| A | B |
|---|
| Black Cowboys of Texas | former slaves from the Civil War who moved west and helped herd the cattle along cattle trails like the Chisholm Trail to the slaughter houses in eastern and northern states |
| Chisholm Trail | The Chisholm Trail was a trail used in the post-Civil War era to drive cattle overland, from ranches in Texas to Kansas railheads |
| Great Western Cattle Trail | The Great Western Cattle Trail was first traveled by Captain John T. Lytle in 1874 when he was transporting 3,500 longhorn cattle up from Southern Texas into Nebraska. In five short years, it became one of the most traveled and famous Cattle Trails in U.S. history.,  |
| Wright Brothers | Invented and flew the first successful airplane in Kitty Hawk, N.C.,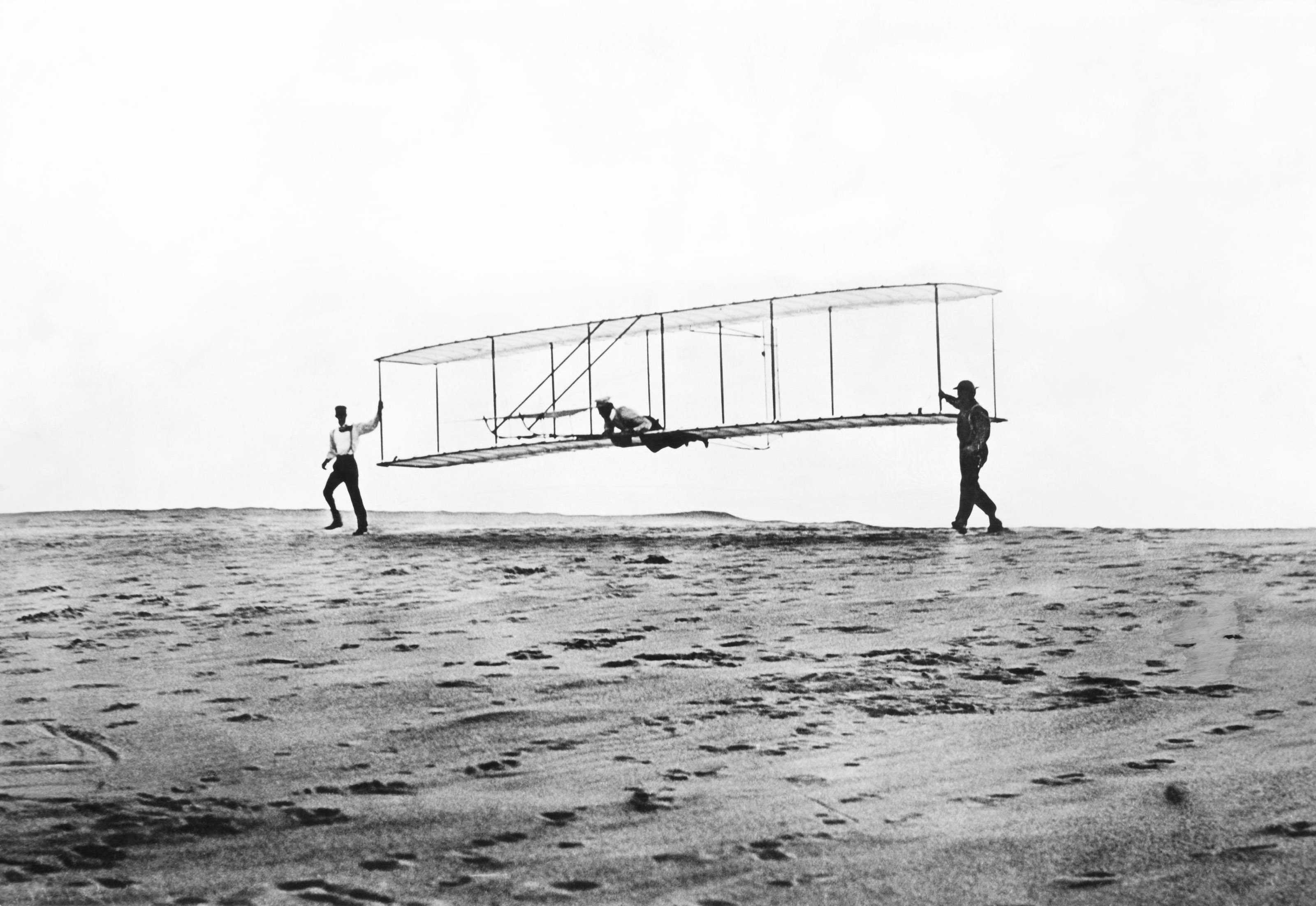  |
| George Washington Carver | Tried to help poor farmers by teaching them how to alternate crops from just cotton to peanuts and sweet potatoes; repeated planting of same type of crop led to soil depletion (unhealthy soil),  |
| Alexander Graham Bell | credited with patenting the first practical telephone and founding the American Telephone and Telegraph Company in 18 |
| Thomas Edison | Inventor of the light bulb, camera, and phonograph, |
| William Mckinley | William McKinley (January 29, 1843 – September 14, 1901) was the 25th President of the United States from March 4, 1897 until his assassination in September 1901, six months into his second term. McKinley led the nation to victory in the Spanish–American War |
| Teddy Roosevelt | Became president when Mckinley was assassinated; believed in expansionism and was famous for his efforts to get the Panama Canal built,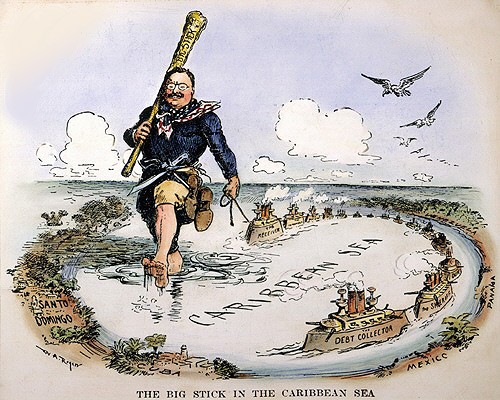  |
| Panama Canal | a man-made waterway connecting the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean across the Isthmus of Panama; this created a shortcut for ships so they didn't have to travel around the South American continent,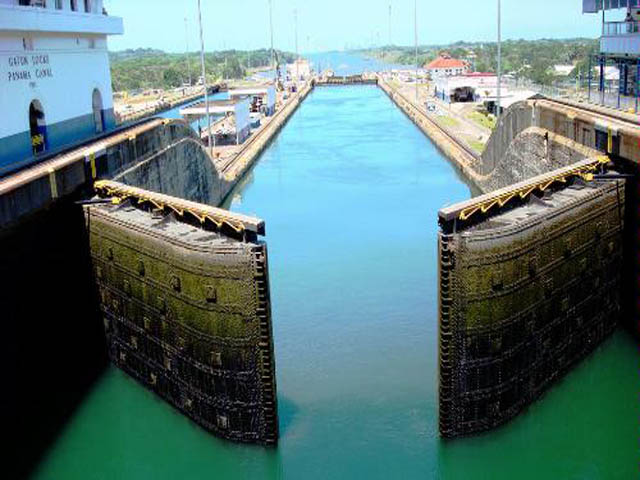  |
| Spanish American War | The Spanish–American War was fought between the United States and Spain in 1898. Hostilities began in the aftermath of the internal explosion of the USS Maine in Havana Harbor in Cuba |
| Jazz Age | The Jazz Age was a period in the 1920s, ending with the Great Depression, in which jazz music and dance styles became popular, mainly in the United States |
| Roaring 20's | A time when Jazz, dance, stocks, and the use of credit became very big; many new inventions were built and people bought on credit based on "what they wanted not needed" |
| Louis Armstrong | Louis Armstrong, nicknamed Satchmo, Satch, and Pops, was an American trumpeter, composer, singer and occasional actor who was one of the most influential figures in jazz |
| Langston Hughes | Jazz poet during the Harlem Renaissance during the Roaring 20's |
