| A | B |
|---|
| * The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane from areas of high free water concentration to areas of low free water concentration is called ___. | osmosis p.111 |
| * If a cell membrane allows glucose to pass through it, then the cell membrane is said to be ____ to glucose. | permeable p.104, 
|
| * The movement of particles of any substance so that they spread out into the available space is called ____. | diffusion p.109,  |
| * The cell membrane is said to exhibit ___________ because it lets some substances pass through but not others. | selective permeability p.104 |
| * The type of substances that can most easily diffuse across a cell membrane are ____ substances. | small non-polar substances p.109 |
| * The lipid composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a __________ | lipid bilayer p.104 |
| * Charged particles usually pass through a type of tunnel-like transport protein called a ____ protein to get into cells. | channel pp. 109 and 112 |
| * Cells without ____ will shrink if placed into a _____ solution. | hypertonic p.111 |
| * When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ is taking place. | active transport p.113,  |
| * Cells without _____ will grow bigger if placed in a ____ solution. | cell walls, hypotonic p.111 |
* When osmotic pressure increases in plant cells, why don't the cells usually burst?, 
| Plant cells have a tough cell wall that keeps the cell from expanding enough to burst. pp.111 & 112 |
| * If a solution is 6% solutes, it will be ____ % water. | 94 (see your notes) |
| * If a solution is 90% water, it will have ___ % solutes. | 10 (see your notes) |
| * A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic p.111 |
| * Active transport requires _____. | energy p.113 |
| * If a substance is diffusing across a cell membrane, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration. | high, low pp.109 & 110 |
* When osmotic pressure decreases in a plant, the ______ shrinks and the plant ____., 
| central vacuole, wilts (see your notes) |
| * When osmotic pressure increases in plants, the ______ gets bigger and the plant ___. | central vacuole, gets turgid/stiff (see your notes) |
* The elodea cells in this picture are surrounded by a ______ solution.,  | hypotonic p.111,  |
* The process pictured below is called ____., 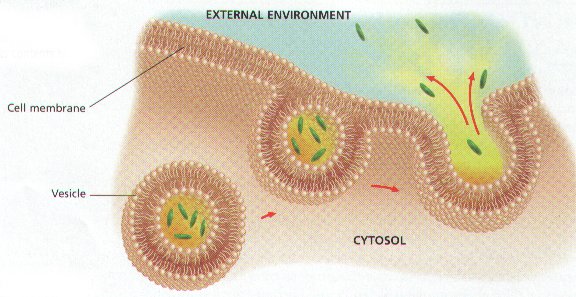 | exocytosis p.116,  , , 
|
* The elodea cells pictured below have been soaking in a ____ solution.,  | hypertonic p.111,  |
* The process pictured below is called ____., 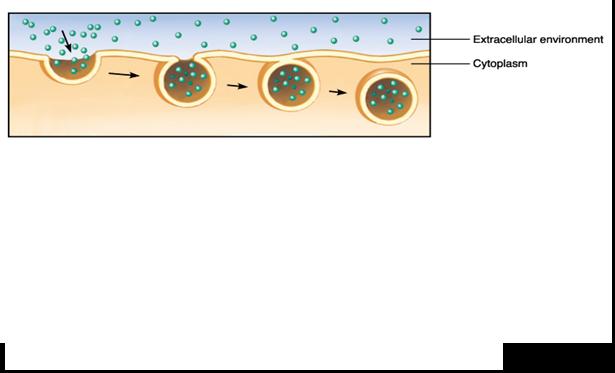 | endocytosis p.116,  , , 
|
| * The type of endocytosis that takes in solid particles (usually food) is called ____. | phagocytosis pp.116 & 117 |
| * The type of endocyctosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes is called _____. | pinocytosis pp.116 & 117 |
| * In _____, the cell takes in molecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane. | endocytosis p.116,  |
| * _______ transport involves the diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane. | Passive transport p.110 |
| * Passive transport involves the ______ of a substance across a biological membrane. | diffusion p.110 |
| * The cellular secretion of macromolecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane. | exocytosis p.116,  |
| * _______ involves the movement of a substance across a biological membrane against its concentration or electrochemical gradient with the help of energy input and specific transport proteins. | Active transport pp.113 & 114,  |
| * A property of biological membranes that allows some substances to cross more easily than others is called _____. | selective permeability p.104 |
| * A(n) ______ protein is a transmembrane protein that helps a certain substance or class of closely related substances to cross the membrane. | transport protein p.109 |
| * _______ diffusion is the spontaneous passage of molecules and ions, bound to specific carrier proteins, across a biological membrane down their concentration gradients. | Facilitated diffusion p.112,  |
