| A | B |
|---|
| constructive forces | build up or make new things like sand dunes, deltas, mountains, or islands,  |
| destructive forces | natural forces that break down the earth. Water, ice, wind, etc. lead to erosion and weathering of rocks and other landforms over time,  |
| seismograph | an instrument used to measure the vibrations in the Earth caused by plate movements; sense earthquakes, 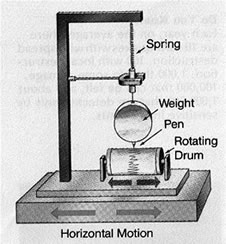 |
| satellite imagery | provide aerial footage of the changes that occur in a variety of places around the world that often can't be seen in person. |
| deltas | triangular shaped deposition that occurs at the mouth of rivers as the water slows down and dumps what it is carrying; deposition,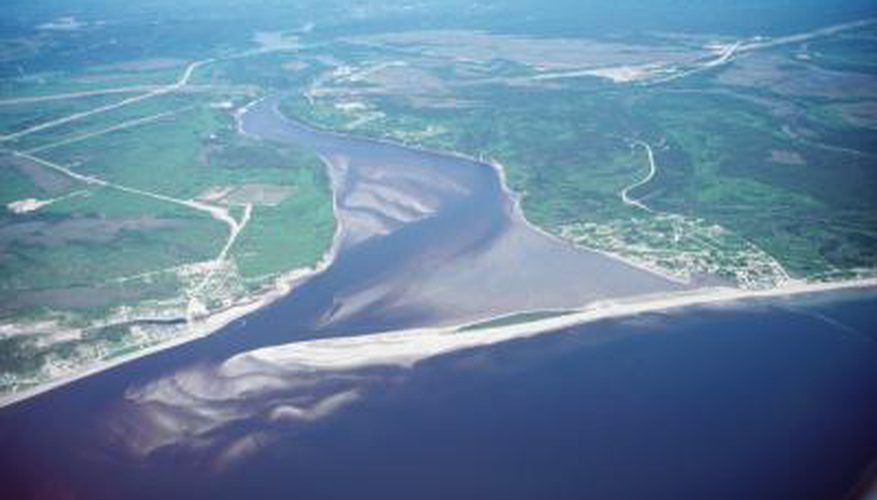  |
| sand dunes | piles of sand that are created as the wind slows down and deposits the sand; deposition,  |
| mountains | Converging boundaries; constructive forces, 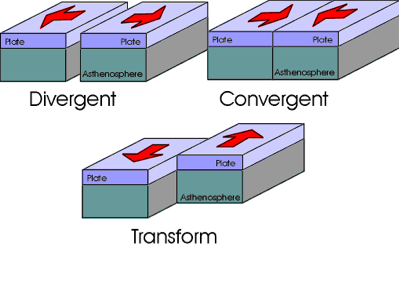 |
| volcanoes | destructive forces; created by divergent boundaries under water or convergent boundaries on land, 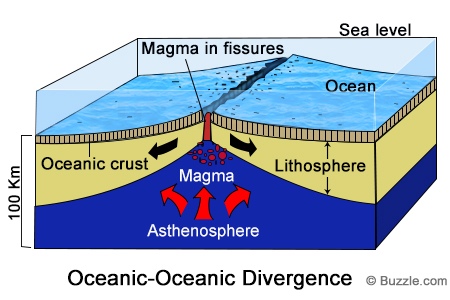 |
| deposition | Erosion is when materials, like soil or rocks, are moved by wind or water. All these materials are called sediments. Deposition is when those sediments are deposited, or dropped off, in a different location. THIS HAPPENS BECAUSE THE WIND OR WATER IS SLOWING DOWN AND CAN'T CARRY THE MATERIALS ANYMORE.,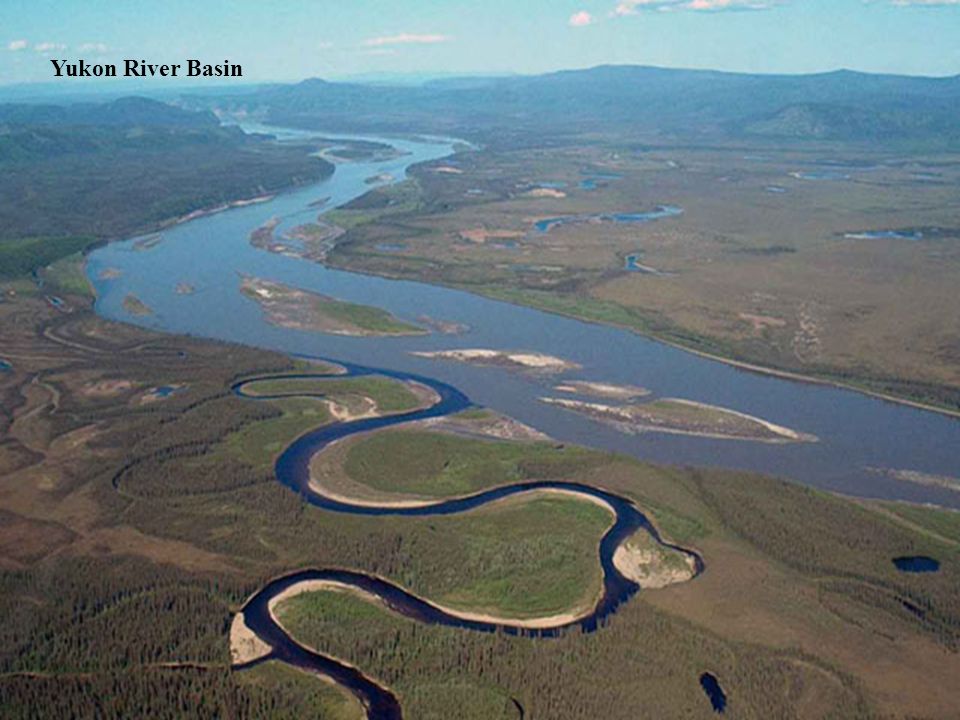  |
