| A | B |
|---|
| Pantheon | Temple dedicated to all of the Roman Gods |
| Forum | The roman center for politics and trade |
| Colosseum | Large stadium built for public entertainment such as Gladiator battles |
| Pax Romana | Rome's 200 year period of peace and prosperity |
| Pope | the Patriarch of Rome, became the religious leader for the western Roman empire |
| Constantine | The first Christian emperor, he made Christianity legal in the Roman Empire, and moved the capital of the empire to Constantinople |
| Theodosius | Emperor of Rome who banned all reliugions other than Christianity |
| Bishops | religious leaders in the early Christian Church |
| The Roman Arch | an architectural design that was able to support more weight than previous structures |
| Diocletian | Roman emperor who divided Rome into two separate halves (Eastern and Western) |
| Ptolemy | Astronomer who made advancements in Astronomy and planetary motion during the Pax Romana. He falsely believed in a Geocentric theory of the solar system |
| The Aeneid | written by Virgil it is a great piece of Roman literature and is somewhat similar to the Odyssey |
| Constantinople | The capital of the Eastern Roman Empire, named after Constantine |
| Odoacer | Visigoth king who conquered Rome in 476 AD, ending the Rule of Roman Emperors |
| Germanic Tribes | Groups from Northern and Eastern Europe who invaded Rome's empire repeatedly, weakening the empire |
| Battle of Teutoburg Forest | Battle where Rome's expansion to the north was stopped |
| Arch of Titus | built to commemorate Rome's victory over the Jews |
| Judaea, Egypt, Turkey | Territories in Near east Rome conquered to solidify their rule |
| Roman Baths | publi meeting places, where people exercised, discussed politics and cleaned themselves |
| Civil Service System | giving government jobs to people on the basis of merit and skill |
| Edict of Milan | issued by Constantine it gave Christians the right to practice their faith |
| Mercenary | paid soldiers, as Rome's empire began to include them discipline in Rome's army broke down |
| Inflation | the decrease in value of $ (and rise in prices), Rome experienced this due to the decreased amount of silver in their $ |
| Attila the Hun | Germanic tribe Leader that weakened the Roman Empire |
| Galen | person knwon for advances in medicine during roman Empire |
| Forum (Image) |  |
| Colosseum (Image) |  |
| Pantheon (image) |  |
| Roman Arch (Image) | 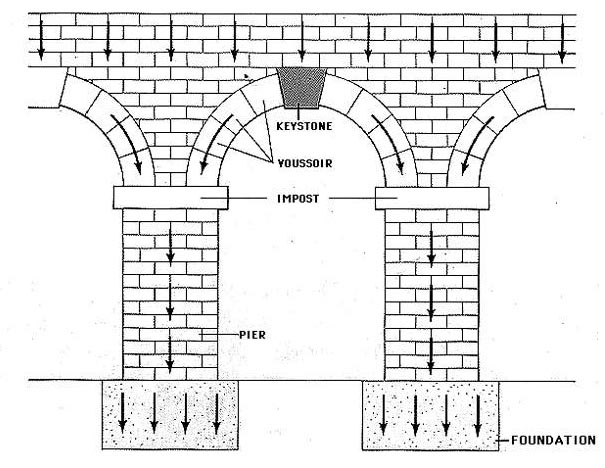 |
| Latins | the original settlers of Rome, they contributed their language to Roman culture |
| Etruscans | first kings of Rome, they brought their culture but were eventually overthrown |
| The Aeneid | written by Virgil, it is an epic poem that tells a myth of the founding of Rome after the Trojan War |
| Latin | the language of the Romans it influenced many other European languages |
| Romance languages | any language descended from Latin (French, Spanish, Portuguese, Romanian, and Italian) |
| Aqueducts | built by the romans to move water into their cities |
| Appian Way | famous road constructed by the Romans to link them with southern Italy |
| Roman Arch | a new architectural design that could support more weight |
| Circus maximus | famous chariot racing track that entertained Romans |
| Gladiators | warriors who fought (often to the death) form entertainment |
| Citizens | anyone who could participate in government in Rome |
| Patricians | the wealthy class in Roman society |
| Plebeians | the commoners in Rome's society |
| Representative Democracy | a system where people vote for people to make decisions for the, |
| The Senate | the most important branch of Rome's republic, they advised the consuls and set foreign policy |
| Consuls | 2 people that headed up Rome's government under normal conditions they each held veto power |
| Censors | kept an accurate count of the population and regulated people's moral behavior |
| Praetors | served as judges or military commanders in times of war |
| The Assemblies | designed to represent common interests they had a major role on laws passed |
| Dictator | someone who was given total control of the republic for a temporary amount of time |
| 12 tables | Rome's public law code, it established the principle of "innocent until proven guilty" |
| Punic Wars | series of conflicts between Rome and Carthage, Rome's victory allowed them to increase power and influence |
| Hannnibal | famous Carthaginian general he invaded ITaly through the Alps mountains |
| Fabius | Roman general who used Guerilla Warfare to resist hannibal |
| Scipio | Roman general who invaded Carthage and defeated Hannibal |
| inflation | rise in prices/decrease in value of $ |
| The First Triumvirate | an alliance between Julius Caesar, Pompey, and Crassus that briefly ruled Rome |
| Julius Caesar | Popular General, he took control of Rome after a civil war with Pompey and became the last dictator of Rome before his assassination |
| Marc Antony | Caesar's 2nd in command, he fought a war with OCtavian after the death of Caesar but lost |
| Octavian/Augustus Caesar | Caesar's nephew, he became the first emperor of rhe Roman Empire after defeating Marc Antony |
| Jupiter | Roman equivalent to Zeus (king of gods) |
| Juno | Roman equivalent to Hera (queen of the Gods) |
| Apollo | Roman equivalent to Apollo (god of Sun and prophecy) |
| Venus | Roman equivalent to Aphrodite (goddess of love and beauty) |
| Diana | Roman equivalent to Artemis (goddess of the hunt and the moon) |
| Minerva | Roman equivalent to Athena (Goddess of wisdom) |
| Vesta | Roman equivalent to Hestia (goddess of the home) very important in Rome |