| A | B |
|---|
| * The study of the biological form of an organism is the study of its _______. | anatomy p.673 |
| * The study of the biological function of an organism is the study of its _______. | physiology p.673 |
| ** The fluid that fills the spaces between cells is called ________. | interstitial fluid p.684 |
| * Cells are organized into _____, groups of cells with similar appearance and common function. | tissues p.674 |
| * Different types of tissues are organized into functional units called _____. | organs p.674 |
| * Groups of organs that work together make up a(n) ______. | organ system p.674 |
| ** Which two organ systems does the pancreas belong to? | Digestive and endocrine (The pancreas produces digestive enzymes, and it produces the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels) p.674,  |
| * What are the four main types of animal tissues? | Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous pp.674&675,  |
| * Which system's main function is food processing? | Digestive system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is the internal distribution of materials? | Circulatory system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is gas exchange? | Respiratory system p.674,  |
| * Which two systems' main function is to defend the body against pathogens? | Immune and lymphatic system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to dispose of metabolic waste and regulate the osmotic balance of blood? | Excretory system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to create offspring? | Reproductive system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to coordinate body activities and maintain homeostasis by producing hormones? | Endocrine system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to detect and respond to stimuli? | Nervous system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to protect against mechanical injury, infection, dehydration, and to maintain thermoregulation? | Integumentary system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to provide body support, protect internal organs, and facilitate movement? | Skeletal system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is locomotion and other movement? | Muscular system p.674,  |
| * ________ tissues cover the outside of the body and line the organs and cavities within the body? | Epithelial pp.674,  |
| ** The ______ surface of epithelial cells is the surface that would facing either the lumen (cavity) of an organ or the outside of an organ. | apical p.675, 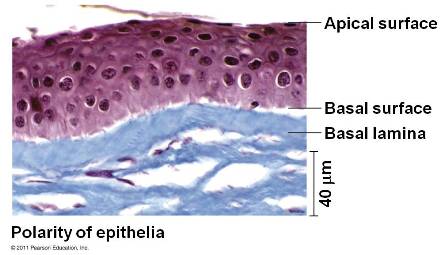 |
| ** The ______ surface of epithelial cells is the surface that would be attached to a dense mat of extracellular matrix that separates the epithelium from the underlying tissue. | basal surface p.675,  |
| ** The dense mat of extracellular matrix that separates the epithelium from the underlying tissue is called called the _______. | basal lamina p.675,  |
| * ________ tissue, consisting of a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix, holds many tissues and organs together and in place. | Connective tissue p.675,  |
| ** Within the matrix that holds connective tissue cells are _______ which are cells that secrete fibrous proteins, and _______ which engulf foreign particles and any cellular debris by the process of phagocytosis. | fibroblasts, macrophages p.675,  |
| ** Which type of connective tissue binds epithelial tissue to underlying tissues and holds organs in place? | Loose connective tissue p.675,  |
| ** Which type of connective tissue is found in tendons and ligaments and is dense in strong but flexible collagenous fibers? | Fibrous connective tissue p.675,  |
| ** Which type of connective tissue consists of collagen that becomes mineralized to form hardened structures? | Bone p.675,  |