| weathering | process where rock is dissolved, worn away or broken down into smaller and smaller pieces. There are mechanical, chemical and organic weathering processes. Organic weathering happens when plants break up rocks with their growing roots or plant acids help dissolve rock. WEATHERING HAS TO OCCUR BEFORE EROSION CAN HAPPEN OR THE THINGS WOULD BE TO BIG TO MOVE., 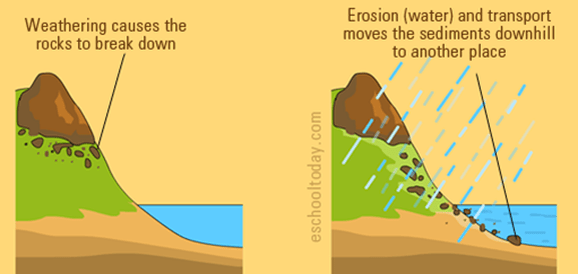 |
| erosion | movement of broken down material by wind, water, or organism,  |
| organisms impact | Plants and animals can weather and erode things by digging, walking on, growing in, breaking up by roots, etc.,  |
| Physical changes | cutting, mixing, crushing, smashing, molding, painting, freezing, evaporating, etc. that doesn't make something new,  |
| phases of water | changes in water are always a physical change because they can be changed back to water, 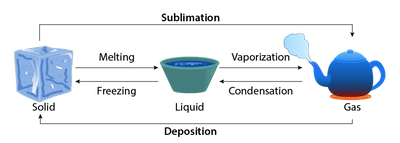 |
| chemical changes | due to color change, gives off gas, temperature change, smell, new substance created, irreversible, 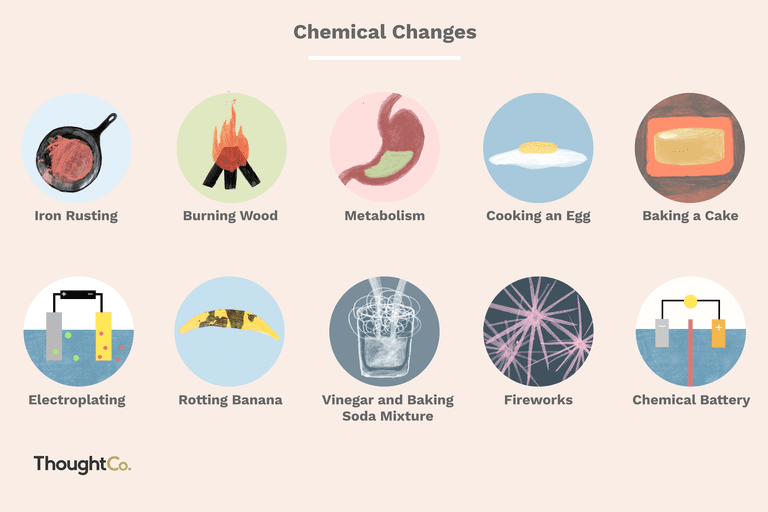 |
| vertebrates | have backbones,  |
| invertebrates | no backbone,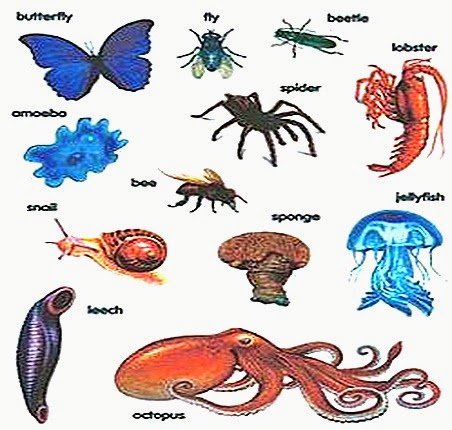  |
| fish | gills, fins, scales, breathe under water, and are cold blooded |
| mammals | hair or fur, live births, get milk from mother, warm blooded |
| reptiles | scales, dry skin, usually lay eggs, cold blooded |
| amphibians | amphi- means both. Moist skin, cold blooded, lay eggs, webbed feet, on land and water. |
| birds | feathers and wings, lay eggs, warm blooded |
| arthropods | a large group of animals with hard shells on the outsides of their bodies, legs with joints, and no bones inside their bodies. Insects, spiders, centipedes, and crabs are arthropods. |
| Vascular Plants | have veins on their leaves that help with transport of water and nutrients,  |
