| A | B |
|---|
| * What was the name of the paper that Charles Darwin had published in 1859 that layed out his mechanism for evolution? | On the Origin of Species (the full title is actually On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection) p386 & p389 |
| * What was the mechanism that Darwin and Wallace proposed to explain how evolutionary change could occur? | Natural Selection p389 |
| * Remains or traces of organisms from the past are called ______. | fossils p387 |
| * Which type of rock are fossils usually found in? | sedimentary (this type of rock is caused by sediments washing down from the weathered rocks and being deposited in layers, or strata) p387 |
| * The study of fossils is called _______. | paleontology p387 |
| * Paleontology is the study of _____. | fossils p387 |
| ** The idea that changes in Earth's surface can result from slow continuous actions was put forth by the geologists _____ and ______. They exerted a strong influence on Darwin's thinking. | Lyell, Hutton p387 |
| ** Lamarck's theory of evolution hypothesized that species evolve through ____ and _____ and the inheritance of _____ traits. This idea was later proved to be wrong. | use, disuse, acquired p387,  |
** ________ theory of evolution hypothesized that species evolve through "use" and "disuse" and the inheritance of acquired traits. This idea was later proved to be _____.,  | Lamarck's, wrong p387,  |
| * Where was Darwin's most famous stop during his travels around the world on the HMS Beagle? | The Galapagos Islands (off the west coast of South America) p388 |
| ** Who was the other person who proposed a theory of Evolution similar to Darwin's around the same time period? | Alfred Russel Wallace p389 |
| * The phrase "______" summarizes Darwin's perception of the unity of life, stating that all organisms are related through descent from an ancestor that lived in the remote past. | Descent with modification p390 |
| * One of the observations that helped Darwin form his theory of evolution is that for any species, population sizes would increase ______ if all individuals that are born reproduce successfully. | exponentially (Thomas Malthus, an economist worried about the ability to feed a growing human population, influenced Darwin's thinking in this area) p391 |
| * One of Darwin's observations that led him to his ideas of evolution based on natural selection was that members of a population often ____ in their inherited traits. | vary p391 |
| * Another of Darwin's observations that led him to his ideas of evolution based on natural selection was that all species can produce more ______ than their environment can support and many of these will fail to _____ and ______. | offspring, survive, reproduce p391 |
| * One of the inferences that Darwin made based of his observations was that individuals whose inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to ________ than do other individuals. | leave behind more offspring p391 |
| * One of the inferences that Darwin made based of his observations was that the unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of _____ in the population over generations. | favorable traits p391 |
| * The process of humans modifying other species over many generations by selecting and breeding individuals that possess desired traits is called ________. | artificial selection (farmers have been doing this for the last 10,000 years) p391 |
| * Natural selection is a process in which individuals that have certain heritable traits ____ and ____ at a higher rate than do other individuals because of those traits. | survive, reproduce p392 |
| * Over time, natural selection can increase the ____ of adaptations that are favorable in a given environment. | frequency p392 |
| * A drug (such as a particular antibiotic) does not cause resistant pathogens; it selects for resistant individuals that are ____ in the population. | already present p395 |
| * In species that produce new generations in short periods of time, evolution by natural selection can occur _____. | rapidly p395 |
| * What is favored by natural selection depends on the current ____ and can change if the ____ changes. | environment, environment p394 |
| * In humans, the use of antibiotic drugs selects for pathogens that through _____ _____ are resistant to the drugs’ effects. | chance/random mutations p395 |
| * Homology is similarity resulting from common ______. | ancestry p395 |
| * ________ is similarity resulting from common ancestry. | Homology p395 |
| * _________ structures between organisms are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme that was present in a common ancestor. | Homologous p395,  |
* The picture below shows ______ structures.,  | homologous p395,  |
* Homologous structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through ________ evolution.,  | divergent (This term seems to have been taken out of this chapter, but they do talk about convergent evolution, and divergent evolution is just as important, so you need to know this term),  |
| * _________ structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through divergent evolution. | Homologous p395,  |
| ** Comparative ________ reveals additional anatomical homologies not visible in adult organisms, such as the post-anal tale, and pharyngeal arches (that develop into gills in fish but don't in most other vertebrates). | embryology p395, 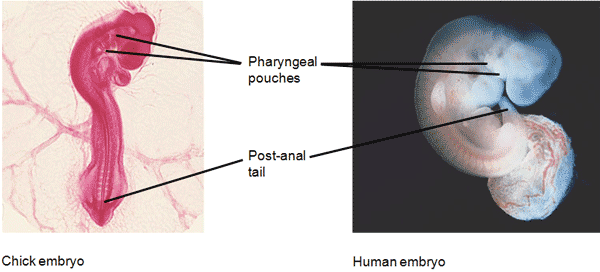 |
* ______ structures are structures that no longer seem to have a function and are remnants of structures that served important functions in the organism's ancestors.,  | Vestigial p395,  |
| * The human appendix is an example of a(n) ______ structure. | vestigial p395 |
| ** Biologists also observe homologies among organisms at the molecular level such as ______ that are shared among organisms inherited from a common ancestor. | genes p395 |
| ** At the molecular level, a _____ would be the equivalent of a vestigial structure at the anatomical level. | pseudogene p396 |
| ** At the molecular level, a pseudogene would be the equivalent of a ______ at the anatomical level. | vestigial structure p396 |
| * _______ structures are very similar in look and purpose due to convergent evolution, but are not thought to have common origin. | Analogous p396,  |
* Analogous structures (like the wings in the picture below) are very similar in look and purpose due to ______ evolution, but are not thought to have common origin.,  | convergent p396,  |
* The two structures below are examples of _______ structures.,  | analogous p396,  |
| In science, a ______ accounts for many observations and data, and attempts to explain and integrate a great variety of phenomena. | theory |
| * In science, a _____ is a well-tested explanation that accounts for many observations and explains and integrates a great variety of phenomena that represents the most likely explanation given the present evidence. | theory p398 |
| ** The study of the past and present distribution of species is called _____. | biogeography p397 |
| * ______ are an accumulation of inherited characteristics that enhance organisms' ability to survive and reproduce in specific environments. | Adaptations p389 |
| * Evolution can also be defined as a change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation. How else does this book define evolution? | Descent with modification p386 |
| * Evolution can also be defined as "Descent with modification." How else does this book define evolution? | A change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation. p386 |
| ** Who was the economist whose ideas on human suffering being related to population size growing faster than our ability to increase food production influenced Darwin's ideas on the role of overpopulation on natural selection? | Thomas Malthus p391 |
| * If an environment changes, or if individuals move to a new environment, _____ may result in adaptation to these new conditions, sometimes giving rise to _____. | natural selection, new species p392 |
| * Analogous features share ______, but not common ancestry, while homologous features share common ancestry, but not necessarily ______. | similar function, similar function p396 |
| * Analogous features share similar function, but not ______, while homologous features share _______, but not necessarily similar function. | common ancestry, common ancestry p396 |
| * _____ features share similar function, but not common ancestry, while ____ features share common ancestry, but not necessarily similar function. | Analogous, homologous p396 |
| ** Species that are ____ to a certain area are species that are found nowhere else in the world. | endemic p397 |
| * In science, a theory is a ____ explanation that accounts for many observations and explains and integrates a great variety of phenomena that represents the most likely explanation given the present evidence. | well-tested p398 |