| A | B |
|---|
| Which gas was absent from Earth's atmosphere for the first 2 billion years? | oxygen, 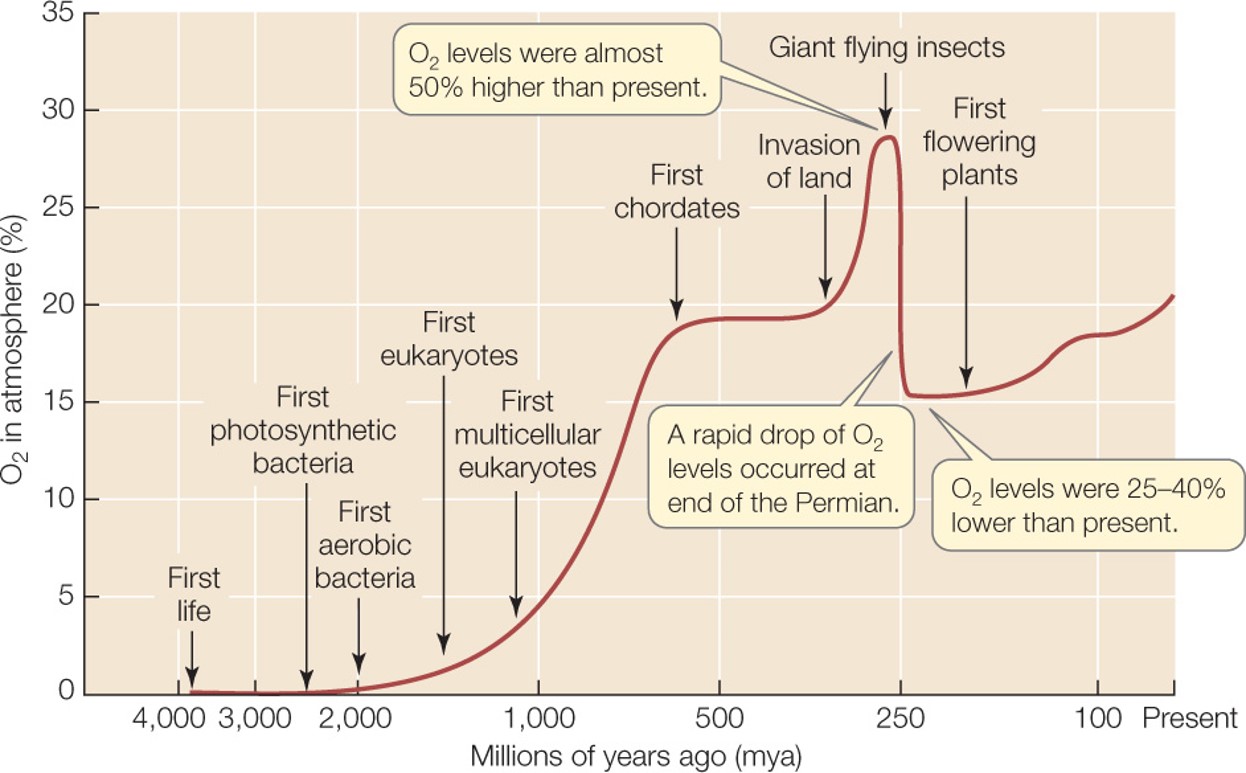 |
| Which organism had to evolve before oxygen gas could start to build up in Earth's atmosphere? | photosynthetic bacteria,  |
| The density of the atmosphere ___________ as you get further away from the surface. | decreases |
| Atmospheric pressure ___________ as you get closer to the surface of the Earth. | increases |
| The atmosphere protects Earth’s surface from the __________, helps to regulate ________, and is a source of important gases needed for living things. | Sun's radiation, temperature |
| Which gas makes up over 3 quarters of the Earth's atmosphere? | nitrogen |
| TRUE or FALSE: Plants get the nitrogen that they need in order to make amino acids and DNA from the air. | FALSE (N2 in the air is very unreactive and doesn't want to bind with anything else. Plants need bacteria to break N2 in half so that they can use the nitrogen atoms to make things like amino acids, DNA and RNA) |
| Which organism is needed to change nitrogen gas into forms that are useful for plants? | bacteria |
| Which biological process adds oxygen to the air? | photosynthesis (Photosynthesis uses up carbon dioxide and water to make glucose and oxygen. The chemical equation is the opposite of cellular respiration) |
| Which biological process adds carbon dioxide to the air? | Cellular respiration, 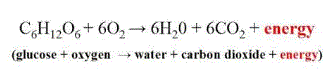 |
| Which biological process removes oxygen from the air? | cellular respiration, 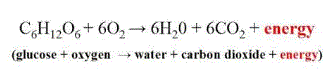 |
| Which biological process removes carbon dioxide from the air? | photosynthesis (Photosynthesis uses up carbon dioxide and water to make glucose and oxygen. The chemical equation is the opposite of cellular respiration)) |
| What has happened in the past when carbon dioxide levels have gone up? | Global temperatures have gone up., 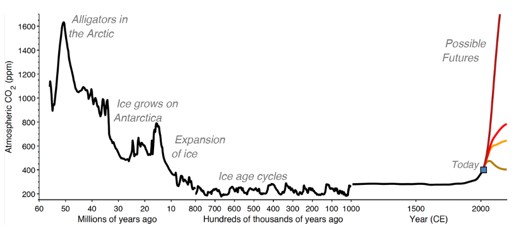 |
| Global carbon dioxide levels have risen over 50% since the start of the _______. | industrial revolution |