| Nonvascular Plants | Don't have veins that help with transport of water and nutrients |
| Flowering (Seeds) | ype of vascular plant that produces flowers in order to reproduce. Flowering plants produce seeds within a fruit. The scientific name for flowering plants is angiosperms. |
| Nonflowering (spores) | wo main groups of non-flowering plants. Plants that use spores to reproduce and plants that use seeds to reproduce. The non-flowering plants that use seeds are called gymnosperms. |
| learned behaviors | Learned behavior is something an animal discovers through trial, error and observation. Most learned behavior comes from the teaching of the animal's parent or through experimentation with its environment.,  |
| instinctual behaviors | these are behaviors that they are born with and don't have a choice about doing. Examples include hibernation and migration or dog's drooling. |
| inherited traits | These are things that you are born with like fur, webbed feet, or scales on your body., 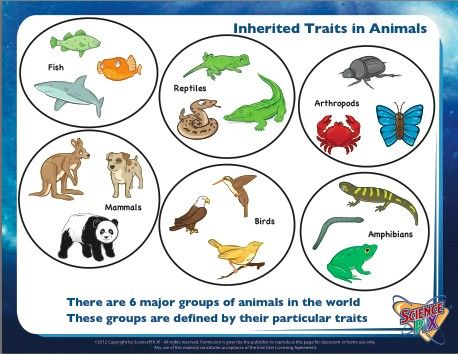 |
| acquired physical traits | Acquired traits include things such as calluses on fingers, larger muscle size from exercise or from avoiding predators. |
| microscope | instrument used to see things that are to small to see with the naked eye. |
| cells | The cell is the basic unit of life. Some organisms are made up of a single cell, like bacteria, while others are made up of trillions of cells. Human beings are made up of cells, too. |
| plant cell | are not necessarily square, but they due tend to have distinct edges and be somewhat rectangular. This structure is caused by the cell wall which is very rigid and therefore forces the cell to have a defined shape.,  |
