| A | B |
|---|
| * Another word for "nerve cell" is _____. | neuron p782 |
| * Communication by neurons largely consists of long-distance ______ signals and short-distance ____ signals | electrical, chemical p782 |
| * Communication by neurons largely consists of _____-distance chemical signals, and _____-distance electrical signals. | short, long p782 |
| ** Nerves are clustered in bigger clumps where information is processed. These clumps of neurons can be called a brain, or if their not quite big or sophisticated enough to be called a brain, they are often referred to as a ______ in simple animals. | ganglion (There are also small clusters of neurons in different parts of vertebrate bodies that would be referred to as ganglions) p782 |
| * The part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles is called the _____. | cell body p783,  |
| * The extensions of the neuron that receive incoming messages are the _____. | dendrites p783,  |
| * The extension of the neuron that transmits a signal to another cell is called the _____. | axon p783,  |
| * The small space between the terminal axon branch of one neuron and the dendrite of the post-synaptic cell is called a(n) _____. | synapse p783, 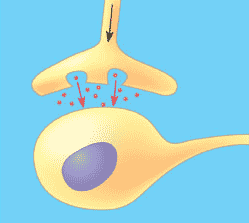 |
| * The cytoplasm at the end of an axon contains many small vesicles. What's in those vesicles? | neurotransmitters p783,  |
| ** _____ cells are supporting cells that are essential for the normal functioning of the neuron. | Glial cells (one type of glial cell is the Schwann cells that make up the myelin sheath in the PNS and oligodendrocytes that make up the myelin sheath in the CNS) p783 |
| ** Information processing by a nervous system occurs in three stages in the following order: _____, ______, and motor output. ______. | sensory input, integration, motor output. p784 |
| * _____-neurons transmit information about external stimuli, such as light, touch, or smell, or internal conditions, such as blood pressure or muscle tension. | Sensory p784 |
| * ____-neurons form the local circuits connecting neurons in the brain or ganglia and are responsible for the integration (analysis and interpretation) of sensory input. | Inter p784 |
| * _______ -neurons transmit signals to muscle cells, causing them to contract. | Motor p784 |
| * The vertebrate nervous system can be broken down into two parts. What are they? | Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) p784,  |
| * The inside of a nerve cell is _____ charged relative to the outside. | negatively p785 |
| ** The charge difference, or voltage, across the plasma membrane of a neuron, is called the ________. | membrane potential (This name reflects the fact that when there is a charge difference, potential energy is being stored) p785 |
| ** The charge difference, or ____, across the plasma membrane of a neuron, is called the membrane potential. | voltage p785 |
| ** For a resting neuron—one that is not sending a signal—the membrane potential is called the _____ potential. | resting p785 |
| * For most neurons, the concentration of ___ is higher inside the cell, while the concentration of is higher outside. | K+, Na+ p785, 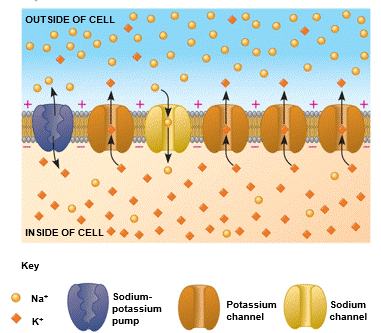 |
| * For most neurons, the concentration of K+ is higher _____ the cell, while the concentration of Na+ is higher ___. | inside, outside p785,  |
| * The gradient of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane of neuron is maintained by the ____. | sodium-potassium pump p785, 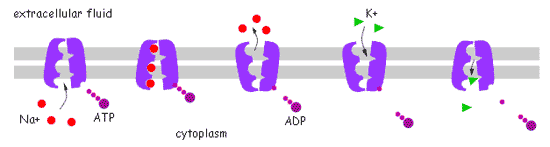 |
| * The sodium-potassium pump uses the energy from ____ to actively transport sodium and potassium ions across the nerve cell membrane against their concentration gradients. | ATP p785,  |
| * The sodium-potassium pump pumps sodium ions ____ the nerve cell and potassium ions ___ the nerve cell. | out of, into p785,  |
| * The sodium-potassium pump pumps potassium ions ____ the nerve cell and sodium ions ___ the nerve cell. | into, out of p785,  |
| * The sodium-potassium pump transports ___ sodium ions out of the cell for every ___ potassium ions that it transports simultaneously into the cell. | 3, 2 p785,  |