| Which gas's atmospheric concentration changes on a regular basis wherever you are in the world? | Water vapor (the amount of water vapor in the air changes with the weather conditions and ranges from less than 1% to almost 4%)) |
| What is the name of the process responsible for turning liquid water into water vapor (a gas)? | evaporation, 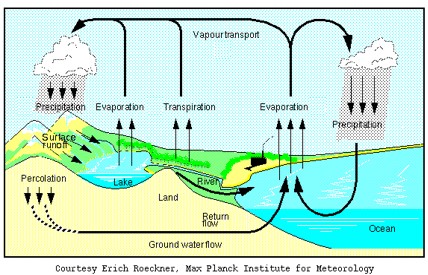 |
| What is the name of the process responsible for turning water vapor (a gas) into liquid water? | condensation,  |
| When water starts to fall from the sky as either rain or snow, it is called ______. | precipitation,  |
| A special type of evaporation that occurs from the surface of leaves is called _____. | transpiration,  |
| When water is a gas, it is called ______. | water vapor |
| TRUE or FALSE: You can see water vapor. | FALSE (water vapor is an invisible gas) |
| TRUE or FALSE: The water you can see in clouds is in the liquid state. | TRUE (You wouldn't be able to see an invisible gas. Clouds occur when water vapor condenses and turns into tiny droplets of liquid water) it if it was still in the gaseous state because water vapor is |
| In which of the four main layers of the atmosphere is most of the ozone found? | the stratosphere, 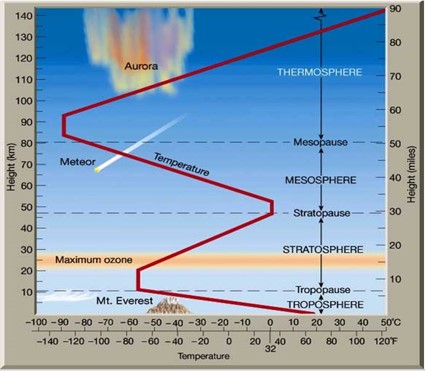 |
| Which gas protects us from most of the harmful rays coming from the Sun? | ozone (O3) |
| What is the name of the type of gas that destroys ozone and was used in many refrigerators and air conditioners before it was banned by most countries late in the last century? | CFC's (That stands for chloroflourocarbons. CFC's act as a catalyst that breaks down ozone in the upper atmosphere. This led to a thinning of ozone, especially over the poles, called the ozone hole. Since they were banned, the ozone layer is no longer shrinking and its making a slow recovery) |
| Tiny solid or liquid pollutants in the air that can irritate lungs and possibly cause lung diseases are called ______. | particulates (Examples include volcanic dust, ash from fires, microscopic organisms, pollen, and incompletely burned exhaust from factories and motor vehicles, especially diesel trucks),  |
