| A | B |
|---|
| * A disease causing agent, such as a bacterium or virus, is called a(n) _____. | pathogen p743 |
| * The first lines of defense offered by immune systems help prevent pathogens from _____. | getting into the hosts body p.743 |
| * the two types of immune defense found among animals are ______ immunity, which is common to all animals, and _____ immunity, which is only found in vertebrates. | innate, adaptive p743 |
| * The barrier defenses of mammals, which block the entry of many pathogens, include the _____ and the ___. | mucous membranes, skin. p745 |
| * In ______ immunity, which includes barrier defenses, molecular recognition relies on a small set of receptor proteins that bind to molecules or structures that are absent from animal bodies but common to a group of viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens. | innate p744 |
| * In _____ immunity, molecular recognition relies on a vast arsenal of receptors, each of which recognizes a feature typically found only on a particular part of a particular molecule in a particular pathogen. | adaptive p744 |
| * The adaptive immune response can also be called the ______ immune response. | acquired p744 |
| * The adaptive immune response is enhanced by _________ to the infecting pathogen. | previous exposure p744 |
| * After an immune cell phagocytizes a pathogen, the vacuole that is formed around the pathogen will merge with a(n) ______ so that the pathogen can be broken down by digestive enzymes. | lysosome p744, 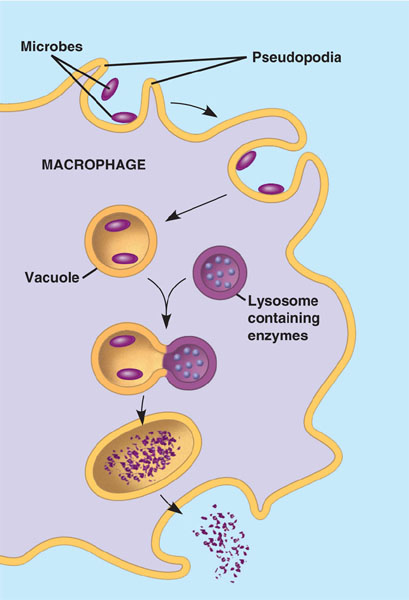 |
| * Some immune cells ingest pathogens through a process called _____. | phagocytosis p744,  |
| * The two main types of phagocytic cells in the mammalian body are _______ and ________. | Neutrophils, macrophages p745 |
| * The _______ system is a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste and other unwanted materials. The primary function of this system is to transport lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body. | lymphatic 746, 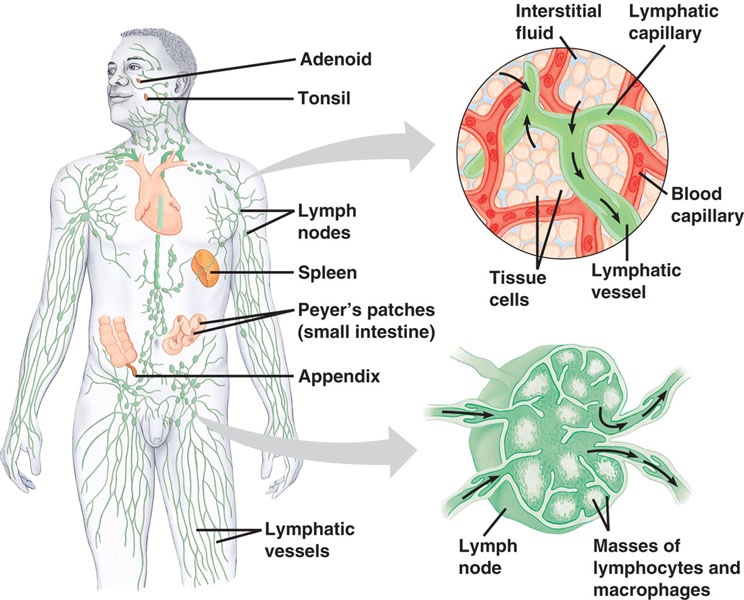 |
| * Virus-infected body cells secrete ______ proteins that induce nearby uninfected cells to produce substances that inhibit viral replication. | interferon (Besides being produced by cells infected by virus, some white blood cells release a different type of interferon that attracts macrophages to come in a phagocytize the pathogen. Interferons are now being produced in the lab and injected into people to help boost their immune system) p.746 |
| * The _____ system consists of roughly 30 proteins in blood plasma. These proteins circulate in an inactive state and are activated by substances on the surface of many pathogens. Activation results in a cascade of biochemical reactions that can lead to lysis (bursting) of invading cells. This system also functions in the inflammatory response. | complement (Notice how these proteins self-assemble to produce a knife-like structure that punctures the targeted cell) p746,  |