| * ________ connective tissue is a specialized type of loose connective tissue that stores fat in cells embedded in the matrix of the tissue. | Adipose p.675,  |
| * Which type of connective tissue has cells suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma? | Blood p.675,  |
| ** Blood is a connective tissue that consists of cells, platelets, and dissolved substances suspended in a liquid matrix called _____. | plasma p.675,  |
| * Which type of connective tissue is found between the discs that separate vertebrae as well as the ends of many bones? | Cartilage p.675,  |
| * All muscle cells consist of filaments containing the proteins ______ and _______. | actin and myosin p.675,  |
| * The three types of muscle tissue in vertebrate bodies are ____, _____, and _____. | skeletal, smooth, and cardiac p.675,  |
| * What type of muscle tissue is responsible for the voluntary movement of bones relative to each other? | skeletal muscle tissue (a.k.a. - striated muscle) p.675,  |
| * What type of muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movement such as the movement of food down the digestive tract or the constriction of blood vessels? | Smooth muscle tissue p.675,  |
| * What type of muscle tissue is responsible for the contraction (beating) of your heart? | cardiac muscle tissue p.675 |
| * Which type of tissue is responsible for the receipt, processing, and transmission of information in the body? | Nervous tissue p.675, 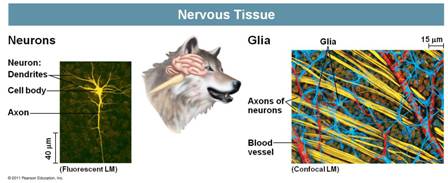 |
| * The more technical name for nerve cells is ______. | neurons p.675,  |
| ** Nervous tissue contains ____ cells which transmit nerve impulses; as well as support cells called ____ cells. | nerve, glial (a.k.a. glia) p.675,  |
| * The part of the neuron that receives information from other neurons is the cell body and extensions from the cell body called _____. | dendrites p.675,  |
| * The part of the neuron that transmits impulses to other neurons, muscle cells, endocrine cells and exocrine cells is the _____. | axon p.675,  |
| ** _____ cells help nourish, insulate, replenish, and in some cases, modulate neuron function. | Glial cells (a.k.a. - glia) p.858,  |
| * Which two systems facilitate communication between various parts of the body? | Nervous and endocrine systems p.678 p.859, 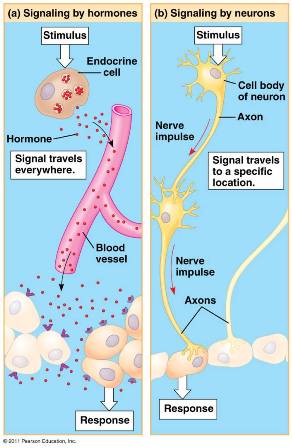 |
| * The signaling molecules used for communication in the endocrine system are called ____. | hormones p.678,  |
| * Which system produces signals for communication that are relatively fast acting but do not endure for long? | Nervous system p.678,  |
| * The _____ system is well-suited for coordinating gradual changes that affect the entire body, such as growth and development, reproduction, metabolic processes, and digestion. | endocrine p.678,  |
| * The _____ system is well-suited for directing immediate and rapid responses to the environment, especially in controlling fast locomotion and behavior. | nervous p.678 |
| ** An animal is said to be a(n) ____ for a particular environmental variable if it uses internal mechanisms to control internal change in the face of external fluctuation. | regulator p.683, 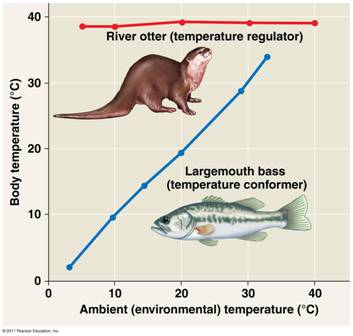 |
** Which animal in the diagram below is a regulator?,  | The otter p.683,  |
** Which animal in the diagram below is a conformer?,  | The bass p.683,  |
| * The maintenance of internal balance at a steady state is called ______. | homeostasis (This term can also be applied to larger systems in ecology, such as the regulation of Earth's global average temperature through negative feedback mechanisms) p684 |
| ** Human bodies try to maintain homeostasis around a body temperature of _____ degrees Celsius and a blood pH of _____ | 37, 7.4 p684 |
