| A | B |
|---|
| Photosynthesis | reqires sun, water (H2O) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) |
| Products of photosynthesis | carbohydrate and oxygen (O) |
| the name carbohydrate comes from the fact that ------ | carbohydrates contain hydrogen and oxygen in a 2:1 ratio |
| What functional groups are in open chains of monosaccharides | hydroxyl group with an aldehyde or ketone groups |
| this sugar is classified as a ketotriose | 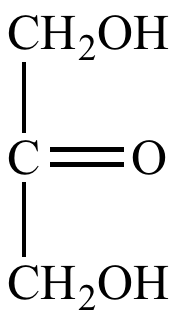 |
This is a cyclic structure of an _________, 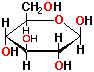 | aldohexose |
This is the haworth structure of,  | glucose |
This is at least one of the products of the complete hydrolysis of________,  | maltose, sucrose, lactose and glycogen |
A benedicts test with this sugar would be_________,  | positive |
This is the monosacharide unit used to build polymers of __________,  | amylose, amylopectin, cellulose, and glycogen |
| Maltose | a dissaccharide that occurs as a breakdown product of amylose |
| sucrose is a _________ that is not a reducing sugar | disaccharide |
| amylopectin | a carbohydrate that is produced as a storage form of energy in plants |
| glycogen | a storage form of energy in humans |
| cellulose | is used for structural purposes by plants (wood) |
| amylose | a polysaccharide composed of many glucose units linked by Alpha-1-4-glycosidic bonds |
| lactose | a sugar containing both glucose and galactose |
| glycogen | a sugar composed of glucose units joined by both alpha-1,4- and alpha-1,6-glycosidic bonds |
| sucrose | composed of glucose and fructose and is also called table sugar |
| sucrose _______ a reducing sugar | IS NOT |
| Lactose is found in _________ | milk and milk products |
| Lactose gives _______ when hydrolyzed | galactose |
| cellulose is a carbohydrate composed of glucose units joined by _______ | beta-1,4-glycosydic bonds |
| When carbonyl group in glucose is reduced ______ is formed | sorbitol |
| carbohydrates are all made of _________ | carbon, hydrogen and oxygen |
| carbon cycle | combination of photosynthesis and respiration in which energy from sun is stored in plants and made available to us when carbohydrates in our diet are metabolized. |
| monosaccharide | simplest form of carbohydrate |
| disaccharide consists of ______ monosaccharide units joined together | two |
| polysaccharide | carbohydrate consisting of many monosaccharide units which is called a polymer |
| Aldose | the first carbon in the chain is an aldehyde, 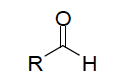 |
| ketose | the second carbon atom is a ketone |
| Besides being classified as an aldose or ketose, monosaccharides are also classified by _______ | the number of carbon atoms |
| tetrose | 4 carbon atoms |
| pentose | 5 carbon atoms |
| hexose | 6 carbon atoms |
| the letter "L" designates | the hydroxy group is located on the left |
| the letter "D" designates | the hydroxy group is located on the right |
| the hydroxy (-OH) group farthest from the aldehyde or ketone group is used to | detrermine "L" or "D" configuration of the monosaccharide |
| a reducing sugar is a carbohydrate that _____ | reduces another substance |
| alditol | sugar alcohols produced by reduction of carbonyl group in monosaccharides |
| glycosidic bond | a hemiacetal bond that connects 2 monosaccharides |
| starch | storage form of glucose in plants; found in rice, bean potato, cereal etc. |
| what is produced when monosaccharides are OXIDIZED | Carboxylic acid; the "ose" at the ending of the monosaccharide is replaced with "onic acid" |
| What is produced in a REDUCTION of a monosaccharide | Sugar alcohols called alditols; the "ose" of the monosaccharide is replaced with "itol" |
| alpha | occurs when the hydroxy group (-OH) occurs below the plane |
| Beta | occurs when the hydroxy group (-OH) occurs above the plane |
| mutarotation | when each anomer converts to an open chain and back again. |