| A | B |
|---|
| * The study of the biological form of an organism is the study of its _______. | anatomy p.673 |
| * The study of the biological function of an organism is the study of its _______. | physiology p.673 |
| ** The fluid that fills the spaces between cells is called ________. | interstitial fluid p.684 |
| * Cells are organized into _____, groups of cells with similar appearance and common function. | tissues p.674 |
| * Different types of tissues are organized into functional units called _____. | organs p.674 |
| * Groups of organs that work together make up a(n) ______. | organ system p.674 |
| * What are the four main types of animal tissues? | Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous pp.674&675,  |
| * Which system's main function is food processing? | Digestive system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is the internal distribution of materials? | Circulatory system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is gas exchange? | Respiratory system p.674,  |
| * Which two systems' main function is to defend the body against pathogens? | Immune and lymphatic system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to dispose of metabolic waste and regulate the osmotic balance of blood? | Excretory system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to create offspring? | Reproductive system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to coordinate body activities and maintain homeostasis by producing hormones? | Endocrine system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to detect and respond to stimuli? | Nervous system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to protect against mechanical injury, infection, dehydration, and to maintain thermoregulation? | Integumentary system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is to provide body support, protect internal organs, and facilitate movement? | Skeletal system p.674,  |
| * Which system's main function is locomotion and other movement? | Muscular system p.674,  |
| * ________ tissues cover the outside of the body and line the organs and cavities within the body? | Epithelial pp.674,  |
| * ________ tissue, consisting of a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix, holds many tissues and organs together and in place. | Connective tissue p.675,  |
| * ________ connective tissue is a specialized type of loose connective tissue that stores fat in cells embedded in the matrix of the tissue. | Adipose p.675,  |
| * Which type of connective tissue has cells suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma? | Blood p.675,  |
| * Which type of connective tissue is found between the discs that separate vertebrae as well as the ends of many bones? | Cartilage p.675,  |
| * All muscle cells consist of filaments containing the proteins ______ and _______. | actin and myosin p.675,  |
| * The three types of muscle tissue in vertebrate bodies are ____, _____, and _____. | skeletal, smooth, and cardiac p.675,  |
| * What type of muscle tissue is responsible for the voluntary movement of bones relative to each other? | skeletal muscle tissue (a.k.a. - striated muscle) p.675,  |
| * What type of muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movement such as the movement of food down the digestive tract or the constriction of blood vessels? | Smooth muscle tissue p.675,  |
| * What type of muscle tissue is responsible for the contraction (beating) of your heart? | cardiac muscle tissue p.675 |
| * Which type of tissue is responsible for the receipt, processing, and transmission of information in the body? | Nervous tissue p.675, 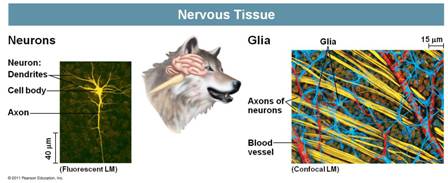 |
| * The more technical name for nerve cells is ______. | neurons p.675,  |
| * The part of the neuron that receives information from other neurons is the cell body and extensions from the cell body called _____. | dendrites p.675,  |
| * The part of the neuron that transmits impulses to other neurons, muscle cells, endocrine cells and exocrine cells is the _____. | axon p.675,  |
| * Which two systems facilitate communication between various parts of the body? | Nervous and endocrine systems p.678 p.859, 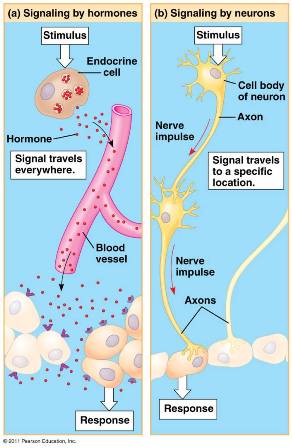 |
| * The signaling molecules used for communication in the endocrine system are called ____. | hormones p.678,  |
| * Which system produces signals for communication that are relatively fast acting but do not endure for long? | Nervous system p.678,  |
| * The _____ system is well-suited for coordinating gradual changes that affect the entire body, such as growth and development, reproduction, metabolic processes, and digestion. | endocrine p.678,  |
