| A | B |
|---|
gamete,  | A sex cell. (egg or sperm) |
homologous chromosome,  | Chromosomes that have the same length, appearance and copies of genes. |
diploid, 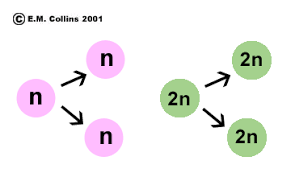 | A cell that has two copies of each chromosome, one from an egg and one from a sperm. |
haploid, 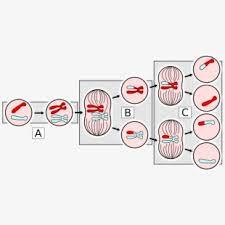 | A cell that has only one copy of each chromosome. |
meiosis, 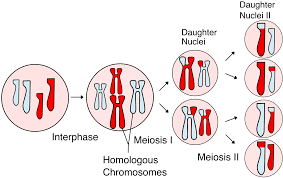 | A form of nuclear division that divides a diploid cell into haploid cells. (forms gametes) |
law of segregation, 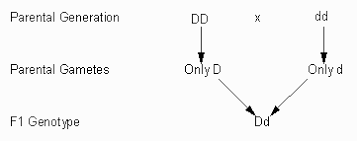 | Mendels first law, stating that organisms inherit two copies of genes, one from each parent, and organisms donate only one copy of each gene in their gametes. |
trait, 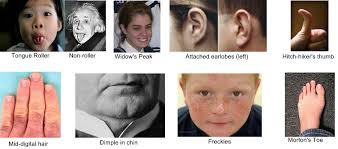 | A characteristic that is inherited |
genetics,  | The study of the heredity patterns and variation of organisms |
gene,  | A specific region of DNA that codes for a particular protein. |
allele, 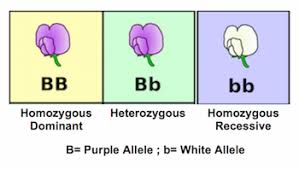 | Any of the alternative forms of a gene that occurs at a specific place on a chromosome |
homozygous,  | A characteristic of having two of the same alleles at the same locus of sister chromatids. |
heterozygous,  | The characteristic of having two different alleles that appear at the same locus of sister chromatids. |
genotype, 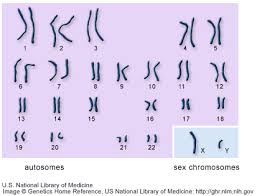 | A collection of all of an organisms genetic information that codes for traits.(the genes of an organism) |
phenotype,  | A collection of all of an organisms physical characteristics.(what an organism looks like) |
dominant, 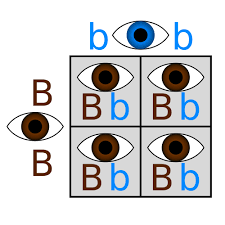 | The allele that is expressed when two different alleles are present in an organisms genotype. |
recessive,  | The allele that is not expressed unless two copies are present in an organism. |
cross, 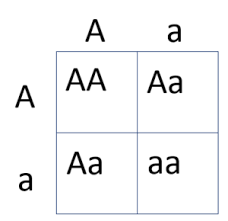 | The mating of two organisms. |
law of independent assortmant, 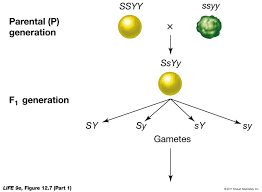 | Mendels 2nd law, stating that allele pairs separate independently from one another during gamete formation. |
Punnett square,  | A model for predicting all possible genotypes resulting from a cross or mating. |
probability,  | The likelihood that a particular event will happen. |
somatic cells, 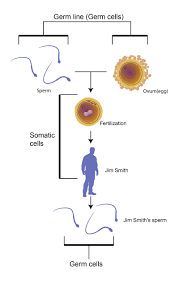 | The type of cell that makes up all of the body tissues and organs except gametes. |
autosomes, 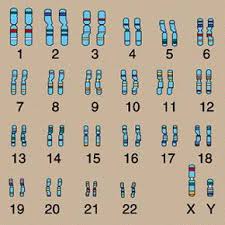 | All your chromosomes except your sex chromosomes. |
purebred,  | A type of organism whose ancestors are genetically uniform. |
crossing over, 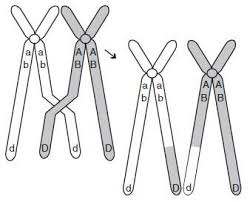 | The exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I. |
gametogenesis, 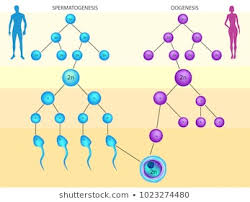 | The process by which gametes are produced. |
carrier, 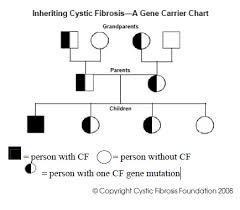 | An organism whose genome contains a gene for a certain trait or disease that is not expressed in the organisms phenotype. |
incomplete dominance, 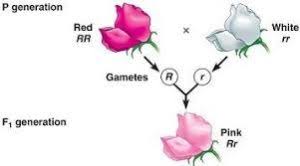 | A heterozygous phenotype that is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes. |
polygenic trait, 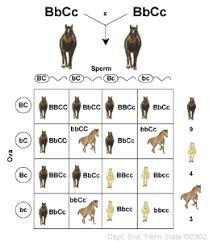 | A trait that is produced by two or more genes. |
sex-linked gene, 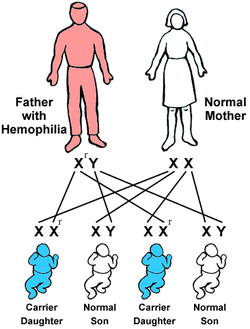 | A gene that is located on a sex chromosome. |
codominance,  | A heterozygous genotype that equally expresses the traits from both alleles. |
pedigree, 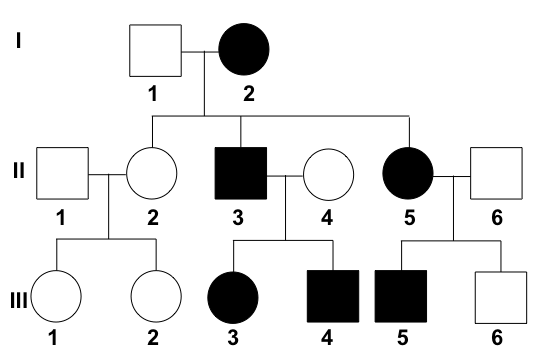 | A chart of the phenotypes and genotypes in a family. |
karyotype, 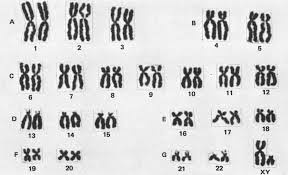 | An image of all of the chromosomes in a cell. |