| * _______, immune cells found in connective tissue, release the signaling molecule histamine at sites of damage. Histamine causes a series of events that lead to ______. | Mast cells, inflammation (You've probably heard of anti-histamines. These are chemicals, often found in nasal spray, that block the effect of histamines and reduce inflammation) p746 |
| * One strategy of the inflammatory response is to induce a slight ____ in the animal. This is thought to make it more difficult for bacteria to reproduce, and it also might speed up phagocytosis and the chemical reactions necessary to fight off infection. | fever p747 |
| * The adaptive response relies on ____ and _____, which are types of white blood cells called _____. | T cells, B cells, lymphocytes p747, 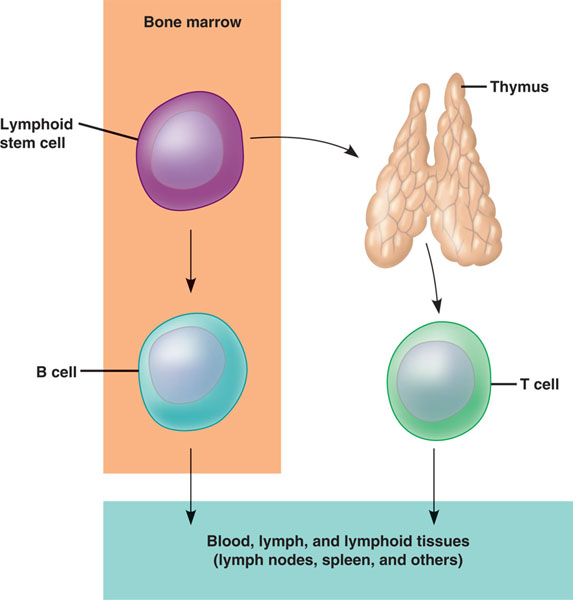 |
| * Like all blood cells originate from stem cells in the ______. | bone marrow p747,  |
| * Any substance that elicits a B or T cell response is called a(n) ____. | antigen p747, 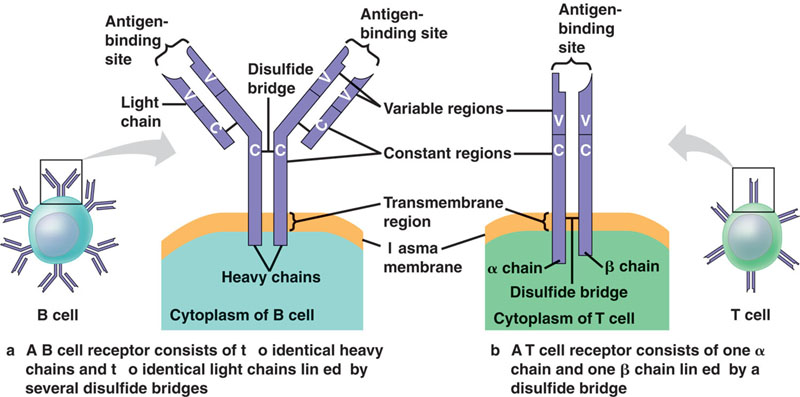 |
| * The part of the T or B cell that binds to a part of a pathogen's outer surface is called a(n) _____. | antigen receptor (The diagram below shows antigen receptors for B and T cells) p747,  |
| * A given lymphocytes antigen receptor can bind to ____ type of antigen. | only one (Yet your body has to recognize millions of different antigen shapes, so it produces millions of different types of antigen receptors. How does it do this. Each antigen receptor is made of protein and we only have about 20,000 different genes and most of them are not for antigen receptors. The answer is random combination of a couple different genes that code for the variable regions of antigen receptors early on in lymphocyte development with all the other genes being cut out and eliminated. The lymphocyte then makes a certain shaped antigen receptor for the rest of its life and passes that trait on when it divides. This random recombination allows there to be over a million B-cell antigen receptors and 10 million different T-cell receptors) p749, 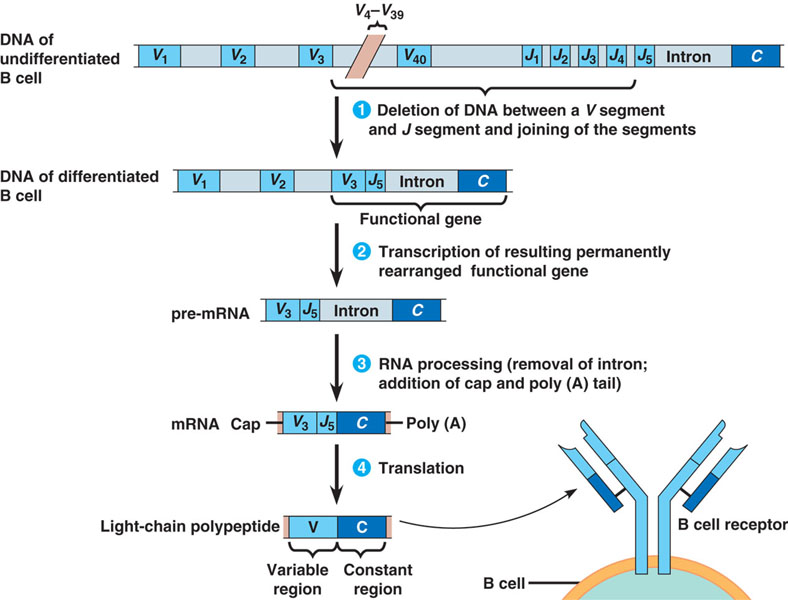 |
| * The small part of an antigen that an antigen receptor can actually bind to is called the _____. | epitope p747, 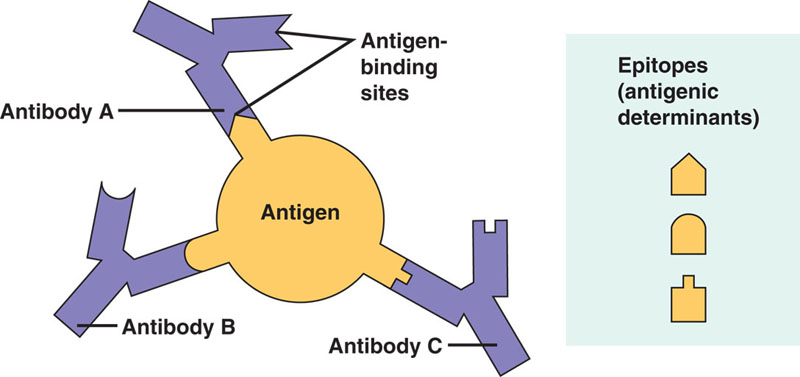 |
| * Each B cell antigen receptor is a(n) ___ shaped protein | Y,  |
| * Binding of a B cell antigen receptor to an antigen is an early step in B cell activation, leading eventually to formation of cells that can release these Y-shaped antigen receptors into blood or lymph. The Y-shaped antigen receptors that are no longer attached to a cell are called ____ or _____. | antibodies, immunoglobulins p748,  |
