| A | B |
|---|
| Oxygen | -O- |
| phenol | a hydroxyl group replaces hydrogen atom on a BENZENE ring |
| Thiol | Contains a sulfur atom similar to alcohol except the -OH is replaced with -SH |
| When naming an alcohol------ | replace the "e" on the alkane name and replace with "ol"; the alkyl group is named first followed by the alcohol; the chain is numbered when there is 3 or more carbons |
| diol | an alcohol with 2 -OH groups |
| triol | an alcohol with 3 -OH groups |
| Naming phenols-------- | used when a hydroxy -OH group is bonded to benzene ring; when there is a 2nd substituent the ring is numbered to give the carbon bonded to -OH #1 |
| ortho (o) indicates what arrangement | 1,2 |
| meta (m) indicates what arrangment | 1,3 |
| para (p) indicates what arrangment | 1,4 |
| Naming ethers-------- | consist of oxygen atom attached by single bond to 2 carbon groups; name the groups on each side of the oxygen -O- written in alphabetical order, followed by the word ether |
| primary alcohol | has 1 alkyl group attached to the carbon atom bonded to the -OH group |
| secondary alcohol | has 2 alkyl group attached to the carbon atom bonded to the -OH group |
| tertiary alcohol | has 3 alkyl group attached to the carbon atom bonded to the -OH group |
| alcohols have higher boiling points than ________ because alcohol require higher temperature to break apart the many hydrogen bonds | ethers |
| Boiling point of ether is similar to _________ because neither can form hydrogen bonds and have low melting/boiling points | alkanes |
| Alcohol with ______ carbons is completely soluble in water | 1 to 3 |
| Alcohol with ______ carbons are slightly soluble | 4 |
| Alcohol with ______ carbons is NOT SOLUBLE in water | 5 or more |
| Phenols have the highest boiling point because ---- | the -OH group allows phenol molecules to bond with other phenol molecules |
| When dehydration of alcohols occurs they lose a H20 molecule to form---- | alkenes |
| Saytzeff's rule | states the major product formed is the one that forms by removing hydrogen from carbon atom that has the SMALLEST number of hydrogen atoms |
| Oxidation of primary alcohols forms what? | aldehyde |
| Oxidation of secondary alcohol forms what? | Ketone |
| Tertiary alcohols _______ because the C-C bonds are too strong to oxidize | DO NOT OXIDIZE |
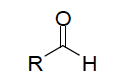 | Aldehyde functional group |
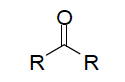 | Ketone functional group |
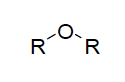 | ether functional group |
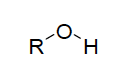 | Alcohol functional group |
| COMMON name for ketones | alkyl group bonded to carbonyl group are named as substituents and are listed alphabetically, followed by ketone |
| IUPAC name for ketones | replace the "e" in the corresponding alkane and change to "one"; carbon chains with 5 or more are numbered from the end nearer the carbonyl group |
| Naming aldehydes using IUPAC | replace the "e" from the alkane group with "al"; name and number the substituent by counting carbonyl group as 1 |
| Aldehydes with 1 to 4 carbons are often referred to by common name which with these roots ending in aldehyde | Form, acet, propion and bytyr |
| the root "form" for an aldehyde is how many carbons | 1 carbon |
| the root "acet" for an aldehyde is how many carbons | 2 carbon |
| the root "propion" for an aldehyde is how many carbons | 3 carbon |
| the root "butyr" for an aldehyde is how many carbons | 4 carbon |
| In a reduction of aldehyde and ketones they are reduced by | H2 |
| When aldehyde is reduced it forms_____Alcohol | Primary |
| When a ketone is reduced it forms________alcohol | seconday |
| Hemiacetal | A hydroxy group (-OH) and a alkoxy group (-OR) on the same carbon atom |
| Acetal | has 2 hydroxy (-OH) groups attached to the same atom |