| A | B |
|---|
| * Humans have about ____ brain cells. | 100 billion p800 |
| ** The simplest animals that have a nervous system can be found in the phylum called ____. | cnidaria (Pronounced "n-eye-dare-e-ah", these animals all have tentacles and stinging cells. They include jellyfish, hydras, corals, and sea anemones. Only the phylum "porifer" with the sponges is simpler and more ancient. Poriferans don't have any nerves. There is no cluster of nerves in cnidarians, just a nerve net that functions to stimulate the contraction of protein fibers) p800,  |
| * In more complex animals, the axons of multiple neurons are often bundled together to form ____, fibrous structures that channel and organize information flow. | nerves p801 |
| ** The evolutionary trend of clustering nerves at the anterior end of a bilaterally symmetrical animal is called ____. | cephalization (The prefix "cephala" refers to the head. Clustering sensory neurons near the anterior portion of the animal where they are likely to encounter the most stimuli lead to a head region where most of the nerves could be found in what could be called a ganglion or a brain, depending on how big the cluster is. The Planaria shown below is in the phylum Platyhelminthes "Flatworms" and shows a primitive degree of cephalization with light-sensing eyespots and what could be considered a brain. The blue stuff is the nervous system)) p801,  |
| * In many animals, neurons that carry out integration form a ____ nervous system. | central p801,  |
| * neurons that carry information into and out of the CNS form a ____ nervous system | peripheral p801,  |
| * In vertebrates, the ___ and together form the central nervous system (CNS). | brain, spinal cord p801,  |
| * _____ are cells that support normal functioning of the neurons. | Glia |
| ** ____ are cells that provide immune defense in the CNS. | Microglia p801 |
| ** ______ cells are glial cells that form the myelin sheath around the axons of neurons in the peripheral nervous system, speeding the passage of impulses. | Schwann cells (Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheet around neurons of the CNS) p801 |
| ** Which type of cells form the myelin sheath in the central nervous system? | oligodendrocytes (in the peripheral nervous system, its the Schwann cells that form myelin) p801 |
| * The ____ barrier is a physiological mechanism that prevents many substances in the blood from entering the CNS. | blood-brain (This system of cells prevents pathogens from entering the central nervous system, but also makes it difficult for drugs that target the central nervous system from getting to the central nervous system. Different strategies are used to get these drugs across the blood-brain barrier) p802 |
| * Another word for the vertebral column is the ___. | spine p802 |
| ** Another word for the spine is the ___. | vertebral column p802 |
| * ____ are fast responses that don't require sensory information to go all the way to the brain before motor neurons can be activated. | Reflexes (Next time you put your hand on a hot stove, notice that your hand will pull away before it even registers in your brain that you touched something hot. You would get burned a lot worse if that message had to go all the way to your brain and you actually had to think about whether or not to pull your hand away) p802,  |
| ** Both the brain and spinal cord have ___ matter which is primarily neuron cell bodies, and ____ matter which is primarily bundled axons. | gray, white p802,  |
| ** Both the brain and spinal cord have white matter which is primarily ____, and white matter which is primarily . | bundled axons, neuron cell bodies,  |
| ** The fluid-filled space in the spinal cord is called the ____ | central canal p802 |
| ** The fluid-filled spaces in the brain are called the ____. | ventricles p802 |
