| A | B |
|---|
| Cells are organized into _____, groups of cells with similar appearance and common function. | tissues p.855 |
| Different types of tissues are organized into functional units called _____. | organs p.855 |
| Which organ belongs to both the digestive system and the endocrine system? | pancreas,  |
| Which system, besides the immune system, has a very important role in defending the body against pathogens? | lymphatic p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to protect against mechanical injury, infection, dehydration, and to maintain thermoregulation? | Integumentary p.855,  |
| __________ tissues cover the outside of the body and line the organs and cavities within the body. | Epithelial p.856,  |
| ________ tissue, consisting of a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix, holds many tissues and organs together and in place. | Connective p.857,  |
| Which type of connective tissue consists of collagen that becomes mineralized to form hardened structures? | Bone p.857,  |
| Which type of connective tissue has cells suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma? | Blood p.857,  |
| ______ connects bone to bone. | ligaments p.857 |
| The signaling molecules used for communication in the endocrine system are called ____. | hormones p.859, 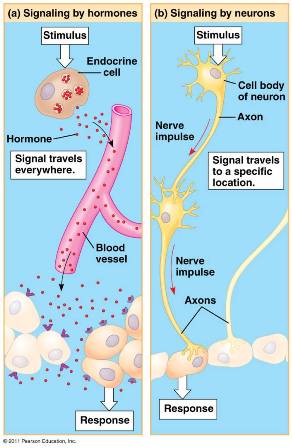 |
| Homeostasis in animals relies largely on ____ feedback. | negative p.861 |
| Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by metabolism are said to be ______. | endotherms p.863 |
| Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by external sources are said to be ______. | ectotherms p.863 |
| An animal whose body temperature remains relatively constant is a(n) _____. | homeotherm (Most endotherms are homeotherms, but not all. For instance, the bats and hummingbirds may periodically enter an inactive state in which they maintain a lower body temperature. Some ectotherms like fish that live in deep ocean waters maintain body temperature that is overall more constant than humans because the water temperature varies so little) p.863 |
| Where does chemical digestion of food start (In humans)? | In the mouth when salivary amylase starts breaking down complex carbohydrates |
| Where would you find chyme? | stomach |
| Water is extracted from undigested food and sent into the bloodstream while the food passes through the ___. | large intestine |
| The stomach breaks down mainly ___. | proteins |
| Lipids are broken down in the ___. | small intestine |
| _____ pushes food down your esophagus into your stomach. | Peristalsis (wave-like contractions of the muscles surrounding the esophagus), 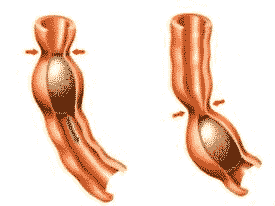 |
| ____ is a substance that is produced in the liver and is released by the gall bladder into the small intestine in order to break up fats into smaller droplets. | Bile |
| Plant growth hormones are called _______. | auxins |
| Hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones are called _____ hormones. | tropic hormones (for example TSH "thyroid stimulating hormone" is a tropic hormone) |
| A(n) ________ is a natural chemical messenger that is released by one animal and triggers a behavioral response in another animal of the same species. | pheromone |
| _____ controls metabolic rate. | thyroxin,  |
| _______ lowers blood calcium levels. | Calcitonin |
| _______ raises blood calcium levels. | Parathormone,  |
| _______ is a hormone produced by beta cells and causes a decrease in blood sugar levels. | insulin (beta cells are found in the pancreas),  |