| ** Like a home heating system, an animal achieves homeostasis by maintaining a variable, such as body temperature or solute concentration, at or near a particular value called the _______. | set point p684, 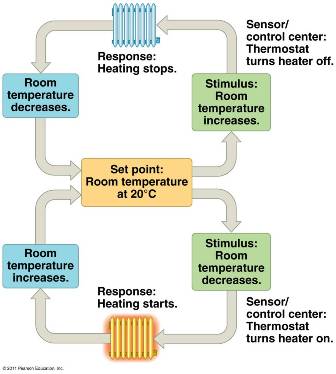 |
| ** What is the set point for human body temperature? | 37C p684 |
| ** What is the set point for human blood pH? | 7.4 p684 |
| * Homeostasis in animals relies largely on ____ feedback. | negative p684 |
| ** One way in which the normal range of homeostasis may change is through _______, the gradual process by which an animal adjusts to changes in its external environment. | acclimitization (The production of more red blood cells when an animal or human moves to higher altitudes is an example) p686 |
| ** _____ is the process by which animals maintain an internal temperature within a tolerable range. | Thermoregulation p684 |
| ** What are the two sources of heat for thermoregulation? | internal metabolism and the external environment p685 |
| * Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by metabolism are said to be ______. | endotherms p685 |
| * Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by external sources are said to be ______. | ectotherms p685 |
| * Why does a bird need to consume more food than a lizard (an ectotherm) of the same size? | The bird needs to use a lot of its energy to generate metabolic heat because it is an endotherm. p.685 |
| ** What are the four physical processes that any organism (and any object for that matter) uses to exchange heat? | Radiation, evaporation, convection, conduction p685, 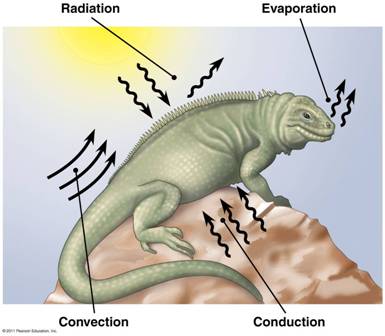 |
| ** _________ is the transfer of heat by the movement of air or liquid past a surface. | Convection (Technically, the movement of heat from the body's core to the extremities via blood flow is considered convection) p685,  |
| ** What is the most cold-blooded animal in the world? | p. 944,  |
| ** The type of heat transfer that occurs when organisms absorb heat from the sun and lose heat to the environment in the form of electromagnetic waves. | Radiation p685,  |
| ** ______ is the removal fo heat from the surface of a liquid that is losing some of its molecules with the highest kinetic energy as a gas. | Evaporation p685,  |
| ** _____ is the direct transfer of thermal motion (heat) between molecules of objects in contact with each other. | Conduction p685,  |
| ** Name three sources of insulation that animals use to reduce the flow of heat between an animal and its environment. | Hair/fur, feathers, fat/adipose tissue p686 |
| ** In response to cold, many animals' blood vessels just below the skin undergo _______ to reduce the transfer of heat from the body core to the extremities where it can be lost to the environment. | vasoconstriction (The diameter of the superficial blood vessels decreases, thereby reducing blood flow and the heat loss to the extremities that comes with warm blood being exposed to the cold near the surface of the skin) p686 |
| ** In response to heat, many animals' blood vessels just below the skin undergo _______ to increase the transfer of heat from the body core to the extremities (where heat can be transferred to the environment) by increasing blood flow to the skin. | vasodialation (Causes the diameter of the superficial blood vessels to increase, thereby increasing blood flow to the skin and also the heat that comes with the blood) p686 |
* Which concept for minimizing heat loss is being illustrated in the diagram below?, 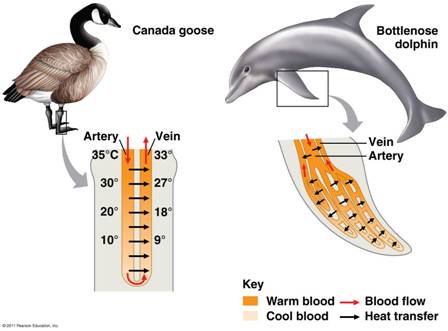 | Countercurrent exchange (This allows the arteries to transfer much of their heat to nearby veins instead of to the environment when the blood reaches skin surfaces. Countercurrent exchange can also be applied to the way blood flows in a fishes gills to maximize the uptake of oxygen from the water) p686,  |