* The picture below is showing _____ transport.,  | active (Notice that ATP is being used as an energy source to pump the substance from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration) p.113,  |
* Which process is shown below?,  | diffusion pp.109 & 110,  |
* Which process is shown below?,  | facilitated diffusion (It's diffusion because the particles are travelling down the concentration gradient. It's facilitated because a channel protein is helping) p.112,  |
* Which type of transport protein is pictured below?, 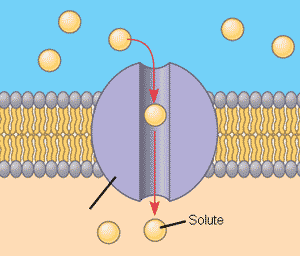 | channel protein pp.109 and 112,  |
* Which type of transport protein is pictured below?,  | carrier protein pp. 109 and 112,  |
* What type of solution was the cell on the left exposed to?,  | hypotonic p.111,  |
* What type of solution was the cell on the middle exposed to?,  | isotonic p.111,  |
* What type of solution was the cell on the right exposed to?,  | hypertonic p.111,  |
| * The most abundant lipids in most membranes are ______. | phospholipids p.104 |
| * ______ is simply the diffusion of water molecules from one side of a cell membrane to the other. | Osmosis p.111 |
| * Osmosis is simply the _____ of water molecules from one side of a cell membrane to the other. | diffusion p.111 |
| * The osmotic pressure applied to the inside of a plant cell wall by the cell itself trying to expand due to water intake in hypotonic environments is called _____ pressure | turgor pressure p.112 |
| * _____ form the main fabric of a cell membrane, but ____ determine most of the membrane's function. | Phospholipids, proteins p.107 |
| * A simple rule of diffusion is that in the absence of other forces, a substance will diffuse from where it is _____ concentrated to where it is ____ concentrated. | more, less (other forces that can interfere with that include ionic concentrations. For instance, even if Na+ is more concentrated on one side of membrane than the other, if there are a lot of positively charged ions of other types, such as Ca++ on the other side, it will produce a force opposing the natural diffusion of Na+ to that side of the membrane) p.110 |
| * Local signaling involves the secretion of signaling molecules that act on ______ cells. | nearby p.118, 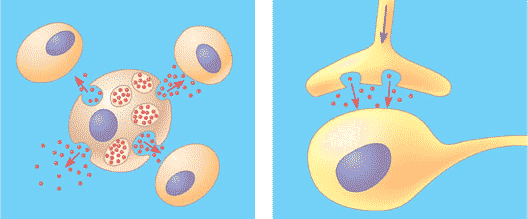 |
| * The narrow space between a nerve cell and its target cell is called the _____. | synapse p.118, 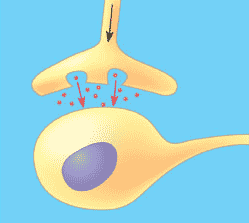 |
| * Signaling molecules that communicate with distantly located cells by entering and travelling through the circulatory (in animals) system until their target is reached are called _____. | hormones (plants have hormones also. Plant hormones are called auxins) p.118, 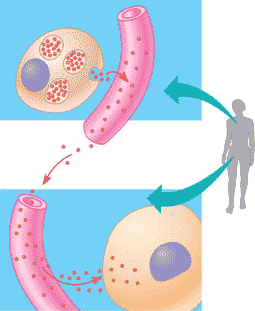 |
| * The transmission of a signal from one end of a long neuron to the other end is accomplished by transmitting a(n) ______ signal down the neuron. | electrical signal (This can be considered a form of long distance signaling due to the long length of most nerve cells) p.118 |
| * The process going on at the receiving end of a cellular conversation can be broken down into three steps; ______, ______, and _______. | reception, transduction, and response p.119,  |
| * A chemical signal is "detected" when it binds to a _____ protein located at the cell's surface or inside the cell. | receptor protein p.119 |
* Which type of long-distance signaling is being shown in the picture below,  | hormonal (or endocrine) signaling (The only other type of signaling that can be considered long-distance is the electrical impulse that travels down the axon of long nerve cells) p.118,  |
* Which type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?,  | local signaling p.118,  |
* Which type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?, 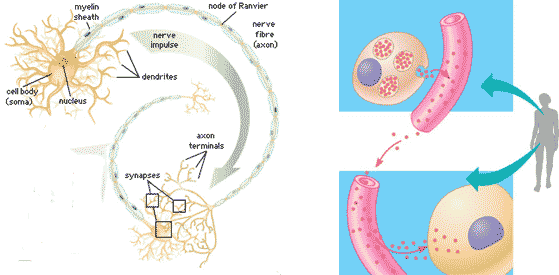 | long-distance signaling p.118,  |
* Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #1?,  | reception p.119,  |
* Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #2?,  | transduction p.119,  |
* Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #3?,  | response p.119,  |
* The space between the two cells in the picture below is called the ______.,  | synapse p.118,  |
| * What does the root word "trans-" mean? | across |