| A | B |
|---|
| * Humans have about ____ brain cells. | 100 billion p800 |
| * In more complex animals, the axons of multiple neurons are often bundled together to form ____, fibrous structures that channel and organize information flow. | nerves p801 |
| * In many animals, neurons that carry out integration form a ____ nervous system. | central p801,  |
| * neurons that carry information into and out of the CNS form a ____ nervous system | peripheral p801,  |
| * In vertebrates, the ___ and together form the central nervous system (CNS). | brain, spinal cord p801,  |
| * _____ are cells that support normal functioning of the neurons. | Glia |
| * The ____ barrier is a physiological mechanism that prevents many substances in the blood from entering the CNS. | blood-brain (This system of cells prevents pathogens from entering the central nervous system, but also makes it difficult for drugs that target the central nervous system from getting to the central nervous system. Different strategies are used to get these drugs across the blood-brain barrier) p802 |
| * Another word for the vertebral column is the ___. | spine p802 |
| * ____ are fast responses that don't require sensory information to go all the way to the brain before motor neurons can be activated. | Reflexes (Next time you put your hand on a hot stove, notice that your hand will pull away before it even registers in your brain that you touched something hot. You would get burned a lot worse if that message had to go all the way to your brain and you actually had to think about whether or not to pull your hand away) p802,  |
| *______ neurons of the PNS bring instructions from the CNS to the muscles, glands, and endocrine cells of the body. (Your choices are afferent or efferent) | Efferent (Efferent means "to carry away") p802, 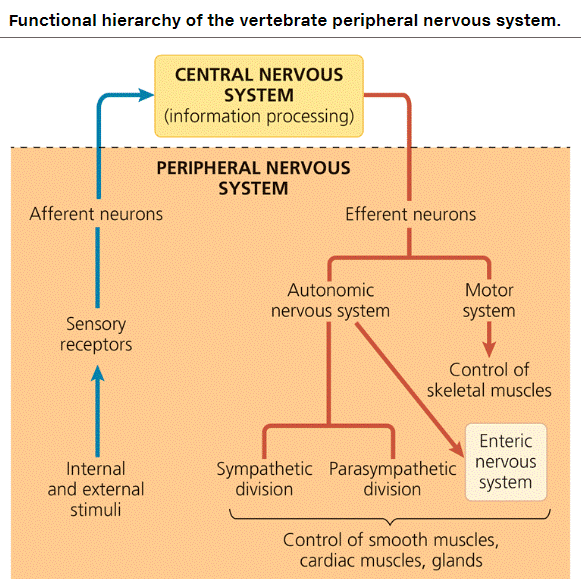 |
| *______ neurons of the PNS bring sensory information to the CNS. (Your choices are afferent or efferent) | Afferent (Afferent means "to carry towards") p802,  |
| ** Most nerves are bundles of both _____ and _____ neurons. | afferent, efferent p802,  |
| * What are the two efferent components of the PNS? | Motor, autonomic p802,  |
| * The neurons of the ____ system of the PNS carry signals to skeletal muscles. | motor p802,  |
| * Regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles by the autonomic nervous system is generally _____. | involuntary p803,  |
| * Activation of the ____ division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the “fight-or-flight” response. | sympathetic (I remember this by thinking that if you have to activate this division, you deserve some sympathy) p803, 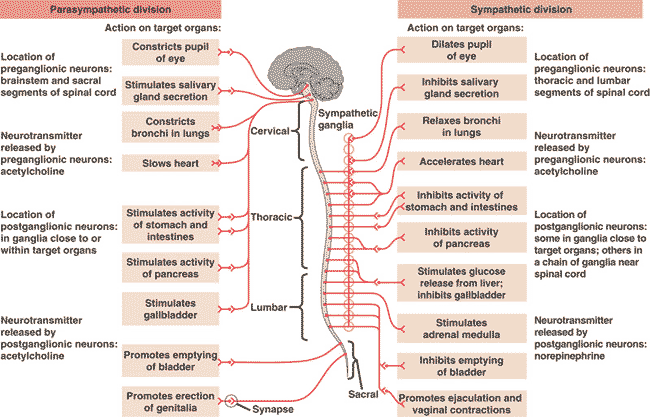 |
