| A | B |
|---|
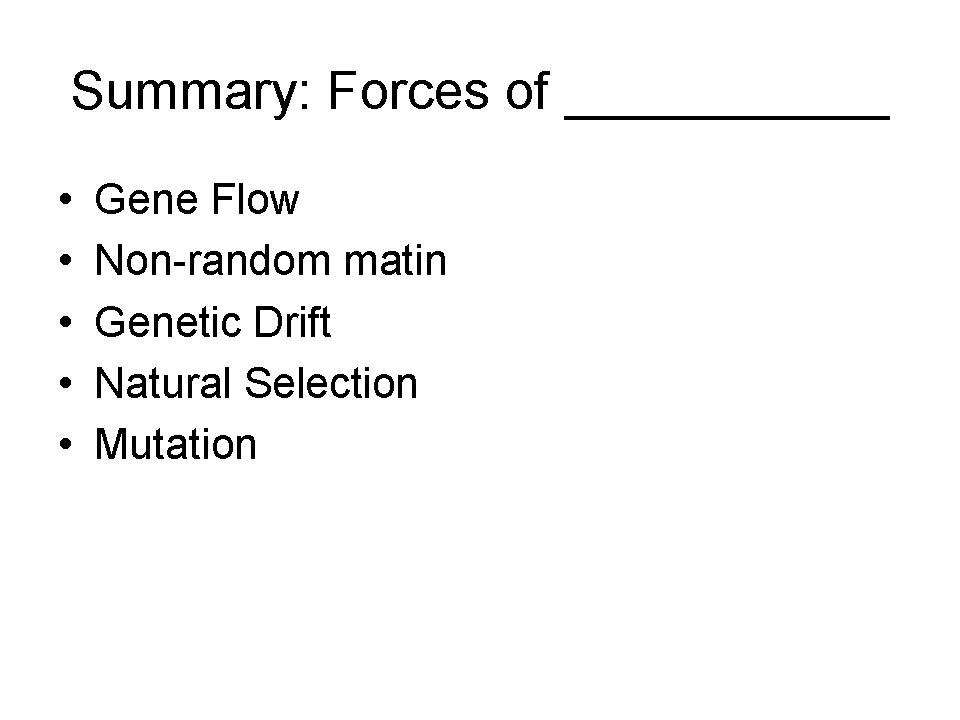 | Genetic Change |
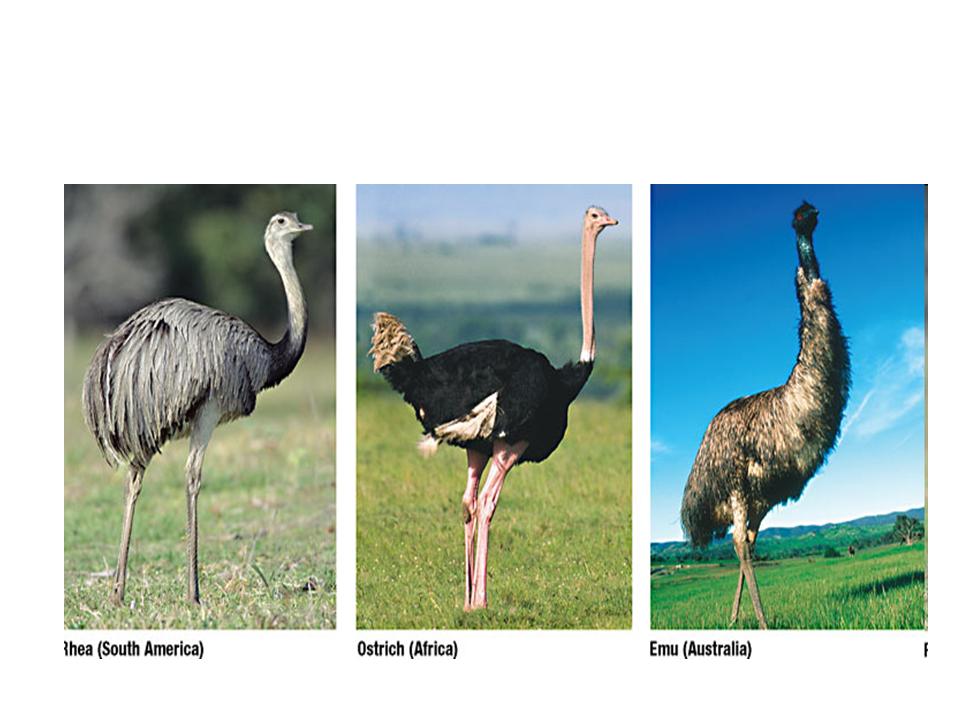 | Convergent Evolution |
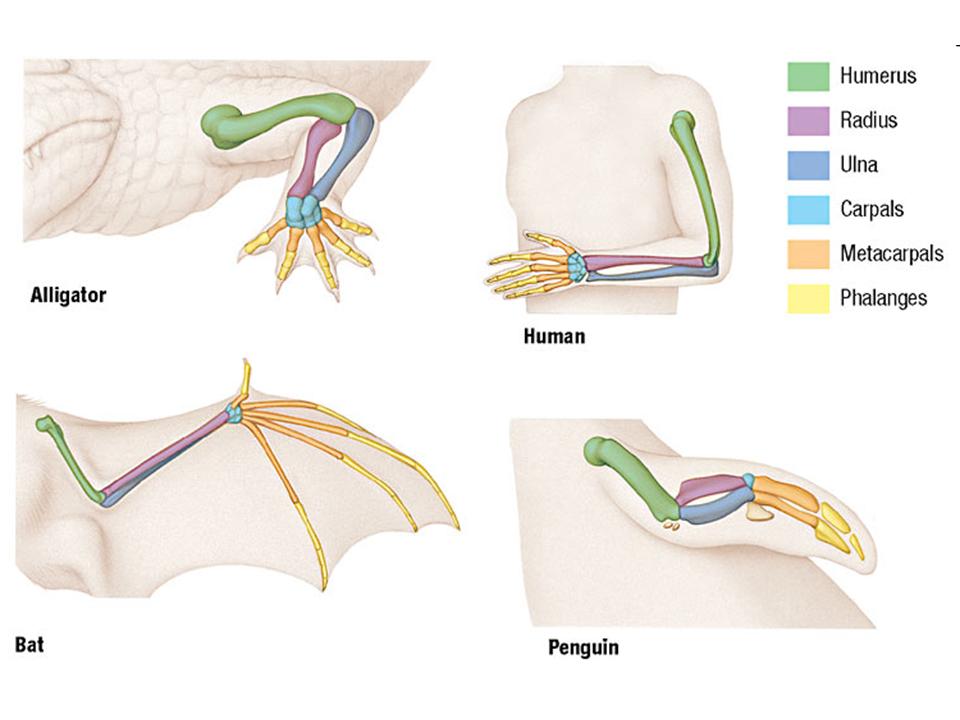 | Homologous Structures |
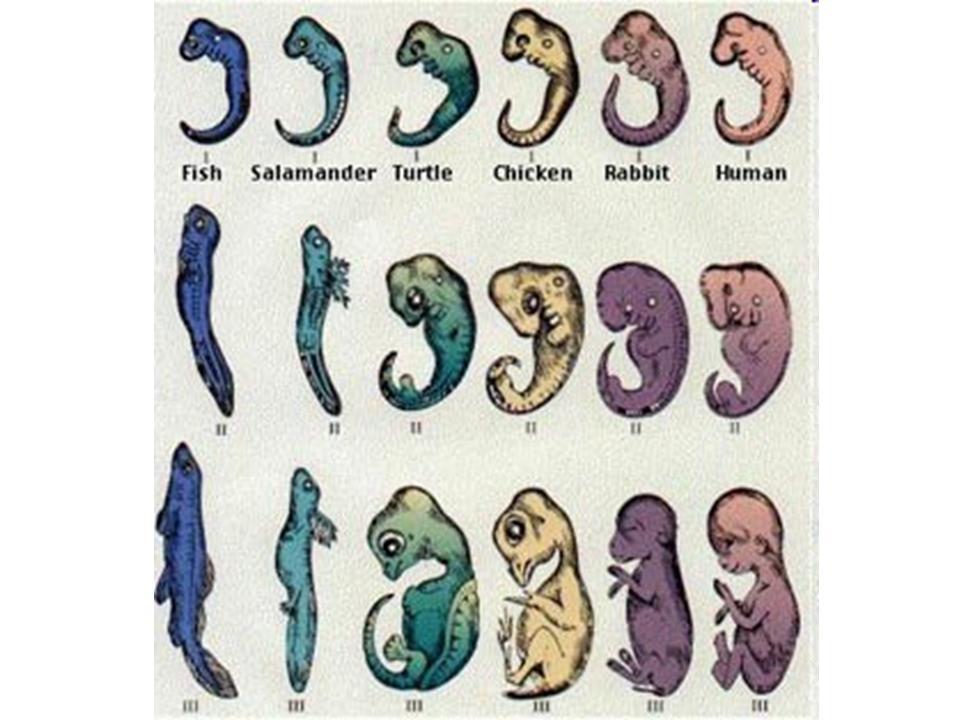 | Embryos show common ancestor |