| ** The fluid that fills the central canal in the spinal cord and the ventricles is called ____. | cerebrospinal fluid (This fluid is formed in the brain by filtering arterial blood. It supplies the CNS with nutrients and hormones and carries away wastes, circulating through the ventricles and central canal before draining into the veins) p802 |
| ** The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and plays a large role in regulating an animal’s _____ and its ______. | movements, internal environment p802, 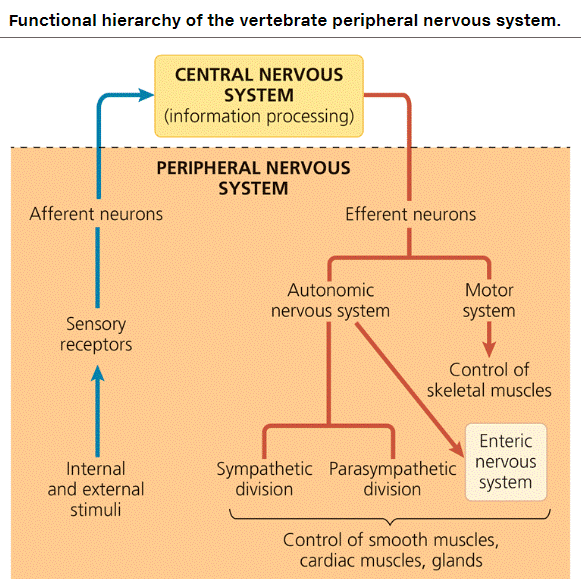 |
| *______ neurons of the PNS bring instructions from the CNS to the muscles, glands, and endocrine cells of the body. (Your choices are afferent or efferent) | Efferent (Efferent means "to carry away") p802,  |
| *______ neurons of the PNS bring sensory information to the CNS. (Your choices are afferent or efferent) | Afferent (Afferent means "to carry towards") p802,  |
| ** Most nerves are bundles of both _____ and _____ neurons. | afferent, efferent p802,  |
| * What are the two efferent components of the PNS? | Motor, autonomic p802,  |
| * The neurons of the ____ system of the PNS carry signals to skeletal muscles. | motor p802,  |
| ** The neurons of the motor system of the PNS carry signals to _____.. | skeletal muscles p802,  |
| ** Motor control can be voluntary, as when you raise your hand to ask a question, or involuntary, as in a(n) ____. | reflex p802,  |
| ** Which type of muscles are regulated by the autonomic nervous system? | smooth and cardiac p803,  |
| * Regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles by the autonomic nervous system is generally _____. | involuntary p803,  |
| **What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system that regulate organs of the cardiovascular, excretory, and endocrine systems? | sympathetic and parasympathetic p803,  |
| ** The part of the autonomic nervous system that exerts direct and partially independent control over the digestive tract, pancreas, and gallbladder is called the ____ nervous system. | enteric p803,  |
| * Activation of the ____ division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the “fight-or-flight” response. | sympathetic (I remember this by thinking that if you have to activate this division, you deserve some sympathy) p803, 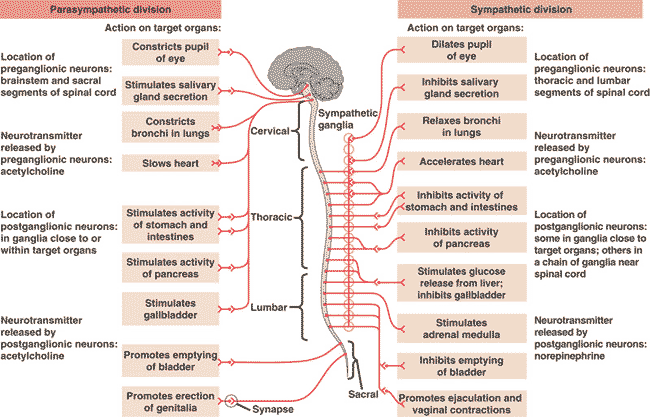 |
| ** Activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the “_____” response. | fight-or-flight p802,  |
| * Which division of the autonomic nervous system causes responses that promote calming and a return to self-maintenance functions (“rest and digest”)? | parasympathetic (The parasympathetic has opposite (antagonistic) effects to each other, with the sympathetic division initiating "fight or flight" responses, including quickening of the heart rate, release of adrenaline, and cessation of digestive activities) p803,  |
| * What do we call the part of the brain essential for language, cognition, memory, consciousness, and awareness of our surroundings? | the cerebrum p808,  |
| ** In which part of the cerebrum do cognitive functions mainly reside in? | the cerebral cortex (This is the outer layer of cerebrum. Whenever you hear the word "cortex" it is referring to the outer layer of something. For instance the adrenal cortex "outer part of the adrenal gland" and the renal cortex "outer layer of kidney") p808,  |
| ** Within this cerebral cortex, ____ areas receive and process sensory information, ____ areas integrate the information, and ____ areas transmit instructions to other parts of the body. | sensory, association, motor p808,  |
