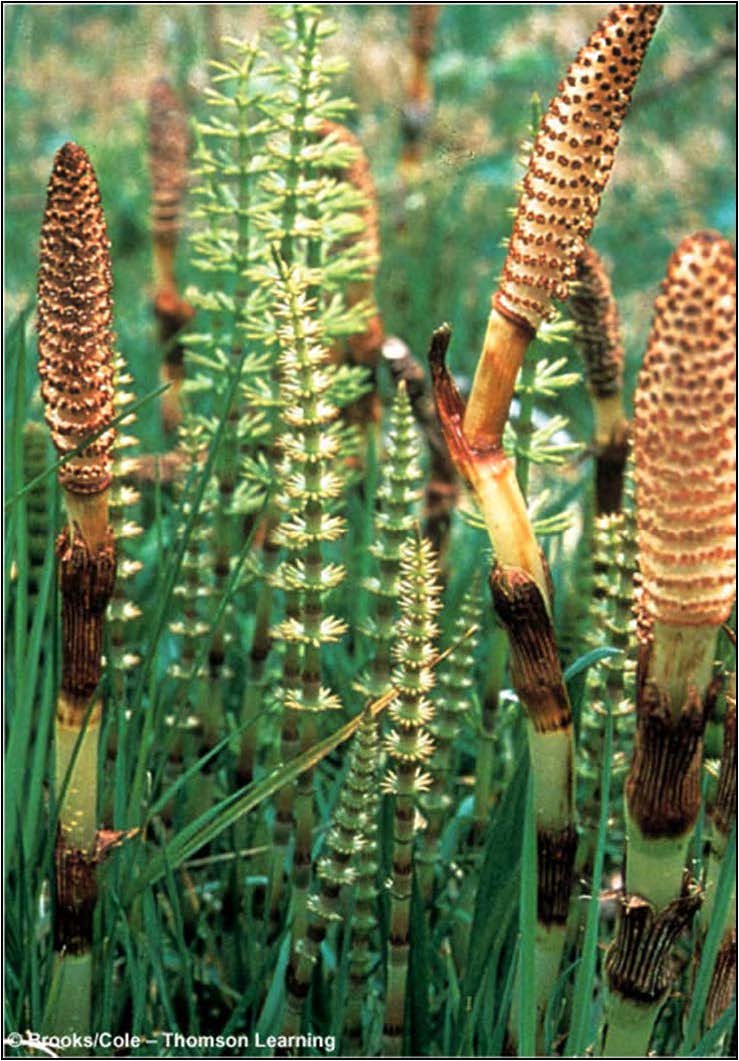 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Equisetum stobilus (horsetails), Facts: Seedless vascular plants, true leaves, stems, and/or roots, sporophyte dominant, leaves can be tiny microphylls with one vein or megaphylls with many veins, used to be the dominant plants on Earth. |
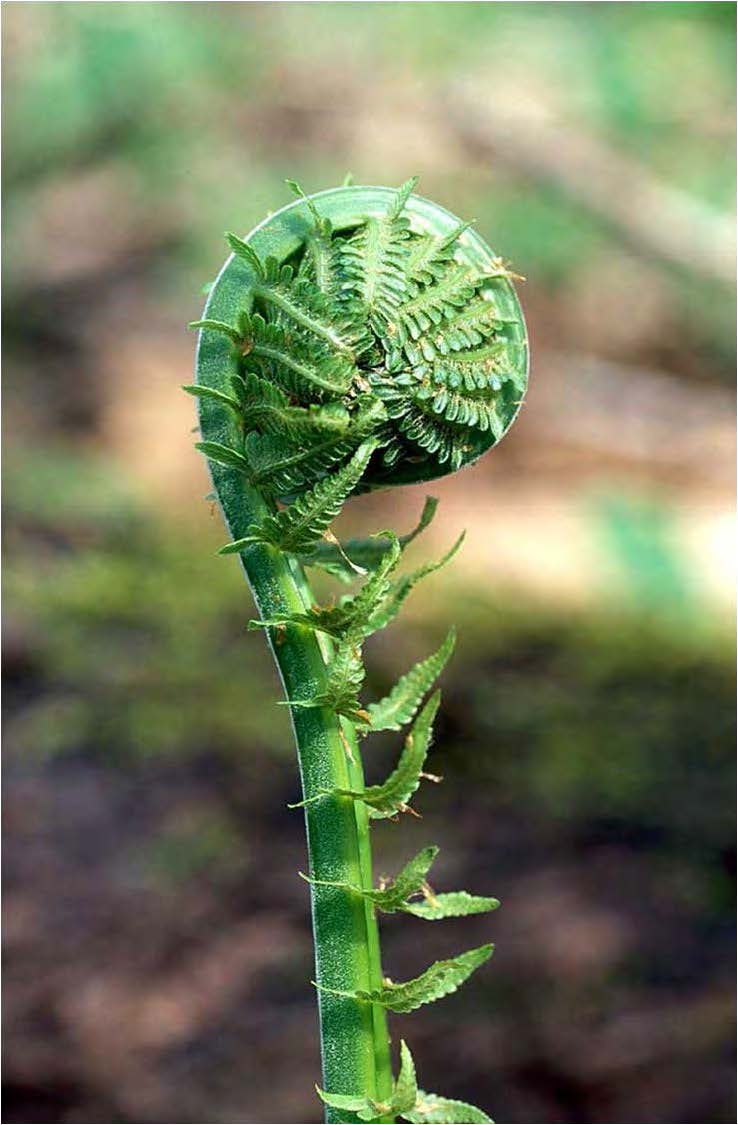 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Ferns, Facts: Ferns start life from haploid spore and geminate into heart-shaped prothallus; the zygote develops into fiddlehead (shown in picture) which unfurls to the mature frond; Sori on underside of frond are the sporangia where meiosis happens producing haploid spores. |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Club mosses, Facts: formed coal deposits of today, true roots and stems, and tiny microphyll leaves |
