| A | B |
|---|
| * The scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environment is called _____. | ecology p.850 |
| *The intensity of sunlight that hits the Earth in any given place or season is determined by the ____. | angle that the sunlight strikes the surface of the Earth (Sunlight strikes the Earth most directly at the equator and the angle becomes lower as you move away from the equator. Winter is caused by the fact that due to the Earth's tilt, the angle that the sun strikes the parts of Earth experiencing winter is much lower than when it strikes the same places in summer. A 90 degree angle would be straight overhead. Many people falsely believe that the seasons are caused by the elliptical orbit of Earth around the sun. In the northern hemisphere, the Earth is actually closer to the sun in the winter) p.852,  |
| * The upper part of an aquatic biome, where enough light penetrates for photosynthesis to occur, is called the ____. | photic zone p.859,  |
| * The lower layer of an aquatic ecosystem, which doesn't receive enough light to support photosynthesis, is called the _____ . | aphotic zone p.859,  |
* The bottom substrate of all aquatic ecosystems is called the ____ zone and the organisms that live there are called the ____., 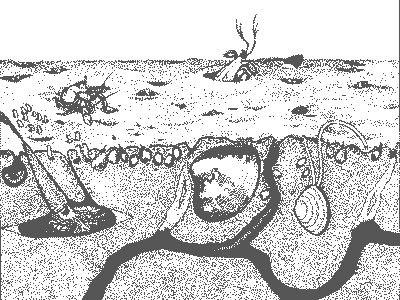 | benthic zone, benthos p.859,  |
| * A(n) ______ is found where fresh and saltwater mix. | estuary p. 859,  |
* The picture below shows a tide pool in the _____ zone.,  | intertidal zone p.860,  |
* Which biome is shown in the picture below?,  | coral reef p.861,  |
* Coral reefs are found in ______ _______ waters.,  | warm clear p.861 (They have to be because the single-celled algae that live in the tissues of reef-building corals are a necessary symbiont for the coral animals and these algae wouldn't be able to survive in deeper waters due to lack of sunlight. Also, warm tropical waters are much clearer than colder waters for reasons you will learn about),  |
| * _____ largely determines the distribution and structure of terrestrial biomes. | Climate p.853 |
* According to the climograph, which factor is most important in determining whether an area will be a broadleaf forest versus a coniferous forest?,  | Average annual temperature (You find the dominant trees changing from broadleaf deciduous to conifers as you go north or up in elevation) p.855,  |
* According to the climograph, which factor is most important in determining whether an area will be a grassland versus a forest?,  | precipitation (Less precipitation causes a shift to grasslands. Even less precipitation would cause a grassland to turn into a desert) p. 1151,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Tropical forest (The map shows the distribution of tropical forests. The picture is a tropical rainforest in Borneo) p.856,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Chaparral p.857,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Northern coniferous forest p.858,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Desert p.857,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Savanna p.856,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Temperate broadleaf forest (a.k.a. Temperate Deciduous Forests) p.858,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | Temperate grasslands p.857,  |
* Which biome is pictured below?,  | tundra p.858,  |
| * Which terrestrial biome has the greatest biodiversity? | Tropical forests (biodiversity relates to the number of different species that can be found in an area) p.856,  |
| * Which biome is characterized by short drought resistant trees and shrubs? | chaparral p.857,  |
| * Which biome is characterized by cold dry winters and hot humid summers? | temperate grasslands p.857,  |
| * Deciduous trees are trees that ______. | drop their leaves in the fall p.858,  |
| * You can find the tundra biome much further south than normal if you ______. | go up in elevation enough (up taller mountains) p.858 |
| * Which biome is characterized by a layer of permafrost just below the surface soils? | Tundra p.858,  |
| * A biome located throughout midlatitude regions where there is sufficient moisture to support the growth of large, broadleaf deciduous trees. | temperate broadleaf forest p.858,  |
| * Which biome is characterized by sparsely scattered individual trees and large herds of herbivores, large carnivores, and occasional fires and droughts? | savanna p.856,  |
| * The _____ is the global ecosystem - the sum of all the planet's ecosystems and landscapes. | biosphere p. 851 |
| * A(n) ______ is the community of organisms in an area and the physical factors with which those organisms interact. | ecosystem p. 851 |
| * An ecosystem is the __________ of organisms in an area and the physical factors with which those organisms interact. | community p.851 |
| * A(n) ____ is a group of populations of different species in an area. | community p. 851 |
| * A(n) ____ is a group of individuals of the same species living in an area. | population p.851 |