| ** Briefly explain how evaporation leads to cooling. | Water absorbs considerable heat when it evaporates. This heat is carried away from the body surface with the water vapor. p685 |
| ** The sensors for thermoregulation are concentrated in a brain region called the _____. | hypothalamus p686, 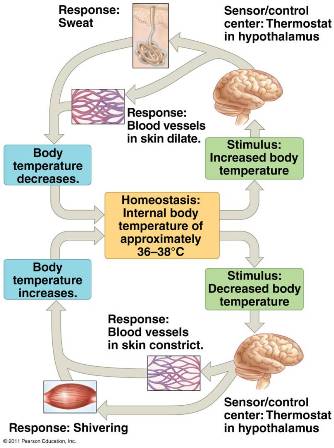 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Plants have hormones to coordinate their growth and physiology. | TRUE (Plant hormones involved with growth are commonly called "auxins.") p676 |
| ** ________ glands secrete hormones directly into surrounding fluids which then enter the circulatory system while ____ glands have ducts that carry enzymes and other secreted substances into body cavities or onto body surfaces. | Endocrine, exocrine p679 |
| ** ____ glands have ducts that carry enzymes and other secreted substances into body cavities or onto body surfaces. while ________ glands secrete hormones directly into surrounding fluids which then enter the circulatory system. | Exocrine, endocrine p679 |
| ** ______ signaling involves the control of hormone release by the nervous system, most often by an almond-sized region of the brain called the _______. | neuroendocrine, hypothalamus p679, 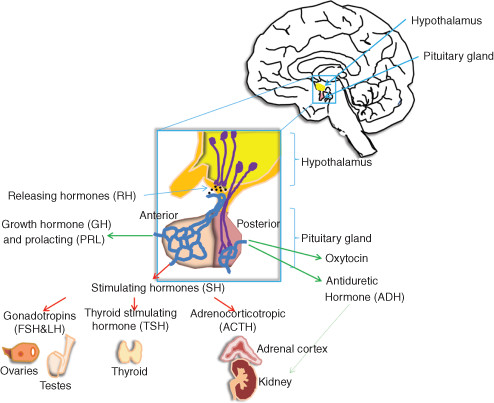 |
| * Endocrine pathways are regulated and shut off by _______ (also known as ______). | negative feedback, feedback inhibition p.679 |
| * The contraction of the uterus during childbirth is amplified when pressure is put on the cervix by the baby's head. This leads to the uterus contracting even harder which leads to more pressure. This is an example of a type of feedback called ____ feedback. | positive p679 |
| ** in a _____ pathway, endocrine cells respond directly to an internal or environmental stimulus by secreting a particular hormone. | simple endocrine (pathway) p680 |
| ** The hormone called secretin is released by endocrine cells in the duodenum (the part of the small intestine closest to the stomach) in response to the entrance of food along with digestive juices from the stomach. The secretin then travels to an organ called the ____ which releases bicarbonate ions that help ____ the pH levels so that enzymes in the intestine can continue to break down the food that just entered. | pancreas, raise (the enzymes of the intestine, unlike the digestive enzymes found in the stomach, can't function at low pH's, so the gastric juices need to neutralized once they enter the intestine) p680 |
| ** The ____ pituitary gland is an extension of the hypothalamus (a part of the brain that synthesizes certain hormones). | posterior p680,  |
| ** The posterior pituitary (under the direct nervous system control of the ________) releases ______ which stimulates mammary glands to produce milk. The other hormone released by the posterior pituitary is ______ hormone which promotes water retention by the kidney. | hypothalamus, oxytocin, antidiuretic (aka vasopressin) p679,  |
| ** The _____ pituitary is an endocrine gland that both synthesizes and secretes a wide variety of hormones in response to the release of other hormones from the _______. | anterior, hypothalamus (unlike the posterior pituitary, which is regulated by direct nerve signals from the hypothalamus, the anterior pituitary is only regulated by hormones produced in the hypothalamus) pp. 680&681,  |
| ** Which part of the pituitary is innervated by by neurons from the part of the brain called the hypothalamus, and can thus be controlled directly by the nervous system? | posterior pituitary pp. 680&681,  |