| animal cell | Animal cells are mostly round and irregular in shape because they don't have a cell wall like a plant cell., 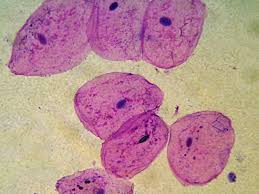 |
| cell membrane | The cell membrane is a thin flexible layer around the cells of all living things.Its basic job is to separate the inside of cells from the outside kind of like skin on a human. |
| cell wall | Cell walls made of cellulose are only found around plant cells and a few other organisms. If a plant cell is like a water balloon, the cell wall is like a cardboard box that protects the balloon., 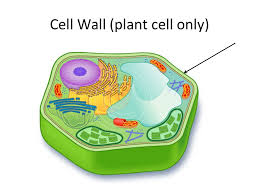 |
| cytoplasm | Cytoplasm is a watery, gel-like substance made of mostly salt and water that provides a structure for the cell parts so they can move freely within the cell membrane. Kind of like the water in a bathtub that allows all the play toys to float and move around., 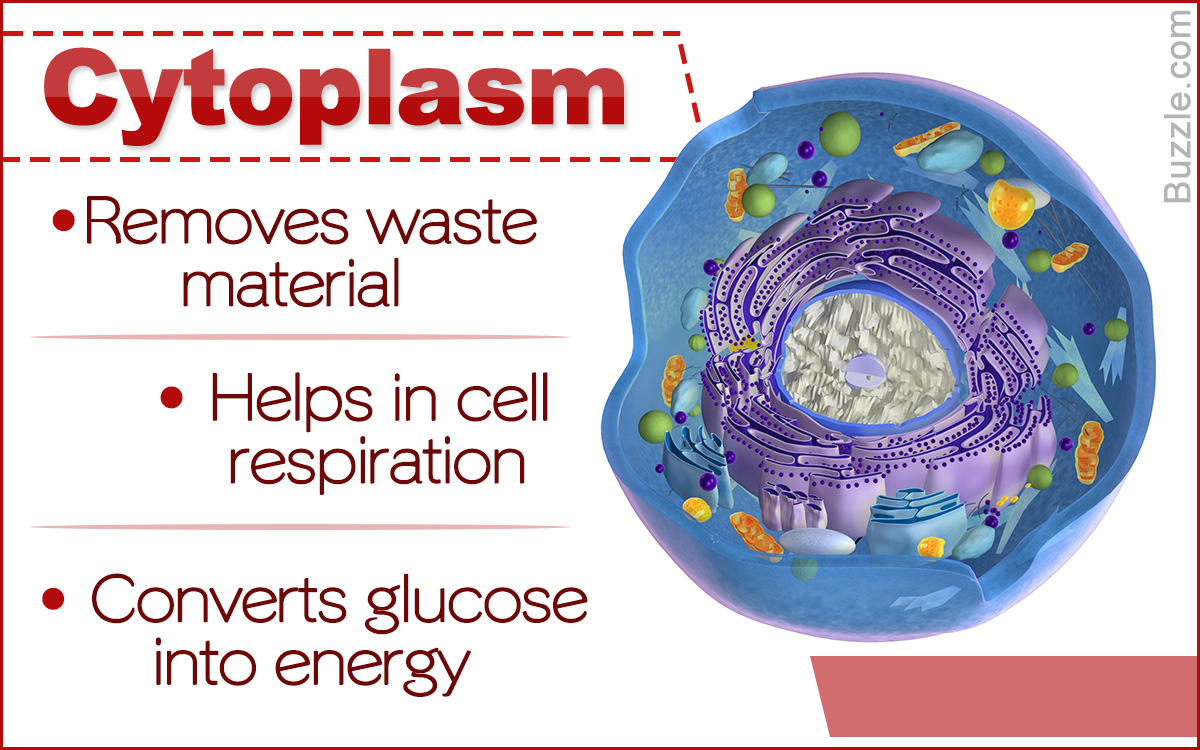 |
| nucleus | It is the main control center for the cell and acts kind of like the cell's brain. |
| chloroplast | only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. ... Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. The entire process is called photosynthesis and it all depends on the little green chlorophyll molecules in each chloroplast.,  |
| microorganisms | also called microbes, are extremely tiny organisms that can only be seen under a microscope. Microorganisms are one of the most diverse organisms and they include bacteria, fungi, archaea, protists, green algae, plankton and amoeba. |
| Beneficial microorganisms | Probiotics, bacteria are used in the stomach for digestion; bacteria are used in yogurt and cheese; plants used them in the nitrogen cycle to help make food; makes vinegar; used to clean up sewage and oil spills,  |