| * The _____ system is well-suited for directing immediate and rapid responses to the environment, especially in controlling fast locomotion and behavior. | nervous p.678 |
| * The maintenance of internal balance at a steady state is called ______. | homeostasis (This term can also be applied to larger systems in ecology, such as the regulation of Earth's global average temperature through negative feedback mechanisms) p684 |
| * Homeostasis in animals relies largely on ____ feedback. | negative p684 |
| * Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by metabolism are said to be ______. | endotherms p685 |
| * Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by external sources are said to be ______. | ectotherms p685 |
| * Why does a bird need to consume more food than a lizard (an ectotherm) of the same size? | The bird needs to use a lot of its energy to generate metabolic heat because it is an endotherm. p.685 |
* Which concept for minimizing heat loss is being illustrated in the diagram below?, 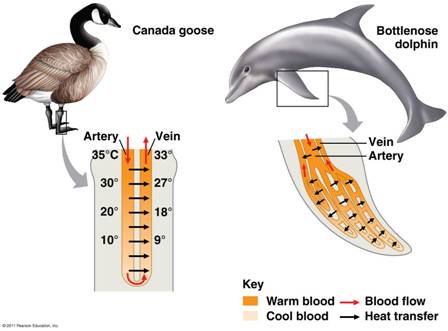 | Countercurrent exchange (This allows the arteries to transfer much of their heat to nearby veins instead of to the environment when the blood reaches skin surfaces. Countercurrent exchange can also be applied to the way blood flows in a fishes gills to maximize the uptake of oxygen from the water) p686,  |
| * Endocrine pathways are regulated and shut off by _______ (also known as ______). | negative feedback, feedback inhibition p.679 |
| * The contraction of the uterus during childbirth is amplified when pressure is put on the cervix by the baby's head. This leads to the uterus contracting even harder which leads to more pressure. This is an example of a type of feedback called ____ feedback. | positive p679 |
| * Which hormone produced by the pancreas causes blood sugar levels to drop? | insulin (if a diabetic takes to much insulin, he/she can die pretty quickly because nerve cells don't store carbohydrates, so they need a certain minimum blood glucose level to function. If you know someone is diabetic and they are having big problems, you need to get something sugary into their mouth quickly) p679 |
| * Which hormone produced by the pancreas causes blood sugar levels to rise? | glucagon p679 |
| * ______ soluble hormones can't pass through the plasma membrane, so they must instead attach to receptor proteins on the cell surface in order to initiate events that lead to a cellular response. | Water p681 |
| * ______ soluble hormones pass through the plasma membrane before they bind to receptors that are located in the cytosol rather than on the plasma membrane. | Lipid (Steroid hormones, which are made of lipids, are an example. Since they are non-polar lipids, they pass through the lipid bilayer easily) p682 |
| * Many hormones can trigger multiple responses. For instance, epinephrine (sometimes referred to as adrenaline) is released during times of extreme stress (life or death situations). It causes glucose levels in the blood to ____, decreases blood flow to the _____ system, and increases blood flow to the ______. | rise, digestive, muscles (This makes sense because when you initiate a "fight or flight" response, you will need more glucose to power your brain and muscles, and you will want increased blood flow to your muscles, while activities like digestion can be put on hold for a little while) p682 |
| * In response to ____ many animals increase the blood flow to their outer surface (skin). | heat p686 |
| * In response to ____ many animals decrease the blood flow to their outer surface (skin). | cold p686 |
| * Humans use ______ found in an organ called the ______ for osmoregulation and excretory purposes. | nephrons, kidney pp690-692,  |
| * The removal of metabolic wastes is called _____. | excretion p687 |
| * The breakdown of nitrogen-containing compounds like proteins and nucleic acids produces a highly toxic compound called _____ that must be excreted quickly or changed into a less toxic substance quickly before being excreted. | ammonia p687 |
| * The functional unit of the kidney is the ______. | nephron p692,  |
| * Where does the filtrate go after it leaves the kidney? | ureter --> urinary bladder --> urethra --> toilet/diaper/ground p691,  |
| * Water enters and leaves cells through a type of diffusion called ______. | osmosis p687 |
| * The process whereby blood pressure forces fluids from blood vessels into tubes of the excretory system is known as ______ and the fluid (now devoid of blood cells but containing water, ions, and waste is called ______. | filtration, filtrate, 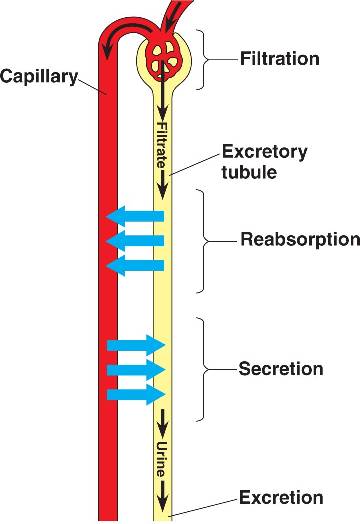 |