* The highlighted part of this human brain is called the ______.,  | cerebrum (which is composed of two cerebral hemispheres) p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "A" pointing to?, 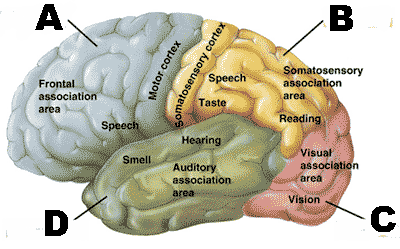 | Frontal Lobe p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "B" pointing to?,  | Parietal lobe p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "C" pointing to?,  | Occipital lobe p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "D" pointing to?,  | Temporal lobe p809,  |
| ** Defects in a small region of the left frontal lobe, known as ____ area, cause people to be unable to speak even though they are able to understand speech. | Broca’s p808,  |
| ** Defects in a small region of the left frontal lobe, known as Broca's area, cause people to be unable to ____ even though they are able to ____. | speak, understand speech p808,  |
| ** Defects in a small region of the posterior portion of the left temporal lobe, known as Wernicke’s area, cause people to be unable to ____ even though they are able to ____. | understand speech, speak p808,  |
| ** Defects in a small region of the posterior portion of the left temporal lobe, known as ____, cause people to be unable to understand speech even though they are able to speak. | Wernicke’s area p808,  |
| ** Which cerebral hemisphere has a greater role in language? | left side p808,  |
| ** Which cerebral hemisphere has a greater role in math and logical operations? | left side p808 |
| ** Which cerebral hemisphere has a greater role in recognition of faces and patterns, spatial relations, and nonverbal thinking? | right side p808 |
| ** The difference in function between the right and left hemispheres is called ____. | lateralization p808 |
| * The thick band of axons that allows communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _____. | corpus callosum pp 805 & 808, 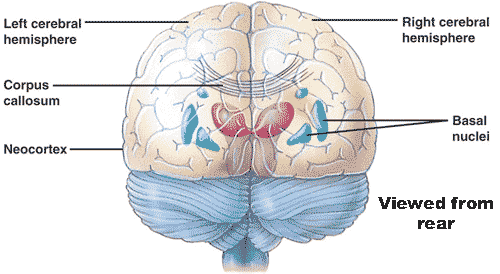 |
| ** ____ receptors provide information about touch, pain, pressure, temperature, and the position of muscles and limbs. | Somatosensory p809 |
| ** Which brain structure's primary function is as a relay center through which sensory nerves transmit signals from the spinal cord and brainstem on the way to the cerebral cortex. | the thalamus p809, 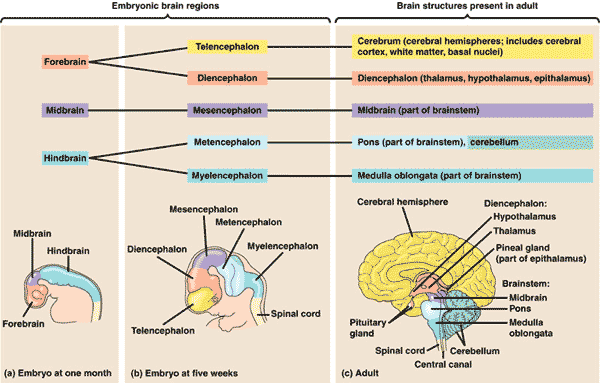 |
| ** Which part of the frontal lobe is involved with decision making and planning? | the prefrontal cortex p809,  |
| * Damage to which lobe of the cerebral cortex would be most likely to change personality and impair decision making? | the frontal lobe p809 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: Vertebrates have the same basic brain structure as any other vertebrate. | TRUE p809, 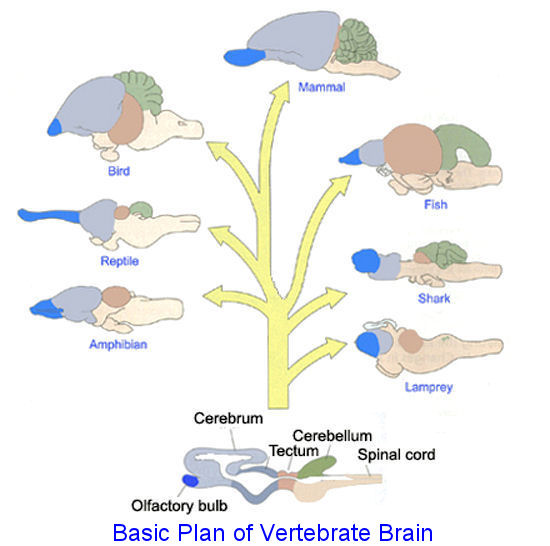 |
| * The capacity for the nervous system to be remodeled (by adding, deleting, strengthening, or weakening synaptic connections), especially in response to its own activity, is called _____. | neuronal plasticity (This is why you need to review material you learn on a regular basis. Otherwise, you will forget it) p810, 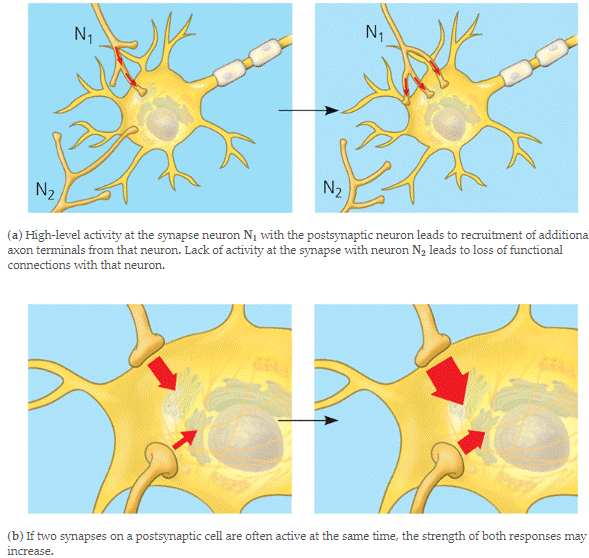 |
| ** Short-term and long-term memory both involve the storage of information in the _____.. | cerebral cortex p811,  |
| ** Where are short-term memories temporarily stored? | the hippocampus p811,  |
| * When is it thought that important information stored in short-term memory gets consolidated into long-term memory? | During sleep (This is why it is a bad strategy to cram for tests by pulling all-nighters. At best, you might be able to recall it for the test, but you will forget everything right after the test. Any gains are probably off-set by being too tired to think straight during the test. Your best strategy in college is to study on a very regular basis and only study slightly more just before a test, but get to bed early. Trust me!) p811 |
| ** Which small region of the brain could be considered the "pleasure center" because of its important role in processing reward stimuli? | The nucleus accumbens p803, .gif) |
