| A | B |
|---|
| * The process of making proteins inside cells is called ______. | protein synthesis (For some reason, this book has all but stopped using the term "protein synthesis," probably because transcription doesn't always lead to a protein product and translation leads to a polypeptide that may need additional modifications before it becomes a functional protein, but the term "protein synthesis" is still commonly used so I want you to know it.) |
* Which type of nucleic acid can't leave the nucleus?, 
| DNA p286 |
| * On which organelle are polypeptides made? | ribosomes p286, 
|
| * Where are ribosomes located? | out in the cytoplasm p286, 
|
| * The process of making a strand of RNA using DNA as a template is called ___. | transcription p285 |
| ** What are four differences between m-RNA and DNA? | 1) m-RNA is single-stranded instead of double 2) m-RNA (as well as other kinds of RNA) has the nucleotide uracil in place of thymine 3) m-RNA can leave the nucleus and DNA can't 4) m-RNA (as well as other kinds of RNA) includes the sugar called ribose while DNA includes the sugar called deoxyribose pp. 285 and 286 |
* Which nucleotide do you find in RNA but not DNA?, 
| uracil p285 |
| * Uracil bonds to across from ______. | adenine p287 |
| * The process of using the instructions on m-RNA to make a polypeptide is called _____. | translation p286 |
| * Which type of molecule brings amino acids to the site of protein synthesis? | transfer RNA (t-RNA) p293 |
| * Which molecule attaches to a ribosome and provides the instructions for putting amino acids together? | messenger RNA (m-RNA) p285 |
* How many nucleotides are needed to code for 1 amino acid?, 
| 3 p287 |
| * How many different types of amino acids are used to make proteins? | 20 p287 |
* Each set of 3 nucleotides on a strand of m-RNA are called a(n) _____., 
| codon p287 |
| * How many nucleotides are found at the bottom of a molecule of t-RNA and are involved with bonding to m-RNA? | 3 p294 |
| * How many amino acids are found attached to a molecule of t-RNA? | 1 p294 |
* A change in the sequence of nucleotides in a molecule of DNA will cause a ____., 
| mutation p303 |
| * Mutations that are harmful are usually weeded out by ______. | natural selection |
| * Mutations in a gene that are helpful usually become part of the gene pool as a new ____. | allele (An allele is a different form of a gene) p306 |
* Which amino acid would the m-RNA codon sequence AGU call for?,  | Serine p288,  |
| * Which enzyme is required for transcription? | RNA Polymerase (remember, you are making RNA during transcription) p289 |
| *Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells? | In the nucleus p286 |
| * Translation occurs in the ___ on ___. | cytoplasm, ribosomes (Remember, ribosomes are not membrane-bound organelles. They are solid structures, so it is incorrect to say that translation occurs "in" ribosomes) * explanation starts on page 293 |
| * Genes contain instructions for assembling ___. | polypeptides (It is often said that genes code for making proteins, but this is not always technically correct. Many proteins have a quaternary structure, with several intertwined polypeptides. In this case, no single gene has the code for making the finished protein. Each polypeptide that makes up the protein is coded for by a different gene. Another exception is that some genes only code for RNA molecules, many of which function as enzymes, but keep in mind that the vast majority of enzymes are made of proteins, not RNA's) p285 |
| * Proteins are made out of ____. | amino acids p285 |
* The picture below is called the ____.,  | genetic code (It's also called the codon table in this book, but it's really the universal code that nearly all organisms use to translate m-RNA codons into a sequence of amino acids, thus, nearly all organisms share the same "genetic code." This implies that this system evolved very early on in the evolution of organisms. We say that "nearly all organisms use it because there are some minor exceptions that have evolved in the translation of the triplet code for some amino acids in some organisms) p288,  |