| ** _______ is involved with biorhythms and is secreted by the _____. | Melatonin, pineal gland p679,  |
| ** Hormones that stimulate other glands to release hormones are called _____. | tropic hormones (for example TSH "thyroid stimulating hormone" is a tropic hormone) p681,  |
| ** _______ stimulates the growth of bones and is secreted by the _____. | Growth hormone (GH), anterior pituitary p679,  |
| ** ______ stimulates ovaries (to release an egg) and testes (to produce testosterone) and is secreted by the _____. | Luteinizing hormone (LH), anterior pituitary p679,  |
| ** ______ stimulates the thyroid gland and is secreted by the ______. | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), anterior pituitary p679,  |
| ** ______ stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids and is secreted by the ______. | Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), anterior pituitary p679,  |
| ** ______ stimulates the gonads to produce sperm and ova and is secreted by the ______ | Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), anterior pituitary p679 |
| ** ______ stimulates the contractions of the uterus and mammary glands and is secreted by the ______. | oxytocin, posterior pituitary p679 |
| ** ______ promotes retention of water by the kidneys and is secreted by the ______. | Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), posterior pituitary p679 |
| ** _____ controls metabolic rate and is secreted by the _____. | thyroid hormone (also known as thyroxin), thyroid p679 |
| ** _____ lowers blood calcium levels and is secreted by the _____. | calcitonin, thyroid p679 |
| ** Which two hormones are secreted by the thyroid? | thyroid hormone and calcitonin p679 p679 |
| ** _______ raises blood calcium levels and is secreted by the ______. | Parathormone (PTH), parathyroid p679 |
| ** What do glucocorticoids do and where are they secreted from? | Raise blood sugar levels, adrenal cortex p679 |
| ** ________ are hormones that raise the blood sugar level, increase metabolic activity and constrict certain blood vessels. They are secreted by the _____ | Epinephrine and norepinephrine, adrenal medulla p679 |
| * Which hormone produced by the pancreas causes blood sugar levels to drop? | insulin (if a diabetic takes to much insulin, he/she can die pretty quickly because nerve cells don't store carbohydrates, so they need a certain minimum blood glucose level to function. If you know someone is diabetic and they are having big problems, you need to get something sugary into their mouth quickly) p679 |
| * Which hormone produced by the pancreas causes blood sugar levels to rise? | glucagon p679 |
| ** _____ hormone stimulates the thyroid to release thyroid hormone (a.k.a. thyroxin) | Thyroid stimulating hormone p679 |
| ** ________ stimulates uterine lining growth and promotes development and maintenance of female sex characteristics. It is secreted by the ______. | Estrogen, ovaries p679 |
| ** _______ promotes uterine lining growth and is secreted by the _____. | Progesterone, ovaries p679 |
| ** ________ (like testosterone) support sperm production and promote male secondary sex characteristics. They are produced by the ____ in males. | Androgens, testes p679 |
| ** Androgens in females are produced by the ______. | adrenal cortex (females have testosterone too, but in smaller quantities than male) p679 |
| * ______ soluble hormones can't pass through the plasma membrane, so they must instead attach to receptor proteins on the cell surface in order to initiate events that lead to a cellular response. | Water p681 |
| * ______ soluble hormones pass through the plasma membrane before they bind to receptors that are located in the cytosol rather than on the plasma membrane. | Lipid (Steroid hormones, which are made of lipids, are an example. Since they are non-polar lipids, they pass through the lipid bilayer easily) p682 |