| harmful microorganisms | Ecoli, Viruses, Salmonella, Streptococcus, some bacteria, 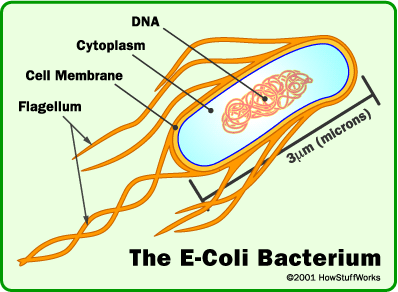 |
| Cell structures (organelles) | perform basic life functions for the cell, such as making energy, growing, repairing, and getting rid of waste. |
| microorganisms | living things that are too small to be seen without magnification from a microscope or hand lens |
| bacteria | single-celled microorganisms that can live in almost every environment and grow and reproduce on their own. |
| viruses | even smaller than bacteria and cannot reproduce or grow unless they infect another organism. |
| How viruses work | uses the organism’s cells to reproduce by making copies of itself, eventually making the host organism sick. |
| beneficial bacteria | like the ones that make cheese, yogurt, or break down chemicals, waste, or help use digest food. |
| animal classification | organize them into groups based on characteristics/physical structures (gills, feathers, scales) they share. Scientists classify things so that they can study ways those things are similar or different. |
| plants | classified by the way in which they transport materials within the organism. They can also be classified by the way in which they reproduce. |
| ferns | plants that don't use seeds to reproduce |
| Pine trees or conifers | use seeds (pine cones) to reproduce but don't have flowers |
| use flowers to make seeds | apple trees and roses |
| traits | physical characteristics that are used to describe an organism |
| inherited traits | passed from parent(s) to offspring. Fur color and beak shape are examples |