| Harlem Renaissance | The Harlem Renaissance was a cultural, social, and artistic explosion that took place in Harlem, New York, spanning the Roaring 20's. During the time, it was known as the "New Negro Movement |
| Henry Ford | Credited with the use of the assembly line technique for mass production which led to things be made cheaper and faster |
| Charles Lindbergh | First to make a transatlantic flight in the "Spirit of St. Louis",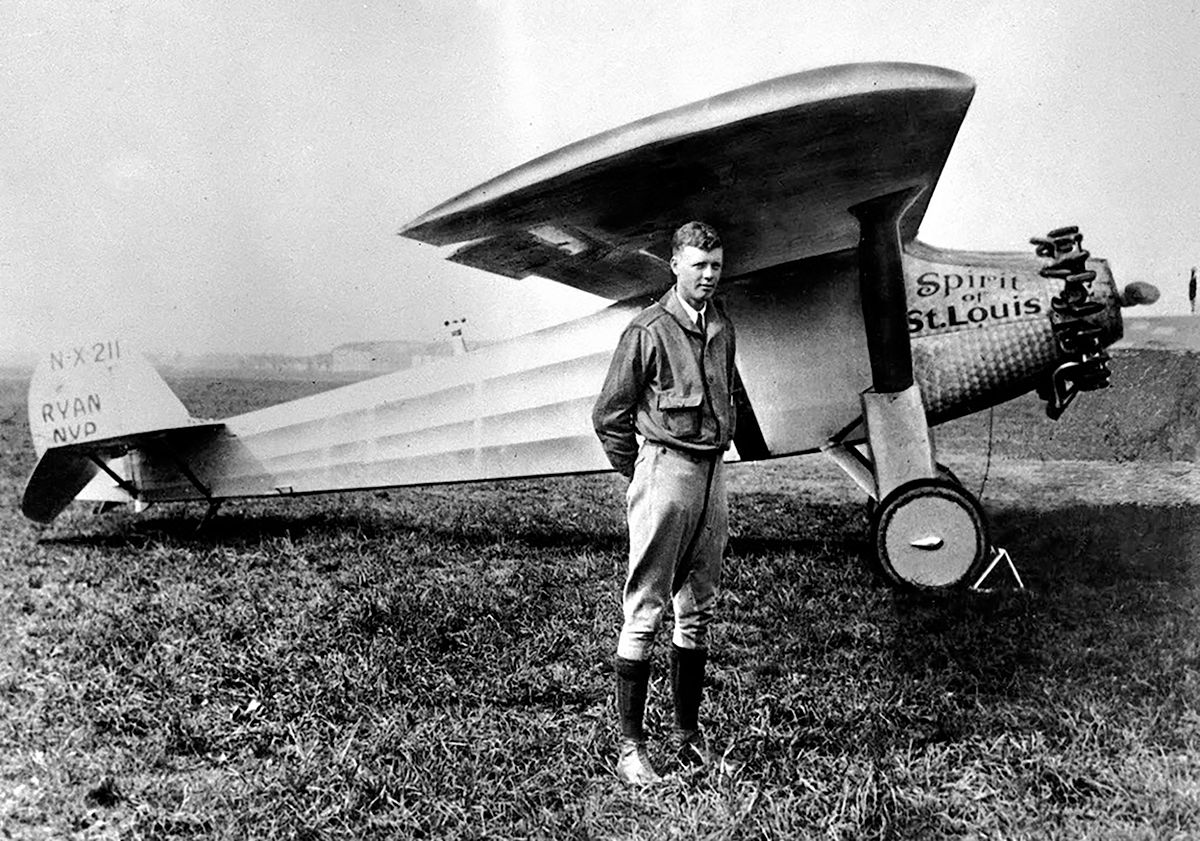  |
| 15th Amendment | The 15th Amendment, ratified in 1870, went a step further, and clearly stated that citizens of the United States had the right to vote without regard to race, color, or previous condition of servitude. |
| 19th Amendment | it gave women the right to vote in 1920,  |
| 23rd Amendment | The 23rd Amendment grants presidential voting rights to citizens of the District of Columbia and representation for D.C. in the Electoral College. |
| 24th Amendment | The 24th amendment was important to the Civil Rights Movement as it ended mandatory poll taxes that prevented many African Americans. Poll taxes, combined with grandfather clauses and intimidation, effectively prevented African Americans from having any sort of political power, especially in the South.,  |
| 26th Amendment | Allows you to vote when you are 18,  |
| Assembly Line | Henry Ford installs the first moving assembly line for the mass production of an entire automobile. His innovation reduced the time it took to build a car from more than 12 hours to two hours and 30 minutes.,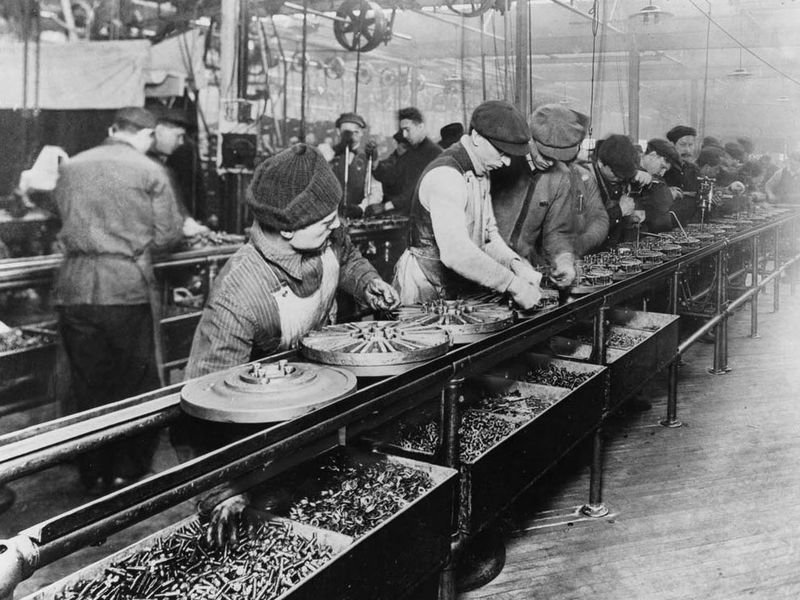  |
| supply | how much you have of something |
| demand | how much it is wanted by the consumer |
| scarcity | things that are in low supply and have a very high demand for them; example would be diamonds and gold |
| opportunity cost | Opportunity cost is a term used in economics, to mean the cost of something in terms of opportunity foregone. For example, if a city decides to build a hospital on some vacant land, the opportunity cost is the other things that might have been done with that same land instead.,  |
| economics | how we use resources |
| consumers | people who buy things |
| producers | people who make things to be bought |
| consumerism | buy what you want not what you need,  |
| New Deal | series of federal programs, public work projects, financial reforms and regulations enacted in the United States during the 1930s in response to the Great Depression. GOAL TO CREATE JOBS SO PEOPLE COULD EARN AND THEN SPEND MONEY.,  |
| Cold War | was a long period of tension between the democracies of the Western World and the communist countries of Eastern Europe. The west was led by the United States and Eastern Europe was led by the Soviet Union. These two countries became known as superpowers. LASTED ABOUT 40 YEARS AND WAS BASED ON THE THREAT TO USE NUCLEAR WEAPONS.,  |