| * Many hormones can trigger multiple responses. For instance, epinephrine (sometimes referred to as adrenaline) is released during times of extreme stress (life or death situations). It causes glucose levels in the blood to ____, decreases blood flow to the _____ system, and increases blood flow to the ______. | rise, digestive, muscles (This makes sense because when you initiate a "fight or flight" response, you will need more glucose to power your brain and muscles, and you will want increased blood flow to your muscles, while activities like digestion can be put on hold for a little while) p682 |
| ** A ______ is an animal that allows its internal conditions to change in accordance to external changes. | conformer p684 |
| * In response to ____ many animals increase the blood flow to their outer surface (skin). | heat p686 |
| * In response to ____ many animals decrease the blood flow to their outer surface (skin). | cold p686 |
| ** The management of the body's water and solute concentration is called _____. | osmoregulation p687 |
| ** Marine fish are constantly losing water due to their hypertonic environment. What are three things they do to counteract the problem? | produce very little urine and drink large amounts of water, and get rid of salt through their gills by active transport p688,  |
** Flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) like this planarian, use ____ for osmoregulation and excretion. At the tip of each protonephridium is a structure called a(n) _____.,  | protonephridia, flame bulb ("Proto" means "first." This structure works basically the same way that nephrons work in the kidneys of more complex organisms, like us) p690,  |
| ** Insects use _____ for osmoregulation and excretory purposes. | malphigian tubules p690, 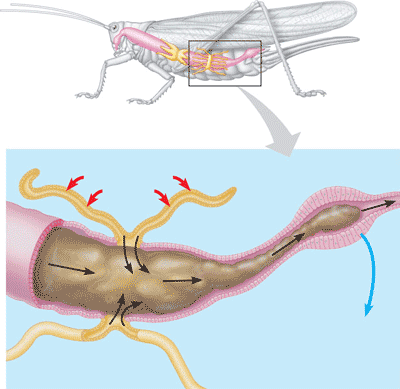 |
| * Humans use ______ found in an organ called the ______ for osmoregulation and excretory purposes. | nephrons, kidney pp690-692,  |
| * The removal of metabolic wastes is called _____. | excretion p687 |
| ** The three types of nitrogenous waste are ____, _____, and ______. | ammonia, urea, uric acid p689 |
| * The breakdown of nitrogen-containing compounds like proteins and nucleic acids produces a highly toxic compound called _____ that must be excreted quickly or changed into a less toxic substance quickly before being excreted. | ammonia p687 |
| ** Ammonia is a nitrogenous waste that is very soluble, highly toxic and is excreted, along with large amounts of water, by _____ (a type of animal, not an organ). | fish (and other organisms that live in water and don't have to worry too much about water loss, because they are surrounded by it) p689 |
| **_____ is a nitrogenous waste excreted by earthworms and humans. | Urea p689 |
| ** _____ is a nitrogenous waste that is pastelike and insoluble. It is excreted by insects, many reptiles and birds to minimize water loss. | Uric acid p689 |
| ** Which type of nitrogenous waste produces the least water loss? | Uric acid (Uric acid, unlike urea, and especially ammonia, requires very little water to be excreted with it. It can be excreted as a semi-solid paste like substance. Organisms like reptiles and birds whose evolutionary history involved adapting to dry climates use this method. The acid in uric acid is what can do damage to your car's paint job if you let bird $&!# stay on there too long) p689 p689 |
| ** The kidney filters about _______ liters of blood per day. | 1600 liters (That's almost 400 gallons!) p692 |
| ** The normal solute concentration of blood is _______. | 300 mosm/L (milli osmoles per liter) p694 |
