| A | B |
|---|
| Stress | A force that acts on a rock to change its shape or volume |
| tension | Stress force that pulls on the crust |
Normal fault, 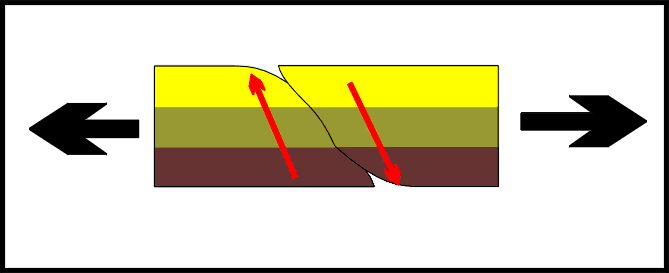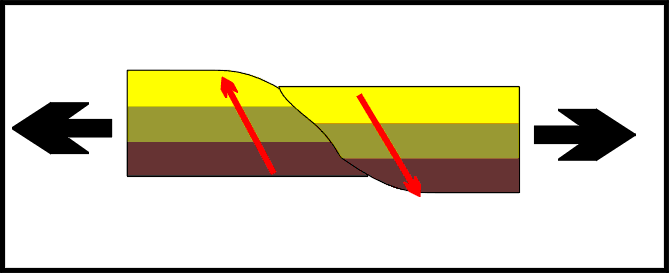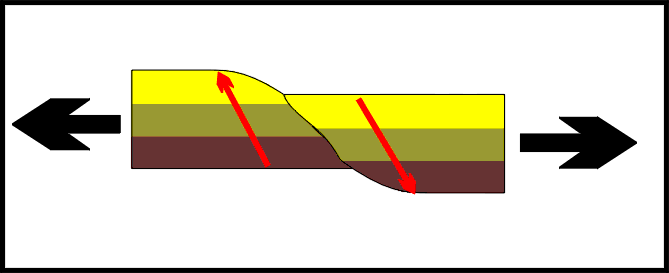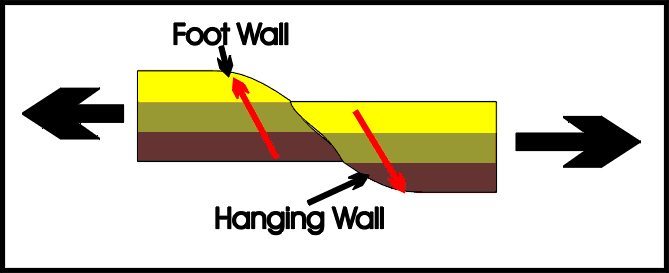 | Fault caused by tension forces |
Reverse fault, 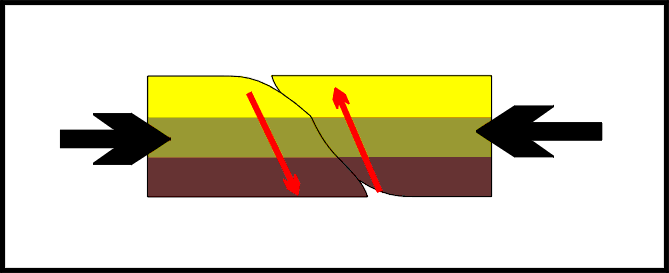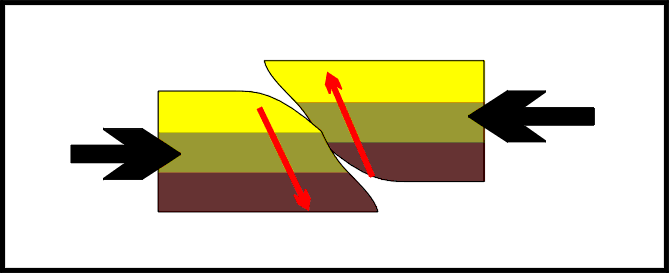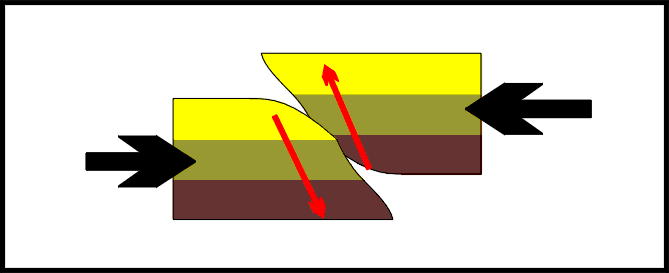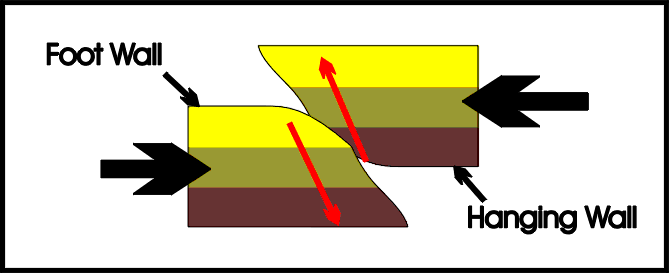 | Fault in rock caused by compression forces |
Strike-slip fault,  | Rocks on either side of fault slip past each other |
S-Waves (secondary waves),  | Seismic waves that vibrate side to side as well as up and down |
| Seismograph | An instrument that detects and measures seismic waves |
| Anticline | A fold in rock that bends upwards into an arch |
| focus | The area beneath Earth's surface where rock that is under stress breaks, triggering an earthquake. |
| epicenter | The point on the surface above the focus. |
earthquake,  , , 
| Shaking of earth that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface. |
| Richter scale | Rating of earthquake magnitude based on size of seismic waves. |
| Mercalli Scale | Scale rating earthquakes according to level of damage. |
| Moment magnitude scale | Earthquake rating system based on estimates of total energy released by an earthquake. |
| P-Waves (Primary waves) | Seismic waves that compress and expandthe ground. |
| syncline | A fold in rock that bends downward to form a valley. |