| The resting potential of a neuron is between ___ and ___ millivolts. | -60 to -80 (The negative represents the charge inside the cell which is negative) p785, 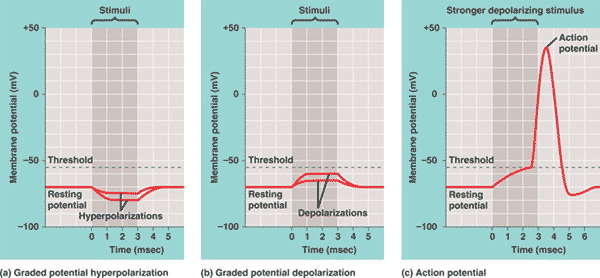 |
| ** ____ channels are always open, so they constantly leak ___ ions back across the nerve cell membrane by passive transport. | Potassium (This is why potassium channels are sometimes called "leak channels." This leaking of potassium ions back to the outside of the neuron helps maintain the resting potential in the negative range because potassium ions are positively charged, so when they go outside the cell, the inside becomes even more negative) p785,  |
| ** Most of the time, there are many more open ____ channels than there are ____ channels. | potassium, sodium (This is why the inside of a nerve cell has a negative charge. Positive charge of the potassium ions is flowing out faster than positive charge from sodium ions is flowing in) p785,  |
| ** What are the two types of gradients that exert influence on whether sodium and potassium ions flow and in which direction? | Chemical and electrical gradients (For instance, even though there is a strong chemical gradient favoring the flow of potassium ions out of the cell, there is an electrical gradient that opposes this flow, seeing as how the outside of the cell is positive. Potassium ions still flow out of the cell, but not nearly as fast as they would if there wasn't positive charge outside the cell opposing their flow in that direction) p786 |
| ** At what voltage is a neuron at it's equilibrium potential (that's the voltage that would stop the net movement of potassium ions down their concentration gradient to the outside of the cell where there are few potassium ions because the negative charge inside the cell is attractive enough to positively charged potassium ions that the flow is now in equilibrium, ie. no net flow)? | -90mV p786 |
| ** Even though the equilibrium potential of a neuron is -90mV (that's the amount of negative charge inside the cell that would stop the net outflow of potassium ions through the constantly open potassium channels), the resting potential of a neuron is usually between -60 and -80 mV. This is due to the fact that ___. | a small number of sodium channels are constantly leaking Na+ back in (which makes the inside of the cell a bit less negative than -90mV) p786 |
| ** If only sodium channels were open and not potassium, what would the equilibrium potential be for sodium ions? (In other words, what would the charge inside the cell be at the point where sodium would stop flowing in because the positively charged sodium ions would have their chemical gradient that favors their inflow opposed by a positive charge on the inside of the neuron) | + 62 mV (You might recall that the resting potential of a neuron is much closer to the equilibrium potential of potassium (-90mV) than it is to the equilibrium potential of sodium ions (=+62mV). That is because there are many more permanently open potassium channels than sodium channels, leading to a resting potential of somewhere between -60 and -80mV) p786 |
| ** Gated ion channels that open or close in response to a change in membrane potential are called _____. | voltage-gated ion channnels p788 |
| * In a resting neuron, _______ results from any stimulus that increases the outflow of positive ions or the inflow of negative ions. | hyperpolarization p788,  |
| ** What always leads to the greatest action potential possible? | .,  |
| * In a resting neuron, _______ results from any stimulus that increases the inflow of positive ions or the outflow of negative ions. | depolarization (In neurons, depolarization often involves the opening of gated Na+ channels) p788,  |
| * In neurons, depolarization often involves the opening of gated ____ channels (The answer is not "ion." Be more specific) | sodium (Na+) p788 |
| ** Small changes in membrane potential that don't lead to an action potential are called _____ potentials. | graded p788,  |
| * If an axon is stimulated, sodium channels will briefly open to allow the neuron to become slightly _______. If the stimulation is great enough, the membrane potential will exceed the threshold potential (-55 mV) to initiate the _______ potential. | depolarized, action potential p789,  |