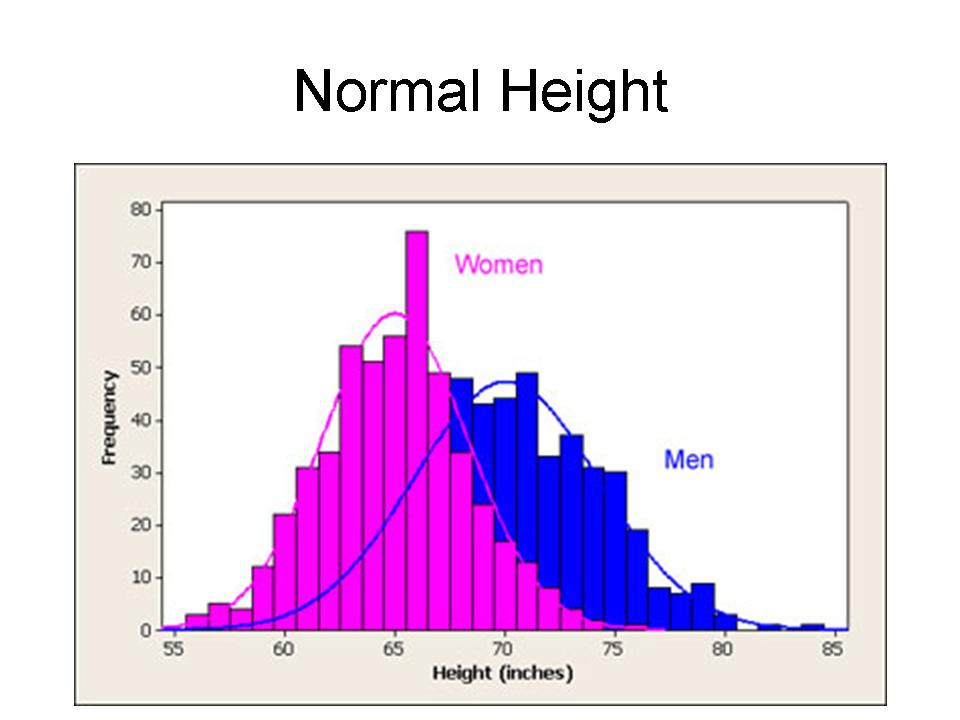 | Normal Distribution |
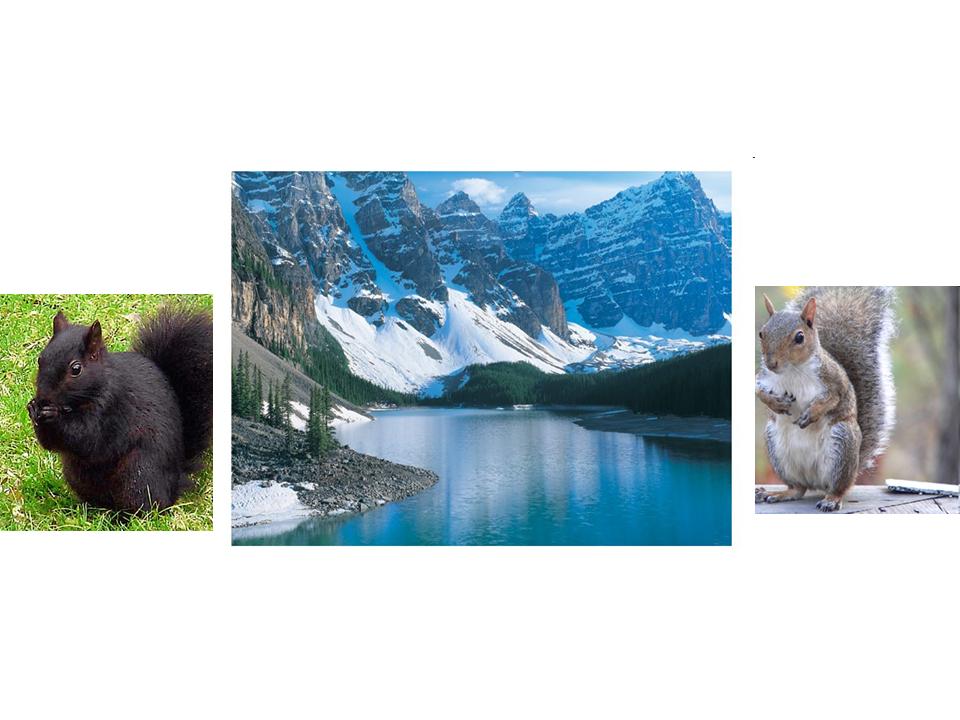 | Geographic Isolation |
 | Reproductive Isolation |
| Vestigial Organs |  |
| Father of Evolutionary Theory | Charles Darwin |
| Speciation | caused by Reproductive Isolation |
| Macroevolution | Evolution on the Population Scale |
