| A | B |
|---|
| mountain | landscaped formed by tectonic plates |
| landscape | different parts of the earths surface. |
| land degradation | reducing the quality of the soil |
| mining, farming and deforestation | factors that cause land degradation |
| soil erosion | the is the removal of topsoil from an area. |
| tectonic plates | the Earth's surface is cracked into large pieces called |
| divergent | term to describe tectonic plates pulling apart from one another |
| convergent | term used to describe tectonic plates pushing against one another |
| subduction | when two tectonic plates meet and one is forced under the other |
| core | centre of the earth is called this |
| crust | outside layer of the earth is called this |
| outer core | layer of earth that is made up of metals such as iron |
| mountain | fold and volcanic are types of |
| mount vesuvius | a famous volcanic mountain located in italy |
| fold | name this type of mountain,  |
| volcanic | name this type of mountain, 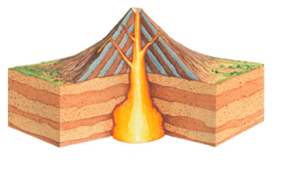 |
| fault block | name this type of mountain,  |
| crater | The name given to the hole at the top of a volcano |
| fire | The majority of Earth’s volcanoes and earthquakes take place along the Ring of ? |
| pacific ocean | The ring of fire is found where, 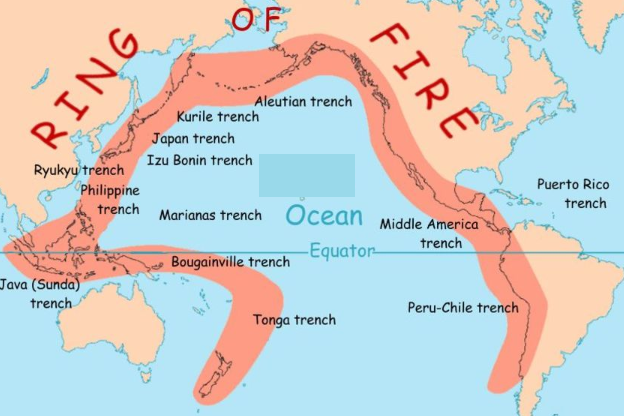 |
| lava | The molten material that flows from the volcano |
| Ash | Very fine rock and mineral particles |
| shield volcano | A volcano characterised by gentle eruptions that emit runny lava over a wide area |
| cone volcano | A triangle shaped mountain formed as material from volcanic eruptions piles around the volcanic vent (opening) in the Earths crust |
| Mount Kilimanjaro | An example of a shield volcano |
| Mount Fuji | An example of a cone volcano |