| * If an axon is stimulated, sodium channels will briefly open to allow the neuron to become slightly depolarized. If the stimulation is great enough, the membrane potential will exceed the _____ potential (____) to initiate the action potential. | threshold, -55 mV p789,  |
| ** The ______-feedback loop of channel opening and depolarization triggers an action potential whenever the membrane potential reaches threshold, about -55mV, for many mammals. | positive p789 |
| * TRUE OR FALSE: Once initiated, the action potential has a magnitude that is dependent on the strength of the triggering stimulus. | FALSE (An action potential is an "all-or-none" response. As long as the stimulus is sufficient to decrease the membrane potential past -55mV, the action potential will proceed the same way no matter how strong the stimulus was that triggered the action potential) p789,  |
| * Which type of voltage-gated ion channel opens first at the start of an action potential? | sodium p789, 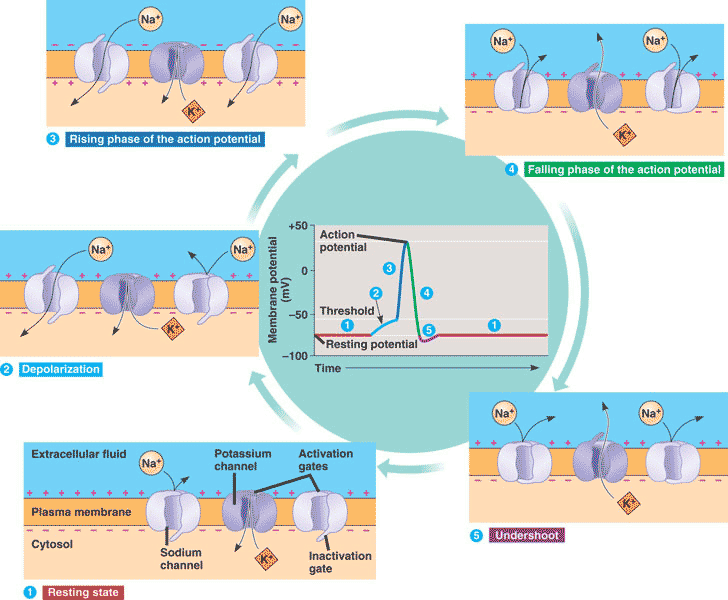 |
| ** There are two gates (a.k.a. loops) on a voltage-gated sodium channel. The gate that opens once the membrane potential reaches -55mV is called the ______ loop. At the peak of the action potential, the other gate, which is normally open all the time and is called the _____ loop, closes. | activation, inactivation (Once the inactivation loop closes, it takes awhile to reopen to its normal open state. No further action potentials can fire off until these gates reopen. Their re-opening is not dependent on voltage, only on time) p789,  |
* What is "A" referring to in the diagram below?, 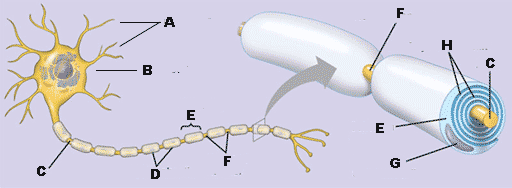 | dendrites p783,  |
** What is "B" referring to in the diagram below?,  | cell body p783,  |
* What is "C" referring to in the diagram below?,  | axon (it extends from the cell body to the end of the neuron) p783,  |
* The strong rapid depolarization seen in part B of the graph is caused by the ___ of ____ voltage-gated channels., 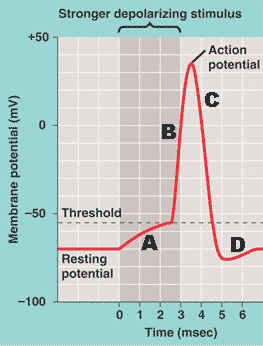 | opening, sodium 789,  |
* The change in membrane potential seen in part C of the graph is caused by,  | closing of sodium channels and the opening of potassium channels p789,  |
** The part of the graph in part D is called the ____.,  | undershoot pp789&790,  |
** Explain why the undershoot (part D of the graph) occurs.,  | In addition to the potassium channels that are always open at resting potential, some voltage-gated potassium (K+) channels that opened during the action potential remain open for a little while longer. pp789&790,  |
| ** The “downtime” when a second action potential cannot be initiated is called the _____ period | refractory (Your book doesn't completely explain this, but the refractory period actually has two phases. During the "relative refractory period", a neuron can't respond to another stimulus as easily It takes more stimulus to start another action potential because a lot of the sodium channels and potassium channels haven't reset themselves to the point where they can be opened again, plus the membrane potential is hyperpolarized and therefore further from the threshold potential. Parts B and C of this graph are in the absolute refractory period because none of the channels are capable of opening again, because they haven't reset themselves) p791,  |
| ** What needs to occur for the refractory period to end, allowing a neuron to be capable of firing off a new action potential without having to be hyperstimulated? | The inactivation loops (gates) on the sodium channels need to reopen (and this takes time because they are slow to reopen even though they are stimulated to do so once the cell starts to become repolarized) p790,  |