* Which type of lymphocyte is shown below?,  | B-cell p747,  |
* Which type of lymphocyte is shown below?,  | T-cell p747,  |
| * What do histamines do to blood vessels? | Causes them to dialate and become more permeable (This increases the amount of blood plus white-blood cell and immune protein-rich fluids that go to the site of an injury. This is the purpose of inflammation) p746 |
| * Lymphocytes that happen to develop antigen receptors that bind to your own body cell antigens are eliminated or inactivated after being tested for self-reactivity while they are being formed in the bone marrow. This ensures the concept of ______. | self-tolerance p750 |
| * What happens immediately after a B or T cell is activated by having its antigen receptor bind to an epitope from a pathogen. | The lymphocyte will start dividing over and over again (This allows an immune response to develop. Some of the new cells will turn into short-lived effector cells that fight the infection while others will turn into long-lived memory cells that will allow for much quicker recognition and immune response initiation if the infection re-occurs in the future) p750 |
| * Once a lymphocyte is activated (by binding to an antigen), it will divide over and over again. Some of these cells become ____ cells that are short-lived and fight the infection. The rest become long-lived _____ cells that stay in the body and help make recognition of the same pathogen quicker in the future if re-infection were to occur. | effector, memory p750 |
| * What do you call B cell effector cells? | Plasma cells (These are cells that are capable of secreting antibodies into blood and lymph), 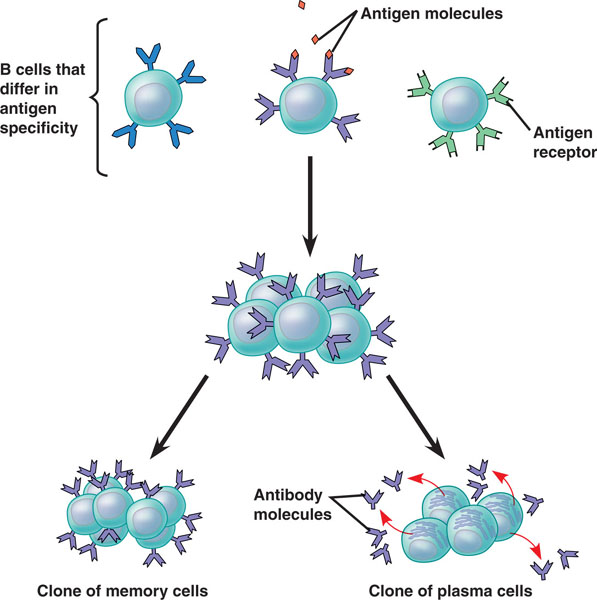 |
| * Which type of cells, once activated, can become plasma cells that secrete antibodies? | B cells p750,  |
| * What do plasma cells do? | secrete antibodies into the blood or lymph (Remember, these are the effector cells that B cells turn into once they've bumped into a pathogen. B cells will also develop into memory cells) p750,  |
| * The ______________ immune response protects the blood and lymph by using antibodies to neutralize or eliminate toxins or pathogens in the body fluids. | humoral p752 |
| * The humoral immune response protects the blood and lymph by using ______ to neutralize or eliminate toxins or pathogens in the body fluids. | antibodies p752 |
| * The _____ immune response uses specialized T cells to destroy infected host cells. | cell-mediated p752 |
| * The cell-mediated immune response uses specialized T cells to destroy _____. | infected host cells p752 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: Only immune cells can display foreign antigens on their surface. | FALSE (Both immune cells and infected body cells can display antigens on their surface that help activate T cells) p752 |