| * Which division of the autonomic nervous system causes responses that promote calming and a return to self-maintenance functions (“rest and digest”)? | parasympathetic (The parasympathetic has opposite (antagonistic) effects to each other, with the sympathetic division initiating "fight or flight" responses, including quickening of the heart rate, release of adrenaline, and cessation of digestive activities) p803,  |
| * What do we call the part of the brain essential for language, cognition, memory, consciousness, and awareness of our surroundings? | the cerebrum p808,  |
* The highlighted part of this human brain is called the ______.,  | cerebrum (which is composed of two cerebral hemispheres) p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "A" pointing to?, 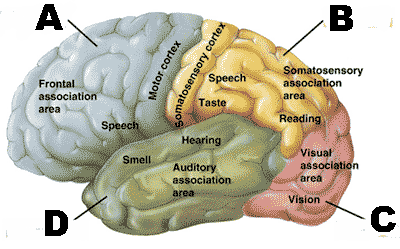 | Frontal Lobe p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "B" pointing to?,  | Parietal lobe p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "C" pointing to?,  | Occipital lobe p809,  |
* Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is "D" pointing to?,  | Temporal lobe p809,  |
| * The thick band of axons that allows communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _____. | corpus callosum pp 805 & 808, 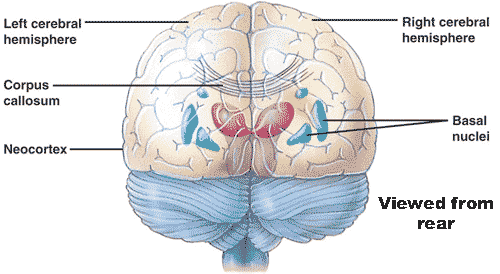 |
| * Damage to which lobe of the cerebral cortex would be most likely to change personality and impair decision making? | the frontal lobe p809 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: Vertebrates have the same basic brain structure as any other vertebrate. | TRUE p809, 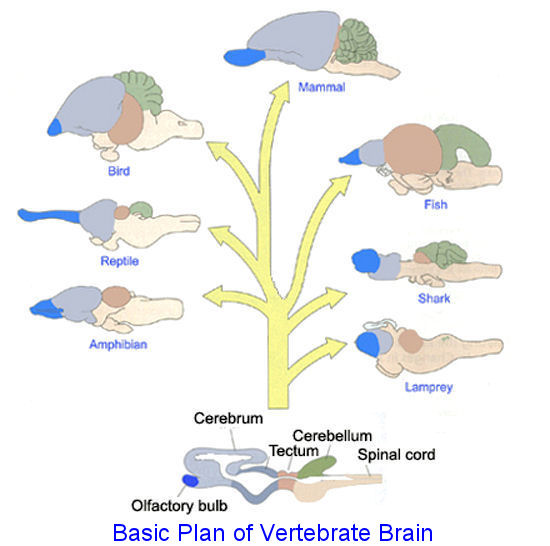 |
| * The capacity for the nervous system to be remodeled (by adding, deleting, strengthening, or weakening synaptic connections), especially in response to its own activity, is called _____. | neuronal plasticity (This is why you need to review material you learn on a regular basis. Otherwise, you will forget it) p810, 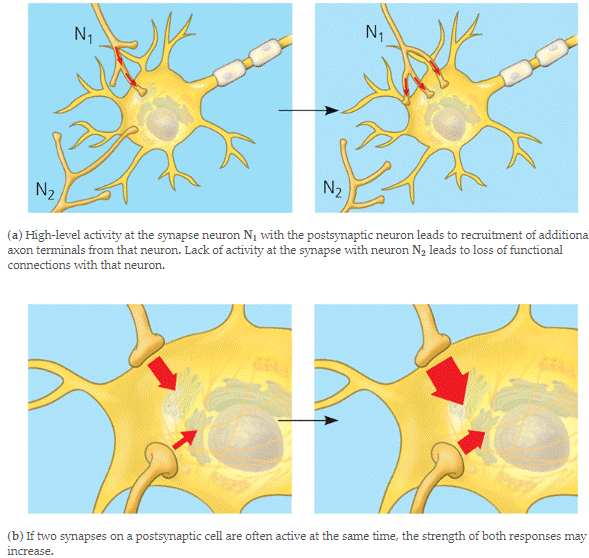 |
| * When is it thought that important information stored in short-term memory gets consolidated into long-term memory? | During sleep (This is why it is a bad strategy to cram for tests by pulling all-nighters. At best, you might be able to recall it for the test, but you will forget everything right after the test. Any gains are probably off-set by being too tired to think straight during the test. Your best strategy in college is to study on a very regular basis and only study slightly more just before a test, but get to bed early. Trust me!) p811 |
| * As a human embryo develops, the neural tube forms three anterior bulges—the _____, , and ______ —that together produce the adult brain. | forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain p804, 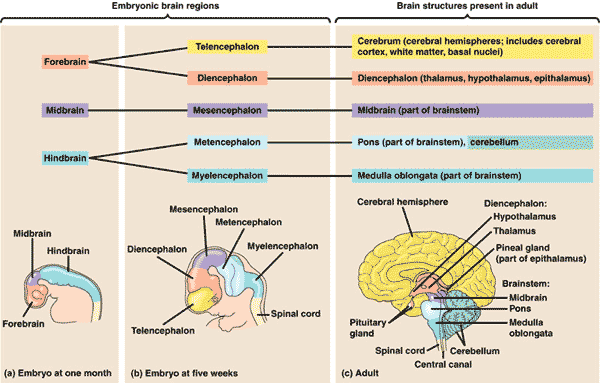 |
| * The outer layer of the cerebrum is called the ____ and is vital for perception, voluntary movement, and learning. | cerebral cortex p804,  |
| * TRUE or FALSE: The left cerebral hemisphere receives information from, and controls the movement of, the left side of the body while the right cerebral hemisphere does the same for the right side of the body. | FALSE (The both receive information from and control the opposite sides of the body) p805,  |