** TRUE or FALSE: At the peak of the action potential, there are now more sodium ions on the inside of the cell than outside, and more potassium ions outside the cell than inside.,  | FALSE (Only a small fraction of sodium and potassium ions change place during the action potential. Even though the concentration of each changes slightly, there are always way more sodium ions outside the cell and potassium ions inside the cell) p791,  |
** The inward current of Na+ that depolarizes the axon membrane ahead of the action potential cannot produce another action potential behind it to go in both directions because _____. This is the reason action potentials do not travel back toward the cell body.,  | the voltage-gated sodium channels behind it that were recently opened closed their inactivation gates and they don't respond to voltage (so even though the voltage is still in the range that would open a voltage-gated sodium channel, it won't open. Only the gates ahead of the action potential can open) p791,  |
| * It's the ___ of action potentials, not their ____, that conveys information about the stimuli that are being received. | frequency, strength (All action potentials have the same strength. How frequently they are triggered matters. In hearing, for example, louder sounds trigger more frequent action potentials in neurons linking the ear to the brain.) p791 |
* What is "D" referring to in the diagram below?,  | myelin sheath p792,  |
** What is "E" referring to in the diagram below?,  | Schwann cell p792,  |
** What is "F" referring to in the diagram below?,  | nodes of Ranvier p792,  |
| ** _____ cells are supporting cells that are essential for the normal functioning of the neuron. | Glial cells (one type of glial cell is the Schwann cells that make up the myelin sheath in the PNS and oligodendrocytes that make up the myelin sheath in the CNS) p792,  |
| ** ______ cells are glial cells that form the myelin sheath around the axons of neurons in the peripheral nervous system, speeding the passage of impulses. | Schwann cells (Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheet around neurons of the CNS) p792 |
| ** Which type of cells form the myelin sheath in the central nervous system? | oligodendrocytes (in the peripheral nervous system, its the Schwann cells that form myelin) p792 |
| * What does the myelin sheath do to nerve impulses? | speed them up (the action potential jumps from one node of ranvier to the next, speeding up the impulse over what it would have been if the depolarization had to occur along the whole length of the axon. This jumping impulse is called saltatory conduction) p792,  |
| ** What are two structural features of an axon that can lead to faster action potential conduction? | larger diameter and the myelin sheath p792 |
| ** If an axon is ______, the action potential (impulse) moves down the axon even faster because it leaps from node to node in ______ (jumping) fashion. | myelinated, saltatory p792,  |
| ** In myelinated axons, voltage-gated sodium channels are restricted to gaps in the myelin sheath called ____. | nodes of Ranvier p792,  |
| ** An action potential propagating along a myelinated axon appears to jump from one such node to another, a process called ____. | saltatory conduction p792,  |
| ** Action potentials propagate more rapidly in myelinated axons because the time-consuming process of ______ occurs at only a limited number of positions along the axon. | opening and closing ion channels p792,  |
| ** Neurotransmitters are packaged inside ______ near the axon terminal (synaptic terminal). | synaptic vesicles p793,  |
| ** _____ are packaged inside synaptic vesicles near the axon terminal (synaptic terminal). | Neurotransmitters p793,  |
| * The entrance of _____ through gated channels in the presynaptic membrane stimulates vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane, releasing neurotransmitters into the synapse. | calcium ions (Ca++) p793,  |
| ** What opens the calcium channels in the presynaptic membrane of the axon terminus? | Depolarization of the membrane caused by an arriving action potential (the calcium channels are voltage-gated channels) p793 |
| * Once in the synapse, neurotransmitters bond with ______ embedded in the postsynaptic membrane. | receptors (usually a ligand gated channel that allows ions to flow into the postsynaptic neuron and stimulate an action potential) p793 |
| * Neurotransmitters in the synapse are either destroyed by _____ in the synapse, taken back into the presynaptic neuron (reuptake) by active transport, or diffuses out of the synapse. | enzymes (Many drugs and poisons work by interfering with enzymes meant to degrade neurotransmitters or by interfering with the re-uptake of neurotransmitters back into the pre-synaptic neuron. Both of these events lead to higher than normal amounts of neurotransmitter in the synapse) p793 |
