| A | B |
|---|
| Sarturated hydrocarbons | alkanes containing SINGLE BONDS between carbons |
| Unsatruated hydrocarbons | Alkenes and Alkynes containing DOUBLE or TRIPLE BONDS |
| Hydration | an alkene reacts with water (H-OH); |
| What functional group is produced in hydration | alcohol |
| Hydrogenation | H atoms add to each of the carbon atoms in the DOUBLE BOND |
| A double bond is converted to a_____, ______ when hydrogenation occurs | single bond, alkane |
| extended structural formula | shows all the atoms and bonds connected to each atom |
| condensed structural formula | shows the carbon atoms grouped with the attached NUMBER of hydrogen atoms |
| Markinov's Rule | when water adds to the double bond in which carbon atoms are attached to DIFFERENT NUMBERS of HYDROGEN atoms, the the H- from the H-OH attaches to the carbon that has the GREATER number of H atoms and the -OH attaches to the other carbon from the double bond |
| Polymer | Consists of small repeating units called monomers |
| Monomer | the samll repeating units that form a polymer |
| Cycloalkenes | hydrocarbons forming a ring structure containing one or more double bonds; "ene" |
| cycloalkanes | hydrocarbons forming a ring structure contining only single bonds; "ane" |
| Alkanes with __________ masses have higher melting/ boiling points than Alkanes with _________ masses | higher; lower |
| Boiling/melting points of Alkanes with substituents (branches) are generally ___________ than straight chain alkanes | Lower |
| Cycloalkanes have _________ boiling/melting points than straight chain with the same number of atoms | higher |
| Alkanes are highly flammable T or F | True |
| Alkanes are ___________ which makes them _________ in water | nonpolar; insoluble |
| Alkenes | have one or more double bonds |
| Alkynes | have one or more triple bonds |
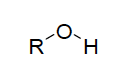 | Functional group alcohol |
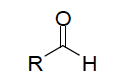 | Functional group aldehyede |
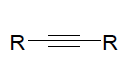 |  |
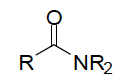 | Functional Group Amide |
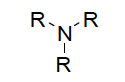 | Functional group Amine |
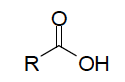 | Functional Group carboxylic acid |
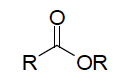 | Functional group Esters |
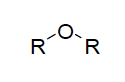 | Functional Group Ethers |
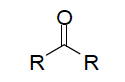 | Functional Group ketone |