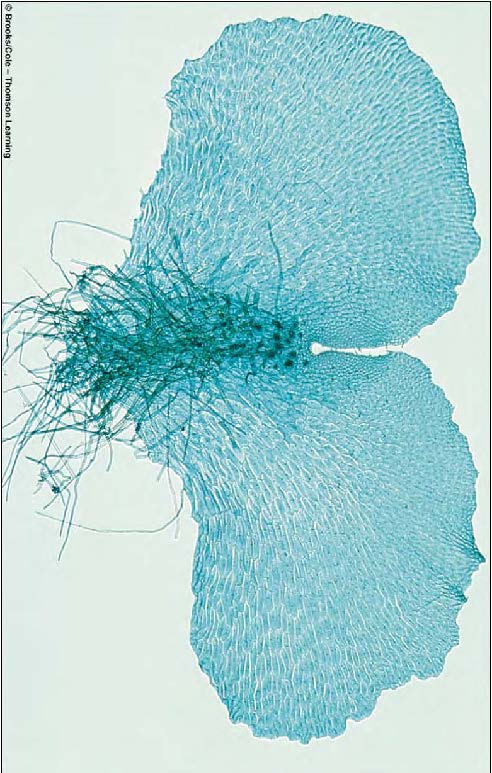 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Ferns, Facts: Ferns start life from haploid spore and geminate into heart-shaped prothallus (shown in picture); the zygote develops into fiddlehead which unfurls to the mature frond; Sori on underside of frond are the sporangia where meiosis happens producing haploid spores. |
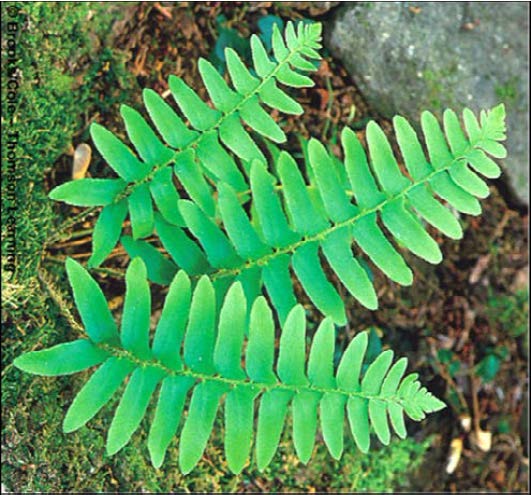 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Ferns, Facts: Ferns start life from haploid spore and geminate into heart-shaped prothallus; the zygote develops into fiddlehead which unfurls to the mature frond (shown in picture); Sori on underside of frond are the sporangia where meiosis happens producing haploid spores. |