| ** At many chemical synapses, the receptor protein that binds and responds to neurotransmitters is a ____-gated ion channel | ligand p794 |
| ** If a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that opens up channels to both Na+ and K+ ions on the post-synaptic membrane, the membrane potential starts to depolarize, making it easier to reach the threshold for an action potential to fire off. This type of depolarizing stimulus is referred to as a(n) ____ postsynaptic potential | excitatory p794 |
| ** If a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that opens up channels to only K+ ions (not Na+) on the post-synaptic membrane, the membrane potential starts to hyperpolarize, making it harder to reach the threshold for an action potential to fire off. This type of depolarizing stimulus is referred to as a(n) ____ postsynaptic potentia | inhibitory p794 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: The input from a single action potential coming from a pre-synaptic neuron is typically not strong enough to cause the post-synaptic neuron to fire off. | TRUE (It usually takes the input of axons from several different pre-synaptic neurons to cause the post-synaptic neuron to fire off. It can also be triggered to fire off by the rapid arrival of several action potentials in succession coming from the same pre-synaptic neuron.This cumulative effect of multiple excitatory stimuli is called summation) p794 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: Stimulation from a pre-synaptic neuron can inhibit the firing off of a post-synaptic neuron. | * TRUE (If the stimulus causes only K+ ions to enter the post-synaptic neuron, the post-synaptic neuron will hyperpolarize, causing it to have a harder time firing off) p794 |
| ** The cumulative effect of multiple excitatory and inhibitory stimuli on a post-synaptic neuron is known as ____. | summation (If the sum of both the excitatory (positive) and inhibitory (negative) post-synaptic potentials causes the membrane potential to reach the threshold of -55mV, then an action potential will fire off in the post-synaptic neuron) pp794&795,  |
| * If the sum of both the excitatory (positive) and inhibitory (negative) post-synaptic potentials causes the membrane potential in the post-synaptic neuron to reach the threshold of -55mV, it will lead to a(n) ______ potential in the post-synaptic neuron. | action (The purple stimulus is inhibitory and the green ones are excitatory in the graphic below) pp794&795,  |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Some neurotransmitters are excitatory while others are inhibitory, but never both. | FALSE (It depends on what type of receptor the neurotransmitter binds to, and often times, a certain neurotransmitter can bind to several different receptors, some of which might be excitatory and some of which might be inhibitory) p 796 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: All neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated ion channels. | FALSE (Most are, but some activate a G protein-coupled receptor which starts a signal transduction pathway in the cell. This leads to a slower but more long-lasting response) p795 |
| ** Which two neurotransmitters affect a person's mood the most? | Dopamine and seratonin (In fact, most anti-depressants either inhibit the re-uptake of seratonin or mimic dopamine) p796 |
| ** Which neurotransmitter is essential for muscle stimulation and memory formation, and can be mimicked by nicotine which causes a stimulating effect by binding to certain types of receptors for this neurotransmitter? | acetylcholine (Ach) pp795&796 |
| ** Neurotransmitters called ____ function as natural analgesics, decreasing pain perception (and can also lead to sensations of euphoria) | endorphins (Runners "high" is caused by the release of endorphins when you put your body under high physical stress during a long run. Opiates like heroin and morphine mimic endorphins) p796 |
| ** A gas that is used as both a neurotransmitter between neurons and a local regulator between other types of cells is ____. | nitric oxide (NO) p797 |