| ** Which small region of the brain's limbic system could be considered the "emotional center" of the brain due to its key role in processing emotional stimuli? | the amygdala (This part of the brain also plays a key role in memory retention. Learning that is accompanied by higher levels of activity in the amygdala leads to stronger and longer lasting long-term memory. When an emotion can be paired with a learning event, things tend to be remembered better) p803 & 806,  |
| ** The limbic system is your _____ control center. | emotional (Notice that the limbic system involves several regions of the brain, but most notably, the amygdala which has a crucial role in processing emotions) p806,  |
| ** The ____ system is your emotional control center. | limbic (Notice that the limbic system involves several regions of the brain, but most notably, the amygdala which has a crucial role in processing emotions) p806,  |
| ** Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) measures brain activity by measuring an increase in ____ to particular parts of the brain during various activities. | blood flow p803 |
| * As a human embryo develops, the neural tube forms three anterior bulges—the _____, , and ______ —that together produce the adult brain. | forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain p804,  |
| ** The midbrain and portions of the hindbrain give rise to the ____, a stalk that joins with the spinal cord at the base of the brain. | brainstem pp804 & 805,  |
| ** The brainstem, going from anterior to posterior, is made of the ____, _____, and _____. | midbrain, pons, medulla pp804 & 805,  |
| ** The hindbrain gives rise to the ____, ____, and ____ in the adult brain. | pons, medulla, cerebellum p804,  |
| ** The forebrain develops into the ____, including the neuroendocrine tissues of the brain (thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus), and the ______, which becomes the cerebrum. | diencephalon, telencephalon p804,  |
| ** The telencephalon of the forebrain develops into the ____ in adults. | cerebrum (The cerebrum includes the cerebral cortex and basal nuclei) p804,  |
| * The outer layer of the cerebrum is called the ____ and is vital for perception, voluntary movement, and learning. | cerebral cortex p804,  |
| * TRUE or FALSE: The left cerebral hemisphere receives information from, and controls the movement of, the left side of the body while the right cerebral hemisphere does the same for the right side of the body. | FALSE (The both receive information from and control the opposite sides of the body) p805,  |
| ** Deep within the white matter of the cerebrum, clusters of neurons called ___ serve as centers for planning and learning movement sequences. Damage to these sites during fetal development can result in cerebral palsy, a disorder resulting from a disruption in the transmission of motor commands to the muscles. | basal nuclei (Remember, the cerebrum is made up of the cerebral cortex which is composed of gray matter, mostly cell bodies of neurons. The cerebral cortex also includes the basal nuclei found interior to the cerebral cortex in the white matter region which is composed mostly of axons) p805,  |
* The highlighted portion of the brain in the picture below is the ______., 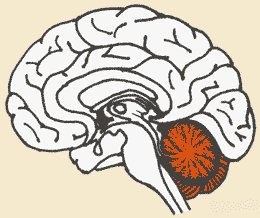 | cerebellum (The cerebellum is responsible for coordinating movement, planning, motor activities, learning and remembering of physical skills and for some cognitive abilities) p805,  |
| * Which part of the brain is associated with coordination and the memorization of physical skills (like skiing)? | the cerebellum p805,  |
* The portion of the brain highlighted below is called the _____ and consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. It functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, and conduction of information to higher brain centers., 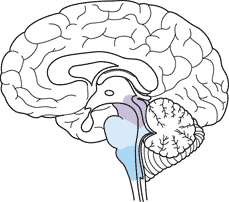 | brainstem pp804 & 805,  |