| _______ is a hormone produced by alpha cells and causes an increase in blood glucose levels. | Glucagon (alpha cells are found in the pancreas),  |
| ________ support sperm production and promote male secondary sex characteristics. They are produced by the testes. | Androgens (like testosterone) |
| The principle of running water across gills in the opposite direction that blood flows in the gills in order to maximize diffusion is called _______. | Countercurrent exchange,  |
| The microscopic air sacs where diffusion of gases occur in the lungs are called _______. | alveoli |
| Air is drawn into lungs by _____ pressure. | negative pressure (As the diaphragm contracts and the muscles of the rib cage cause the chest cavity to expand, the pressure decreases as the volume of the chest cavity increases. This reduces the pressure on the lungs causing it to be less than air pressure from outside. Air is drawn into the lungs due to this "negative" pressure., 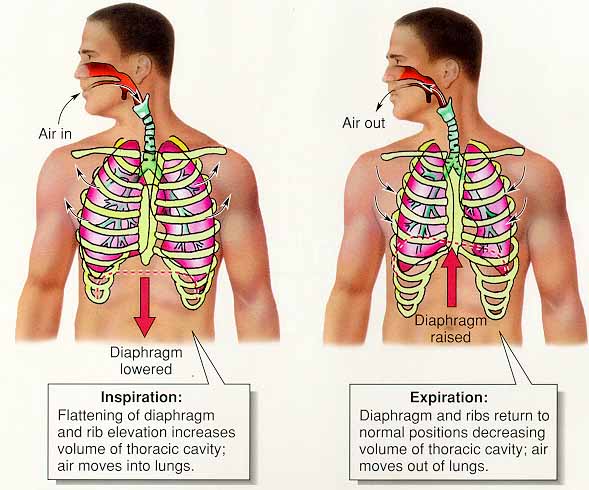 |
| Which part of the brain controls breathing? | The medulla (it senses changes in pH caused by changing carbon dioxide levels in the blood and adjusts the breathing rate accordingly) |
| Which substance dissolved in blood acts as a buffer against rising pH? | carbon dioxide (notice in the bottom equation how carbon dioxide removes hydroxide ions which would otherwise cause pH to rise),  |
| Which substance dissolved in blood acts as a buffer against increasing acidity? | The bicarbonate ion (notice in the top equation how an increase in the hydrogen ion equation will cause a reaction that will produce more carbonic acid as it combines with the bicarbonate ion. This prevents large increases in the acidity that the hydrogen ion would otherwise cause),  |
| The scientifc name for red blood cells is ________. | erythrocyte, 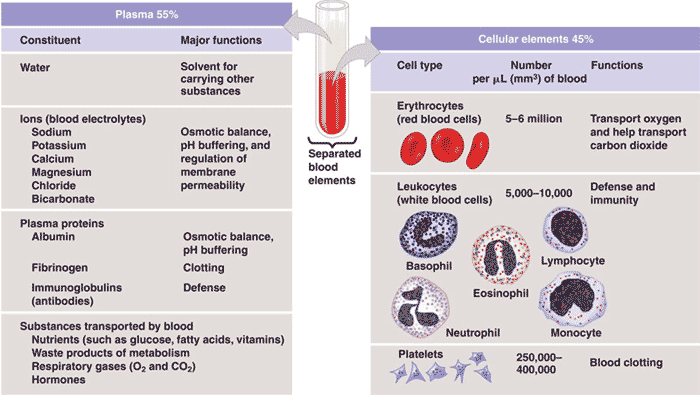 |
| The scientifc name for white blood cells is ________. | leukocyte,  |
| The scientific name for platelets is ________. | thrombocyte,  |
| Fragments of cells that are involved with blood clotting are called ____. | platelets (a.k.a. thrombocytes),  |
| What type of animal has a zero chambered heart? | Chuck Norris, who doesn't have a heart. Just ask his victims.,  |
| The _____ nervous system consists of all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. | peripheral nervous system (PNS),  |
| An extension of the neuron that receives incoming messages is called a(n) _____. | dendrite,  |
| The extension of the neuron that transmits a signal to another cell is called a(n) _____. | axon,  |
| The ________ branch of the autonomic nervous system is associated with the "fight or flight" response. | sympathetic (In response to danger the sympathetic nervous system increases heart and breathing rate, converts glycogen in the liver to glucose and releases it into the bloodstream, dilate blood vessels in lungs to increase gas exchange, and releases adrenalin) |
| The _________ branch of the autonomic nervous system is associated with calming the body. | parasympathetic |
| In order to maintain the high concentration of ______ ions inside the neuron and the high concentration of _____ ions outside the neuron when the neuron is at "rest," energy must be used to power the sodium-potassium pump. | potassium (inside), sodium (outside), 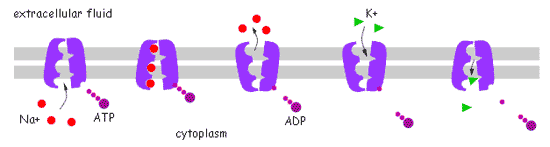 |
| As an action potential propagates down an axon, ____ channels open first followed by _____ channels. | sodium, potassium,  |
| The cytoplasm at the end of an axon contains many small vesicles. What's in those vesicles? | neurotransmitters,  |