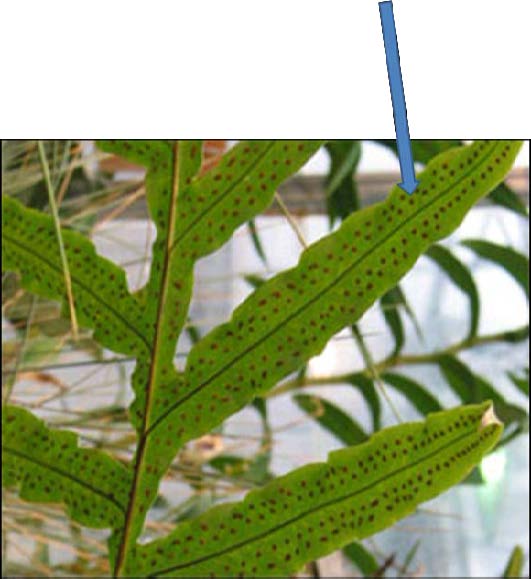 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Ferns, Facts: Ferns start life from haploid spore and geminate into heart-shaped prothallus; the zygote develops into fiddlehead which unfurls to the mature frond; Sori (shown in picture) on underside of frond are the sporangia where meiosis happens producing haploid spores. |
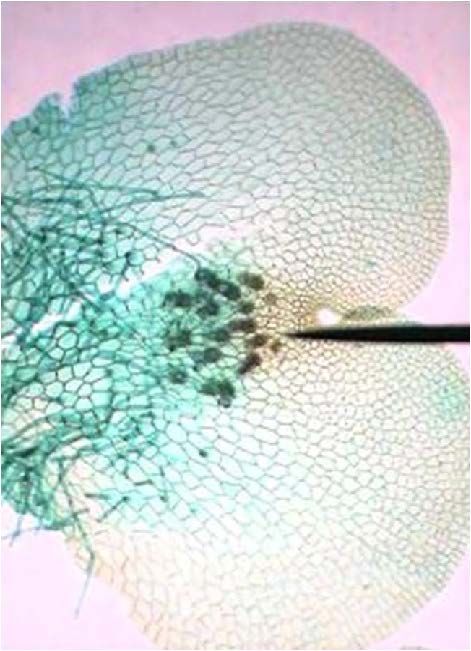 | <needs info> |
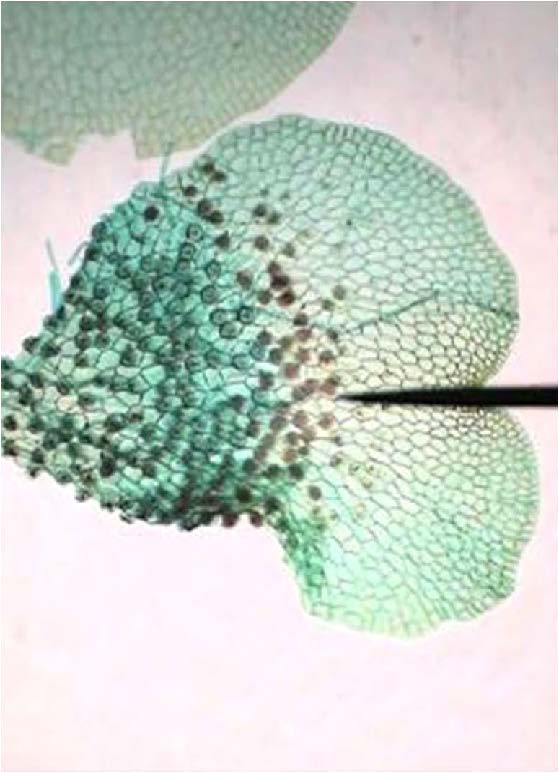 | <needs info> |
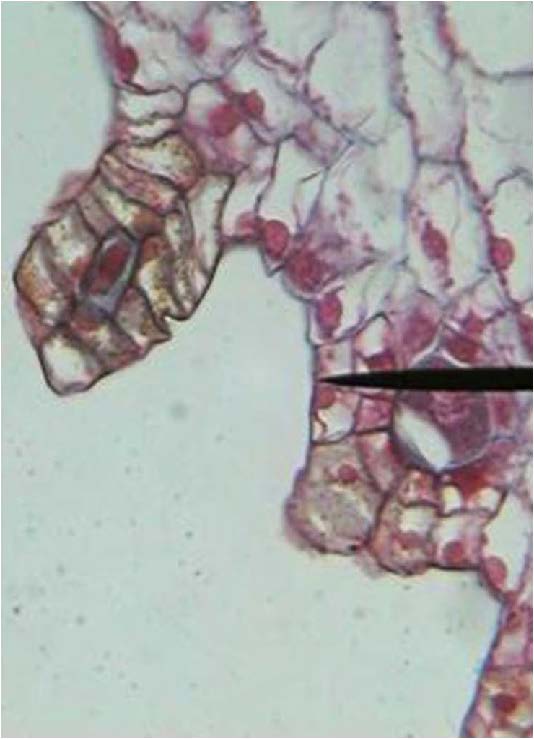 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Ferns, shows female archaegonia |
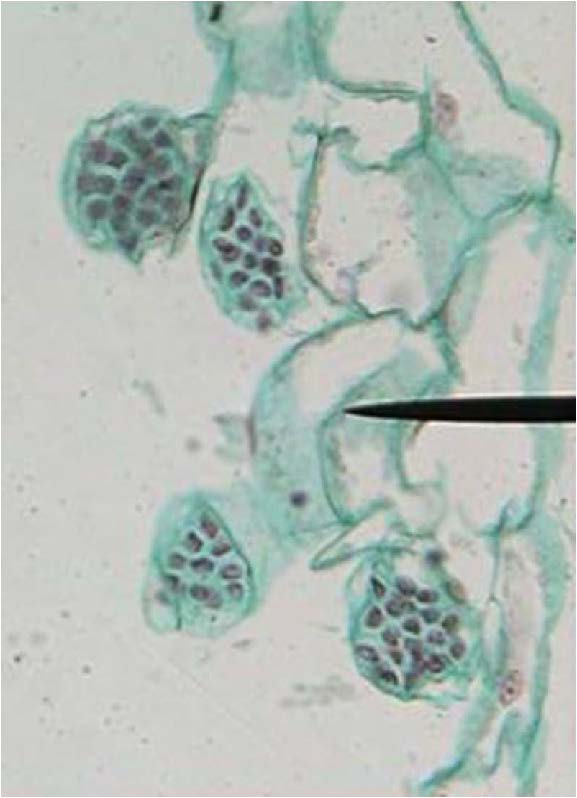 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Pteridophytes, Name: Ferns, shows male antheridia |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Cycads, Name: Zamia, Seed plants, sporophyte dominant, sperm