| Microevolution | Evolution on the Genetic Scale |
| Evolution works at the ___ Level | Phenotypic |
| Overproduction, Variation, Selection, and Adaptation | Natural Selection |
| Too many organisms that can survive are born | Overproduction |
| Genetic Variation | Necessary for Adaptations |
| Extinction | Gone Forever |
| Directional Selection | 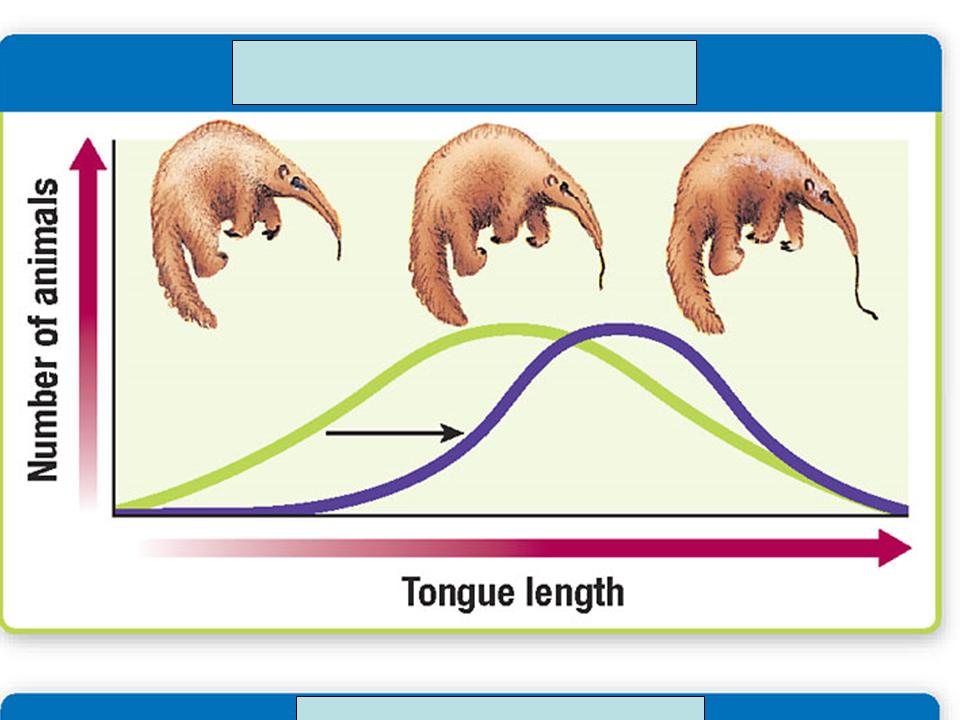 |
| Disruptive Selection | 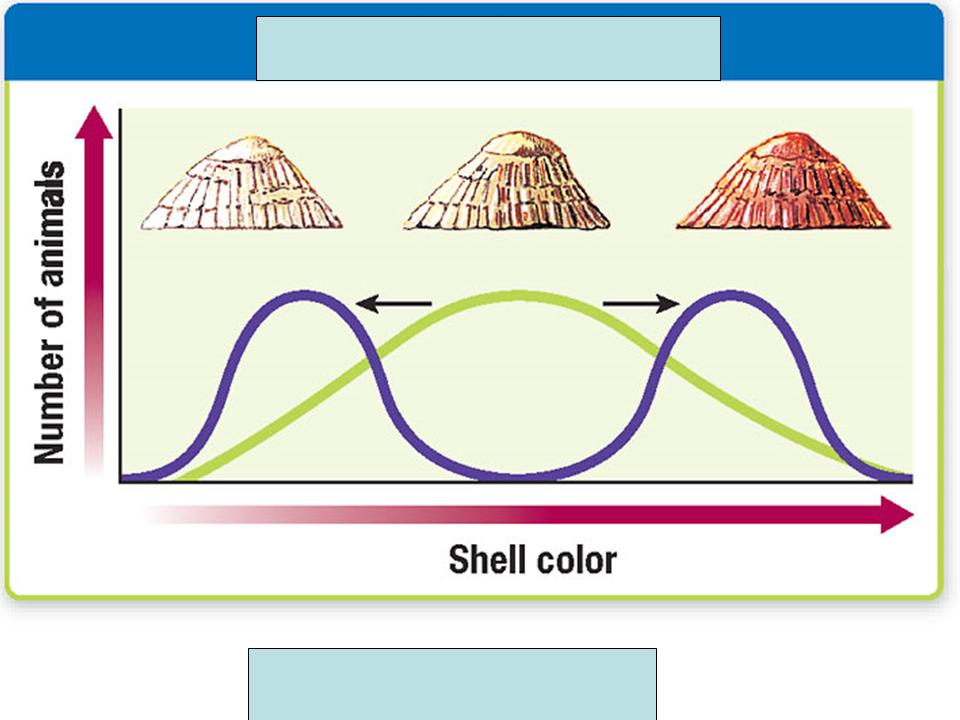 |
| Species | Population that can interbreed |
| Hybridization | Unusual occurence where 2 species successfully mate |