| Civil Rights Movement | was an ongoing fight for racial equality that took place for over 100 years after the Civil War. Leaders such as Martin Luther King, Jr., Booker T. Washington, and Rosa Parks paved the way for non-violent protests which led to changes in the law. GOAL WAS TO CREATE EQUALITY FOR ALL REGARDLESS OF RACE.,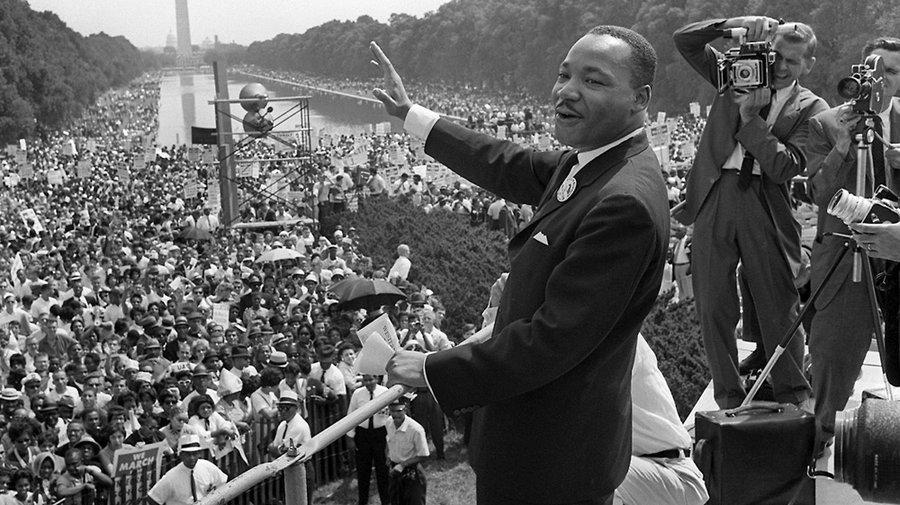  |
| World War 1 | fought between the Allied Powers and the Central Powers. The main members of the Allied Powers were France, Russia, and Britain. The United States also fought on the side of the Allies after 1917. The main members of the Central Powers were Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria. US BECAME MORE INVOLVED WITH THE SINKING OF THE LUSITANIA BY A GERMAN U-BOAT.,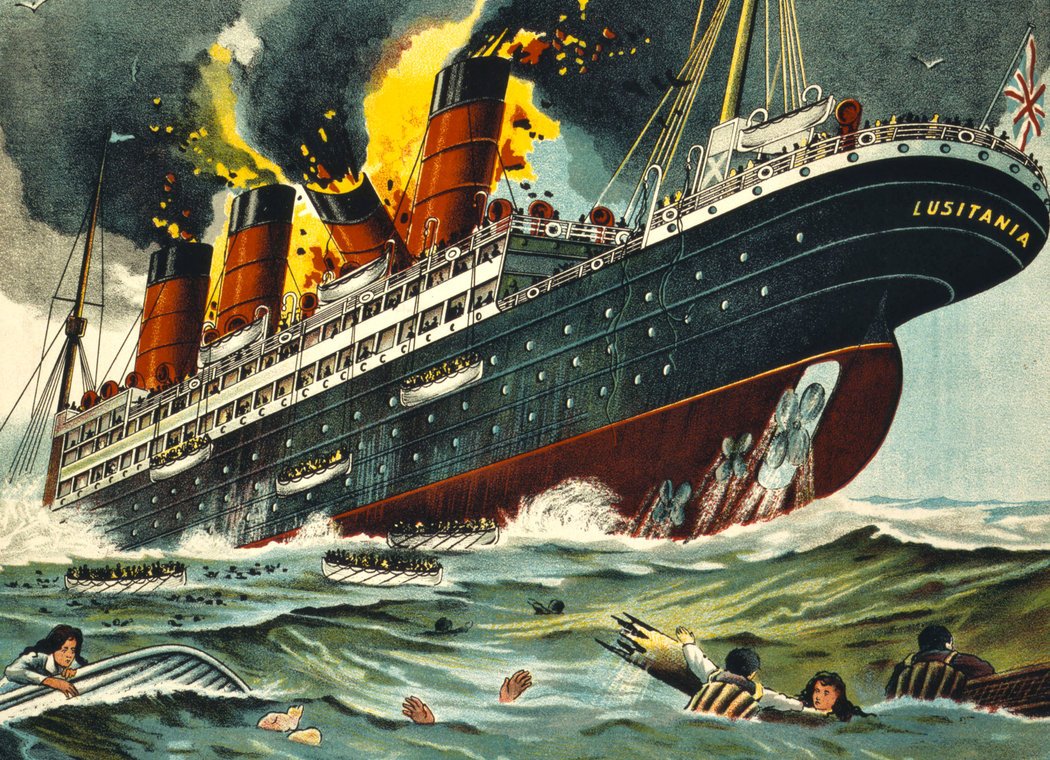  |
| December 7th, 1941 | Attack on Pearl Harbor that led to the US fighting in the Pacific theater against Japan.,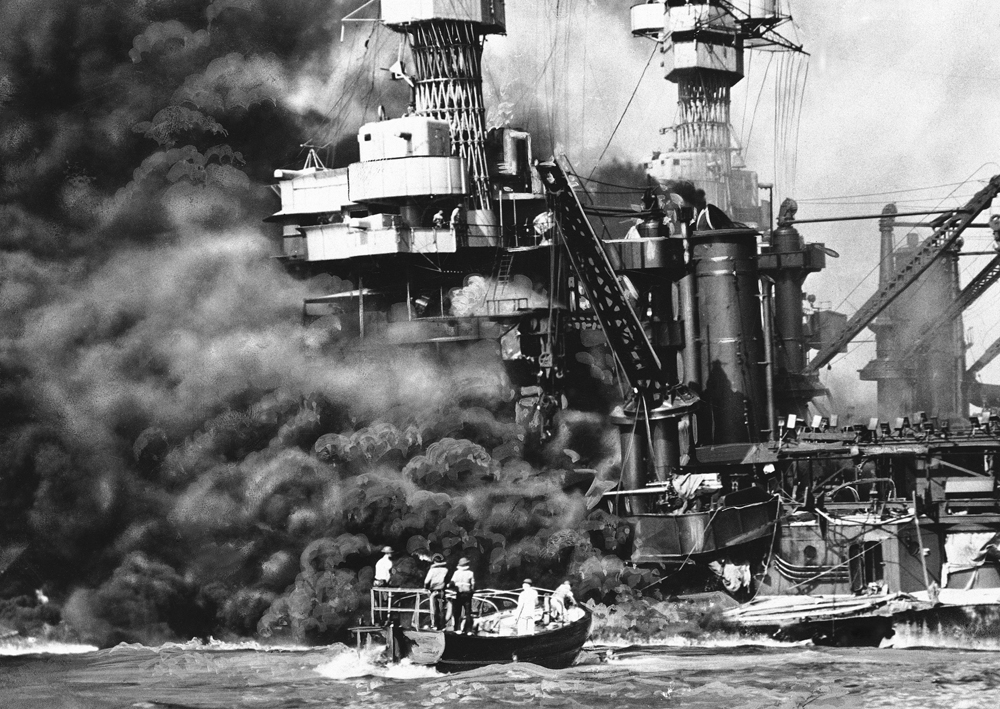  |
| Legislative Branch | Made up of House of Representatives and Senate; in charge of making the laws and approving things done by executive, .bmp) |
| Executive Branch | Made up of president, vice-president, and cabinet (advisers to the president); they enforce laws, veto, appoint judges, and the president is commander and chief of armed forces,  |
| Judicial Branch | Determine if things are constitutional or not; are appointed not elected so they aren't effected by popular demand of the people,  |
| Bay of Pigs Invasion | In 1961 the United States sent trained Cuban exiles to Cuba to try and overthrow Fidel Castro's government. They failed miserably. The invasion is considered part of the Cold War because the United States was trying to prevent communism from taking hold in the Americas. Read more at: http://www.ducksters.com/history/cold_war/bay_of_pigs.php This text is Copyright © Ducksters. Do not use without permission.,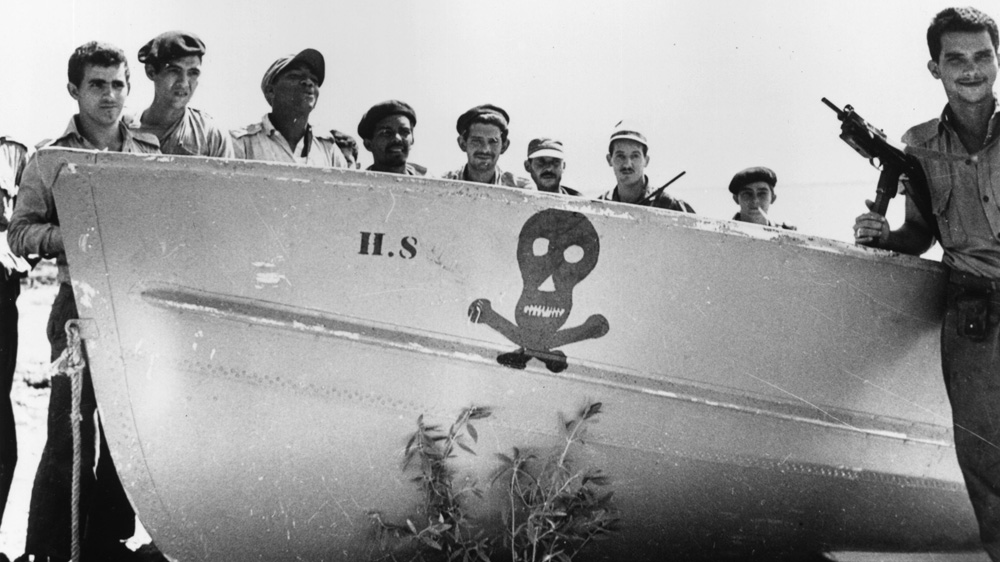  |
| McCarthyism and Red Scare | The fear of communism, known as the Red Scare, led to a national witch hunt for suspected communist supporters, which was known as McCarthyism,  |
| Berlin Wall | Known as the "Iron Curtain"; was built to stop East Germans from defecting to the West. West Germans were able to visit East Germany by way of permit.,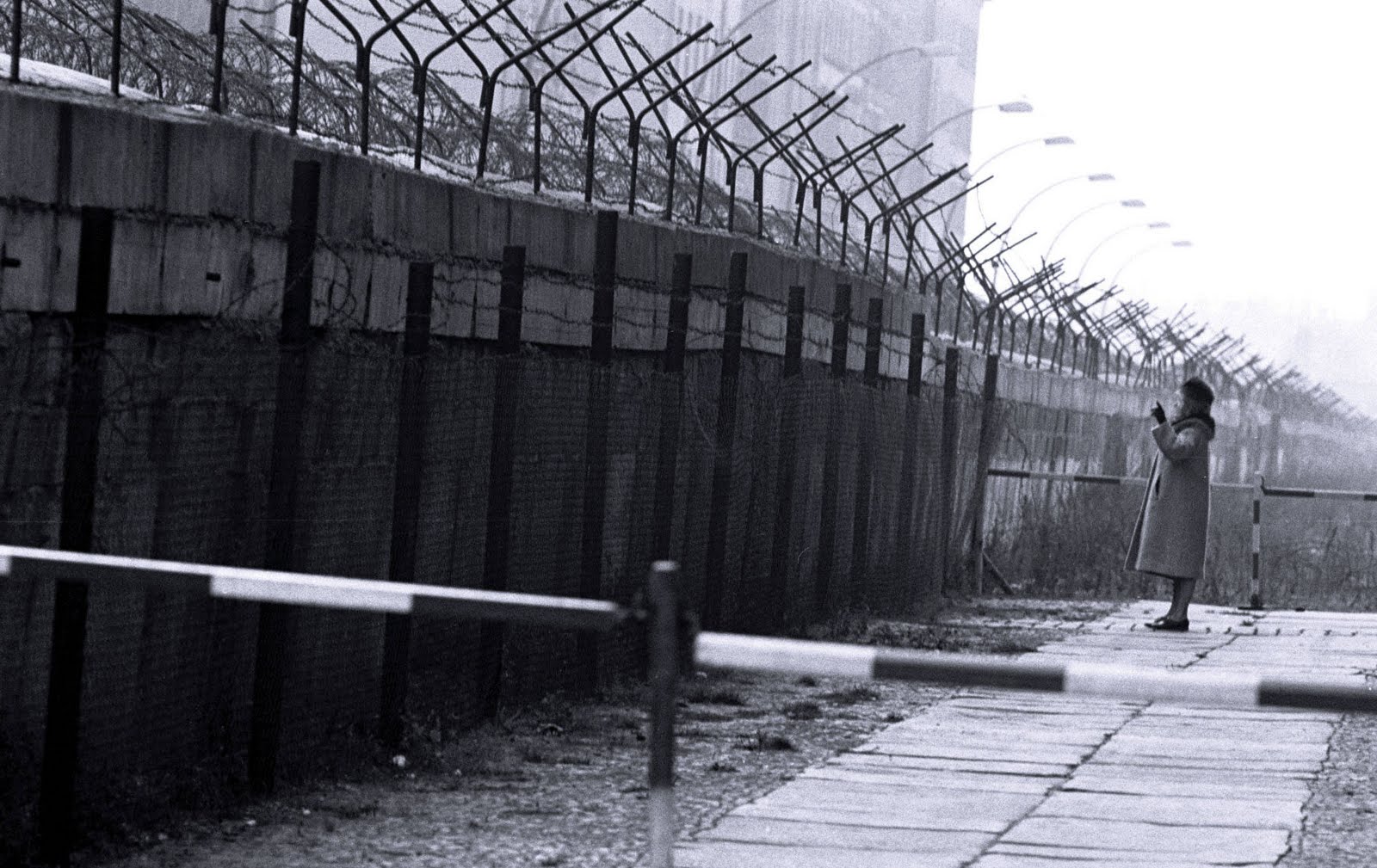  |
| Cuban Missile Crisis | Following the failed CIA-backed Bay of Pigs invasion, Fidel Castro made an alliance with the communists and the Soviets began to install nuclear missiles in Cuba. An American U-2 spy plane captured photographs of the missile installations in Cuba on October 14, 1962 triggering the crisis,  |