must still swim to egg, dioecious - pollen cones on male plants * seed cones on female plants |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Conifers Name: Pinus contorta (Lodgepole Pine), Facts: Seed plants, sporophyte dominant, sperm must still swim to egg, monoecious - separate male & female cones on the same plant |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Ginkgoes, Name: Ginkgo biloba, Facts: Seed plants, sporophyte dominant, sperm must still swim to egg, dioecious - pollen cones on male plants & seed cones on female plants, has stinky female seeds |
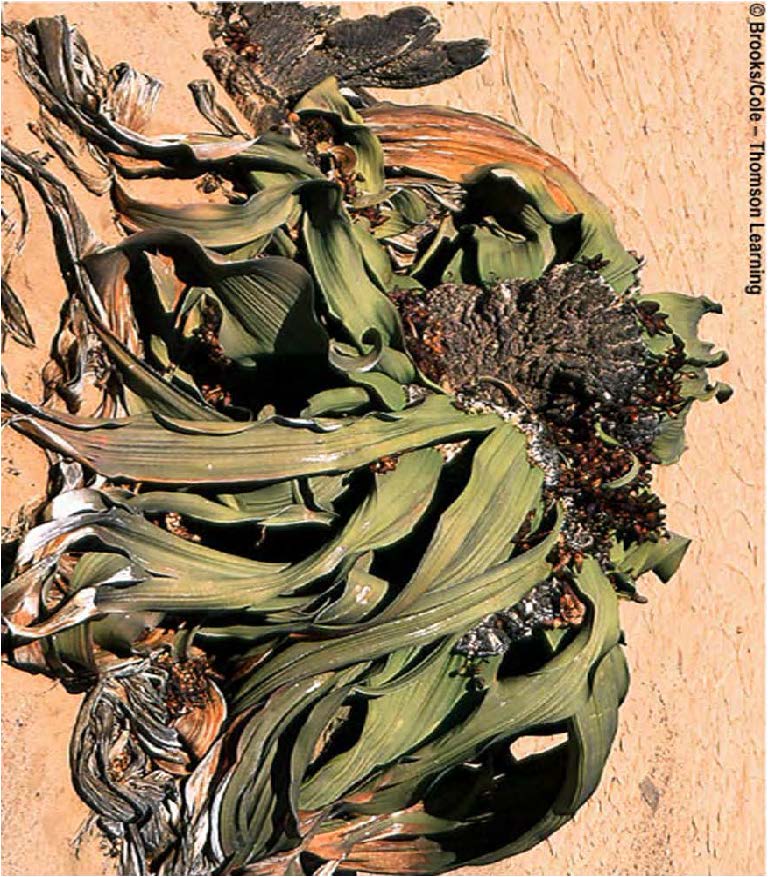 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Gnetophytes, Name: Welwitschia, Facts: Seed plants, sporophyte dominant, sperm must still swim to egg, first and only gymnosperm with vessel elements |