| What happens to atmospheric pressure as you go up in altitude? | goes down, 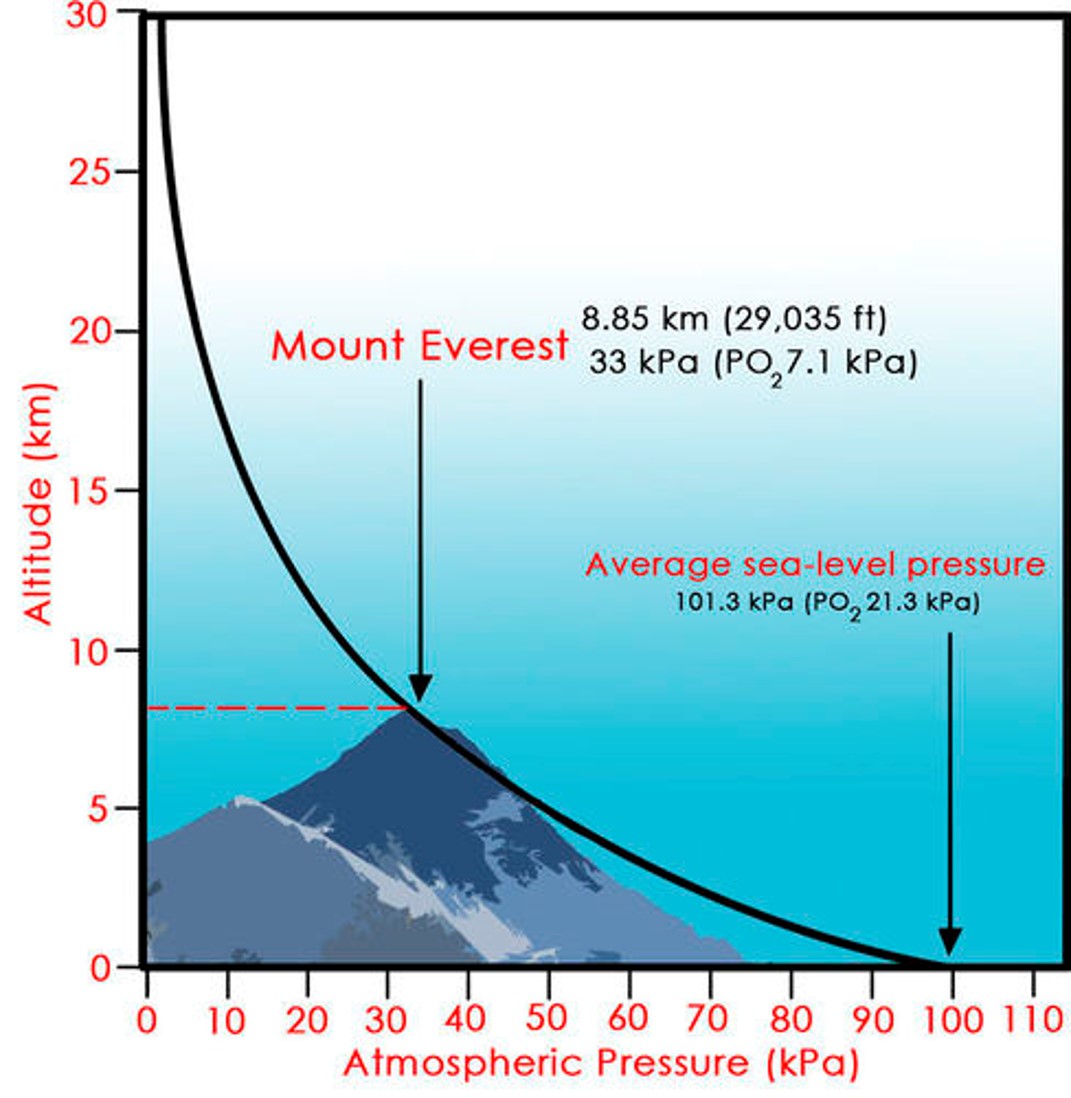 |
| Besides altitude, atmospheric pressure is also influenced by _______ and the amount of _______ in the air. | temperature, water vapor |
| In general, there is ____ atmospheric pressure in air that is warmer. | less (this is due to the fact that warm air is less dense and the molecules are further apart from each other) |
| In general, there is ____ atmospheric pressure in air that is colder. | more (this is due to the fact that colder air is denser and the molecules are closer each other) |
| In general, moister air has a _____ atmospheric pressure than dryer air. | lower (H2O vapor is lighter than nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) so air with more water vapor is less dense leading to less pressure) |
| In general, dryer air has a _____ atmospheric pressure than moister air. | higher (H2O vapor is lighter than nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) so air with less water vapor is more dense leading to greater pressure) |
| The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is ___ atm (atmospheres) = _____ mmHg (the height in millimeters of mercury in a barometer) | 1 atm = 760mmHg |
| An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure is called a(n) _____. | barometer, 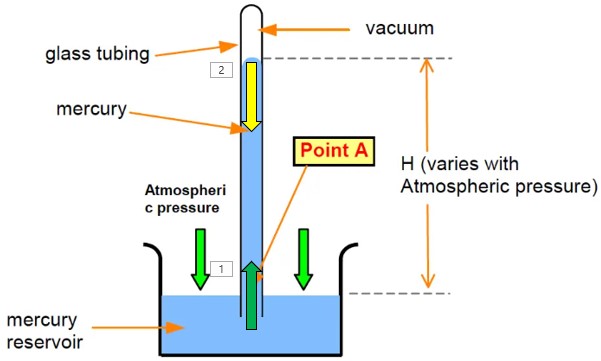 |
| Barometers measure ____. | atmospheric pressure,  |
What is keeping the mercury in this barometer from falling back into the mercury reservoir?, 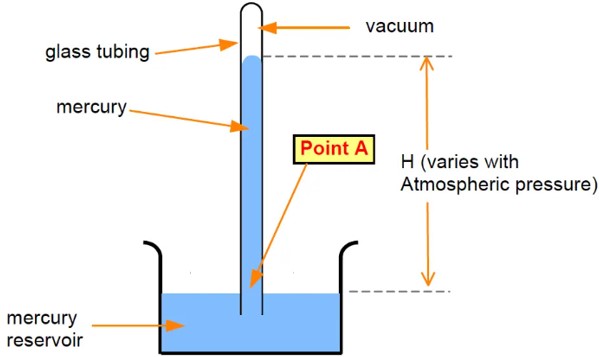 | atmospheric pressure (atmospheric pressure is pushing down on the mercury in the reservoir. Since there is a vacuum above the mercury in the glass tube, the only pressure opposing the atmospheric pressure is the pressure of the weight of the mercury in the tube. Average atmospheric pressure can support a column of mercury 760 mm high in a glass tube),  |