| * The targeted destruction of an infected host cell by a cytotoxic T cell involves the secretion of proteins that disrupt ______ integrity and trigger cell death | membrane p.754 |
| * The targeted destruction of an infected host cell by a(n) ____ cell involves the secretion of proteins that disrupt membrane integrity and trigger cell death | cytotoxic T p754 |
| * _____ is a process that involves the use of antigens artificially introduced into the body to generate an adaptive immune response and memory cell formation. | Immunization p754 |
| * A(n) _______ is a collection of harmless epitopes that are introduced into the body to immunize a person against infection by a real pathogen. | vaccine (vaccines today can be made from inactivated bacterial toxins, killed or weakened pathogens, or even genes encoding microbial proteins) p754 |
| * When antibodies in the blood of a pregnant female cross the placenta to her fetus, this type of protection is called _______ immunity because the antibodies in the recipient (in this case, the fetus) are produced by another individual (the mother) | passive p756 |
| * If you get bitten by a venomous snake and received a dose of antivenin, what your are really getting are _____ that were harvested from the blood of an animal that was vaccinated against the snakes venom. | antibodies p756 |
| * ______ are exaggerated (hypersensitive) responses to certain harmless antigens. | Allergies p757 |
| * When a person's own immune system attacks certain cells or natural proteins in their body, they are said to have a type of ______ disease. | autoimmune (In systemic lupus erythematosus, or lupus, the immune system generates antibodies against histones and DNA. Autoimmunity can also target the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas (in type 1 diabetes) and the myelin sheaths that encase many neurons (in multiple sclerosis) p757 |
| * The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can lead to ____ which stands for ____. This leads to the immune system not being able to fight off secondary infections and cancers that are normally handled by healthy immune systems. | AIDS, acquired immune deficiency syndrome p759 |
| * Which virus can cause cervical cancer? | HPV (This virus, known as the human papillomavirus, is easily spread through sexual contact and can remain latent for years before causing symptoms, most often cervical cancer in females or genital warts in both males and females. It is estimated that over half the human population born before the early 1990's has some form of HPV. This can now be prevented through vaccination as long as it's done at an early age) p759 |