| A | B |
|---|
| A(n) _____ is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. | atom |
| The ____ is a very small region located in the center of the atom. | nucleus |
| The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a(n) _____ and usually one or more neutral particles called _____. | proton, neutron |
| Surrounding the nucleus is a region occupied by negatively charged particles called _____. | electrons |
| Protons, neutrons, and electrons are often referred to as ______ particles. | subatomic |
| Thomson's ________ experiments measured the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron. | cathode-ray tube, 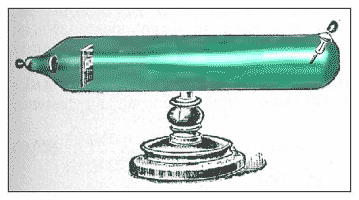 |
| ________ was able to determine the charge-to-mass ratio of an electron with his cathode-ray tube experiments. | J.J. Thomson,  |
| _________ was able to measure the charge of an electron with his oil drop experiments. | Robert Millikan |
| Millikan was able to measure the charge of an electron with his ______ experiments. | oil drop |
| Rutherford's _____ foil experiments led to the discovery of the nucleus. | gold foil,  |
| _______ discovered the nucleus with his gold foil experiment (1911). | Ernest Rutherford,  |
| Most of the alpha particles that Rutherford shot at the thin gold foil ______, indicating that atoms are mostly empty space. | passed through,  |
| Most of the alpha particles that Rutherford shot at the thin gold foil passed through, indicating that atoms are mostly _______. | empty space,  |
| The fact that a small percentage of the alpha particles that Rutherford shot at the thin gold foil seemed to bounce back was evidence for the presence of ______ in atoms. | a small dense nucleus,  |
| The fact that a small percentage of the alpha particles that Rutherford shot at the thin gold foil seemed ________ back was evidence for the presence of a small dense nucleus in atoms. | bounce back,  |
| Except for the simplest type of hydrogen atom, all atomic nuclei are made of _________. | protons and neutrons (the simplest type of hydrogen atom has one proton and no neutrons) |
| The positive charge of a(n) _______ is _______ in magnitude to the negative charge of a(n) ________. | proton, equal, electron |
| A neutron has a ____ charge. | neutral |
| Each element has a different number of _____ in their nucleus. | protons |
| The short-range forces that hold the particles of a nucleus together when they are very close to one another are called _____. | nuclear forces |
| The atomic ______ is the distance from the center of the atom to the outer portion of the electron cloud. | radius |
| Atomic radii are usually measured in _______. | picometers |
What is "A" pointing to and what is its charge?,  | an electron, negative,  |
What is "B" pointing to and what is its charge?,  | The nucleus (positive because it consists of positively charged protons and neutral neutrons),  |
What is "C" pointing to and what is its charge?,  | proton, positive,  |
What is "D" pointing to and what is its charge?,  | neutron, neutral,  |
| What is smaller than an electron? | Chuck Norris' sense of fear (but no one has been brave enough to discover it yet) |