| A | B |
|---|
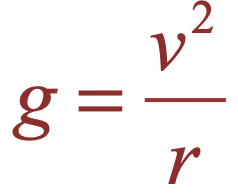 | Equation equating acceleration of gravity and centripetal acceleration |
| 9.80 m/s^2 | acceleration due to gravity at Earth's surface |
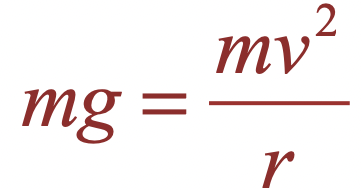 | Equation equating weight with centripetal force |
| Gravitational Potential Energy | Energy of a mass at a height within a gravitational field |
| Kinetic Energy | Any energy due to motion |
| Translational Kinetic Energy | Energy associated with motion from one point to another |
| Rotational Kinetic Energy | Energy associated with spinning about a point or axis |
| entropy | energy that escapes the system usually resulting in disorder |
| First Law of Thermodynamics | Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. It may change forms. |
| Second Law of Thermodynamics | No transformation of energy is 100% efficient. Some of it always becomes entropy. |
| Thermodynamics | The branch of science that deals with energy flowing through a system. |
| Energy | The ability to do work. |
| James Prescott Joule | British brewer who developed the field of thermodynamics. |
| Joule | Energy and work unit equal to a force of one Newton moving a distance of one meter. |
| calorie | Unit of heat energy equal to raising one gram of water one degree Celsius |
| Enthalpy | Total energy in the system |