| * The ____ is the main input center for sensory information going to the cerebrum. | thalamus p805,  |
| * The ____ constitutes a control center that includes the body’s thermostat as well as the central biological clock. Through its regulation of the _____ gland, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behaviors, and initiates the fight-or-flight response. | hypothalamus, pituitary p805,  |
| ** The ___ gland is the source of a hormone called melatonin. | pineal (Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep–wake cycle. It is primarily released by the pineal gland. As a supplement, it is often used for the short-term treatment of trouble sleeping such as from jet lag or shift work. Evidence of benefit, however, is unclear.) p805,  |
| ** The pineal gland is the source of a hormone called _____ | Melatonin (Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep–wake cycle. It is primarily released by the pineal gland. As a supplement, it is often used for the short-term treatment of trouble sleeping such as from jet lag or shift work. Evidence of benefit, however, is unclear.) p805,  |
| ** All sensory axons involved in hearing either terminate in the ___ or pass through it on their way to the cerebrum. In addition, it also coordinates visual reflexes, such as the peripheral vision reflex. | midbrain p805,  |
| ** The ___ and ___ help coordinate large-scale body movements, such as running and climbing. Most axons that carry instructions about these movements cross from one side of the CNS to the other as they pass through the ___. | pons, medulla, medulla p805,  |
| * Which part of the brainstem controls several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion? | The medulla p805,  |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: External stimuli are still received during sleep. | TRUE (but they are not consciously perceived) p803 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Sleep is an active state in the brain. | TRUE (During sleep, there are active changes in brainwave patterns that coincide with different stages of sleep. It is also during sleep that a lot of information in short-term memory is organized and transferred to long-term memory, if it is worth remembering. If you don't think what you are learning is particularly important, you are unlikely to remember it because it is unlikely that your brain will transfer it into long-term memory) p806 |
| ** Cycles of sleep and wakefulness are an example of a ___ rhythm, a daily cycle of biological activity. | circadian p806 |
| ** The suprachiasmatic nucleus is a tiny cluster of neurons in the hypothalamus that acts as our _____. | biological clock (In response to sensory information from the eyes, the SCN acts as a pacemaker, synchronizing the biological clock in cells throughout the body to the natural cycles of day length) p806 |
| ** Emotions are strongly influenced by a neural circuit in the brain called the _____ which provides motivation for activities that enhance survival and reproduction, such as eating in response to hunger, drinking when thirsty, and engaging in sexual activity when aroused. | reward system p807 |
| ** Inputs to the reward system are first received by neurons in a region near the base of the brain called the ____. When activated, these neurons release the neurotransmitter _____ from their synaptic terminals within specific regions of the cerebrum. Targets of this signaling include the prefrontal cortex, discussed shortly, and the nucleus accumbens. | ventral tegmental area (VTA), dopamine (Cocaine is a dopamine re-uptake inhibitor, so it stimulates the reward system without you having to do anything worthy of a reward. This eventually makes it more difficult to naturally activate your reward system, leading to addiction as the only way to really get rewards anymore) p807,  |