| Manhattan Project | the program based in the United States which tried to make the first nuclear weapons. The project went on during World War II, and was run by the U.S. Army. The top scientist on the project was Robert Oppenheimer, a famous physicist, 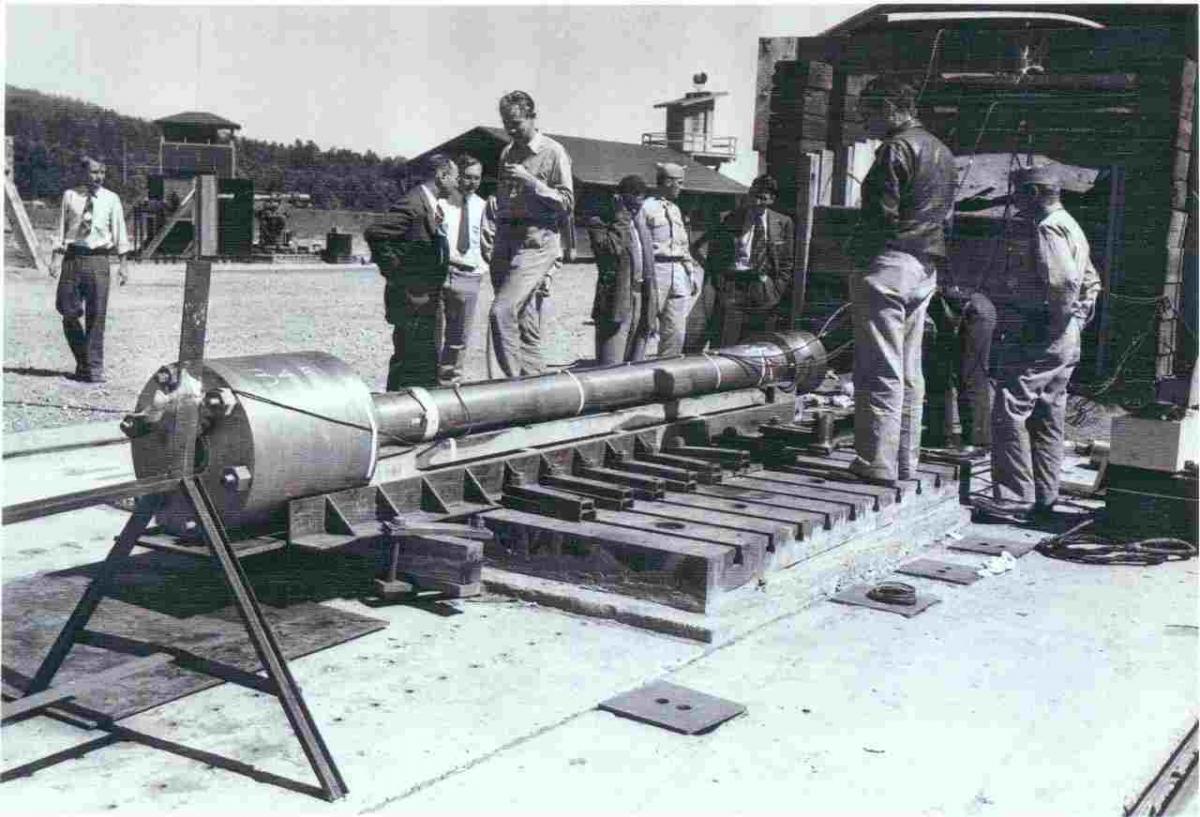 |
| Space Race | was a competition in the exploration of space between the United States and the Soviet Union. The Space Race included the exploration of outer space using rocket technology with artificial satellites to send animals and humans into space, and to land people on the Moon.,  |
| Espionage during Cold War | Rosenbergs selling atomic secrets to USSR,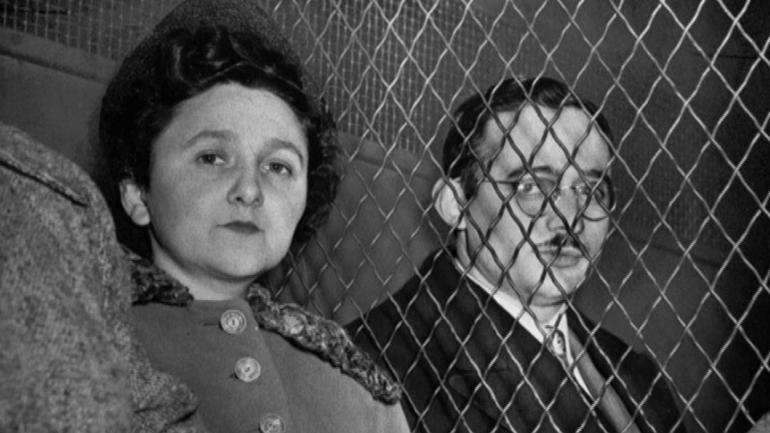  |
| Joseph Stalin | Leader of USSR during WW2 and first part of Cold War; accused of killing more than 20,000,000 people,  |
| Hiroshima and Nagasaki | where first atomic bombs used,  |
| Proxy War | where two larger countries use smaller countries as chess pieces in an indirect confrontation; USA and USSR during Cold War,  |
| Rosa Parks | the driver told the African American passengers to give up their seats for him. Whilst the other black passengers obeyed, Rosa did not. The result? Rosa was arrested by the police and fined for breaking segregation laws! But Rosa refused to pay, and argued that it was the law that was wrong, not her behaviour.,  |
| I have a Dream | a public speech delivered by American civil rights activist Martin Luther King Jr. during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom on August 28, 1963,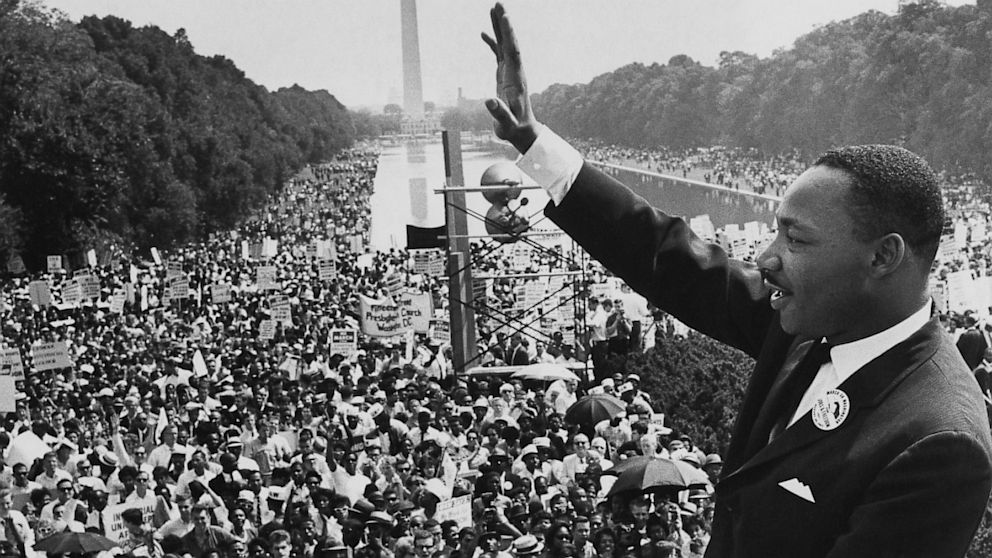  |
| Montgomery Bus Boycott | On December 1, 1955 Rosa Parks, an African American woman, refused to give her bus seat to a white person. She was arrested and sent to jail. In protest about 40,000 black people boycotted the Montgomery city buses, refusing to ride. The boycott lasted 381 days.,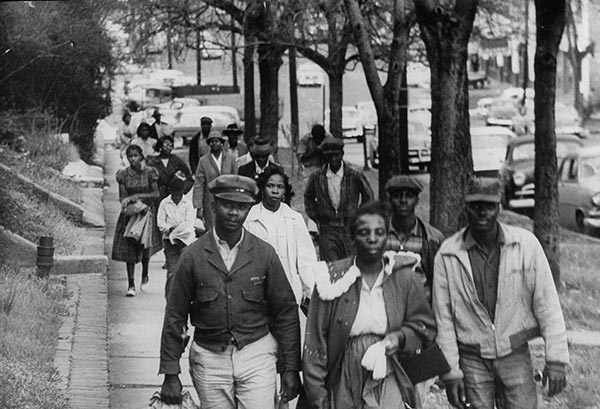  |
| Berlin Airlift | the first battle of the Cold War. It was when western countries delivered much needed food and supplies to the city of Berlin through the air because all other routes were blocked by the Soviet Union., 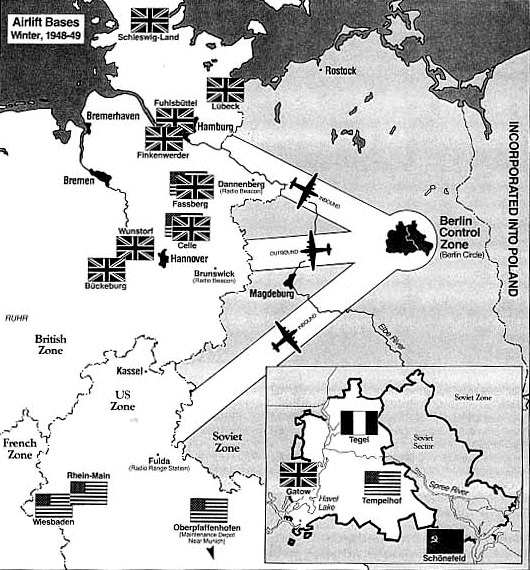 |
| Battle of Midway | of the most important battles of World War II. It was the turning point of the war in the Pacific between the United States and Japan. The battle took place over four days between June 4th and June 7th in 1942., 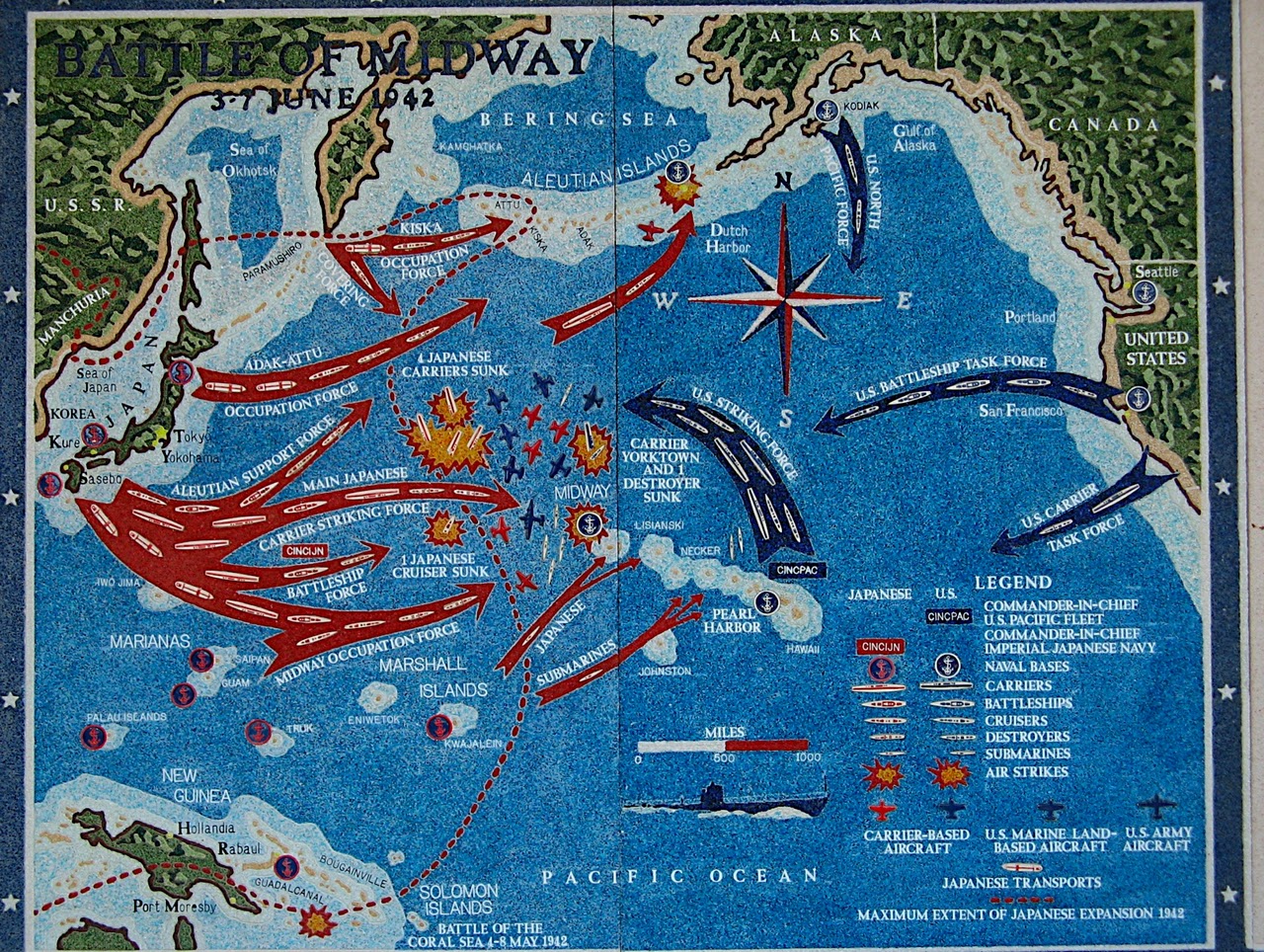 |
| Continental Drift | The theory said that parts of the Earth's crust move slowly on top of a liquid core, 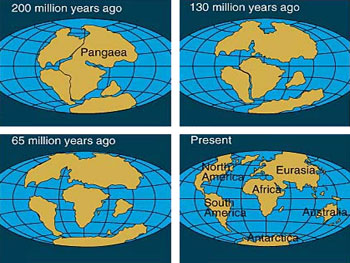 |
| Plate Tectonics | Earth's outer layer is made up of large, moving pieces called plates. All of Earth's land and water sit on these plates. The plates are made of solid rock., 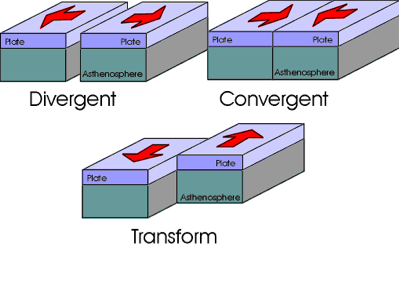 |
| Earth Model | The part of the Earth we live on is solid, but the inside of the Earth is very different. Earth has four different layers: the inner core, the outer core, the mantle, and the crust., 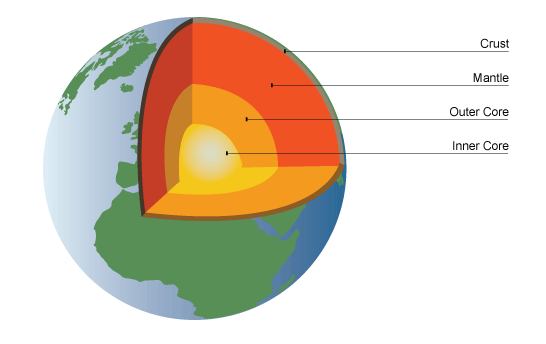 |
