| A | B |
|---|
| The ___ consists of the Sun, planets, dwarf planets, and all the other bodies that orbit the Sun. | Solar System |
| In order to be considered a planet, an object needs to orbit the Sun, be ____ due to having enough gravity, and must have cleared its orbit of smaller objects.. | round |
| A rotating cloud of gas and dust from which a star and its planets can form is called a(n) ______. | Solar Nebula |
| The ______ states that the Sun and the planets condensed at about the same time out of a rotating cloud of gas and dust. | Nebular Hypothesis |
| When temperatures at the center of the newly forming Sun reached ____________ degrees Kelvin, a type of nuclear reaction called fusion began using hydrogen as fuel. | 10 million |
| Of all the matter in our solar system, the Sun used up ____ % of it when it was being formed. | 99% |
| If an object outside of the Sun ended up orbiting a planet, it was called a(n) _____. | moon |
| If an object orbiting the Sun was big enough to be round but not big enough to clear out or capture into orbit all the smaller chunks of matter in its orbit, it was called a(n) ______. | Dwarf Planet |
| About 75% of the Sun's mass is made of _____ | hydrogen |
| Inside the Sun, hydrogen nuclei fuse together to produce _______ nuclei plus a lot of energy. | helium, 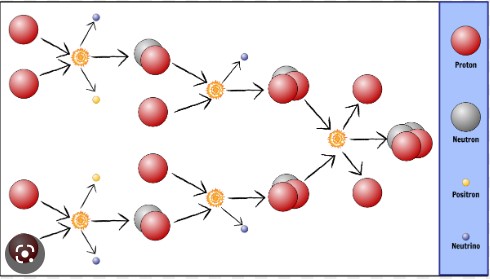 |
| In which layer or layers of the Sun does nuclear fusion take place? | the core, 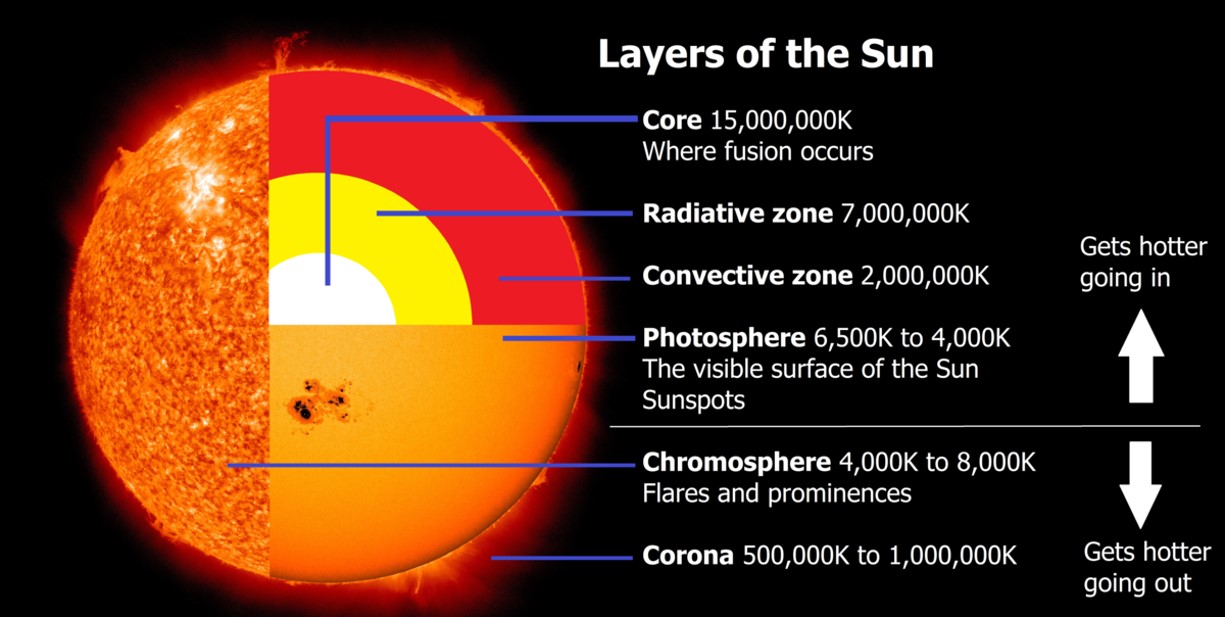 |
| The interior of the Sun is _______ K. | 15 million K |
| The surface of the Sun is about ______ K | 6000K |
| Out of the four states of matter, which state is the matter within the Sun categorized as? | Plasma (Plasma is matter that is so hot that the electrons no longer stay in orbitals around the atom. They are stripped away and move freely) |
| Which layer of the Sun has energy going through it in the form of electromagnetic waves that bounce off of or are absorbed and re-emitted in all directions, making it take a long time for energy to get through this layer? | Radiative Zone, 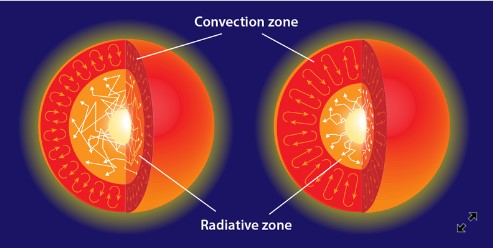 |
| Which zone of the Sun has gases that rise toward the surface, cool off, sink back toward the hotter interior, heat up again, and rise again forming a looping pattern of gas movement? | Convection Zone,  |
| Which layer of the Sun is usually considered to be the Sun's surface? | Photosphere (Which is strange because it is also considered to be the inner-most layer of the the Sun's atmosphere, but when you look at the light coming from the Sun, most of it is coming from the photosphere, so we see that as its surface),  |
| Which thin layer of the Sun's atmosphere glows with a reddish color, most likely from energized hydrogen that is emitting the reddish wavelengths typical of hydrogen emission? | Chromosphere,  |
| Which layer of the Sun's atmosphere is the hottest? | The Corona (Which is strange because it is the furthest away from the interior of the Sun, but it is believed to have something to do with energy from the interior of the Sun travelling along magnetic field lines into the Corona region) |
| Cooler less bright areas on the Sun's surface are called _____. | Sunspots,  |
| Solar flares, prominences, and coronal mass ejections are all types of ______. | solar eruptions |
| The most violent and hot type of solar eruption is called a(n) _____. | solar flare |
| Solar eruptions that disturb Earth's magnetic field are called ______. | geomagnetic storms |
The yellow lines in the picture represent ______., 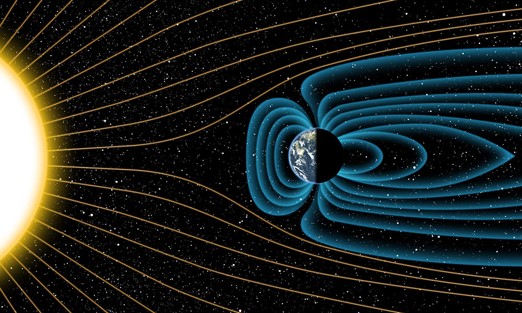 | solar winds,  |