* The highlighted portion of the brain in the picture below is the ______., 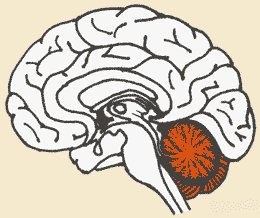 | cerebellum (The cerebellum is responsible for coordinating movement, planning, motor activities, learning and remembering of physical skills and for some cognitive abilities) p805,  |
| * Which part of the brain is associated with coordination and the memorization of physical skills (like skiing)? | the cerebellum p805,  |
* The portion of the brain highlighted below is called the _____ and consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. It functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, and conduction of information to higher brain centers., 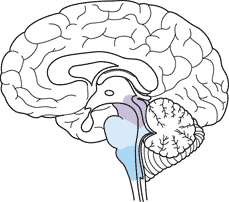 | brainstem pp804 & 805,  |
| * The ____ is the main input center for sensory information going to the cerebrum. | thalamus p805,  |
| * The ____ constitutes a control center that includes the body’s thermostat as well as the central biological clock. Through its regulation of the _____ gland, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behaviors, and initiates the fight-or-flight response. | hypothalamus, pituitary p805,  |
| ** The pineal gland is the source of a hormone called _____ | Melatonin (Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep–wake cycle. It is primarily released by the pineal gland. As a supplement, it is often used for the short-term treatment of trouble sleeping such as from jet lag or shift work. Evidence of benefit, however, is unclear.) p805,  |
| * Which part of the brainstem controls several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion? | The medulla p805,  |
| * Stimuli are detected by ____ receptors. | sensory p811 |
| * If a sensory receptor is a neuron, a larger stimulus results in more _____. If the receptor is not a sensory neuron, a larger stimulus usually causes more ____. | frequent action potentials, neurotransmitter to be released p812 |
| * If a sensory receptor is not a neuron, a larger stimulus results in more _____. If the receptor is a neuron, a larger stimulus usually causes more ____. | neurotransmitter to be released, frequent action potentials p812 |
| * Perceptions—such as colors, smells, and sounds—are constructions formed in the brain and do not ___. | exist outside it (This is really interesting if you think about. What you and I think of as color is just the frequency of electromagnetic energy waves that reflect off of a surface. We all call frequencies of 700nm "red" but what your brain makes this frequency look like may not be the same as what my brain makes it look like, yet we've both learned to call it "red." Same goes for smell. Smell is just the detection of a certain chemical that we breathed in. Our brain turns the detection of that chemical into a smell. But what smells good to some people might not smell good to others. If the smell indicates a chemical that we should stay away from, it is an evolutionary advantage for our brain to perceive it as something bad) p.812 |