| The 4 main layers of Earth's atmosphere are based on changes in ______ patterns as you rise in altitude. | temperature,  |
| Which layer of Earth's atmosphere is closest to the ground? | The troposphere,  |
| Which is the second closest atmospheric layer to the ground? | The stratosphere,  |
| In the troposphere (the layer closest to the ground), temperatures ______ as you go up in altitude. | decrease (that is because this layer is heated mostly by infrared radiation being radiated back out toward space coming from the ground) |
| In the stratosphere (the second closest layer to the ground), temperatures ______ as you go up in altitude. | increase (this is because the stratosphere is heated by incoming solar radiation that is being absorbed by ozone) |
| TRUE or FALSE: We want more ozone in the stratosphere? | TRUE (The stratosphere is where the ozone layer is. CFC's pollution had been getting into the stratosphere and destroying ozone until it stopped being used in the 90's. Ozone in the stratosphere absorbs the most harmful rays from the Sun, protecting us from things like x-rays, gamma rays, and UV radiation. The ozone layer has only recently started to recover) |
| TRUE or FALSE: We want more ozone in the air near Earth's surface. | FALSE: Although ozone is good to have at higher altitudes because it protects us from the Sun's most harmful radiation, at ground level, it is bad for our lungs. Ozone pollution at ground level doesn't really make it up to the ozone layer anyways because the troposphere and stratosphere don't mix with each other much.) |
| Name the four main layers of the atmosphere in order starting with the one that is closest to Earth's surface. | Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere,  |
| A temperature inversion involves a layer of ______ over a layer of _____ at ground level that can trap pollutants. | warmer, colder, 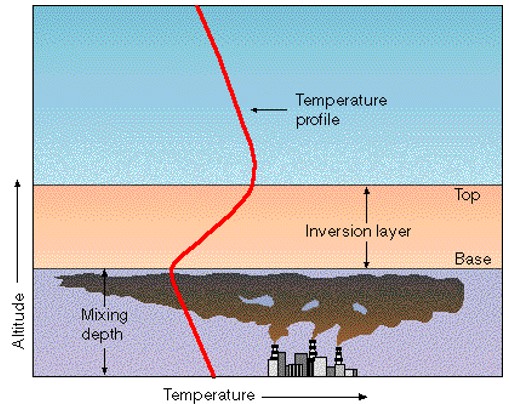 |
| A weather condition that can trap air pollution at ground level by preventing air from being able to rise and spread out is called a(n) _____. | temperature inversion,  |