| Mantle | Traveling beyond the Earth's crust, we next encounter the mantle. The mantle extends to a depth of approximately 1,800 miles (2897km), and is made of a thick, solid, rocky substance that represents about 85% of the total weight and mass of the Earth. |
| Inner Core | The Earth's Inner Core. Finally, we would reach the Earth's inner core. The inner core extends another 900 miles (1448km) toward the center of the Earth. It is believed that this inner core is a solid ball of mostly iron and nickel. It is the densest layer. |
| OUter core | outer core, which extends to a depth of around 3000 mile (4828km) beneath the surface. It is believed that this outer core is made up of super-heated liquid molten lava. This lava is believed to be mostly iron and nickel. |
| density | how close together the molecules of a substance are or how much mass a substance has in a given space. The more density the less air so it sinks in water quicker., 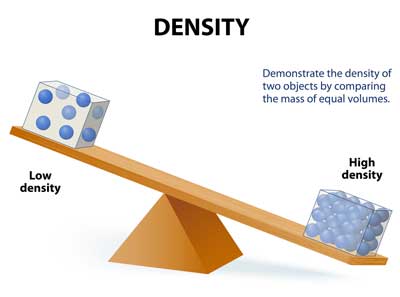 |
| Chemical change | Making something new and is irreversible. Burning wood ,Souring milk ,Mixing acid and base ,Digesting food ,Cooking an egg ,Heating sugar to form caramel ,Baking a cake, Rusting of iron, 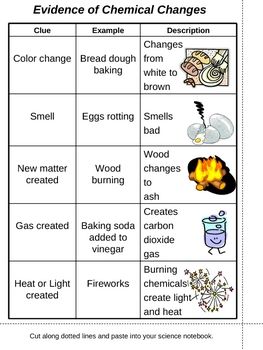 |
| physical change | a change in which no new substance s are formed.Examples: changes of shape, changes of states, passing electricity through a copper wire. Some physical changes are melting, freezing, boiling, and mixing.,  |
| states of matter | changing from solid to liquid to gas. Changes in states of matter are physical changes. Examples include boiling, freezing, condensation, and evaporation.,  |
| vertebrates | A vertebrate is an animal with a backbone.Fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, including humans, are all vertebrates. |
| invertebrates | An invertebrate is a species of animal which does not have a backbone, such as spiders, insects, mollusks, lobsters and crabs. It is estimated that as much as 97% of all animal species are invertebrate. |
| mammals | Mammals include humans and all other animals that are warm-blooded vertebrates (vertebrates have backbones) with hair. They feed their young with milk and have a more well-developed brain than other types of animals. |
| amphibians | All amphibians begin their life in water with gills and tails. As they grow, they develop lungs and legs for their life on land. They are cold-blooded. Members of this animal class are frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians or blindworms.,  |
| consumers | Predators and prey that don't make their own food within their body.,  |
| producers | They make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. They are plants and usually green.,  |