| * Which type of molecule is a codon found on? | m-RNA (the term codon is also sometimes used for the DNA base triplet along the non-template strand. These codons are complementary to the template strand and thus identical to the m-RNA codon other than the substitution of uracil for thymine in the m-RNA) p287 |
| ** What were the names of the scientists whose work on bread mold, using X-rays to disable genes, provided strong support for the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis? | Beadle and Tatum (the one-gene one enzyme hypothesis was later modified to the one gene-one polypeptide hypothesis since not all proteins are enzymes and proteins with a quaternary structure are coded for by several genes) p284 |
| ** The transcription of a protein-coding eukaryotic gene results in pre-mRNA (a.k.a. ___________) and _________ yields the finished mRNA. | primary transcript, RNA processing pp286&291 |
| * Only one of the two DNA strands is transcribed during transcription. This strand is called the _____ strand. | template strand (Interestingly enough, one of the two DNA strands may serve as the template strand for some of the genes on the chromosome, but not others) p287 |
| ** Messenger RNA codons are both read and assembled in the _______ direction by the transcription and translation machinery. | 5' --> 3' direction pp287&294 |
| * If a recently manufactured protein has a primary structure that is 1000 amino acids long, how many nucleotides long was the coding part of the mRNA molecule used as the instructions for that protein? | 3000 (remember, it takes 3 nucleotides to code for each amino acid) p287 |
| * A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene is called a(n) _______. | insertion p305 |
| * A noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene is called a(n) ______. | intron (the part of the mRNA that is transcribed from DNA introns, but is cut out before the mRNA exits the nucleus, is also called an intron) p292 |
| ** A violation of the base-pairing rules in that the third nucleotide (5'end) of a tRNA anticodon can form hydrogen bonds with more than one kind of base in the third position (3' end) of a mRNA codon. | wobble (This helps to partly explain why several different mRNA codons can code for the same amino acid) p295 |
| ** A stretch of amino acids on a polypeptide that targets the protein to a specific destination in a eukaryotic cell is called a(n) ______. | signal peptide p300,  |
| * The specialized base triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that recognizes a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule is called a(n) _______. | anticodon ("B" in the picture below) p295, 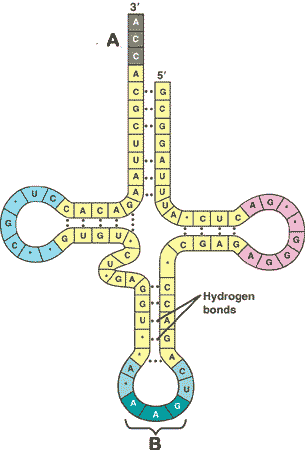 |
* Which amino acid is represented by the shape with the question mark in the picture below? Use the chart to find the answer.,  | Serine (Remember, the table represents the mRNA codon, not the tRNA anticodon) p288,  |
| * The removal of the noncoding portions (introns) of the RNA molecule after initial synthesis and the subsequent attachment of the remaining coding portions (exons) to each other is called ______. | RNA splicing p292 |
| ** The 5' end of a pre-mRNA molecule modified by the addition a of guanine triphosphate is called the _____. | 5' cap (Both the 5' cap and poly-A-tail share several important functions. First, they seem to facilitate the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus. Second, they seem to help protect the mRNA from degradation by hydrolytic enzymes in the cytoplasm. And third, once the mRNA reaches the cytoplasm, both structures help ribosomes attach the 5' end of the mRNA) pp.291 & 292, 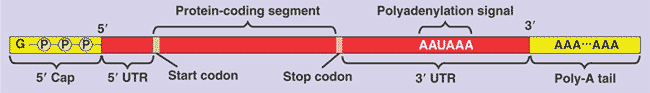 |
| * A(n) _____ mutation occurs when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is NOT a multiple of three, resulting in the improper grouping of the following nucleotides into codons. | frameshift p305 |
| * Which type of mutations can lead to frameshift mutations? | insertions or deletions that are not in multiples of three p305 |
