| A | B |
|---|
| 4 major types of joints | Bony (synotosis), fibrous, Cartiloginous, synovial |
| Bony joints | 2 separate bones fuse to become one |
| Fibrous joints | connect one bone to another with collagenous fibers |
| Cartilogious joints | bones held together by cartilage |
| Synovial joints | two bones in capsule that contains synovial fluid |
| types of fibrous joints | suture; gomphosis, syndemosis |
| example of suture (fibrous joint) | frontal and parietal bones |
| example of gomphosis (fibrous joint) | teeth and mandible |
| example of syndemosis (fibrous joint) | inerosseous membrane between tibia and fibula or ulna and radius |
| 2 types cartilaginous joints | synchodrosis and symphysis |
| synchrodosis joint | composed of hyaline cartilage |
| symphysis joint | composed of fibrocartilage; example pubic synthesis and bodies of vertebrae and vertebral discs |
| Serrate sutures | wavy line like jigsaw puzzle |
| Examples of serrate sutures | coronal, sagital and lamboidal joints |
| lap (squamous) | 2 bones hav e overlapping beveled edges |
| example of lap (squamous) suture | where temporal bone meets sphenoid and temporal bones |
| Plane (butt) sutures | 2 bones have straight non-overlapping edges |
| Example of plane (butt) suture | intermaxillary suture in the roof of the mouth |
| Label synovial joint | 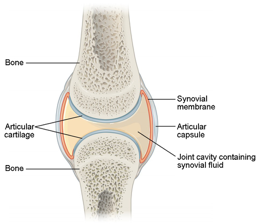 |
| 6 types of synovial joints | Plane, hinge, pivot, condylar, saddle, ball and socket |
| example of plane joint (synovial joint) | allow movement between 2 flat surfaces; intertarsal or intercarpal joints |
| example of hinge joint (synovial joint) | allows for angular movement (elbow, knees, phalanges of fingers |
| example of pivot joints (synovial joint) | allow for rotational movement between 2 bones; atlas and axis of neck |
| example of condylar joints (Synovial joint) | allow significant movement in 2 planes; convex surface paired with concave; junction between radius and scaphoid and metacarpals and phalnages |
| example of saddle joints (synovial joint) | 2 concave surfaces articulate with each other; between tranpezium and 1st metacarpal of thumb |
| examples of Ball and socket joints (synovial joint) | consist of spherical head in a round concavity; shoulder and hip joints |
| flexion | a movment that DECREASES the joint angle |
| Extension | movement that STRAIGHTENS a joint and returns it to zero position |
| hyperextension | extension of joint BEYOND ZERO POSITION |
| Abduction | body part moves AWAY from the midline of body |
| Adduction | body parts moves TOWARD the midline of the body |
| elevation | RAISES body part VERTICALLY in FRONTAL plane |
| depression | LOWERS a body part VERTICALLY in FRONTAL plane |
| Protraction | ANTERIOR movement of body part in TRANSVERSE (horizontal) plane |
| Retraction | POSTERIOR movement of body part in transverse plane |
| Dosiflexion | elevates toes |
| Plantarflexion | movement of foot so toes point downward (pressing a gas peddle) |
| tooth held in bone by | peridonatal ligament |
| intraosseus membrane | allow radius and ulna to supinate and pronate |
| synovial joint is the most ______ joint in the body | movable and most likely to develop painful dysfunction |
| prosthesis | artificial joints |
| arthritis | painful inflammation of joints |
| osteoarthritis | wear and tear arthritis |
| rhuematodi arthritis | autoimmune attach on joint tissue |
| rheumatologist | specializes in treatment of arthritis and other joint disorders |