| reptiles | Reptiles are cold-blooded vertebrates. (Vertebrates have backbones.) They have dry skin covered with scales or bony plates and usually lay soft-shelled eggs., 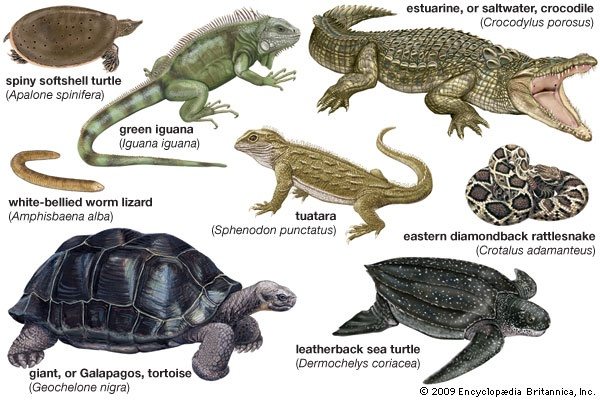 |
| birds | Birds are warm-blooded vertebrates (vertebrates have backbones) and are the only animals with feathers. |
| Decomposers | play an important role in nature. They break down the unused dead material and turn them into nutrients in the soil, which plants use to grow. They are an important part of the food chain.,  |
| static electricity | is the build up of an electrical charge on the surface of an object. It's called "static" because the charges remain in one area rather than moving or "flowing" to another area.,  |
| electrical current | is the flow of an electric charge from positive to negative or visa versa. The electrons are moving from one object to another., 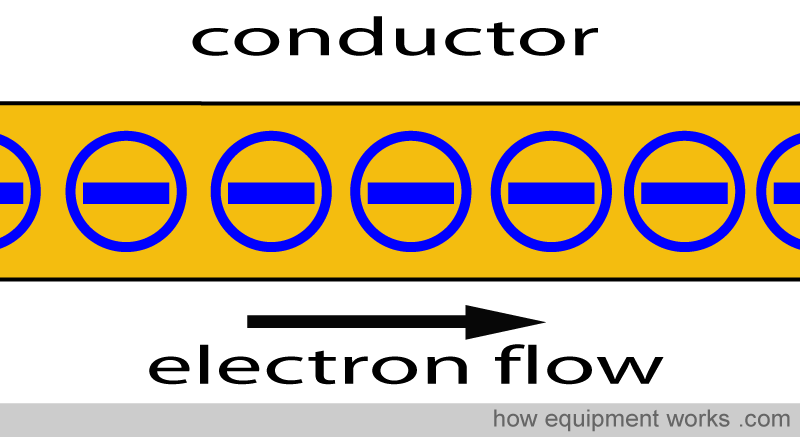 |
| circuit | A circuit is usually made by linking electrical components together with pieces of wire cable. You will need a source of energy, a conductor, an insulator, a switch, and something to prove electricity is flowing (light bulb)., 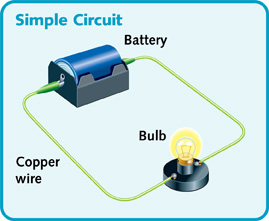 |
| conductors | Electricity travels easily through electrical conductors, like metals,  |
| insulators | Materials that do not let electricity pass through them easily are called electrical insulators. Plastic, wood, glass and rubber are good electrical insulators.,  |
| Types of Sentences | Declarative, imperative, exclamatory, and interrogative,  |
| 180 degrees | How many degrees are in any triangle, 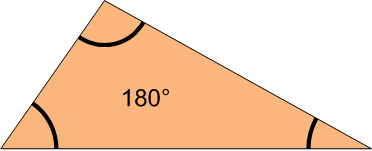 |
| 360 degrees | How many degrees are in any quadrilateral, 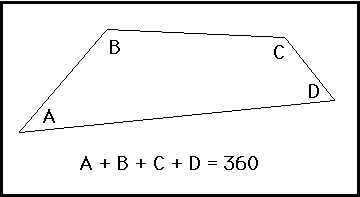 |
| Deposition | is the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or land mass. Wind, ice, water, and gravity transport previously weathered surface material until it slows down and drops it,  |
| Constructive forces | processes that help build up the earth, either by depositing soil or silt in a river, or by volcanoes and lava flows that generate new land.,  |
| destructive forces | the process by which rock is broken down, such as erosion and weathering either through the violent actions of volcanoes and earthquakes or by the steady flow of a river.,  |
| Faults | fractures in the crust where rocks move parallel to the break.,  |
| erosion | fractures in the crust where rocks move parallel to the break. Required movement of bits of the Earth to do this.,  |
| weathering | the process where rock is dissolved, worn away or broken down into smaller and smaller pieces by temperature (mechanical), organic things (plants and animals), or chemical (chemical changes),  |