The blue lines in the picture represent ______.,  | Earth's magnetic field (be sure not to forget to say that it's Earth's magnetic field, because the Sun also has a magnetic field),  |
| When charged particles from solar winds get funneled down into Earth's atmosphere near the north and south poles, the gases in our atmosphere start to glow. This glowing phenomenon is called a(n) ______. | aurora (The one in the northern hemisphere is called the Aurora Borealis or "Northern Lights" while in the southern hemisphere, it's called the Aurora Australis, or "Southern Lights."),  |
| The Sun isn't expected to run out of hydrogen fuel for another ______ years. | 5 billion |
| After the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel, it will contract, heat up to more than 100 million K, and start burning ______ for fuel instead. | helium |
| The largest element that the Sun will ever be able to make through nuclear fusion is ______. | carbon (Once the Sun leaves the main sequence and heats up past 100 million K, it will start fusing helium. The largest element that can be formed this way is carbon and our Sun is not expected to ever get hot enough to fuse carbon into even heavier elements) |
| After the Sun runs out of hydrogen for fuel, it will get much bigger, becoming a ________. | Red Giant, .jpg) |
| What will the Sun become after it runs out of helium for fuel? | A white dwarf, .jpg) |
| Which planet has the biggest temperature swings between day and night? | Mercury |
| The reason that temperatures on Mercury can drop from 427C during the day -173C at night is because it lacks a(n) _____ to slow heat from escaping. | atmosphere |
| The planet that gets the hottest at its surface is _____. | Venus,  |
| Which planet is closest in size to Earth? | Venus |
| The atmosphere of Venus is mostly made of _______ which is an important greenhouse gas. | carbon dioxide |
| Which planet is the brightest object in the night sky, other than our moon? | Venus,  |
| Venus has a cloud layer made of _______. | sulfuric acid (These clouds give Venus it's hazy white look),  |
| Which planet besides Earth had significant amounts of liquid water on its surface? | Mars |
| How old is Earth (along with all the other planets)? | 4.5 billion years old |
| Which planet is closest to Earth as far as size? | Venus,  |
Mars is red because it has a large amount of ____ in the soil.,  | iron (iron itself isn't red, but when it combines with oxygen atoms, it forms rust, which is red),  |
| Which planet has a volcano that is 2.5 times taller than Mt. Everest and a canyon that is as long as the United States and 3 times deeper than the Grand Canyon? | Mars,  |
| Mars has 4 seasons, just like Earth, because it has a similarly ______. | tilted axis |
The polar ice caps on Mars are made of frozen _____.,  | carbon dioxide,  |
| Asteroids are made of rock and ______. | metal |
| What is the region between Mars and Jupiter called? | the asteroid belt, 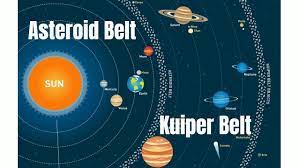 |
| What's the only thing that can survive on Venus? | Chuck Norris, of course!!,  |
| Uranus and Neptune are sometimes referred to as "____ Giants"? | ice,  |
| What happens to temperature on a "Gas Giant Planet" as you move from the outer atmosphere toward the middle? | It goes up (For example, Jupiter's outer atmosphere is about minus 160 Celsius while at the center, the temperature is around 30,000 Celsius) |
| Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are referred to as the "____ Giants." | gas |
| The smallest planet in the solar system is _____ | Mercury |
| The biggest planet in the solar system is _____ . | Jupiter |