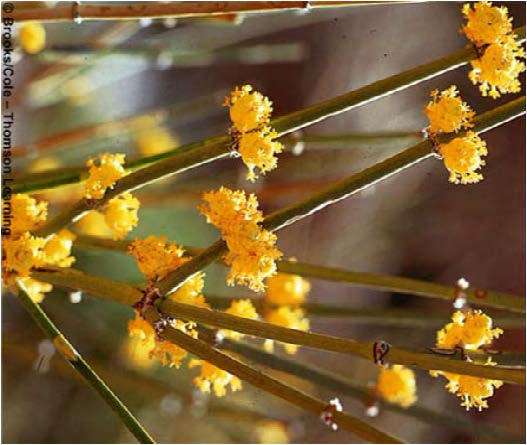 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Gnetophyta, Name: Ephedra, Facts: Used to make Mormon tea and other stimulants |
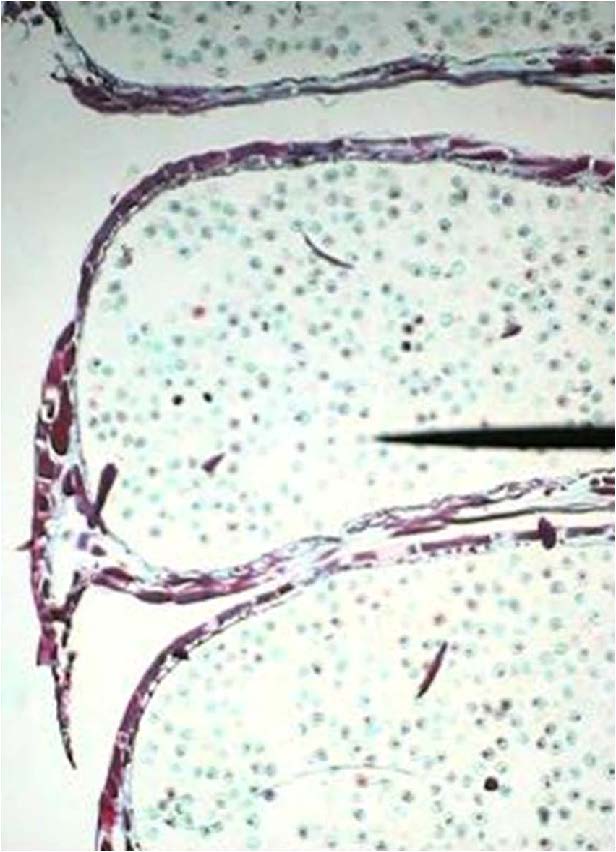 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Conifers, shows pine male cone with developing pollen |
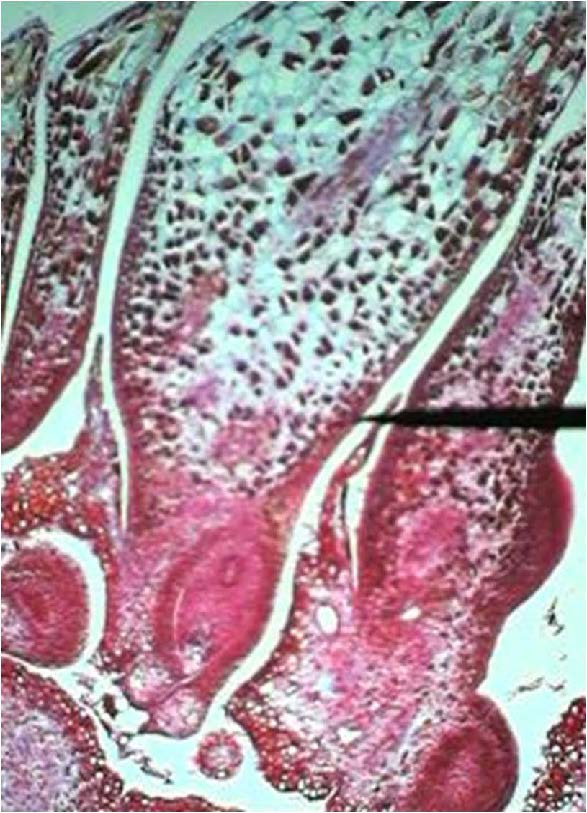 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Conifers, shows female cone with ovule |
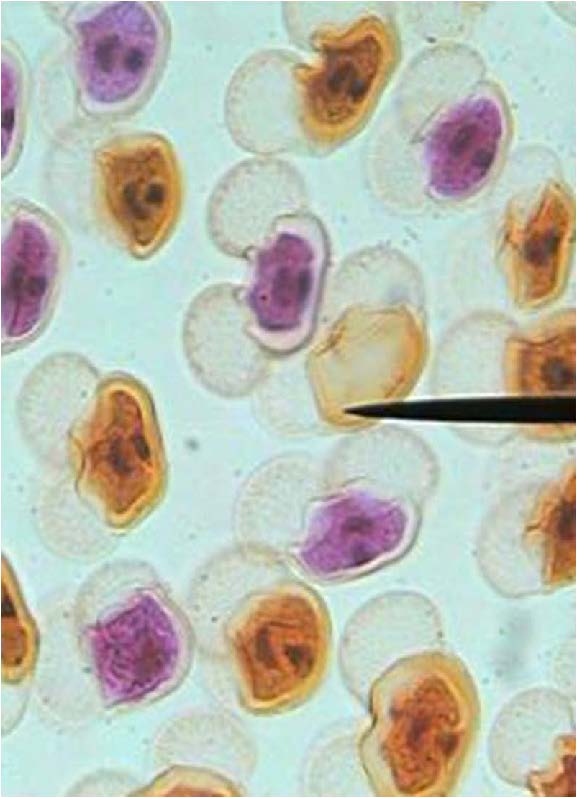 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Gymnosperms, Phylum: Conifers, shows pine pollen |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Angiosperms, Facts: Flowering plants, picture shows monocot |
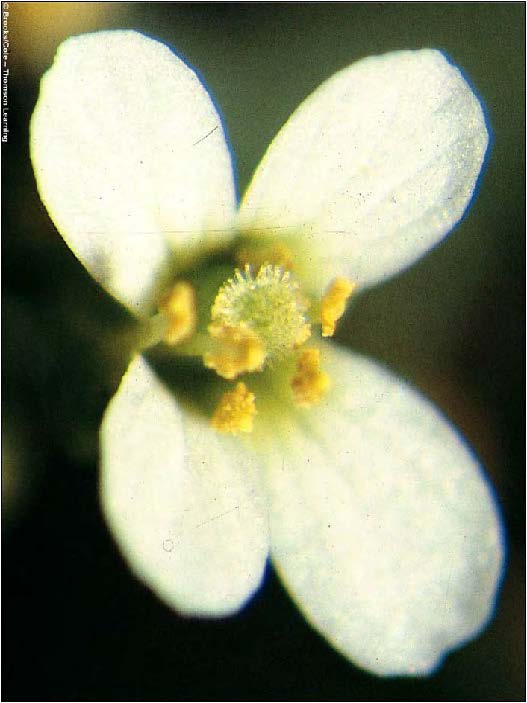 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Angiosperms, Facts: Flowering plants, picture shows dicot |