| The entrance of _____ through gated channels in the presynaptic membrane stimulates vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane, releasing neurotransmitters into the synapse. | calcium ions (Ca++),  |
| The thick band of axons that allows communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _____. | corpus callosum, 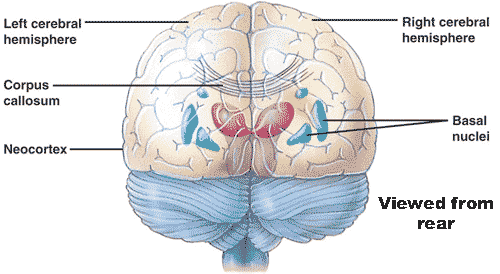 |
| The ____ system is your emotional control center. | lymbic,  |
| Which part of the brain is associated with coordination and the memorization of physical skills (like skiing). | the cerebellum, 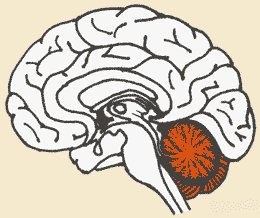 |
| The ____ lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is responsible for hearing and smell. | temporal lobe,  |
| The ____ lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is responsible for speech, reading, and taste. | parietal lobe,  |
| The ___ lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is responsible for vision. | occipital lobe,  |
| The ___ lobe of the cerebral hemisphere is most responsible for critical thinking, learning, and maturity. | frontal lobe,  |
| The part of the brain that is a bridge between the nervous and endocrine system is the _____. | hypothalamus |
| Smooth muscles are under the control of the _____ nervous system. | autonomic nervous system (smooth muscles are also called involuntary muscles because they are controlled by a part of the nervous system that is not under the direct control of conscious thought) |
____ ions allow thick and thin filaments in muscles to develop cross bridges so they can interact and cause the muscle to contract.,  | calcium ions (Ca++),  |
| Which neurotransmitter stimulates muscle contraction? | acetylcholine (Ach), 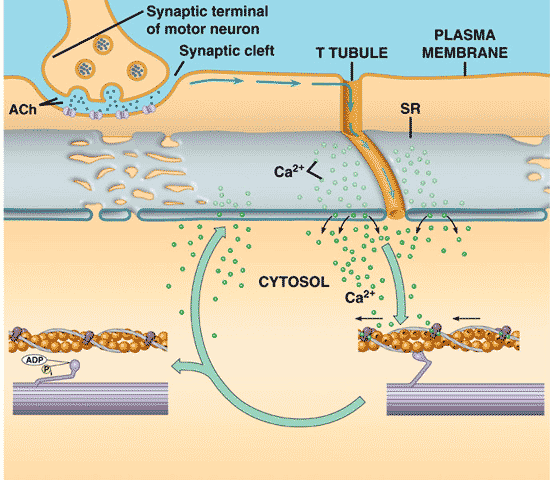 |
| _____ connects muscle to bone. | Tendons (ligaments connect bone to bone), 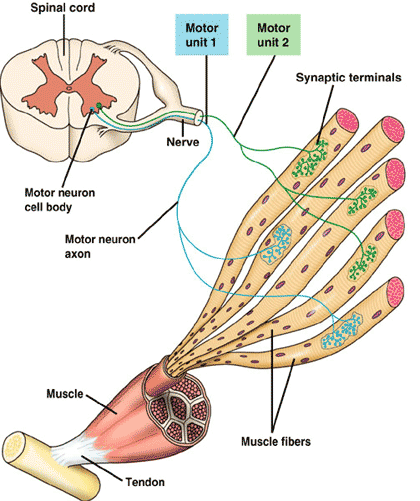 |
| _____ is a nitrogenous waste that is very soluble, highly toxic and generally excreted by fish and other organisms that live in water. | Ammonia |
| _____ is a nitrogenous waste excreted by earthworms and humans. | Urea |
| Which type of nitrogenous waste produces the least water loss? | Uric acid |
| Transport of fluids across a membrane due to high pressure is called ______. | filtration (this occurs in Bowman's capsule because the blood pressure inside the capillaries of the glomerulus is under very high pressure, even higher than blood pressure in most capillaries), 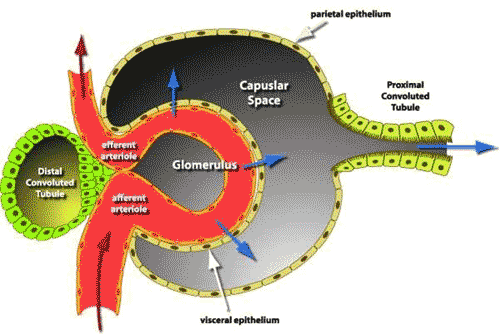 |
| The ____ and collecting tubule of the nephron is where urine is concentrated by allowing the diffusion of water out of the nephron | descending,  |
| The ____ of the nephron is where salt is removed from the filtrate in order to maintain a hyperosmotic gradient in the renal medulla. | ascending loop of Henle,  |
| The ____ is where most of the filtrate is reabsorbed into the bloodstream from the nephron. | proximal tubule,  |
| Where in the nephron does pH regulation, secretion, and reabsorption happen? | Proximal and distal tubules (cells that line the proximal tubule maintain a constant pH by controlling the secretion of hydrogen ions),  |
| Whether the walls of the collecting tube in the nephron are permeable or not depends on the presence of _______. Its presence makes the walls permeable so that water can diffuse out of the tubule, making the urine very concentrated. | Antidiuretic hormone (ADH promotes retention of water by the kidneys),  |
| Alcohol blocks the release of ___, causing less water retention and more urination. | ADH,  |
| The ____ system is a complex feedback mechanism that initiates a change in the kidneys in response to a loss of blood pressure. | RAAS (renin-angiotensis-aldosterone-system),  |