| A | B |
|---|
| Denaturing agents | heat above 50 C, acids and bases, heavy metal ions and agitation |
| Beta pleated sheet, secondary structure, consists of hydrogen bonds | 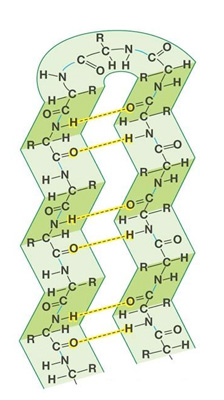 |
| Alph helix a secondary structure in which H+ bonds connect the N-H of one peptide bond with the C=O of another peptide bond to form a coil | 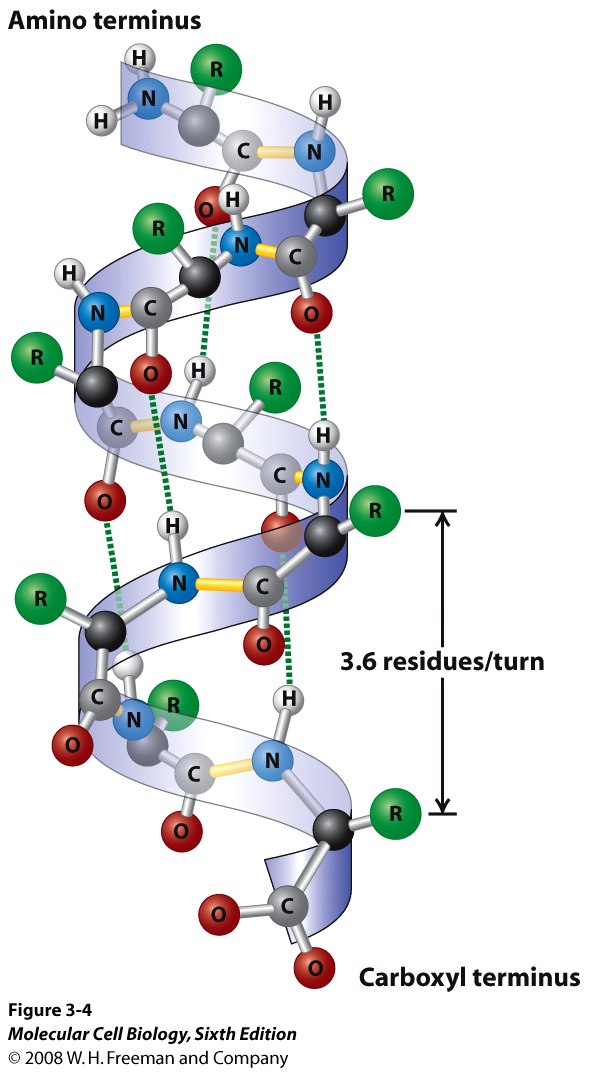 |
| primary structure is a specific sequence of amino acids held together by peptide bonds |  |
| collagen | most abundant protein in body, provides structural components, becomes less elastic with age causing wrinkles; made up of triple helix |
| triple helix | protein structure found in collagen consisting of 3 helical polypeptide chains woven together like a braid |
| alzheimer's disease | beta amyloid proteins change from normal alpha helical shape to beta pleated sheets that stick together forming plaque |
| tertiary structure | folding of secondary structure into a compact structure stabilized by ionic and disulfide bonds |
| hydrophilic interactions "water loving" | attraction between the POLAR residues on protein surface and water |
| hydrophobic interactions "water fearing" | the attraction between NONPOLAR residues on the inside of a globular protein |
| Polar amino acids | amino acid with a POLAR R group - hydroxyl (-OH), thiol (-SH) or amide (-CONH2) |
| Polar ACIDIC amino acid | contains a carboxylate (-COO-) R group |
| Polar BASIC amino acid R groups | contains an amine R group -NH3 (ammonium) |
| Zwitterion | ionized form (neutral) of amino acid occurs at it pI (isoelectric point) contains a _NH3+ (ammonium group) and COO_ (carboxylate group) |
| isoelectric point (pI) | a specific pH at which a zwitterion exists with a charge of zero (neutral) |
| when the pH is above (base) the zwiterrion pI (pH at which it is neutral) | carboxilic acid -COOH group loses H+ to form carboxylate -COO- or ammonium group -NH3 loses H+ -NH2 |
| when pH is below (acidic) the zwiterrion pI (pH where it is neutral) this happens | the carboxylate group -COO- gains H+ -COOH- |
| peptide bonds | amide bonds formed between the -COO- (carboxylate group) of one amino acid and the -NH#+ (ammonium group) of another amino acid in PRIMARY STRUCTURE |
| peptide | 2 or more amino acids linked by peptide bonds |
| Salt bridges | ionic attractions between the residues of acidic and basic in a tertiary structure of an amino acid |
| hydrogen bond | interaction between water and the polar residues (-OH, -NH3+, and -COO-) on the outside of a polypeptide chain |
| Disulfide bond (bond in tertiary structure) | covalent bonds (-S-S-) forms between -SH group of 2 cysteine in a protein which stabilizes the tertiary and quaternary structures |
| Tertiary structure of protein | polypeptide folds into a specific 3 dimensional shape stabilized by interactions between amino acid residues to form biologically active protein |
| Nonpolar amino acids | amino acid with R group containing only C and H atoms |
| Hemoglobin structure | 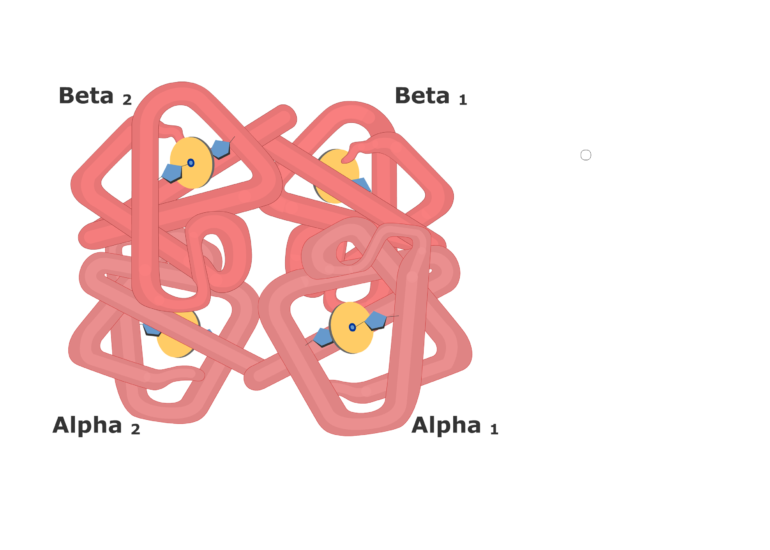 |
| Nonpolar amino acids | amino acids containing H+, ALJYL (CH3) OR AROMATIC R GROUPS |