| A | B |
|---|
| heterotroph | organisms that cannot make their own food. Also called consumers. |
| autotroph | organisms that can make their own food. Also called producers. |
| Chloroplast | the organelle inside the cell where photosynthesis takes place. |
| chlorophyll | the main pigment found inside the chloroplast that absorbs light energy. |
| photosynthesis | the process whereby the plant uses the energy from the sun to produce glucose. |
| cellular respiration | the process by which oxygen is used to break down glucose to produce energy. |
| The reactants of photosynthesis | carbon dioxide + water + light energy |
| The products of photosynthesis | glucose + oxygen (out of the chloroplast) |
| The reactants of cellular respiration | glucose + oxygen (into the mitochondria) |
| The products of cellular respiration | carbon dioxide + water + ATP |
| Glucose | the sugar that is made during photosynthesis |
| pigments | colored chemical compounds that absorb light |
| mitochondria | the organelle inside the cell where cellular respiration takes place |
| fermentation | the process of breaking down glucose without the use of oxygen |
| stomata | small pores in the leaves of plants that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to enter and leave the plant |
| xylem | tubes in the plant that carry water throughout the plant |
| phloem | tubes in the plant that carry sugar to all parts of the plant |
| How many glucose molecules are made from 6 carbon dioxide molecules and six water molecules | one glucose |
| Carbon dioxide molecule | 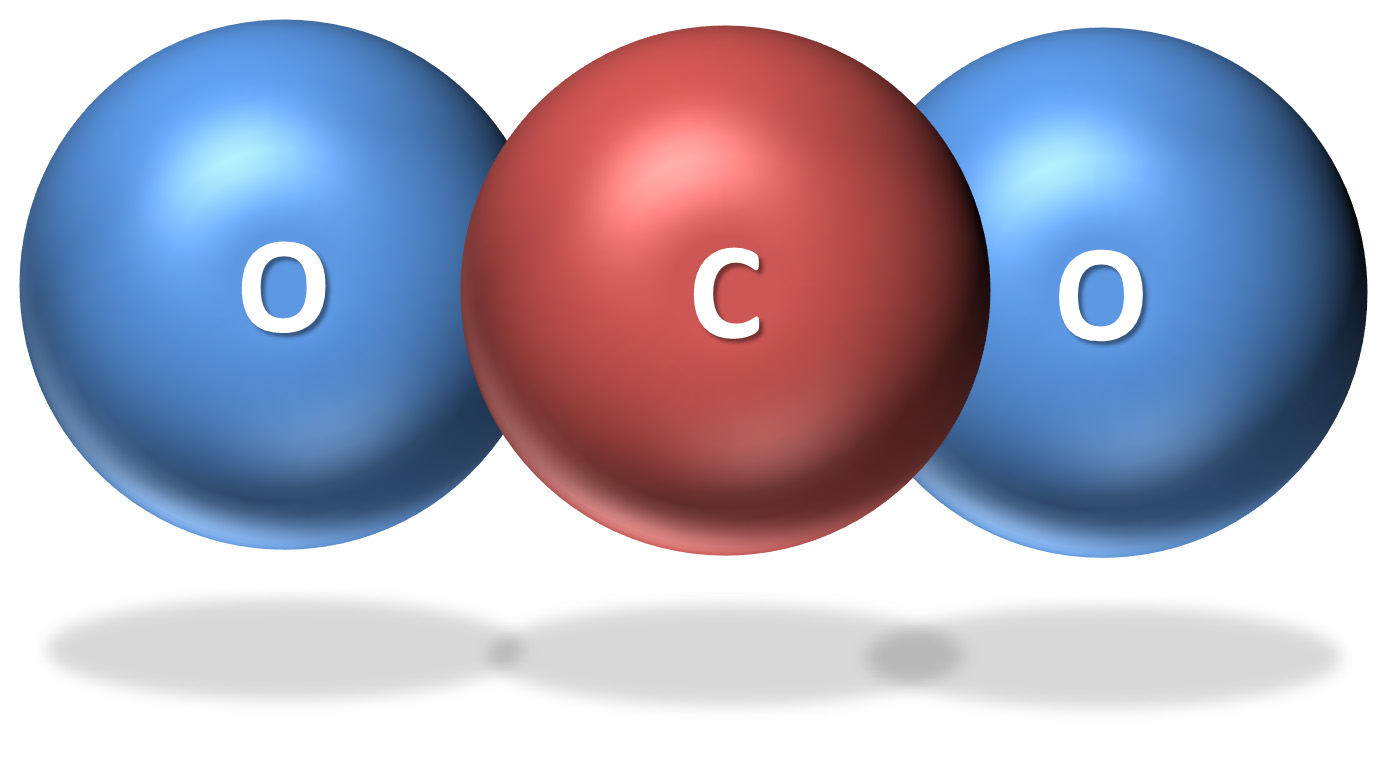 |
| Water molecule | 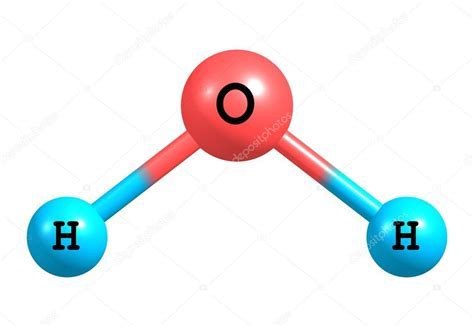 |
| Glucose molecule | 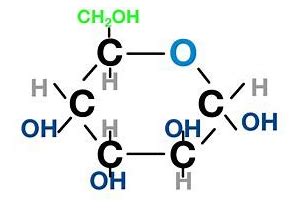 |