| A | B |
|---|
| * The process of making proteins inside cells is called ______. | protein synthesis (For some reason, this book has all but stopped using the term "protein synthesis," probably because transcription doesn't always lead to a protein product and translation leads to a polypeptide that may need additional modifications before it becomes a functional protein, but the term "protein synthesis" is still commonly used so I want you to know it.) |
* Which type of nucleic acid can't leave the nucleus?, 
| DNA p286 |
| * On which organelle are polypeptides made? | ribosomes p286, 
|
| * Where are ribosomes located? | out in the cytoplasm p286, 
|
| * The process of making a strand of RNA using DNA as a template is called ___. | transcription p285 |
* Which nucleotide do you find in RNA but not DNA?, 
| uracil p285 |
| * Uracil bonds to across from ______. | adenine p287 |
| * The process of using the instructions on m-RNA to make a polypeptide is called _____. | translation p286 |
| * Which type of molecule brings amino acids to the site of protein synthesis? | transfer RNA (t-RNA) p293 |
| * Which molecule attaches to a ribosome and provides the instructions for putting amino acids together? | messenger RNA (m-RNA) p285 |
* How many nucleotides are needed to code for 1 amino acid?, 
| 3 p287 |
| * How many different types of amino acids are used to make proteins? | 20 p287 |
* Each set of 3 nucleotides on a strand of m-RNA are called a(n) _____., 
| codon p287 |
| * How many nucleotides are found at the bottom of a molecule of t-RNA and are involved with bonding to m-RNA? | 3 p294 |
| * How many amino acids are found attached to a molecule of t-RNA? | 1 p294 |
* A change in the sequence of nucleotides in a molecule of DNA will cause a ____., 
| mutation p303 |
| * Mutations that are harmful are usually weeded out by ______. | natural selection |
| * Mutations in a gene that are helpful usually become part of the gene pool as a new ____. | allele (An allele is a different form of a gene) p306 |
* Which amino acid would the m-RNA codon sequence AGU call for?,  | Serine p288,  |
| * Which enzyme is required for transcription? | RNA Polymerase (remember, you are making RNA during transcription) p289 |
| * Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells? | In the nucleus p286 |
| * Translation occurs in the ___ on ___. | cytoplasm, ribosomes (Remember, ribosomes are not membrane-bound organelles. They are solid structures, so it is incorrect to say that translation occurs "in" ribosomes) * explanation starts on page 293 |
| * Genes contain instructions for assembling ___. | polypeptides (It is often said that genes code for making proteins, but this is not always technically correct. Many proteins have a quaternary structure, with several intertwined polypeptides. In this case, no single gene has the code for making the finished protein. Each polypeptide that makes up the protein is coded for by a different gene. Another exception is that some genes only code for RNA molecules, many of which function as enzymes, but keep in mind that the vast majority of enzymes are made of proteins, not RNA's) p285 |
| * Proteins are made out of ____. | amino acids p285 |
* The picture below is called the ____.,  | genetic code (It's also called the codon table in this book, but it's really the universal code that nearly all organisms use to translate m-RNA codons into a sequence of amino acids, thus, nearly all organisms share the same "genetic code." This implies that this system evolved very early on in the evolution of organisms. We say that "nearly all organisms use it because there are some minor exceptions that have evolved in the translation of the triplet code for some amino acids in some organisms) p288,  |
| * Which type of molecule is a codon found on? | m-RNA (the term codon is also sometimes used for the DNA base triplet along the non-template strand. These codons are complementary to the template strand and thus identical to the m-RNA codon other than the substitution of uracil for thymine in the m-RNA) p287 |
| * Only one of the two DNA strands is transcribed during transcription. This strand is called the _____ strand. | template strand (Interestingly enough, one of the two DNA strands may serve as the template strand for some of the genes on the chromosome, but not others) p287 |