| ** A promoter DNA sequence crucial in forming the transcription initiation complex. | TATA box p290,  |
| ** The DNA strand that temporarily binds RNA nucleotides during transcription is called the _________. | template strand p287 |
| ** Where are ribosomes constructed and what are they composed of? | nucleolus, r-RNA and protein (the large and small subunits of the ribosome are constructed in the nucleolus but never come together until they start the process of transcription in the cytoplasm, after which, they come apart again) p296,  |
| ** A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation is called a(n) ______. | mutagen p306 |
** What is "A" in the picture below?,  | polyribosome (a.k.a. polysome) p301,  |
| * A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates where to start transcribing RNA is called the _____. | promoter p290,  |
| * A type of point mutation; the replacement of one nucleotide and its partner in the complementary DNA strand by another pair of nucleotides is called a(n) ______. | nucleotide-pair substitution (a.k.a. - base pair substitution) p303 |
| * The enzyme that links together the growing chain of ribonucleotides during transcription is called _____. | RNA polymerase p289, 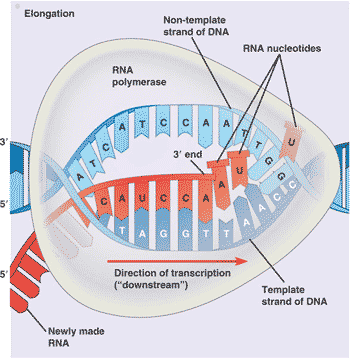 |
| ** The most common type of mutation; a base-pair substitution in which the new codon makes sense in that it still codes for an amino acid (just a different one) | missense mutation ("A" in the picture below) p304, 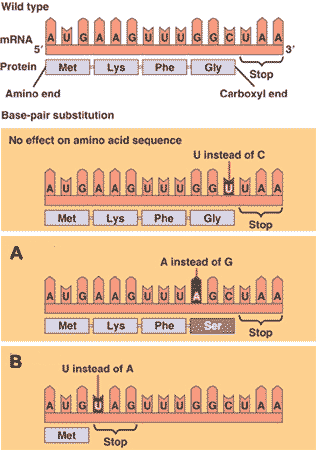 |
| * A point mutation in which one or more nucleotides pairs are lost from a gene is called a(n) ______. | deletion (deletions can also happen at the chromosomal level in which case they are called chromosomal deletions) p305 |
| ** The modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides. | poly-A-tail (Both the 5' cap and poly-A-tail share several important functions. First, they seem to facilitate the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus. Second, they seem to help protect the mRNA from degradation by hydrolytic enzymes in the cytoplasm. And third, once the mRNA reaches the cytoplasm, both structures help ribosomes attach the 5' end of the mRNA) pp291&292,  |
| ** A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein. | nonsense mutation p304 |
| ** In prokaryotes, a special sequence of nucleotides in DNA that marks the end of a gene. It signals RNA polymerase to release the newly made RNA molecule, which then departs from the gene. | terminator (Remember, this is for prokaryotes only) p290 |
| ** What breaks a ribosome into the large and small subunits? | A Chuck Norris knife-hand chop, of course.,  |
| ** RNA molecules that function as enzymes are called _____.. | ribozymes p293 |
| ** The way a cell's mRNA-translating machinery groups the mRNA into codons depends on their correct grouping of the 3 nucleotides into the correct _____. | reading frame (The book gives the analogy of reading the following sentence, "The red dog ate the bug." If the letters weren't grouped into the correct reading frame, they might be read as "t her edd oga tet heb ug." Frameshift mutations can cause the analogous problem) p288 |
| ** What are two names for the initial RNA transcript? | primary transcript or pre-mRNA p286,  |
| * _____ is the most abundant type of RNA, which together with proteins forms the structure of ________. | rRNA (ribosomal-RNA), ribosomes p296 |
| ** One of a ribosome's three binding sites; it holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain. | P site (P stands for peptidyl tRNA site) p296,  |
| ** Modification of RNA before it leaves the nucleus in eukaryotes is called _____. | RNA processing p291, 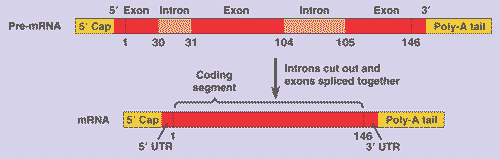 |
| ** A protein-RNA complex that recognizes a signal peptide as it emerges from the ribosome and helps target it to | signal-recognition particle (SRP for short. This particle functions as an escort that brings the ribosome to a receptor protein built into the ER membrane) p300,  |