| * The living factors in an environment are called ____ factors. | biotic pp.853&863 |
| * The non-living factors in an environment are called ____ factors. | abiotic pp.853&863 |
| * _______ are major life zones characterized by vegetation type (in terrestrial ones) or physical environments (in aquatic ones). | Biomes p.854 |
| *______ biomes are aquatic biomes with salt concentrations somewhere around 3% while _____ biomes have salt concentrations near or below 0.1%. | Marine, freshwater p.859 |
| * Oceans cover about ____ of the planet's surface. | 75% p.859 |
| * Any organism that is not strong enough to swim against the current (and therefore basically floats and drifts) is referred to as ______. If they are photosynthetic, they are called _____. If they are heterotrophs, they are referred to as ____. | plankton, phytoplankton, zooplankton pp. 860, 861, 862, 885&886 |
| * The different seasons are caused by ______. | Earth's tilted axis (Sunlight strikes the Earth most directly at the equator and the angle becomes lower as you move away from the equator. Winter is caused by the fact that due to the Earth's tilt, the angle that the sun strikes the parts of Earth experiencing winter is much lower than when it strikes the same places in summer. A 90 degree angle would be straight overhead. Many people falsely believe that the seasons are caused by the elliptical orbit of Earth around the sun. In the northern hemisphere, the Earth is actually closer to the sun in the winter) p. 853, 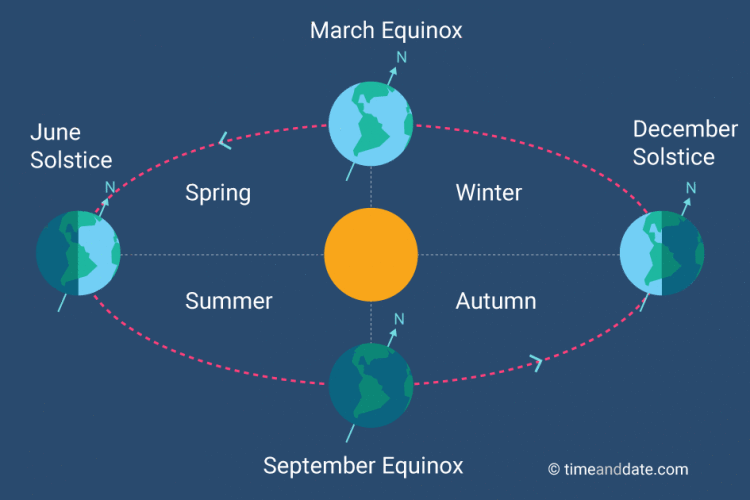 |
| * The movement of organisms into a given area from another area is called ____. | immigration p.864 |
| * When organisms leave a certain area, the movement is called ___. | emigration p.865 |
| * For a population to grow, the ____ must be bigger than the ____ | birthrate must be larger than the deathrate (assuming no immigration or emigration) p.867 |
| * The number of individuals per unit area or volume is a population’s ____. | density p.864 |
| * Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow _____. | exponentially p.868 |
* Which type of population growth does this graph show?,  | Exponential growth (Can only happens under ideal conditions with unlimited space, food and no predators) p.868,  |
* Which type of population growth does this graph show?,  | Logistic growth p.869,  |
* At which point in the graph below is the population growth rate accelerating?,  | Point A (The graph line should be more curved in an upward direction. It looks a little too linear, but I had a hard time drawing it that way) p.869,  |
* At which point in the graph below is the population growth rate the highest?,  | The population growth "rate" is the highest at point B. (You can determine the growth rate by finding the slope of the line tangent to the curve. Remember, slope = rise divided by run. In this case, the rise is the current population. The run is time. Dividing population by time gives you the population growth "rate.") p.869,  |
* At which point in the graph below is the population growth rate starting to slow down?,  | Point C p.869,  |
* At which point in the graph below is the population the highest?,  | The population is the highest at point D (look along the y-axis) p.869,  |
* At which point on the graph below is the population growth rate the lowest?,  | The population growth rate is lowest at point D (notice that the population, even though it is at its highest, has stopped growing) p.869,  |
* At which point in the graph below is the population at the carrying capacity?,  | Point D (Remember, the carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals that the environment can support) p.869,  |
| * _______ is the study of the vital statistics of populations and how they change over time. | Demography p.866 |
* Which survivorship curve would represent the human species? Which would represent a typical fish species?, 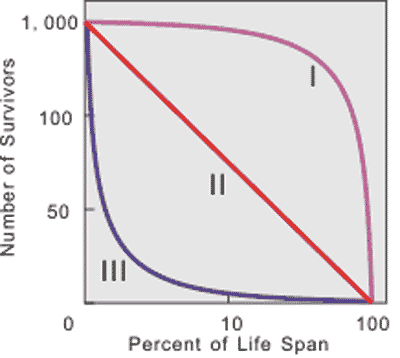 | Humans would be type I (due to their fairly high infant survival rate) Fish would be type III (because most lay many eggs and generally don't guard them or protect the juveniles, so most fish are eaten when they are small, if they even manage to make it out of their egg) p. 866,  |
| * The maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources, symbolized as K. | carrying capacity p.869 |
| *Factors that affect either a birth-rate or death-rate as population in a given area increases are said to be _____. | density-dependent p.872 (Examples include competition, disease, and predation) |
| * A model describing population growth that levels off as population size approaches carrying capacity. | logistic population growth pp.869 & 870 |
| *Factors that affect either a birth-rate or death-rate, but do not increase in affect as an area increases in population are said to be _____. | density-independent p.872 |
| * Disease is a density-_____ factor that limits population growth. | density-dependent p.872 |
| * Harsh winters would be considered as density-______ factors that limit population growth. | density-independent p.872 |