| * Stimuli are detected by ____ receptors. | sensory p811 |
| * If a sensory receptor is a neuron, a larger stimulus results in more _____. If the receptor is not a sensory neuron, a larger stimulus usually causes more ____. | frequent action potentials, neurotransmitter to be released p812 |
| * If a sensory receptor is not a neuron, a larger stimulus results in more _____. If the receptor is a neuron, a larger stimulus usually causes more ____. | neurotransmitter to be released, frequent action potentials p812 |
| * Perceptions—such as colors, smells, and sounds—are constructions formed in the brain and do not ___. | exist outside it (This is really interesting if you think about. What you and I think of as color is just the frequency of electromagnetic energy waves that reflect off of a surface. We all call frequencies of 700nm "red" but what your brain makes this frequency look like may not be the same as what my brain makes it look like, yet we've both learned to call it "red." Same goes for smell. Smell is just the detection of a certain chemical that we breathed in. Our brain turns the detection of that chemical into a smell. But what smells good to some people might not smell good to others. If the smell indicates a chemical that we should stay away from, it is an evolutionary advantage for our brain to perceive it as something bad) p.812 |
| ** Upon continued stimulation, many receptors undergo a decrease in responsiveness known as ___. | sensory adaptation (One form of this is olfactory fatique. Olfaction refers to the sense of smell. If you smell something for long periods of time, you won't be able to smell it very well anymore. This is the reason why you usually don't smell your own body odor even though everyone else does) p812 |
| ** Our senses of hearing and of balance, as well as our response to pressure, touch, stretch, and motion, rely on ____. (Hint: The word I'm looking for ends in "receptor") | mechanoreceptors p812 |
| ** Our senses of sight relies on ____. (Hint: The word I'm looking for ends in "receptor") | electromagnetic receptors (Humans seem to be limited to detecting a small subset of electromagnetic wavelengths between 380 and 700nm. Some other species can detect light in the infrared or UV range. Some species, like sharks, can detect electric fields generated by the electrical activity of neurons in their prey. Some animals can detect Earth's magnetic fields to help them find their way while migrating) p813 |
| Our senses of temperature relies on ____. (Hint: The word I'm looking for ends in "receptor") | thermoreceptors p813 |
| ** Extreme pressure or temperature, as well as certain chemicals, can damage animal tissues. To detect stimuli that reflect such noxious (or harmful) conditions, animals rely on ____ , also called ___ receptors. | nociceptors, pain p813 |
| ** The perceptions of olfaction (smell) and gustation (taste) both depend on ____. (Hint: The word I'm looking for ends in "receptor") | chemoreceptors p813 |
| * The perceptions of olfaction is the perception of ____. | smell p813 |
| * The perceptions of gustation is the perception of ____. | taste p813 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: The only chemicals that you can smell are chemicals that are suspended in or part of air. | TRUE p813 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: Chemicals that you can taste must be dissolved in solution. | TRUE p813 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: All chemoreceptors are either involved with detecting taste or smell. | FALSE (Some chemoreceptors detect the concentration of substances, such as hydrogen ions or salt concentrations in your body. As an example, your brain has chemoreceptors that detect your H+ ion concentrations, pH, in your blood and use this information to automatically speed up or slow down your breathing) p813 |