| ** One of the ribosomes three binding sites; it holds the tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain. | A site (Aminoacyl tRNA site) p296,  |
| ** An enzyme that joins each amino acid to the correct tRNA. | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase p295, 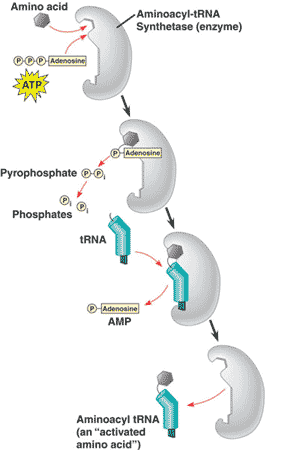 |
| ** A type of regulation at the RNA-processing level in which different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns. | alternative RNA splicing p293 |
| ** Regulatory proteins (in eukaryotes) that binds to the DNA promoter sequence and stimulate transcription of a specific gene. | transcription factors p290,  |
| ** The region of a DNA molecule that is transcribed into an RNA molecule. | transcription unit (The transcription unit located just "downstream" of the promoter where the RNA polymerase first attaches) p290,  |
| ** A complex assembly that interacts with the end of an RNA intron in splicing RNA, releasing the intron and joining the two adjacent exons. | spliceosome p293,  |
| * DNA and RNA are read as a _____ code. | triplet code p287 |
| * A change in a gene at a single nucleotide pair. | point mutation p303 |
| ** The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase bound to the promoter. | transcription initiation complex p290 pp332&333,  |
| * The coding region of a eukaryotic gene; when transcribed into mRNA, it is the coding part of mRNA that leaves the nucleus. | exon p292,  |
* What is "A" in the picture below?,  | an amino acid p295,  |
** What is "B" in the picture below?,  | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (an enzyme that pairs amino acids with their correct t-RNA) p295,  |
* What is "C" in the picture below?,  | t-RNA p295,  |
** What is "A" in the picture of the mRNA below?, 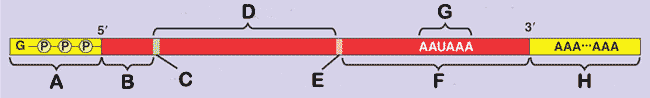 | 5' cap (Both the 5' cap and poly-A-tail share several important functions. First, they seem to facilitate the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus. Second, they seem to help protect the mRNA from degradation by hydrolytic enzymes in the cytoplasm. And third, once the mRNA reaches the cytoplasm, both structures help ribosomes attach the 5' end of the mRNA) p292,  |
** What is "B" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | 5' UTR (Untranslated regions are parts of the mRNA that will not be translated into proteins, but they have other functions such as ribosome binding) p292,  |
** What is "F" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | 3' UTR (Untranslated regions are parts of the mRNA that will not be translated into proteins, but they have other functions such as ribosome binding) p292,  |
** What is "C" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | start codon p292,  |
** What is "D" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | protein-coding segment p292,  |
** What is "E" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | stop codon p292,  |
** What is "G" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | Polyadenylation signal (When this appears, proteins bind to it and cut the pre-mRNA loose from the RNA polymerase about 10 to 35 nucleotides downstream from this AAUAAA signal) pp291&292,  |
** What is "H" in the picture of the mRNA below?,  | Poly-A-tail (Both the 5' cap and poly-A-tail share several important functions. First, they seem to facilitate the export of mature mRNA from the nucleus. Second, they seem to help protect the mRNA from degradation by hydrolytic enzymes in the cytoplasm. And third, once the mRNA reaches the cytoplasm, both structures help ribosomes attach the 5' end of the mRNA) p334,  |
* Which process belongs in the darker red box in the picture below?,  | transcription p286,  |
* Which process belongs in the pink box in the picture below?,  | RNA processing p286,  |
* Which process belongs in the light blue box in the picture below?,  | translation p286,  |