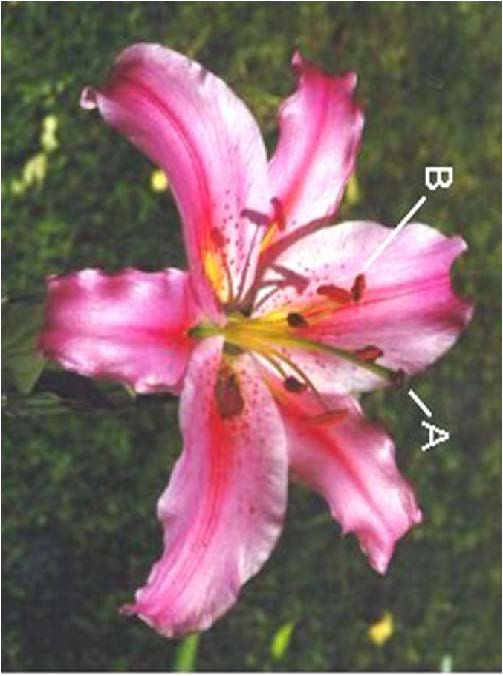 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Angiosperms, Facts: Flowering plants, picture shows monocot |
 | Domain: Eukarya, Kingdom: Plantae (superclade Archaeplastida), Derived homology: Angiosperms, Facts: Flowering plants, picture shows dicot |
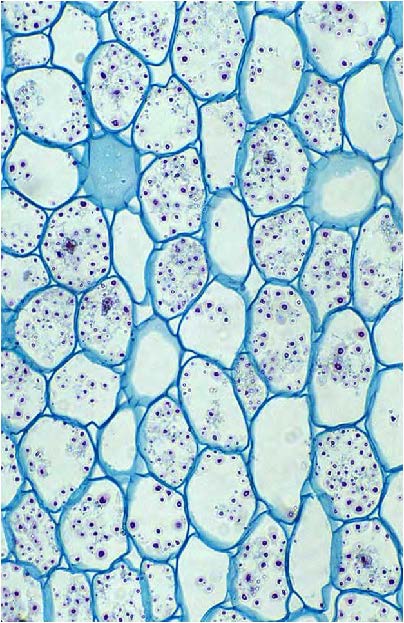 | shows root parenchyma for starch storage in vascular plants |
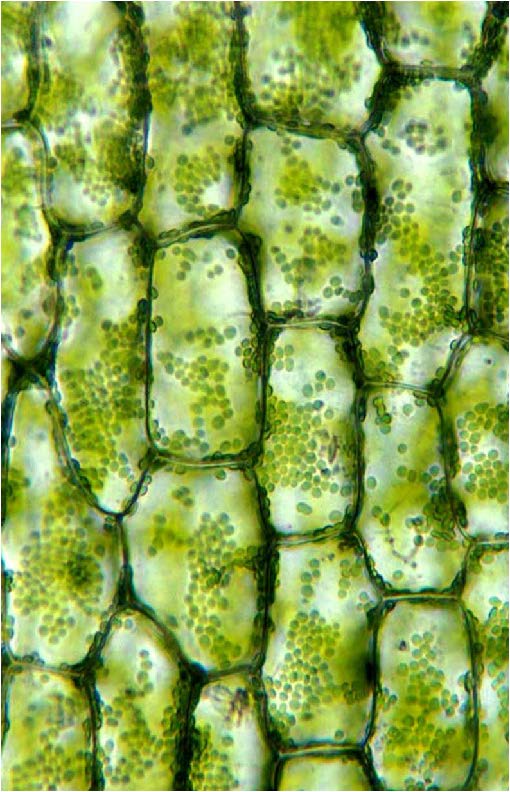 | shows leaf parenchyma for photosynthesis in vascular plants |
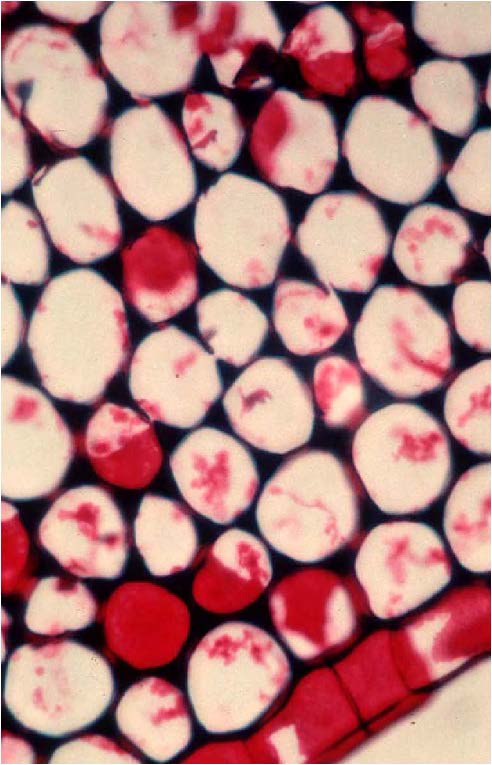 | shows collenchyma for structural support in vascular plants |
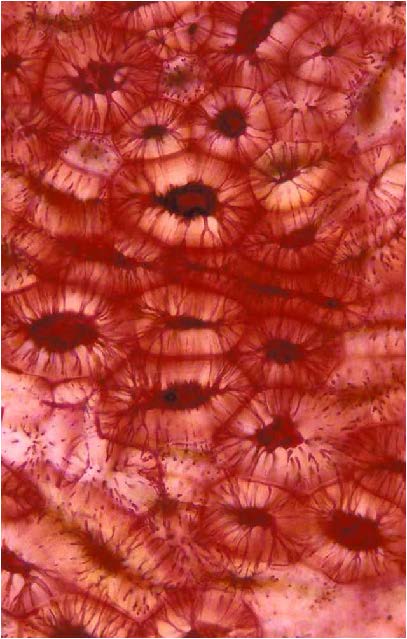 | shows sclerenchyma or dead cells |
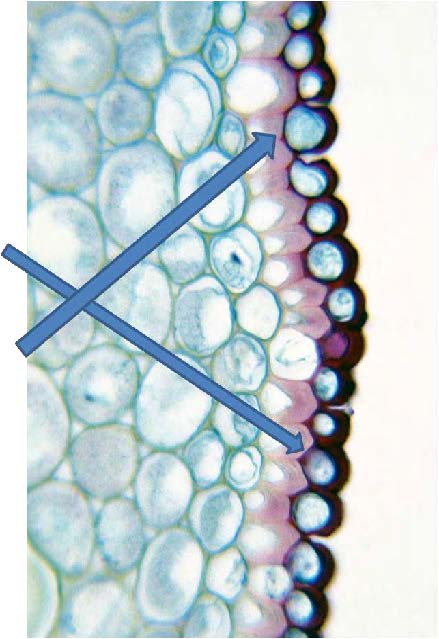 | shows epidermal cell covered by a cuticle; arrows pointing to collenchyma |