| prepositions | word (often a short word) that expresses the relationship between two other nearby words. Often times answers the question, "Where?". Examples include above, about, across, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, since, to, toward, through, under, until, up, upon, with and within.,  |
| conjunction | join two parts of a sentence and help to show the connection between the two parts of the sentence. Examples include and, or, nor, but, either, neither, although, because, yet.,  |
| Scientific Process | Research question, hypothesis, equipment, procedures, observations, and conclusion,  |
| order of operations | parenthesis, exponents, multiply or divide, then add or subtract, 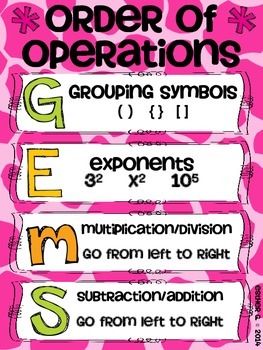 |
| multiplying fractions | multiply straight across without making denominators the same,  |
| dividing fractions | change the division sign to multiplication and flip the second number, 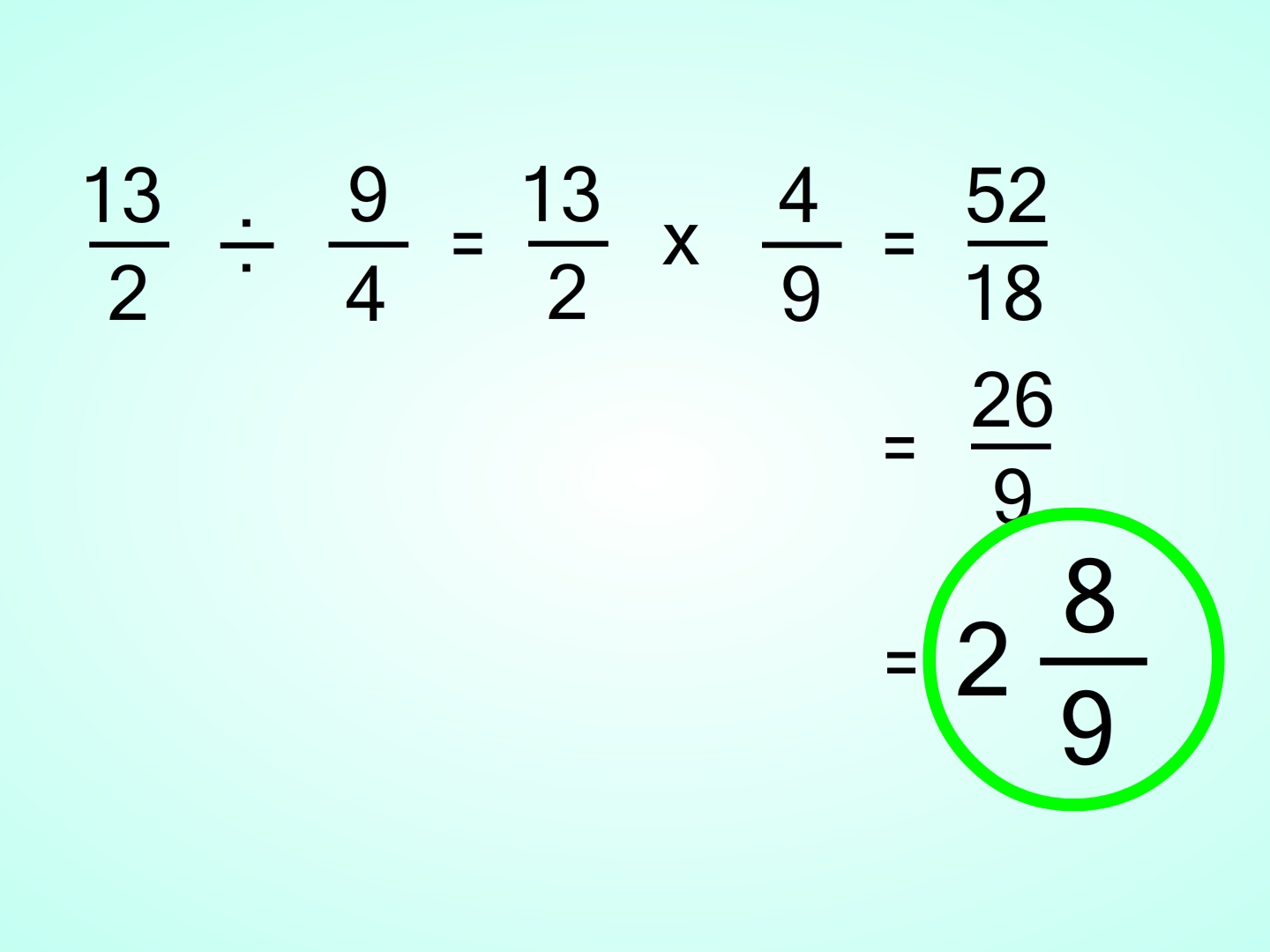 |
| simplifying fractions | what is the number that they both have in common that you can divide it by, 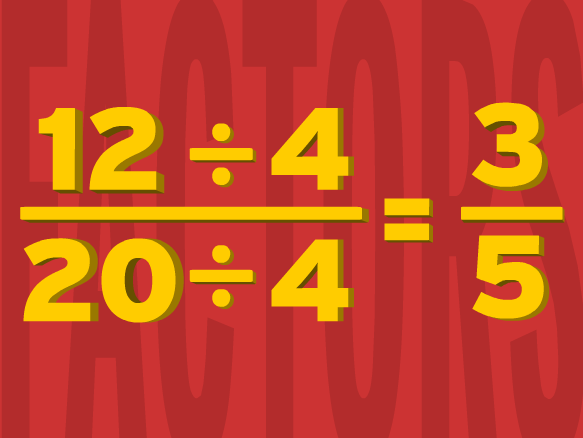 |
| mixed number to improper fraction | multiply the denominator times the whole number and add the numerator, 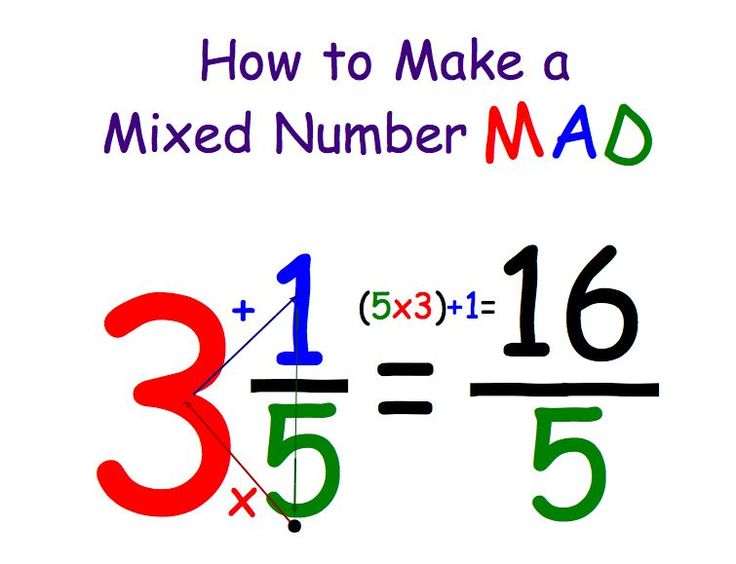 |
| improper fraction to mixed number | how many times does the denominator go into the numerator? That represents your whole number and the remainder is your numerator in the fraction., 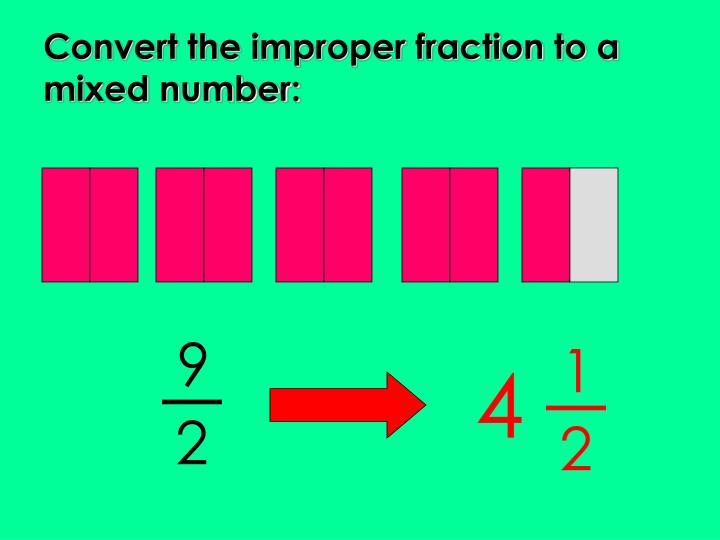 |
| product | answer to multiplication problem |
| quotient | answer to division problem |
| difference | answer to subtraction problem |
| sum | answer to addition problem |
| pentagon | five sided |
| octagon | 8 sided |
| hexagon | 6 sided |
| parallelogram | quadrilateral with two sets of parallel lines |
| behavioral adaptations | Learned from others,  |
| physical adaptations | These are things that help the animal survive like fur, horns, burrowing feet, sharp teeth, or echolocation,  |
| inherited traits | things that you received from your parents like hair color, eye color, height, ...., 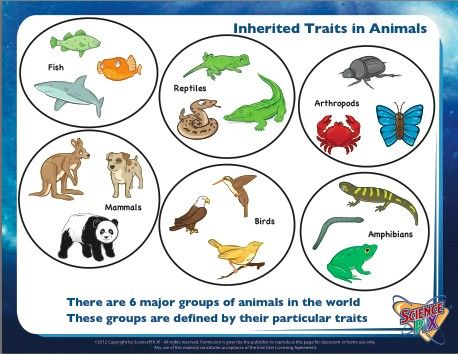 |
| learned behaviors |  |
| bar magnet | permanent magnet with a North and South Pole,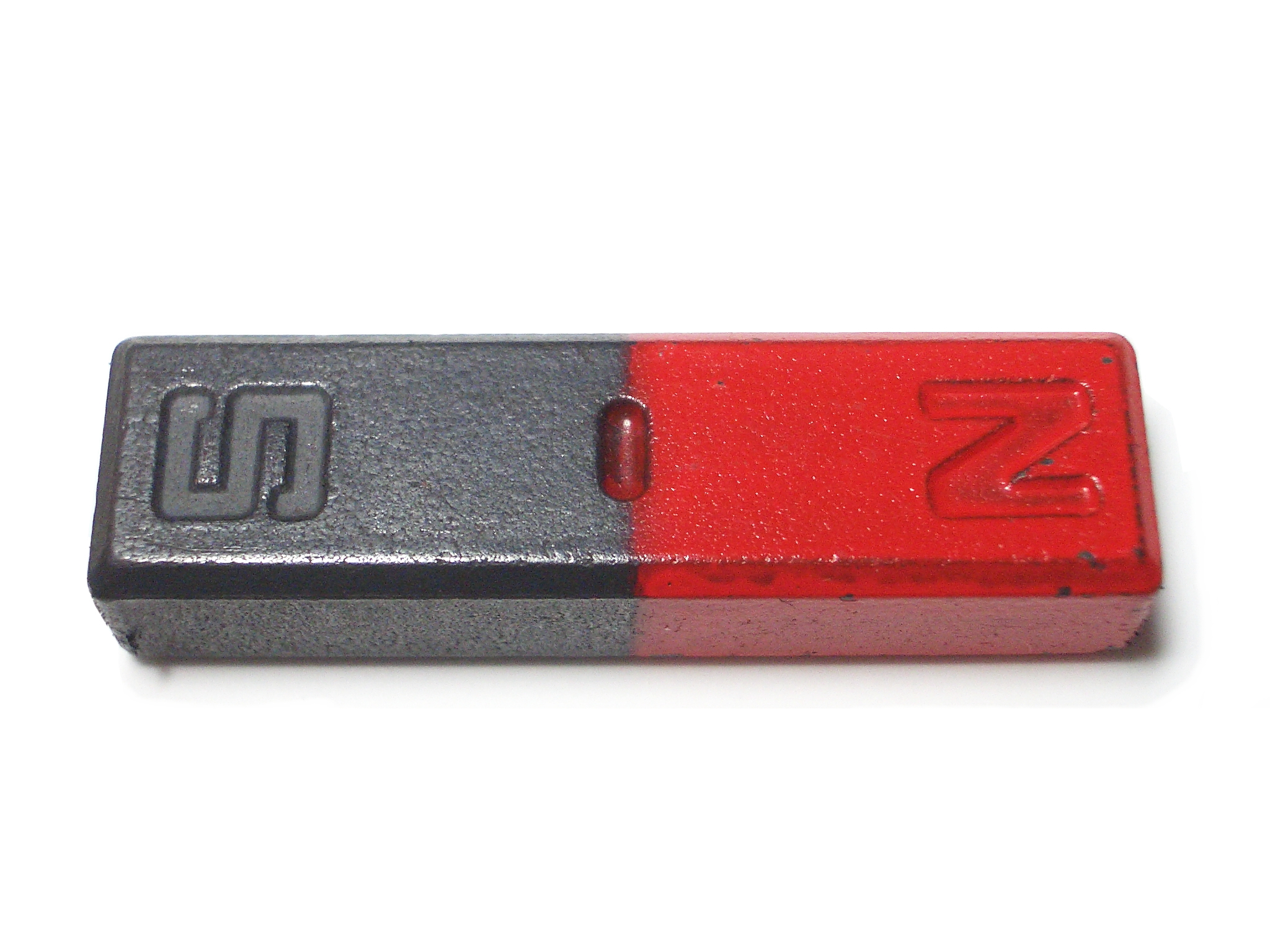  |
| electromagnet | temporary magnet created by using coils that have electricity flowing through them, 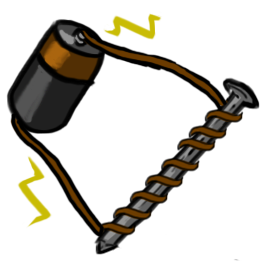 |
| beneficial microorganisms | antibiotics, yeast, yogurt, cheese, bacteria in roots, and stomach bacteria for digestion |
| harmful microorganisms | Ecoli, viruses, protozoa, some molds, and amoebas |
| Axis Powers | Germany, Italy, Japan |
| Allied Powers | US, England, Russia |
| Pacific Theatre |  |
| European Theatre | 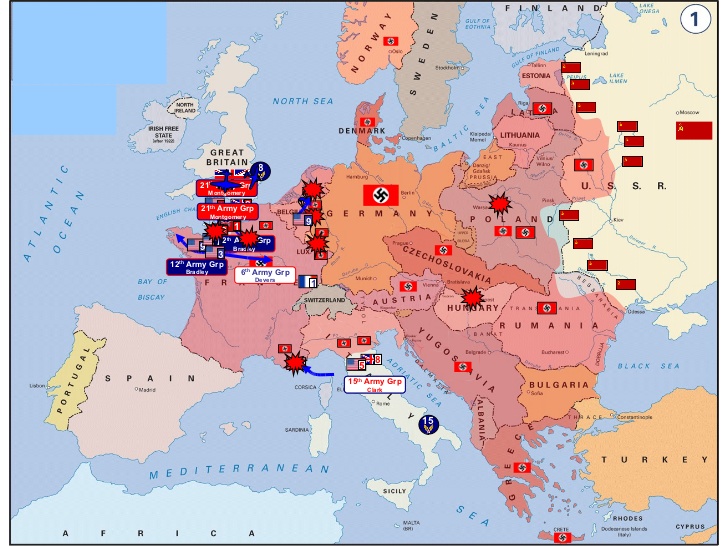 |
| Prime Minister of England during WW2 |  |
| Leader of Italy during WW2 |  |
| Protractor | instrument used to measure the degrees in an angle, 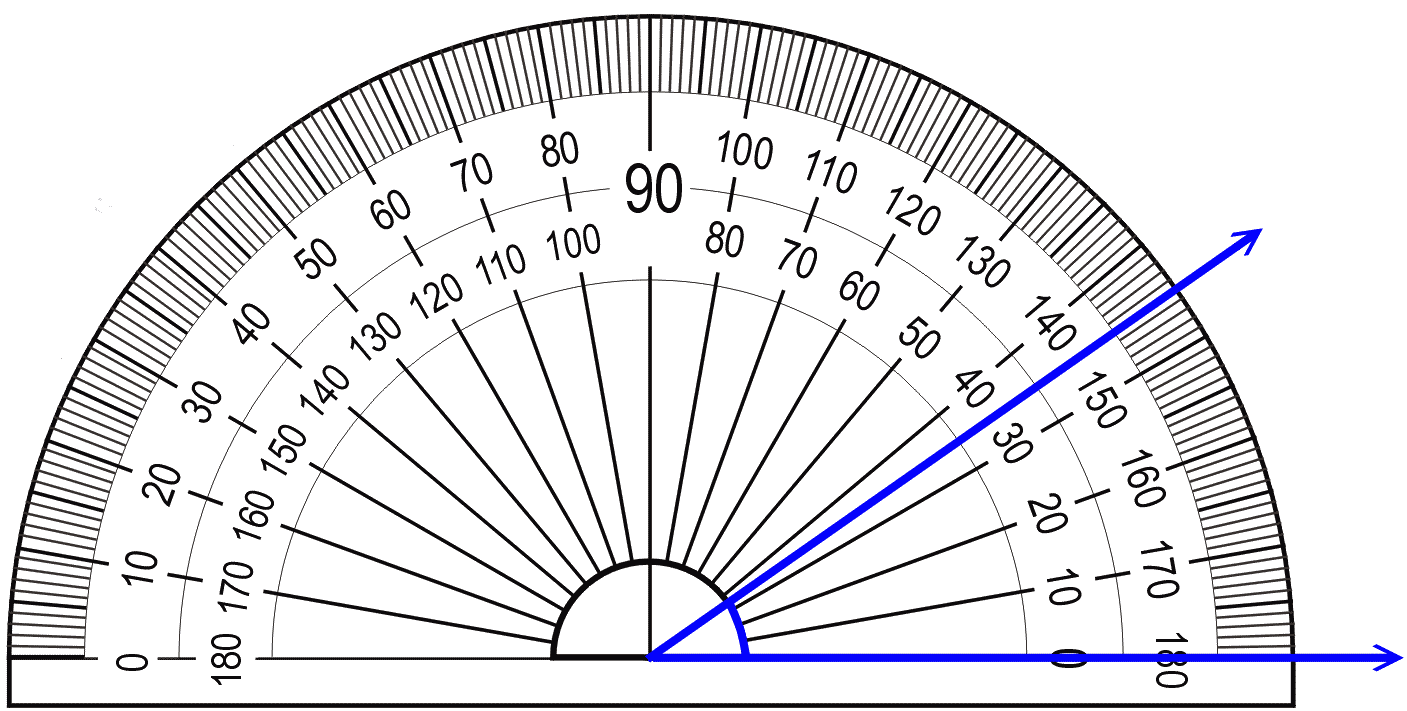 |