** What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 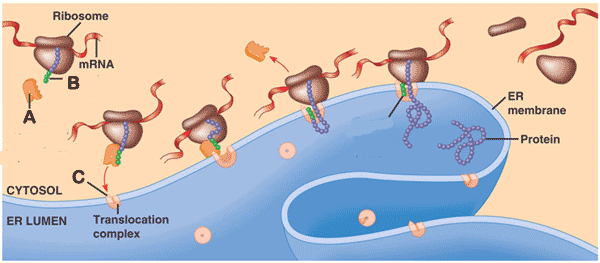 | signal recognition particle (SRP for short. This particle functions as an escort that brings the ribosome to a receptor protein built into the ER membrane) p300,  |
** What is "B" pointing to in the picture below?,  | Signal peptide (different signal peptides are used to target polypeptides to ER, mitochondria, chloroplasts, the interior of the nucleus and other organelles) p300,  |
** What is "D" pointing to in the picture below?,  | spliceosome p293,  |
* What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 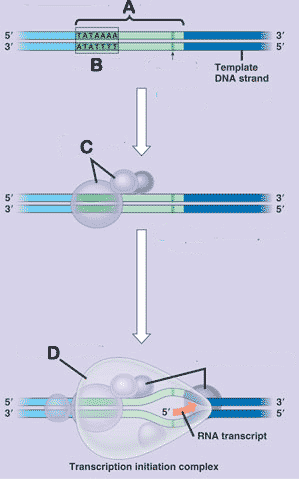 | Promoter p290,  |
** What is "B" pointing to in the picture below?,  | TATA box p290,  |
** What is "C" pointing to in the picture below?,  | transcription factors p290,  |
* What is "D" pointing to in the picture below?,  | RNA polymerase p289,  |
** What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 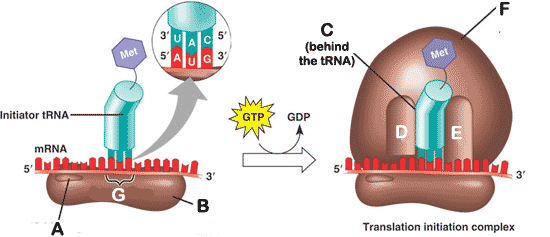 | mRNA binding site p296,  |
** What is "B" pointing to in the picture below?,  | small ribosomal subunit p296,  |
** What is "C" pointing to in the picture below?,  | P site p296,  |
** What is "D" pointing to in the picture below?,  | E site p296,  |
** What is "E" pointing to in the picture below?,  | A site p296,  |
What is "F" pointing to in the picture below?,  | Large ribosomal subunit p298,  |
What is "G" pointing to in the picture below?,  | start codon p298,  |
What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 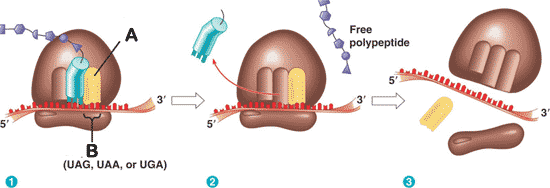 | release factor p299, 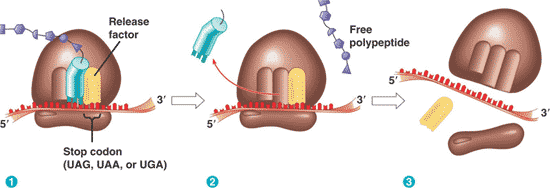 |
** What is "B" pointing to in the picture below?,  | stop codon p299,  |
** What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?,  | amino acid attachment site of tRNA p294,  |
* What is "B" pointing to in the picture below?,  | anticodon of tRNA p294,  |
| ** The process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins (or, in some cases, just RNAs) is called _____. | gene expression p283 |
| ** The concept that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein was dubbed the "________" by Francis Crick in 1956. | central dogma p286 |
| * The concept that genetic information flows from _____ to _____ to _______ was dubbed the "central dogma" by Francis Crick in 1956. | DNA --> RNA --> Protein p286 |
| ** What are the first three nucleotides that are read during the process of translation? | AUG (This codon serves as a start signal (a.k.a. initiation codon). Because AUG also codes for methionine, polypeptide chains begin with methionine when they are synthesized. However, an enzyme may subsequently remove this starter amino acid from the chain) p287 |
| ** When referring to a codon on DNA (as opposed to on RNA), the codon would be found on the _____ strand. | non-template strand (This is because the letters of the triplet codon would be identical, instead of complementary, to the letters on the RNA codon other than there being T's on the DNA codon as opposed to U's on the RNA codon) p287 |
| ** What are the three stages of transcription? (Put them in the correct order) | initiation, elongation, termination p290 |
| * The coding stretches of DNA nucleotides that make up a gene and are eventually expressed. This term also applies to the parts of a pre-mRNA transcript that are not removed (but instead spliced together) and end up leaving the nucleus as m-RNA. | exons p292 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Eukaryotic ribosomes are identical to prokaryotic ribosomes. | FALSE (Eukaryotic ribosomes are very similar but slightly larger and differ somewhat in their composition. This fact allows certain antibiotics like tetracycline and streptomycin to target protein synthesis in bacteria without harming the ability of the human eukaryotic cells to function) p295 |
| * A mutation that has causes a change in a nucleotide in DNA, and thus in the RNA transcript, but does not change the amino acid called for by the mRNA codon. | Silent mutation (It's silent because it doesn't change the protein product. This type of mutation almost always occurs where it affects the 3rd RNA nucleotide in a codon. See the genetic code table to see that many of the codons can have a different 3rd nucleotide but still code for the same amino acid) p303 |