| ** If urine has a solute concentration of 70 mosm/L, it would be considered to be _____ urine. | dilute (the normal blood solute concentration is 300 mosm/L, but if the fluid intake is high and the salt intake low, the kidney will produce dilute urine to get rid of the excess water) p694 |
| ** If urine has a solute concentration of 1200 mosm/L, it would be considered to be _____ urine. | concentrated (The normal blood solute concentration is 300 mosm/L, but if the fluid intake is low and the salt intake high, the kidney will produce highly concentrated urine to conserve water. 1200mOsm/L is about the maximum concentration of urine solutes that humans can excrete, but some desert mammals can produce urine that is 7 to 8 times more concentrated than that. Think about why that is a good adaptation for them) p694 |
| * The functional unit of the kidney is the ______. | nephron p692,  |
| ** Filtration of blood takes place between _____ and _____ of a nephron. | the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule p691, 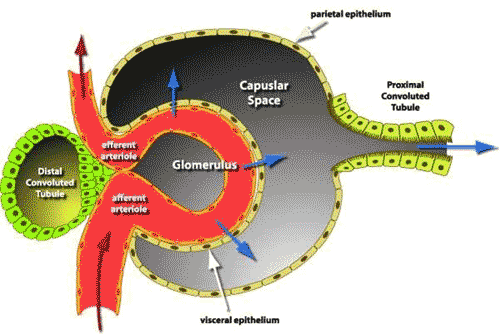 |
| ** Transport of fluids across a membrane due to high pressure is called ______. | filtration (this occurs in Bowman's capsule because the blood pressure inside the capillaries of the glomerulus is under very high pressure, even higher than blood pressure in most capillaries) p690,  |
| ** Substances small enough to enter Bowman's capsule by filtration include _____, _____, _____, and _____ as well as water. | glucose, salts, vitamins, and nitrogenous wastes (urea in most mammals) p692,  |
| ** Filtrate in the nephron enters _____, then passes through the ____, _____, and _____ before entering the _____. | Bowman's capsule --> proximal tubule --> loop of Henle --> distal tubule --> collecting tube/duct pp692 &693,  |
| * Where does the filtrate go after it leaves the kidney? | ureter --> urinary bladder --> urethra --> toilet/diaper/ground p691,  |
| ** ______ is the active, selective uptake of molecules that were too large to get filtered into Bowman's capsule | Secretion p690 |
| ** Where does secretion occur? | In the proximal and distal tubules p693,  |
| ** Secretion in the proximal and distal tubules is a type of _____ transport. | active (by definition, secretion is active transport) pp690 - 693,  |
| ** _______ is the process by which most of the water and solutes that initially entered the tubule during filtration are transported back to bloodstream. | Reabsorption (the capillaries, called peritubular capillaries, that surround the tubules and loop of Henle, are the site of reabsorption back to the bloodstream) p692,  |
| ** The main purpose of the ascending loop of Henle is to move _____ from the loop into the medulla that surrounds the loop in order to draw water out of the tubules in order to concentrate the urine. | salts pp692 & 693,  |
| ** Where in the nephron is urine concentrated by allowing the diffusion of water out of the nephron? | descending loop and the collecting tube p692,  |
| ** Where in the nephron is salt removed from the filtrate in order to maintain a hyperosmotic gradient in the renal medulla? | ascending loop of Henle pp692 & 693,  |
| ** Where is most of the filtrate reabsorbed into the bloodstream? | proximal tubule p692,  |
| ** The descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to _____ but impermeable to ______. | permeable to water but impermeable to salt p692,  |
| ** The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to _____ but impermeable to ______. | permeable to salt but impermeable to water,  |
| ** Salt _______ out of the lower part of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and _______ out of the upper part of the ascending limb. | diffuses, is actively transported p693,  |