| The bands of swirling clouds on Jupiter are caused winds that are produced by _________ currents due to the large temperature difference between the very cold surface and the very hot interior of the planet | convection |
Which planet is shown below?,  | Saturn,  |
Which planet is shown below?,  | Uranus,  |
The blue color of Uranus (on the left) and Neptune (on the right) is caused by the presence of ________ in the atmosphere.,  | methane (Hydrogen and helium are still the most common gases, but methane is a gas that is good at absorbing red wavelengths of visible light and reflecting blue wavelengths. In the picture below, Uranus is on the left and Neptune is on the right. You might think that since Neptune is a darker blue that it has more methane, but it doesn't. The milky white mixed in with the blue on Uranus comes from the product of a chemical reaction that occurs when methane reacts with sunlight, and since Uranus is a lot closer to the Sun than Neptune, it has more of this milky white chemical in its atmosphere),  |
Which planet has the coldest surface temperatures?,  | Uranus (Which is quite surprising considering that it is much closer to the Sun than Neptune and it has more heat-trapping methane gas in its atmosphere. The best explanation seems to be that the core of Uranus lost a lot of its internal heat when it was struck by a very large object causing it to tilt on its side. That never happened to Neptune. Neptune still has a very hot core and some of that heat helps keep the surface of Neptune slightly warmer than that of Uranus)),  |
| What is the second brightest object in a moonless night sky? | Jupiter (This is actually not technically correct since the international space station is brighter. Also, for short periods of time when Earth and Mars are at their closest, Mars can be brighter than Jupiter, but it's usually not)) |
Which of the inner planets is shown below?,  | Venus (The white cloudy appearance of the atmosphere is a dead give-away. Also, the fact that it is not full gives the hint that it is one of the planets that is closer to the Sun than Earth),  |
Which of the inner planets is shown below?,  | Mercury (If you see a planet with a rocky surface but no clouds or water, it is either Mars or Mercury. Mars would appear red and you wouldn't see the extensive cratering due to dust storms that cover up or soften the existing craters),  |
| What is the name of the region found just beyond Neptune? | Kuiper Belt,  |
| A small fragment (smaller than asteroids) of rock and metal out in space is called a(n) _____. | meteoroid |
| What do you call a small fragment of rock and metal as it's burning up from the friction of colliding with Earth's atmosphere at very high speeds? | meteor (this is the answer I want on the flashcard quiz even though they are often called shooting stars) |
| If you find a piece of rock from space that survived the descent through Earth's atmosphere and the impact with the ground, it would be called a(n) _____. | meteorite |
| Large objects made of ice, rock, and dust that have orbits that come in close to the Sun and then go far out into space before returning are called _____. | comets |
| The furthest region of the solar system is called the _______. | Oort Cloud,  |
If you saw something like this in the night sky but it didn't appear to be moving and it was visible for several weeks, you would be looking at a(n) _____.,  | comet (The comet pictured there is Halley's comet which last visited Earth in 1986 and will return in 2061. The clue that this isn't just a meteor is that it stays up in the sky for a long time, not just a second or so, and it has a curved tail)),  |