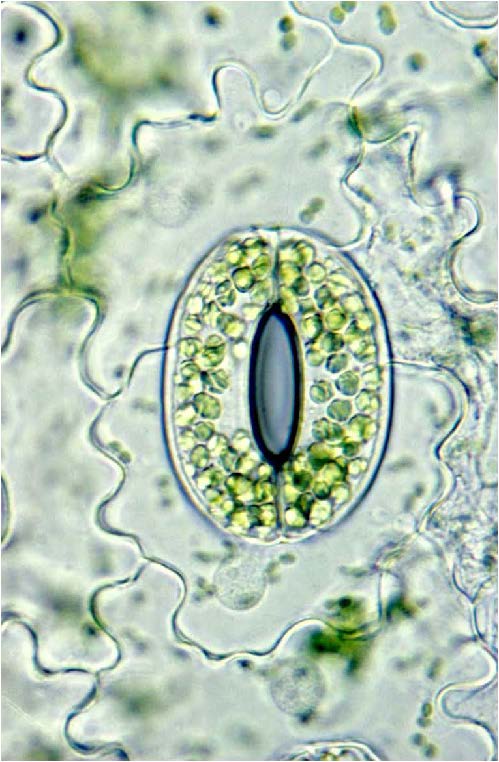 | shows guard cell which regulates water loss and gas exchange in vascular plants |
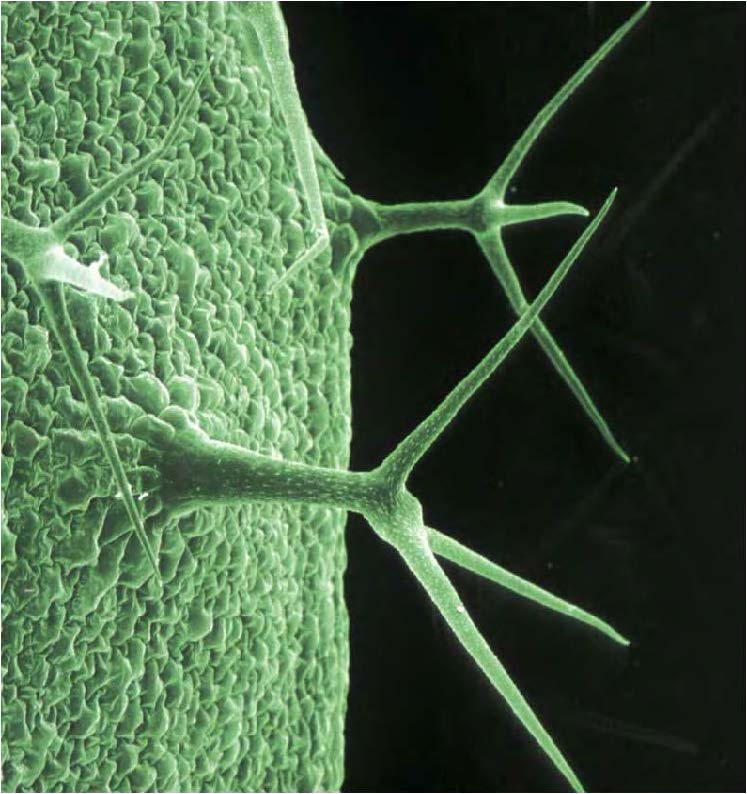 | shows trichome or hair-like outgrowth on vascular plants |
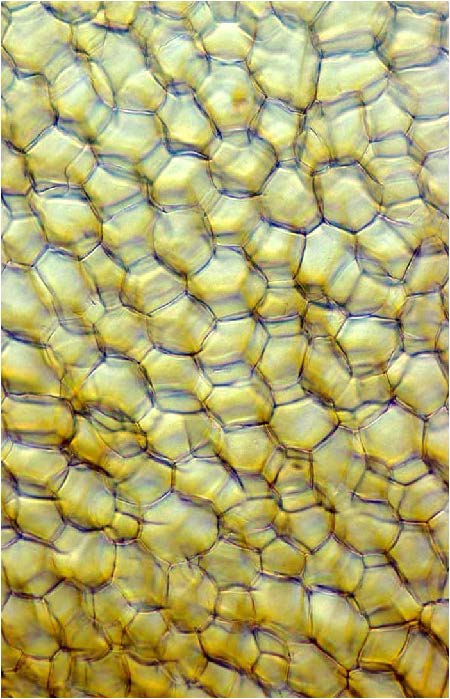 | shows cork cell which are dead at maturity in vascular plants |
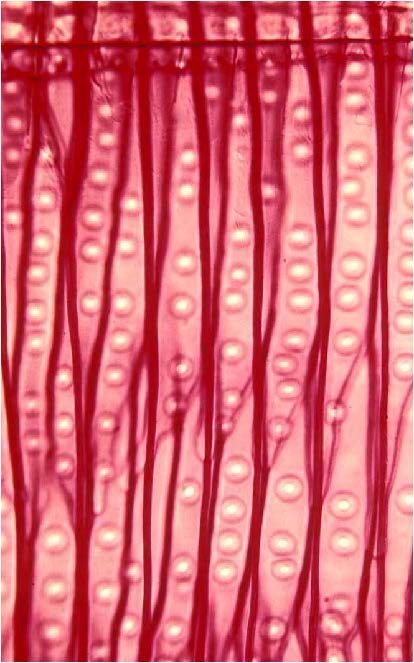 | shows tracheid vascular tissue; it is long, thin, and dead; tissue deals with water and sugar transport |
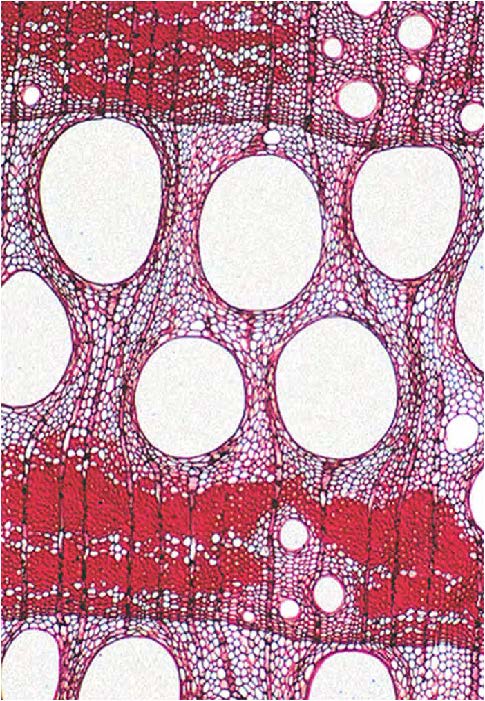 | shows vessel element which is vascular tissue; it is wide and perforated; deals with water and sugar transport |
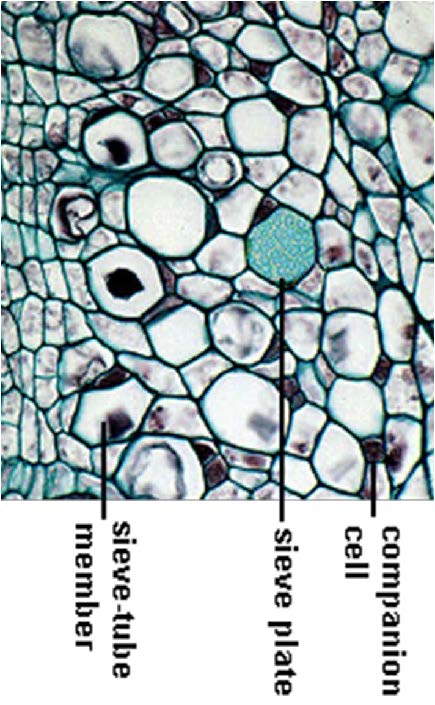 | shows sieve tube of vascular tissue; it is living but has no nucleus; deals with water and sugar transport; arrows from top to bottom: companion cell, sieve plante, sieve-tube member |