| Separate isn't equal | Brown vs. Board of Education of Topeka,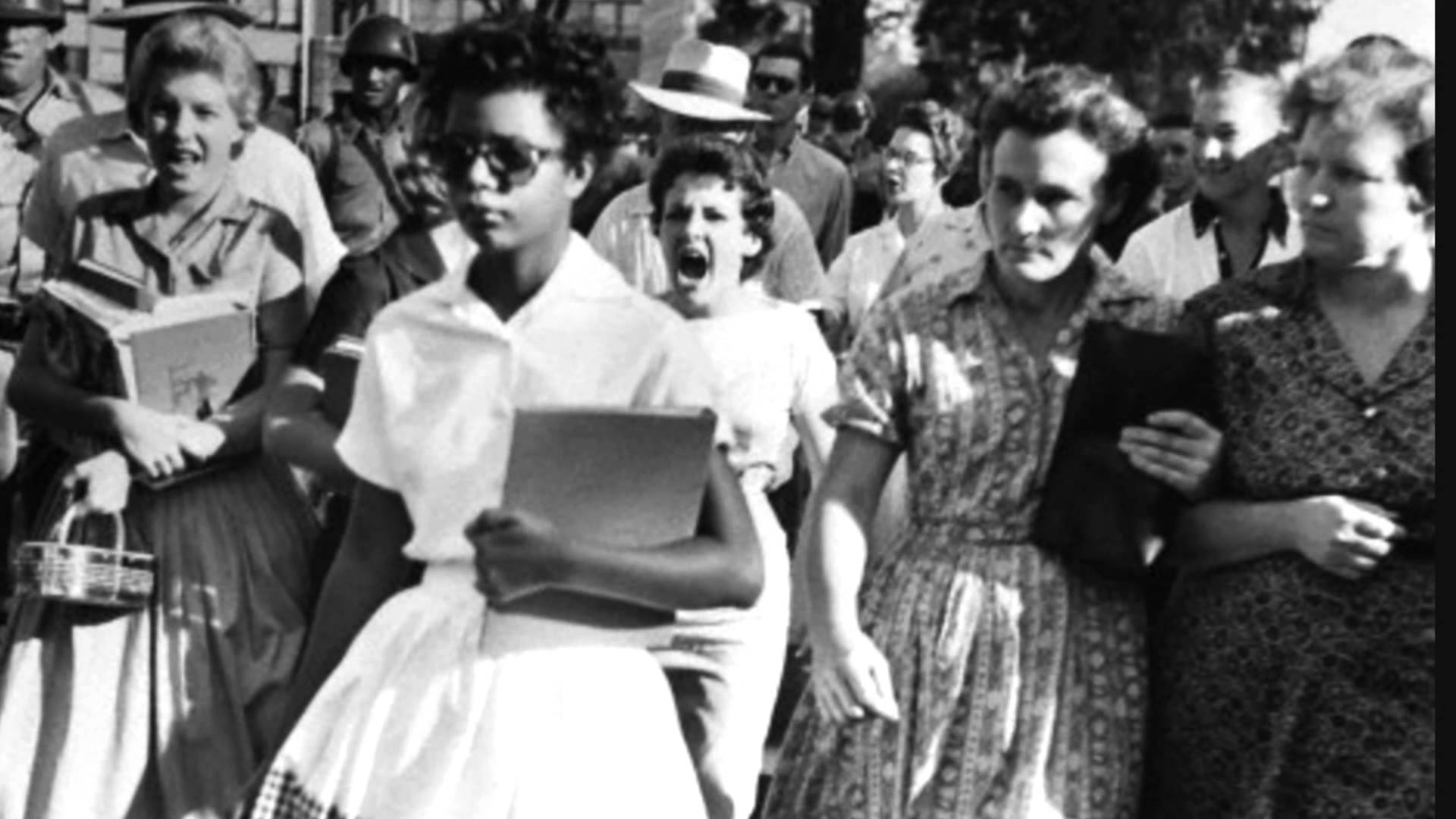  |
| Civilian Conservation Corps, Tennessee Valley Authority, and Works Progress Authority | All New Deal programs used to increase job opportunities thus giving more money to people to spend; help end Great Depression |
| Black Tuesday | he Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as Black Tuesday, the Great Crash, or the Stock Market Crash of 1929, began on October 24, 1929, and was the most devastating stock market crash in the history; people wanted money from banks but banks crashed; start of Great Depression,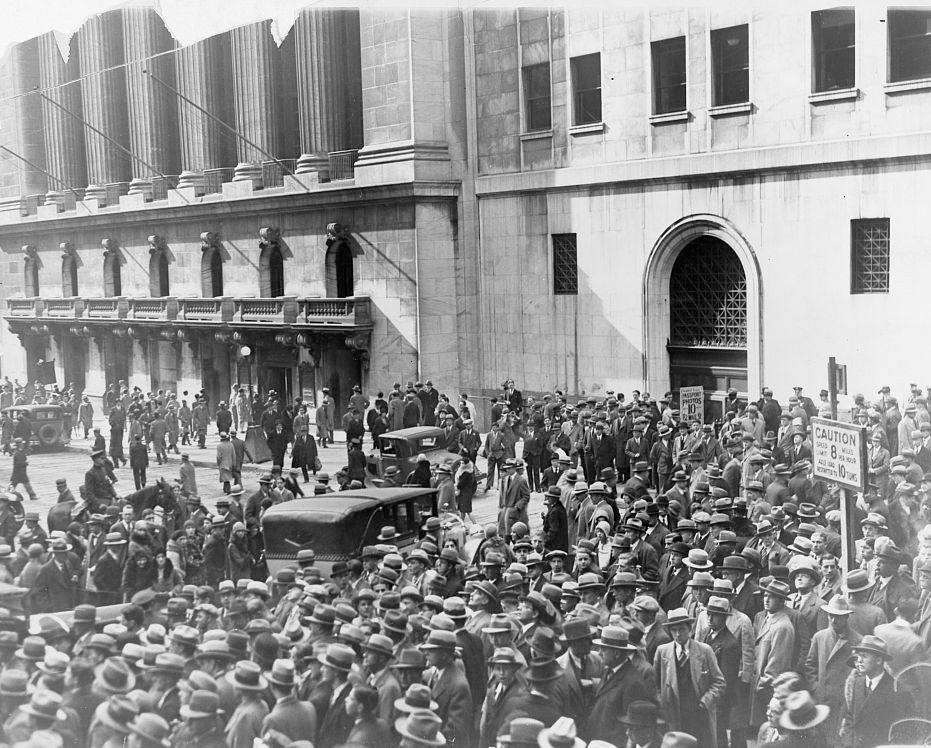  |
| Jesse Owens | The 1936 Summer Olympics were held in Berlin, Germany. This was the time when Adolf Hitler had gained power through his Nazi party, but before WWII had broken out. Part of Hitler's philosophy was the superiority of the white race. He expected Germans to dominate the Olympic games. Jesse Owens, however, had his own chapter to write into history. Jesse won four gold medals in the games including gold for the 100 meter sprint, the 200 meter sprint, the 2x100 meter relay, and the long jump.,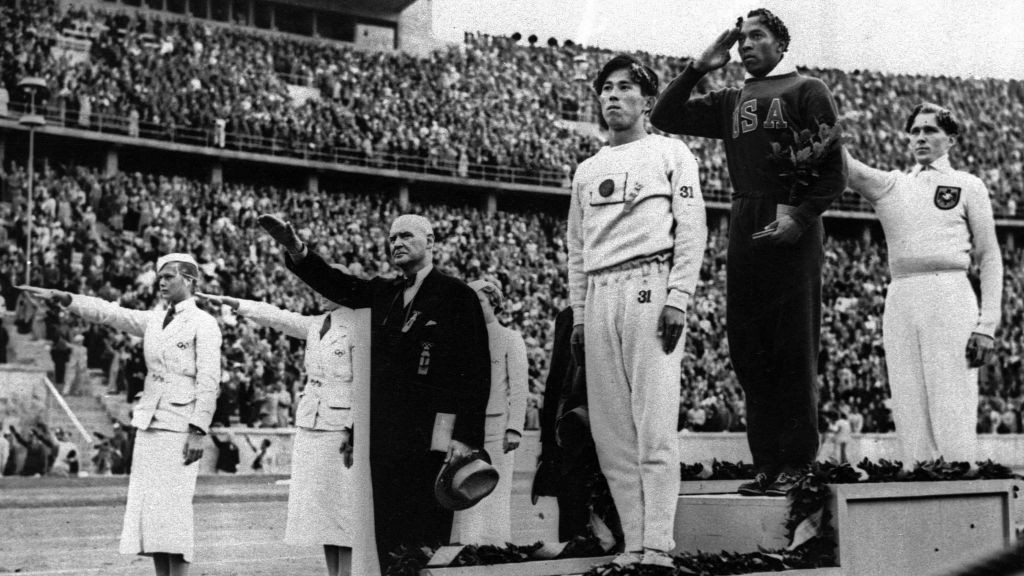  |
| Soup kitchens | Soup kitchens served mostly soup and bread. Soup was economical because water could be added to serve more people, if necessary. At the outset of the Depression, Al Capone, the notorious gangster from Chicago, established the first soup kitchen. |
| dust bowl | The Dust Bowl was the name given to the drought-stricken Southern Plains region of the United States, which suffered severe dust storms during a dry period in the 1930s. As high winds and choking dust swept the region from Texas to Nebraska, people and livestock were killed and crops failed across the entire region. This all happened at the height of the Great Depression.,  |
| Herbert Hoover | Herbert Hoover (1874-1964), America's 31st president, took office in 1929, the year the U.S. economy plummeted into the Great Depression. Although his predecessors' policies undoubtedly contributed to the crisis, which lasted over a decade, Hoover bore much of the blame in the minds of the American people.,  |
| Holocaust | The Holocaust is one of the most terrible events in human history. It occurred during World War II when Hitler was leader of Germany. Six million Jewish people were murdered by the Nazis. This included as many as 1 million Jewish children.,  |
| D-Day | The Invasion of Normandy. On June 6, 1944 the Allied Forces of Britain, America, Canada, and France attacked German forces on the coast of Normandy, France. With a huge force of over 150,000 soldiers, the Allies attacked and gained a victory that became the turning point for World War II in Europe.,  |