| * The perceptions of olfaction is the perception of ____. | smell p813 |
| * The perceptions of gustation is the perception of ____. | taste p813 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: The only chemicals that you can smell are chemicals that are suspended in or part of air. | TRUE p813 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: Chemicals that you can taste must be dissolved in solution. | TRUE p813 |
| * TRUE or FALSE: All chemoreceptors are either involved with detecting taste or smell. | FALSE (Some chemoreceptors detect the concentration of substances, such as hydrogen ions or salt concentrations in your body. As an example, your brain has chemoreceptors that detect your H+ ion concentrations, pH, in your blood and use this information to automatically speed up or slow down your breathing) p813 |
| * Sound is detected in the ear when vibrations that have been transmitted to the cochlea cause ____ to bend which triggers action potentials on the cells that they are attached to. | hairs p816, 
|
| * Insects, crustaceans, and some polychaete worms have ____ eyes | compound (These types of eyes are very good at detecting movement. It must be similar to when you go into Best Buy and there are a bunch of TV's on the wall each showing the same thing. Notice how it captures your attention right away when something moves) p818,  |
| * The clear part layer at the front of the eye is called the ____. | cornea p818, 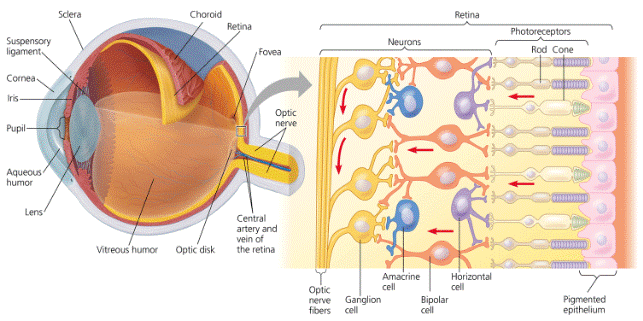 |
| * Which part of the eye changes the diameter of the pupil to regulate how much light enters the eye? | the iris (this is the colored part of your eye) p818,  |
| * The innermost layer of the eye that contains the photoreceptors and neurons is called the ____. | retina p818,  |
| * The part of the eye that changes shape to focus images is called the ____. | lens p818,  |
| * The optic disk, where the optic nerve exits the retina, lacks photoreceptors. As a result, this region forms a “____." | blind spot p818,  |
| * A type of photoreceptor in the retina of an eyeball called a(n) ____ is good at detecting faint light, but doesn't detect color. | rod (Rods are found around the boundary of the retina, whereas cones are found in the center of the retina. That is why if you stare straight at a faints star, it will seem to disappear, because the faint light is no longer hitting rods, but only cones at the center-back of the eyeball, and cones are poor at detecting faint light) p819 |
| * A type of photoreceptor in the retina of an eyeball called a(n) ____ is good at detecting colors, but doesn't detect faint light. | cone p819 |