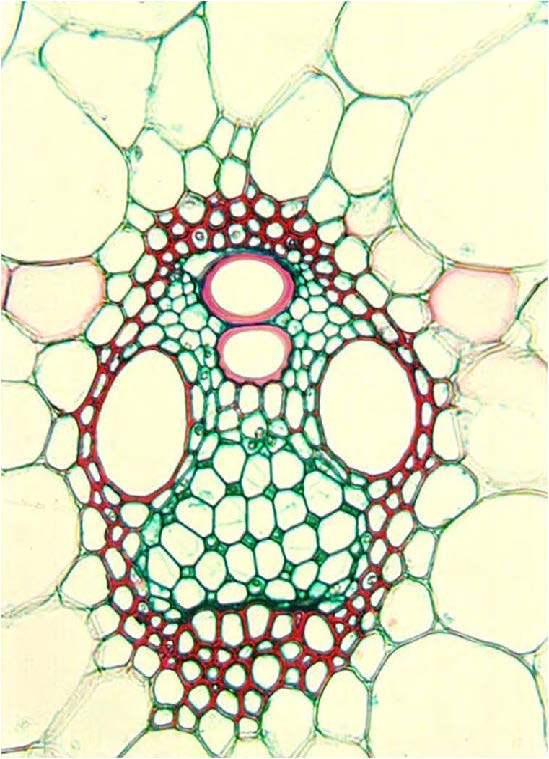 | shows companion cells of vascular tissue; they assist sieve tubes in water and sugar transport of vasular plants |
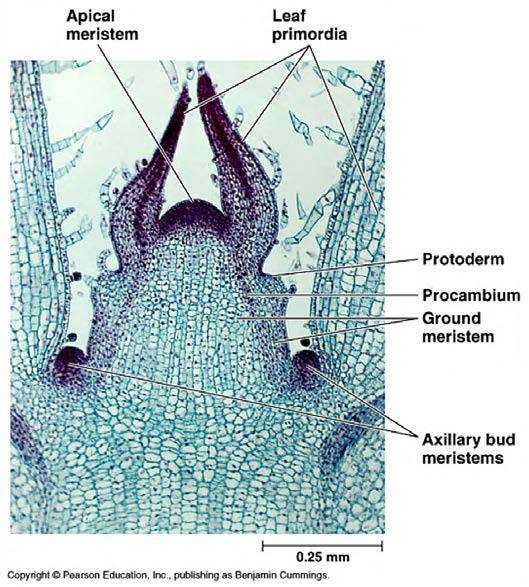 | <needs info> |
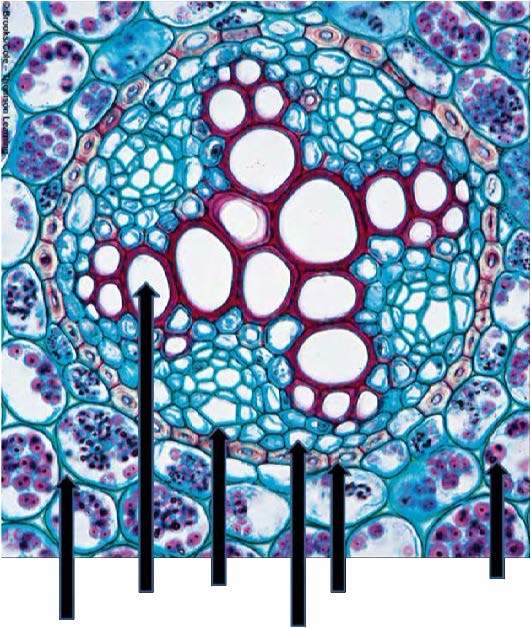 | from left to right: intercellular space, xylem vessel elements, phloem bundles, pericycle cell, endodermis cell, cortex cells - filled with amyloplasts (starch grains) |
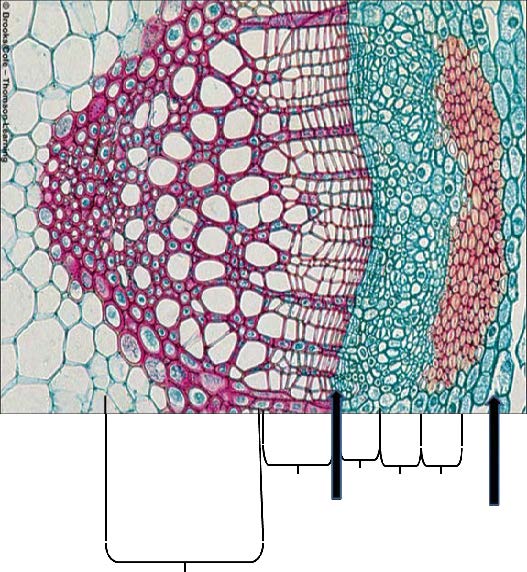 | from left to right: Primary xylem, Secondary xylem, Vascular cambium, Secondary phloem, Primary phloem, Phloem fiber cap, Cortex |
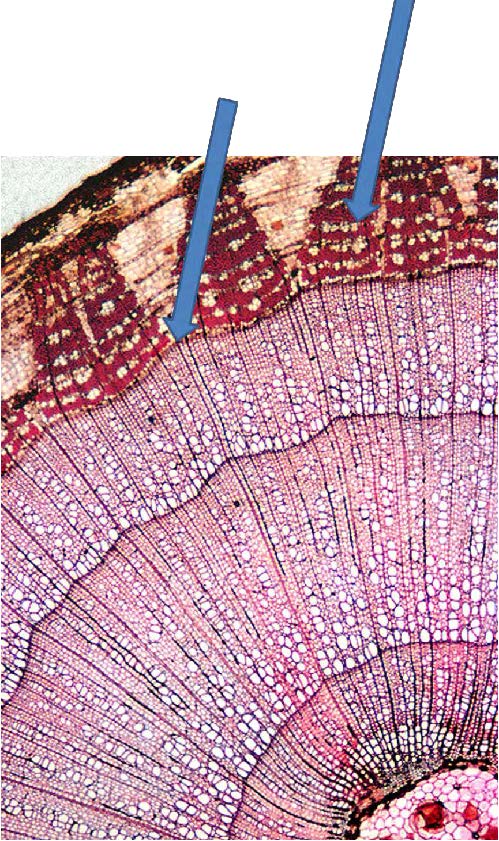 | from left to right: vascular cambium, phloem ray |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
| |