| A | B |
|---|
| * The process by which one species splits into two species is called ____. | speciation p440 |
| * Evolution above the species level (ie - the kind that creates new species) is called _______. | macroevolution p440 |
| * Evolutionary change that occurs within one species but doesn't immediately lead to speciation is called ______. | microevolution p440 |
| * The biological species concept defines a species as a population or group of populations whose members have the potential to _______ in nature and produce ______ but are unable to do the same with members of other populations. | interbreed, viable fertile offspring p441 |
| * ____ isolation is the existence of biological factors that impede members of two different species from producing viable fertile offspring. | Reproductive p441 |
| * ____ barriers cause biological isolation by impeding mating between species or by hindering the fertilization of ova if members of different species attempt to mate. | Prezygotic p441 |
| * Habitat isolation, temporal isolation, behavioral isolation, mechanical isolation, and gametic isolation are all examples of _____. | prezygotic barriers pp442&443 |
| ** _____ isolation occurs when mating is impeded because organisms don't hang out in the same type of area. | Habitat p442 |
| ** ____ isolation occurs when mating is impeded due to two populations having different mating seasons from each other. | Temporal p442 |
| ** ____ isolation occurs when mating is impeded due to incompatible courtship rituals. | behavioral p442, 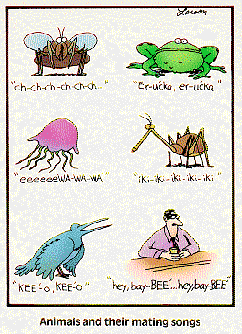 |
| ** ____ isolation occurs when mating is impeded due to incompatible genitalia. | Mechanical (in other words, the bits don't fit) p442 |
| ** ____ isolation occurs when there is reproductive isolation due to the inability of sperm to fuse with the egg and form a zygote. | gametic 443 |
| * ______ barriers cause biological isolation due to the inability of the hybrid zygote to develop into a viable fertile adult. | Postzygotic p441 |
| * Reduced hybrid viability, reduced hybrid fertility, and hybrid breakdown are examples of ______. | Postzygotic barriers p443 |
| ** Hybrids often don't develop correctly (and spontaneously abort) or are born too frail for survival. (What type of postzygotic barrier does this statement describe?) | Reduced hybrid viability p443 |
| ** Hybrids are often sterile. (What type of postzygotic barrier does this statement describe?) | Reduced hybrid fertility p443 |
| ** Hybrids are sometimes fertile, but their offspring become less and less fertile with each successive generation. (What type of postzygotic barrier does this statement describe?) | Hybrid breakdown p443 |
| ** Some limitations of the Biological Species Concept include the fact that the definition is hard to apply to _____, _____, and organisms about which little is known regarding their reproduction. | asexual organisms, fossils p444 |
| ** The ____ concept cannot be applied to asexual organisms, fossils, or organisms about which little is known regarding their reproduction. | biological species p444 |
| ** The ______ species concept characterizes a species in terms of its body shape, size, and other structural features. | morphological p444 |
| ** The _____ species concept views a species in terms of its niche. | ecological p444 |
| *_______ speciation happens when a new species forms while geographically isolated from its parent population. | Allopatric p454 |
| * _______ speciation happens when a small population becomes a new species without geographic separation. | Sympatric ("patric" refers to homeland/country while "sym" means same. Sympatric speciation occurs in an organism's homeland while allopatric speciation occurs in a different homeland from the parent population) p454 |
| * Allopatric speciation occurs when gene flow is interrupted or reduced when a population is divided into two or more _______ isolated subpopulations. | geographically p454 |
| * ______ is the presence of extra sets of chromosomes in cells due to accidents during cell division and is a common source of speciation among ____. | polyploidy, plants p447 |
| ** A(n) ______ is an individual that has more than two chromosome sets, all derived from a single species. | autopolyploid p448, 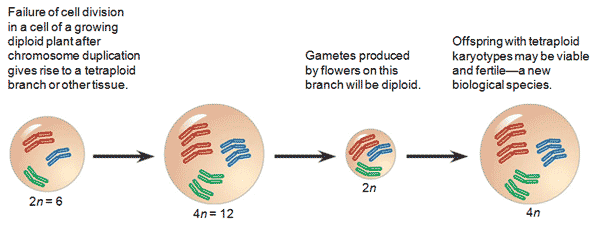 |
| ** A(n) _____ is a species with multiple sets of chromosomes derived from different species. | allopolyploid p448, 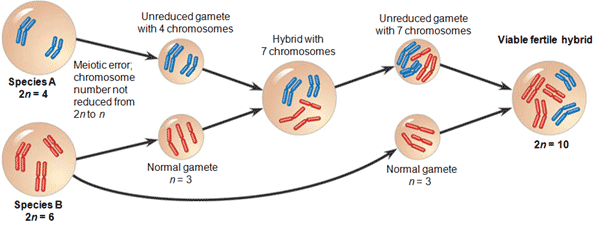 |
| * The _______ model of evolutionary change describes evolution as happening in short fast spurts followed by long periods of little change. | Punctuated Equilibrium p454, 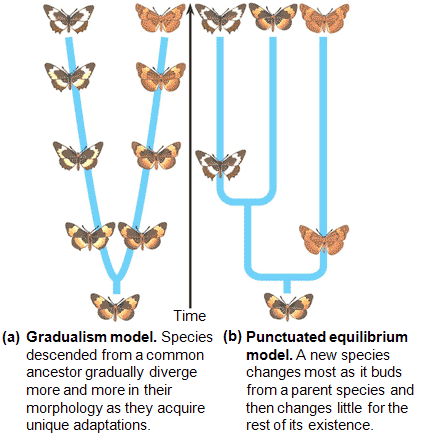 |
| ** The _______ model of evolutionary change describes evolution as happening slowly and steadily. | Gradualism (This term is no longer used in the book, but it is described as a contrast to punctuated equilibrium, so I want you to know it),  |
| * The offspring of crosses between two different species are called _____. | hybrids p441 |
| ** A(n) __________ is a region in which members of different species meet and mate,producing at least some offspring of mixed ancestry. | hybrid zone p450 |
| ** One possible outcome in a hybrid zone is that the two species will become more and more reproductively isolated from each other over time, with fewer and few hybrids being formed. This concept is called ____. | reinforcement (This happens when the hybrids are less fit than either of the non-hybrid species) p452, 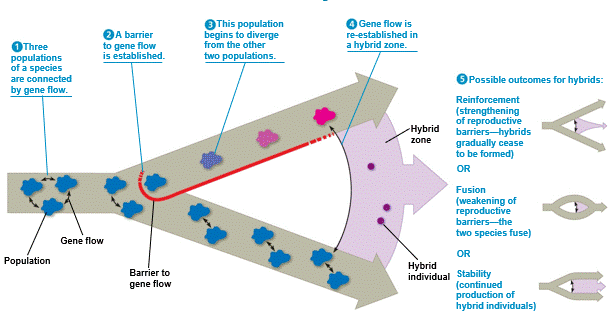 |
| ** One possible outcome in a hybrid zone is that the two species will share more and more genes through gene flow and any reproductive barriers that currently exist will become weaker and weaker over time. This concept is called ____. | fusion p452,  |
| ** One possible outcome in a hybrid zone is that the two species will remain separate but will continue to produce hybrids. This concept is called _____ | stability,  |