| ** What happens in the distal tubule? | secretion, reabsorption, and pH regulation (Like the proximal tubule, the distal is another important site for these events) p693, 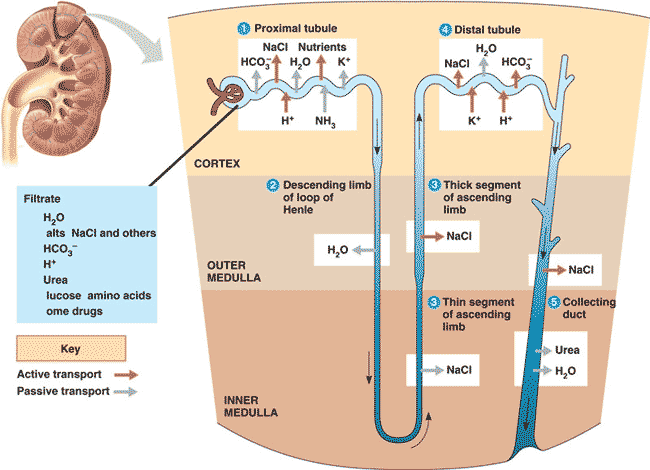 |
| ** Whether the walls of the collecting tube are permeable or not depends on the presence of _______. Its presence makes the walls permeable so that water can diffuse out of the tubule, making the urine very concentrated. | Antidiuretic hormone (ADH promotes retention of water by the kidneys) p695,  |
| ** Where is antidiuretic hormone produced, stored and released from, and what is its target? | hypothalamus, posterior pituitary, collecting tubule of the nephron (where it increase permeability of the tubule wall to allow more retention of water, creating more concentrated urine) pp 679 & 695,  |
| ** ________ cells in the ______ monitor blood solute concentration. When it rises above ______mosm/L, ADH is released into the blood so that more water can be retained and the solutes concentration of urine increases. | Osmoreceptor cells, hypothalamus, 300 p695,  |
| ** Alcohol ____ the release of ADH, causing less water retention and more urination. | blocks (* They took this out of the book, but there's a good chance you will see a scenario type question involving alcohol and the kidney on the AP test),  |
| ** Alcohol blocks the release of ____, leading to less water retention and more urination. | ADH (* They took this out of the book, but there's a good chance you will see a scenario type question involving alcohol and the kidney on the AP test),  |
| ** The ____ system is a complex feedback mechanism that initiates a change in the kidneys in response to a loss of blood pressure. | RAAS (renin-angiotensis-aldosterone-system) p695,  |
| ** The RAAS (renin-angiotensis-aldosterone-system) system is a complex feedback mechanism that initiates a change in the kidneys in response to __________. | a loss of blood pressure p695,  |
| ** The RAAS system stimulates the kidney to _____. | reabsorb more water (in response to falling blood pressure) p695 |
| * Water enters and leaves cells through a type of diffusion called ______. | osmosis p687 |
| ** Water enters and leaves cells whenever two solutions on opposite sides of a membrane differ in ________ (a.k.a. ________) | osmotic pressure, osmolarity p687 |
| ** When two solutions on opposite sides of a membrane have the same osmolarity (solute concentrations), they are said to be _____. | isoosmotic (The prefix "iso" means same) p688 |
| ** When two solutions on opposite sides of a membrane have differ in osmolarity (solute concentrations), the one with the greater solute concentrations is said to be ______ while the more dilute solution is said to be _____. | hyperosmotic, hypoosmotic (Remember, the prefix "hyper" means "too much" and the prefix "hypo" means "too little") p688 |
| ** One way for animals to maintain water balance is to isoosmotic with their surroundings. Some salt water fish have similar concentrations of solutes in their cells to the concentration of solutes in ocean water. Animals who use this strategy are called _____. | osmoconformers p688 |
| ** One way for animals to maintain water balance is to control the concentration of solutes in their cells independent of their surroundings. Fresh-water fish due this because there is no way for them to get their solute concentrations down near zero like that found in fresh-water. Animals that use this strategy are said to be ____. | osmoregulators p688 |
| * The process whereby blood pressure forces fluids from blood vessels into tubes of the excretory system is known as ______ and the fluid (now devoid of blood cells but containing water, ions, and waste is called ______. | filtration, filtrate, 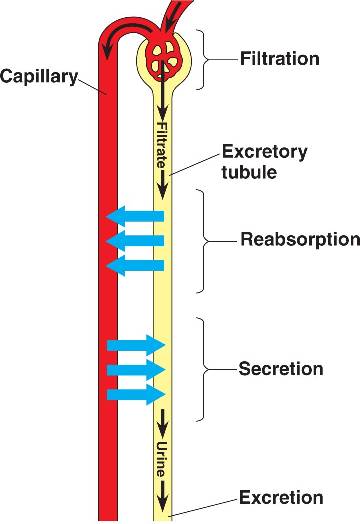 |