| * If a recently manufactured protein has a primary structure that is 1000 amino acids long, how many nucleotides long was the coding part of the mRNA molecule used as the instructions for that protein? | 3000 (remember, it takes 3 nucleotides to code for each amino acid) p287 |
| * A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene is called a(n) _______. | insertion p305 |
| * A noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene is called a(n) ______. | intron (the part of the mRNA that is transcribed from DNA introns, but is cut out before the mRNA exits the nucleus, is also called an intron) p292 |
| * The specialized base triplet at one end of a tRNA molecule that recognizes a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule is called a(n) _______. | anticodon ("B" in the picture below) p295, 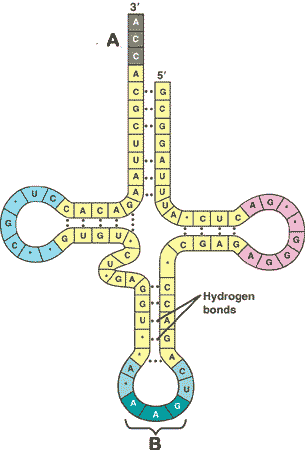 |
* Which amino acid is represented by the shape with the question mark in the picture below? Use the chart to find the answer.,  | Serine (Remember, the table represents the mRNA codon, not the tRNA anticodon) p288,  |
| * The removal of the noncoding portions (introns) of the RNA molecule after initial synthesis and the subsequent attachment of the remaining coding portions (exons) to each other is called ______. | RNA splicing p292 |
| * A(n) _____ mutation occurs when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is NOT a multiple of three, resulting in the improper grouping of the following nucleotides into codons. | frameshift p305 |
| * Which type of mutations can lead to frameshift mutations? | insertions or deletions that are not in multiples of three p305 |
| * A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates where to start transcribing RNA is called the _____. | promoter p290,  |
| * A type of point mutation; the replacement of one nucleotide and its partner in the complementary DNA strand by another pair of nucleotides is called a(n) ______. | nucleotide-pair substitution (a.k.a. - base pair substitution) p303 |
| * The enzyme that links together the growing chain of ribonucleotides during transcription is called _____. | RNA polymerase p289, 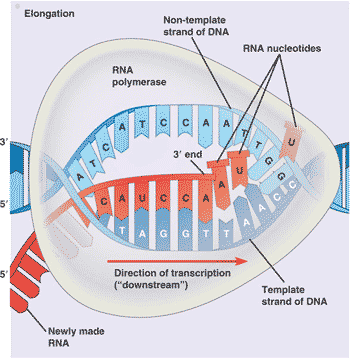 |
| * A point mutation in which one or more nucleotides pairs are lost from a gene is called a(n) ______. | deletion (deletions can also happen at the chromosomal level in which case they are called chromosomal deletions) p305 |
| * _____ is the most abundant type of RNA, which together with proteins forms the structure of ________. | rRNA (ribosomal-RNA), ribosomes p296 |
| * DNA and RNA are read as a(n) _____ code. | triplet code p287 |
| * A change in a gene at a single nucleotide pair. | point mutation p303 |
| * The coding region of a eukaryotic gene; when transcribed into mRNA, it is the coding part of mRNA that leaves the nucleus. | exon p292, 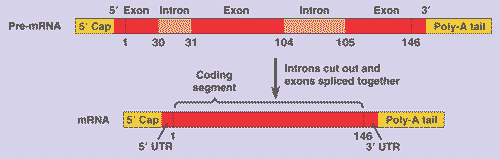 |
* What is "A" in the picture below?,  | an amino acid p295,  |
* What is "C" in the picture below?,  | t-RNA p295,  |
* Which process belongs in the darker red box in the picture below?,  | transcription p286,  |
* Which process belongs in the pink box in the picture below?,  | RNA processing p286,  |
* Which process belongs in the light blue box in the picture below?,  | translation p286,  |
* What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 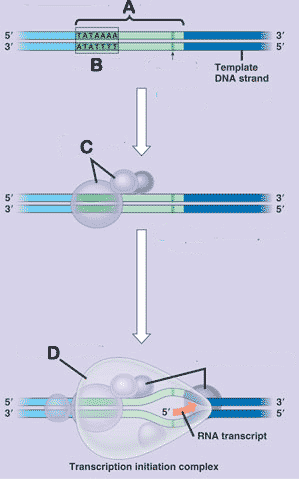 | Promoter p290,  |
* What is "D" pointing to in the picture below?,  | RNA polymerase p289,  |
* What is "B" pointing to in the picture below?,  | anticodon of tRNA p294,  |
| * The concept that genetic information flows from _____ to _____ to _______ was dubbed the "central dogma" by Francis Crick in 1956. | DNA --> RNA --> Protein p286 |
| * The coding stretches of DNA nucleotides that make up a gene and are eventually expressed. This term also applies to the parts of a pre-mRNA transcript that are not removed (but instead spliced together) and end up leaving the nucleus as m-RNA. | exons p292 |
| * A mutation that has causes a change in a nucleotide in DNA, and thus in the RNA transcript, but does not change the amino acid called for by the mRNA codon. | Silent mutation (It's silent because it doesn't change the protein product. This type of mutation almost always occurs where it affects the 3rd RNA nucleotide in a codon. See the genetic code table to see that many of the codons can have a different 3rd nucleotide but still code for the same amino acid) p303 |