| A | B |
|---|
| Gap1 (G1) | 1st stage of cell cycle: Cells grow, carry out normal functions, and replicate their organelles |
| Synthesis (S) | 2nd stage: DNA replication duplicates chromosomes, resulting in two identical copies (sister chromatids) |
| Gap 2 (G2) | 3rd stage: additional growth, duplication of centrioles (centrosomes) |
| Mitosis (M) | 4th stage of cell cycle: division of nucleus and contents (mitosis) and division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis) |
| mitosis | division of the nucleus and its contents (divided into 4 phases) |
| cytokinesis | division of the cytoplasm, producing 2 daughter cells |
| chromosome | one long continues thread of DNA that consists of numerous genes along with regulatory information |
| histones | positively charged proteins that DNA wraps around, forming chromatin |
| chromatin | the loose combination of DNA and proteins in interphase, when the cell is not actively dividing |
| chromatid | one half of a duplicated chromosome (sister chromatids) |
| prophase | chromatin condenses to form chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, centrioles begin to move to opposite poles, spindle fibers form |
| metaphase | spindle fibers attach to each chromosome and chromosomes are aligned along the equator |
| anaphase | chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of the cell |
| telophase | chromosomes begin to decondense, nuclear membranes start to reform, spindle fibers disappear |
| interphase | the cell copies its DNA and grows in preparation for division |
| apoptosis | programmed cell death, used during development to shape tissues and during cell cycle regulation to prevent damaged cells from dividing |
| cancer | uncontrolled cell growth |
| cancer cells | come from normal cells that have suffered damage to the genes that help make proteins involved in cell-cycle regulation |
| asexual reproduction | creation of offspring from a single parent that does not involve the joining of gametes |
| cell differentiation | process by which unspecialized cells develop their mature forms and functions by having different proteins (gene expression) |
| stem cells | a unique type of body cell that have 1) the ability to divide and renew themselves for long periods of time, 2) remain undifferentiated in form, and 3) develop into a variety of specialized cell types |
| adult stem cells | partially undifferentiated cells (multipotent) that can be treated with the right combination of molecules to produce a completely different type of tissue |
| embryonic stem cells | come from donated embryos, are pluripotent and can form any of the body cell types |
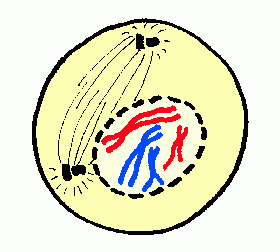 | 1st stage of mitosis, prophase |
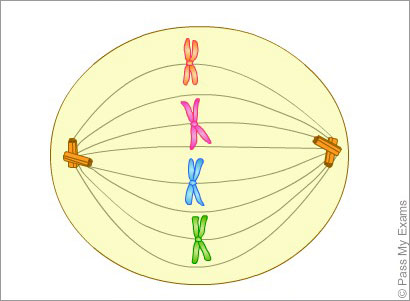 | 2nd stage of mitosis, metaphase |
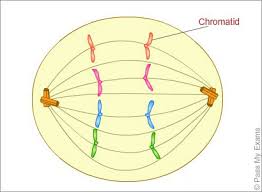 | 3rd stage of mitosis, anaphase |
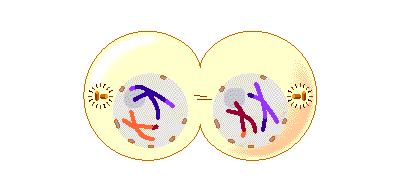 | final stage of mitosis, telophase |
| Gap 0 (G0) | cells have left the cell cycle, are not dividing but are metabolically active |