| ** A(n) ____ is a chemical that can be detected in a solution and turned into the perception of taste. | tastant p813 |
| ** A(n) ____ is a chemical that can be detected in air and turned into the perception of smell. | odorant p813 |
| ** How many types of tastants can humans and other mammals detect? | 5 (The five are sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. Umami (which means “pleasant savory taste” in Japanese) describes the savory quality of meat, aged cheese, and certain other foods that contain high levels of the amino acid glutamate) p813 |
| ** How many types of odorants can humans and other mammals detect? | Hundreds for humans and thousands for some mammals p813 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Different parts of the tongue detect different tastes. | FALSE (This is a common misconception. Each part of the tongue with taste buds has each of the 5 different types of cells that detect the 5 different types of tastes within the taste bud) p814 |
| ** To sense gravity and maintain equilibrium, most invertebrates rely on mechanoreceptors located in organs called ____ where granules formed by grains of sand or other dense materials, sit freely in a chamber lined with ciliated receptor cells. Each time an animal repositions itself, the granules resettle, stimulating mechanoreceptors at the low point in the chamber. | statocysts p814 |
| ** Another word for the eardrum is the ____. | tympanic membrane p815,  |
| ** The _____ is a passage that connects to the pharynx and equalizes pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. | Eustachian tube p815,  |
| ** In the middle ear, three small bones—the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup)—transmit vibrations to the ____, which is a membrane beneath the stapes. | oval window p815,  |
| ** The inner ear consists of fluid-filled chambers, including the ____, which function in equilibrium, and the coiled _____ (from the Latin meaning “snail”), a bony chamber that is involved in hearing. | semicircular canals, cochlea p815,  |
| ** Which part of the ear is responsible for equilibrium and balance? | the semicircular canals p815,  |
| ** Which part of the ear is responsible for hearing (the answer is a bony fluid filled structure that receives vibrations from the middle ear bones through the oval window membrane)? | the cochlea p815,  |
| * Sound is detected in the ear when vibrations that have been transmitted to the cochlea cause ____ to bend which triggers action potentials on the cells that they are attached to. | hairs p816, 
|
| ** Chambers in the inner ear called the utricle and saccule allow us to perceive position with respect to gravity as well as linear movement. Situated in a vestibule behind the oval window, each of these chambers contains hair cells that project into a gelatinous material. Embedded in this gel are small calcium carbonate particles called ______ (“ear stones”). When you tilt your head, they shift position, contacting a different set of hairs protruding into the gel. The hair cell receptors transform this deflection into a change in the output of sensory neurons, signaling the brain that your head is at an angle. The ear stones are also responsible for your ability to perceive acceleration, such as when a stationary car in which you are sitting moves forward. | otoliths p816 |
| ** Sensory cells that contain light-absorbing pigment molecules are called ____. | photoreceptors p817 |
| * Insects, crustaceans, and some polychaete worms have ____ eyes | compound (These types of eyes are very good at detecting movement. It must be similar to when you go into Best Buy and there are a bunch of TV's on the wall each showing the same thing. Notice how it captures your attention right away when something moves) p818,  |