| acquired traits | developed after the organism is born and are not passed to offspring by parents. Having a scar or being a fast runner are examples |
| instinctual behaviors | Some interactions, like babies crying for food or being quiet in the nest when parents are away because the organism knows how to behave without being taught. |
| learned behaviors | like where to find food or how to raise offspring are taught to an organism, or discovered through interactions with the environment |
| physical properties | measurable and can be seen. Color, hardness, area, length, strength, and temperature are some examples |
| chemical properties | properties that can be measured only by chemically changing an object. Paper starts to burn at around 450°F. At this temperature, the paper combines with oxygen in the air and new substances are formed |
| Example of physical change | salt can be dissolved in water, but, if the water evaporates, the salt is still there. |
| Example of chemical change | Hydrogen peroxide forming bubbles on its own is an example of matter breaking down into two substances. Vinegar and baking soda turning into bubbling foam is an example of two substances combining to create other substances |
| mixture | something that contains two or more substances that are not combined chemically. Salted popcorn is an example |
| How can you tell something is a mixture (physical change) | if you can physically separate the mixture into the substances that made up the mixture. You can tell that salt water is a mixture because you can evaporate the water and all that will be left is salt. |
| States of matter (physical change) | changing from solid, to liquid, to gas,  |
| reversible (physical) | is something that can be reversed. You can tear a piece of paper, but you still have a piece of paper because only the dimensions of the paper change. |
| irreversible (chemical) | e torn piece of paper and burned it, you would have some ash. Is that ash the same as the paper, and could you change the ash back to paper, 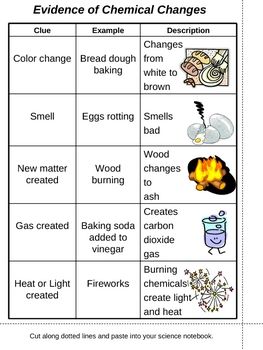 |
| weathering | destructive process where Earth materials such as rocks and soil are broken down into smaller parts. Weathering can also break down roads, buildings, and other materials humans make. |
| erosion | movement of materials from one place to another by natural methods. Erosion can be a destructive process, such as when a landslide moves material from the top of a mountain.,  |
| Deposition | constructive process whereby soil and rock that are eroded from one location are deposited as sediment in another location. As the sediment from a river is deposited at the mouth of a river over time, new land is created, which is called a delta, 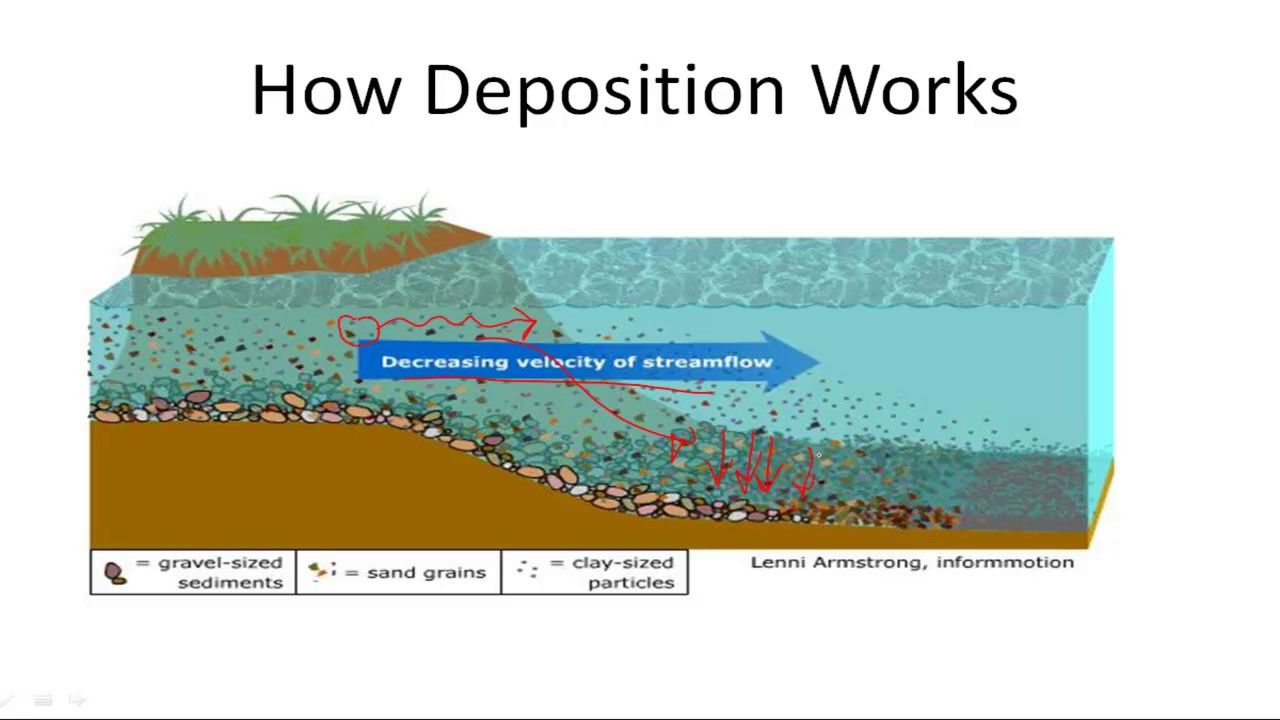 |
| tectonic plates | form sections of the surface of Earth, and some plates move toward (convergent) or away (divergent) from each other. Plates can also slide (transforming) past each other |
| fault | The area where two or more tectonic plates meet and show movement,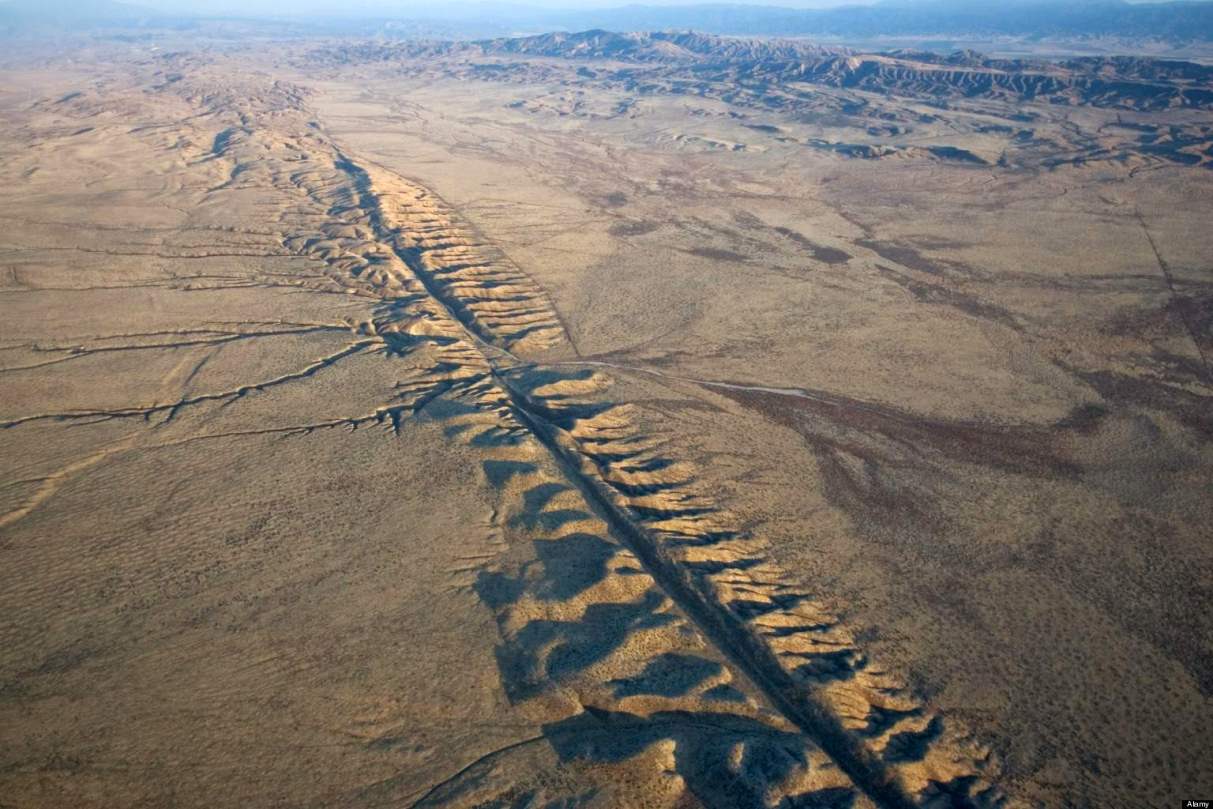  |
| trenches | where faults are located under the ocean. |
| glaciers | sheets of very old ice that are the size of states and that move along Earth’s surface, also create valleys as they slowly grind along the surface.,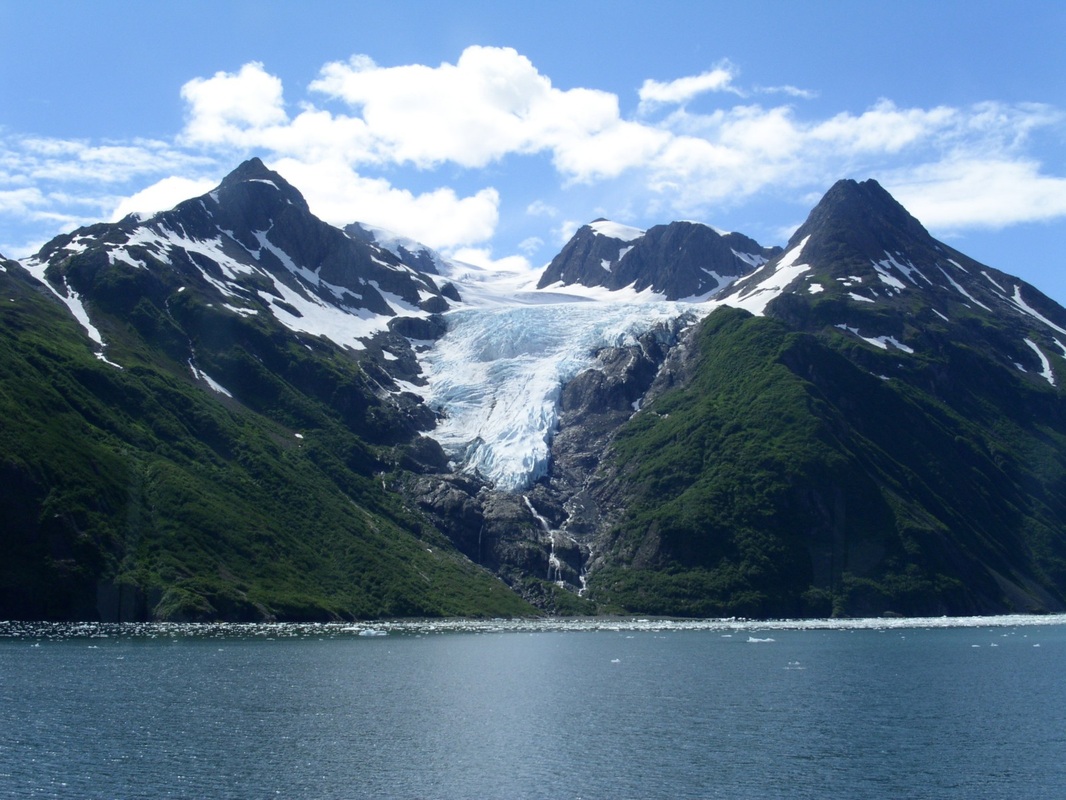  |
| ridges | formed when tectonic plates collide and both push up. This creates hills and mountains, 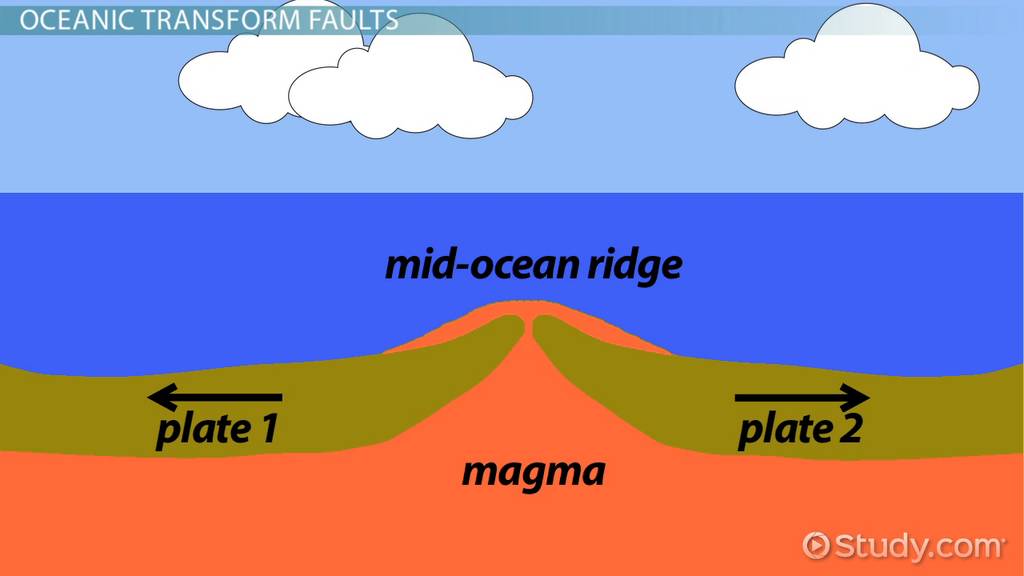 |
| Stone Mountain | individual mountains can also be formed in areas where magma, molten rock from Earth’s core, pushes up between or through tectonic plates. |
| magma | molten rock below Earth’s crust |
| Lava | When magma breaks through the crust |
| Hawaii | created by volcanoes, 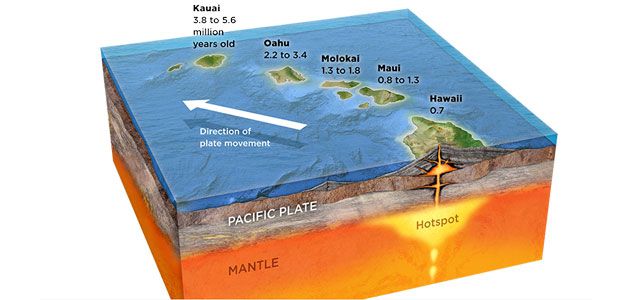 |
| Earthquakes | happen when tectonic plates suddenly slide around. The plates shake, and the energy from that creates waves that echo through Earth.,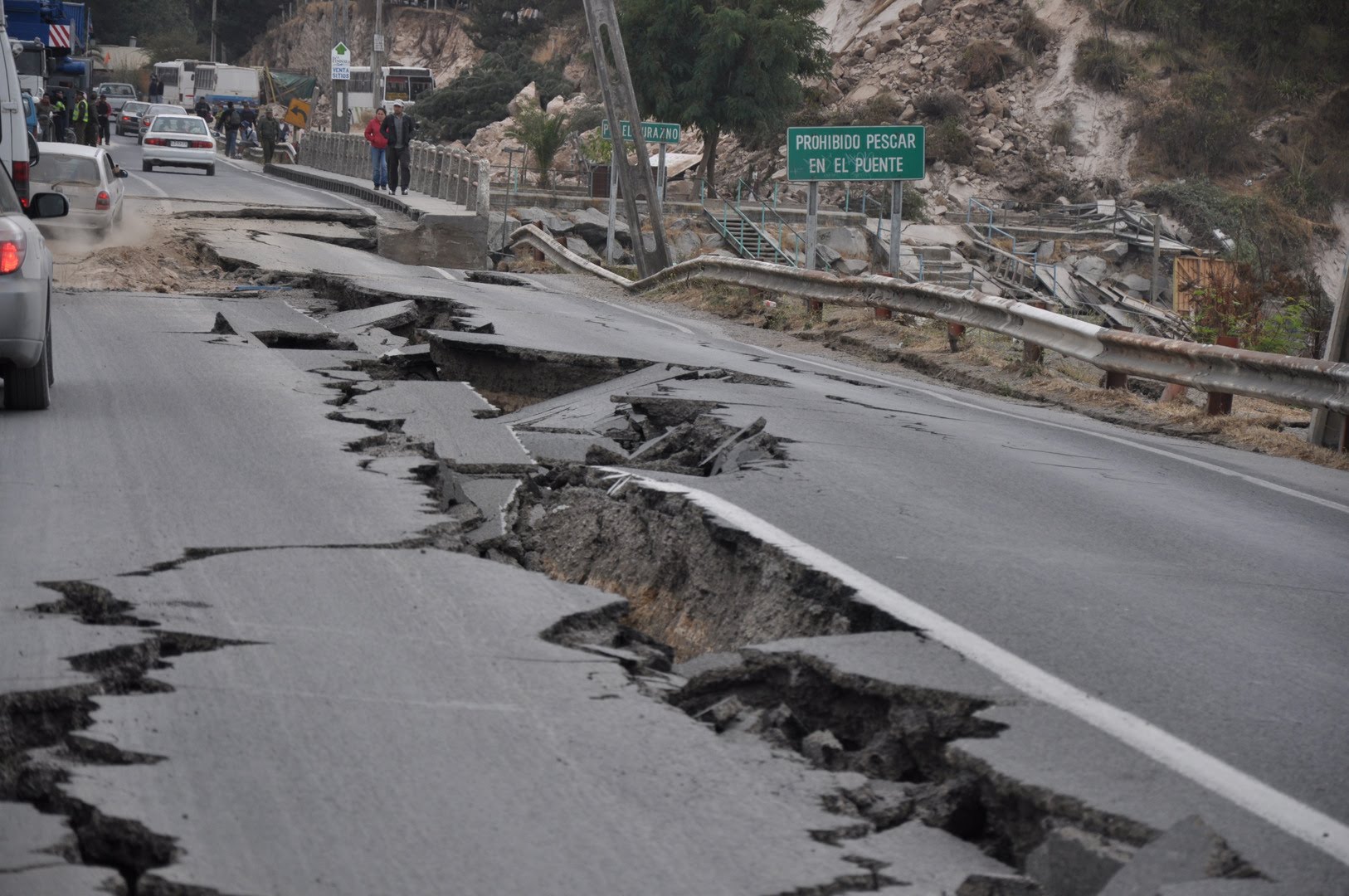  |
| Tsunamis | energy released by an earthquake or underwater volcano is transferred to the column of water above it and creates waves that travel away from the area., 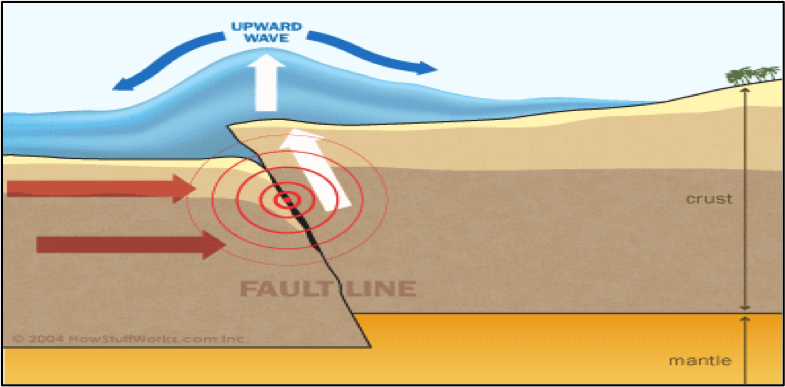 |
| Beach reclamation | to reduce the effects of erosion on beaches can be accomplished by dredging sand from the ocean floor and depositing it back on the beach. F,  |
| Levees | (earthen walls along riverbanks) that prevent rivers from going outside their banks onto surrounding land.,  |
| storm drain systems | direct the drainage flows to retention ponds to slow the runoff of rainwater into streams and rivers to reduce the risk of flooding downstream,  |
| seismic waves | vibrations that move through Earth., 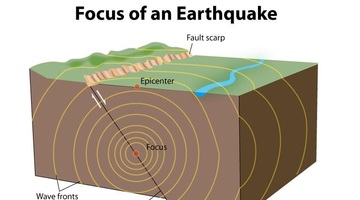 |
| Areas with a lot of weathering | windy areas and places where water freezes (water expands when it freezes breaking rock) like up North |
| Areas with lots of erosion | places that have a lot of water that is flowing downhill like moutains |