| ** Once light enters the eye, the energy of each photon is captured by a shift in configuration of a single chemical bond in ____, the light-absorbing molecule in the visual pigment ____. | retinal, rhodopsin p819 |
| * The clear part layer at the front of the eye is called the ____. | cornea p818, 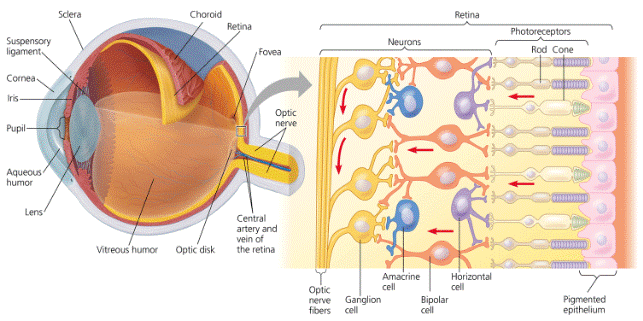 |
| * Which part of the eye changes the diameter of the pupil to regulate how much light enters the eye? | the iris (this is the colored part of your eye) p818,  |
| * The innermost layer of the eye that contains the photoreceptors and neurons is called the ____. | retina p818,  |
| * The part of the eye that changes shape to focus images is called the ____. | lens p818,  |
| * The optic disk, where the optic nerve exits the retina, lacks photoreceptors. As a result, this region forms a “____." | blind spot p818,  |
| * A type of photoreceptor in the retina of an eyeball called a(n) ____ is good at detecting faint light, but doesn't detect color. | rod (Rods are found around the boundary of the retina, whereas cones are found in the center of the retina. That is why if you stare straight at a faints star, it will seem to disappear, because the faint light is no longer hitting rods, but only cones at the center-back of the eyeball, and cones are poor at detecting faint light) p819 |
| * A type of photoreceptor in the retina of an eyeball called a(n) ____ is good at detecting colors, but doesn't detect faint light. | cone p819 |
| ** Three different cones respond to different wavelengths of light. The colors of light they respond best to (starting with the longest wavelength) are ____, _____, and ____. | red, green, and blue (The three visual pigments, called photopsins, are formed from the binding of retinal to three distinct opsin proteins. Slight differences in the opsin proteins cause each photopsin to absorb light optimally at a different wavelength. By combining the relative strength of signal from each of the three different types of cones, the brain is able to visualize all the different colors, whatever that means. Remember, color is just our perception of different wavelengths of the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum) p819&821 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Mammals are the only vertebrates that have good color vision. | FALSE (In fact, most other vertebrates including fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds, have very good color vision. Most mammals do not. Only primates, which includes us, have good color vision among the mammals) p821 |
| ** TRUE or FALSE: Abnormal color vision stems from the inability of the occipital lobe to interpret visual input correctly. | FALSE (Abnormal color vision typically results from mutations in the genes for one or more photopsin proteins. In humans, color blindness nearly always affects perception of red or green and is far more common in one gender than the other: 5–8% of males, fewer than 1% of females. Why? The human genes for both the red and green pigments are X-linked. Thus, males are affected by a single mutation, whereas females are color-blind only if both copies are mutant. The human gene for the blue pigment is on chromosome 7.) p821 |
| ** The center of the visual field is called the ____. | fovea (At the fovea, there are there are no rods but a very high density of cones—about 150,000 cones per square millimeter. The ratio of cones to rods decreases with distance from the fovea, with the peripheral regions having only rods. In daylight, you achieve your sharpest vision by looking directly at an object, such that light shines on the tightly packed cones in your fovea. At night, looking directly at a dimly lit object is ineffective, since the rods—the more sensitive light receptors—are absent from the fovea. For this reason, you see a dim star best by focusing on a point just to one side of it.) p821,  |