| A | B |
|---|
| A collection of small water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air is called a(n) _____. | cloud |
| A cloud that forms near the Earth’s surface is called ____. | fog |
| Microscopic solid particles in the atmosphere that provides a surface on which water vapor condenses. Examples include dust, salt crystals, and ice are called _____. | condensation nuclei |
| In order for clouds to start to form, the air must be ____ with water vapor | saturated |
| Clouds will start forming when the air temperature drops below the ______ of the air mass | dew point |
| TRUE or FALSE: The water that you can see in clouds is in the gaseous phase known as vapor. | FALSE (Water vapor is an invisible gas. You can't see it in clouds until it condenses into tiny liquid droplets) |
| Adiabatic cooling is the process by which the temperature of an air mass ______ as the air mass rises and _________ due to decreasing pressure at higher altitudes. | decreases, expands |
| ______ is the process by which the temperature of an air mass decreases as the air mass rises and expands due to decreasing pressure at higher altitudes. | Adiabatic cooling |
| TRUE or FALSE: The temperature of air increases as it comes under more pressure. | TRUE |
| The _________ is the rate at which the temperature of a parcel of air changes as the air rises or sinks. | adiabatic lapse rate |
| What is the adiabatic lapse rate for air that is clear (ie - not cloudy or foggy) | 1 degree Celsius per 100 meters of elevation change (which is about 5 degrees Fahrenheit per 1000 feet) |
| Air doesn’t cool as fast once clouds start to form because ___________ is released as water vapor condenses and hydrogen bonds start to form | latent heat |
| TRUE or FALSE: Moist cloudy or foggy air cools faster than dry air when it rises in elevation. | FALSE (It cools slower because as water condenses forming hydrogen bonds, latent heat is released, slowing the adiabatic cooling of the air) |
| The ________ is the altitude at which clouds start to form due to rising air cooling below the dew point of the air mass. | condensation level, 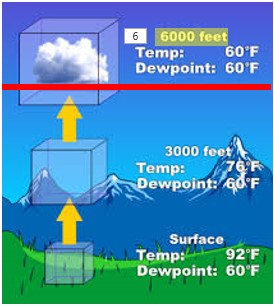 |
Look at the diagram. If the temperature of an air mass is 25 Celsius at an altitude of 300 meters, what will the temperature of the air mass be when it hits an altitude of 1300 meters., 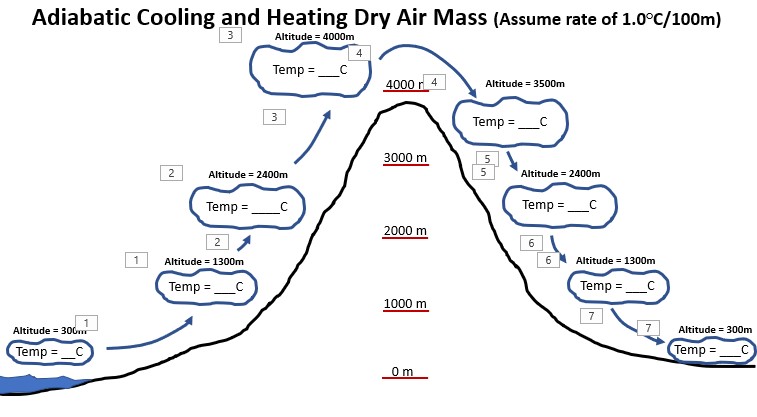 | 15 Celsius (Dry clear air has an adiabatic lapse rate of 1 degree Celsius for every 100 meters of elevation change. Since the air mass rises 1000 meters, it will drop in temperature by 10 degrees Celsius),  |
Look at the diagram. If the temperature of an air mass is Zero Celsius at an altitude of 4000 meters, what will the temperature of the air mass be when it sinks back down the mountain to an altitude of an altitude of 3500 meters.,  | 5 degrees Celsius (Dry clear air has an adiabatic lapse rate of 1 degree Celsius for every 100 meters of elevation change. Since the air is sinking in elevation by 500 meters, it will increase in temperature by 5 degrees Celsisu),  |
TRUE or FALSE: The air on the leeward side of this mountain will be the same temperature at the same elevations as the air on the windward side of the mountain),  | TRUE (Since this is a dry clear air mass that changes temperature at a rate of 1 degree Celsius for every 100 meters of elevation gain or loss, it will cool down on the way up the mountain but heat back up to the same temperature when it is at the same elevation on the other side of the mountain),  |
Look at the diagram. If the temperature of an air mass is 26 Celsius at an altitude of 300 meters, what will the temperature of the air mass be when it hits an altitude of 1300 meters., 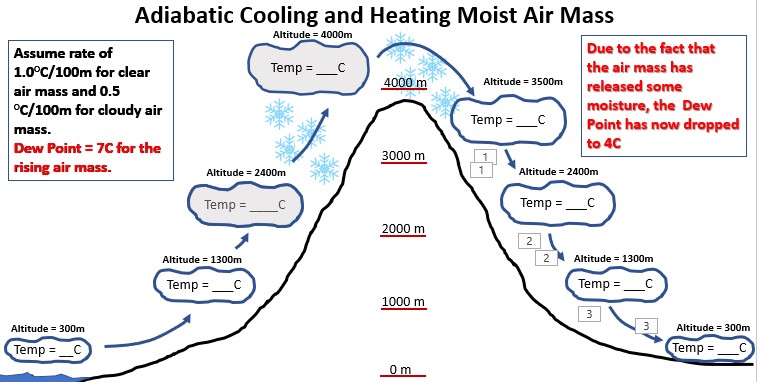 | 16 Celsius (Dry clear air has an adiabatic lapse rate of 1 degree Celsius for every 100 meters of elevation change. Since the air mass rises 1000 meters, it will drop in temperature by 10 degrees Celsius),  |
Look at the diagram. If the temperature of an air mass is Zero Celsius at an altitude of 4000 meters, what will the temperature of the air mass be when it sinks back down the mountain to an altitude of an altitude of 3500 meters.,  | 2.5 Celsius (Since this is a cloudy air mass while descending from 4000m to 3500m, the adiabatic lapse rate will by 0.5 degrees Celsius per 100m of elevation change, and the elevation changed by 500m, you would multiply 0.5C by 5 to get a change in temperature of 2.5C),  |
TRUE or FALSE: The air on the leeward side of this mountain will be the same temperature at the same elevations as the air on the windward side of the mountain),  | FALSE (Since there was condensation and precipitation mostly on the windward side of the mountain, latent heat was added to the airmass during it's journey over the mountain, so my the end, the airmass will have warmed up more on the way down than it cooled off on the way up),  |
| The windward side of a mountain range has a _____ climate than the leeward side of the mountain range. | wetter, 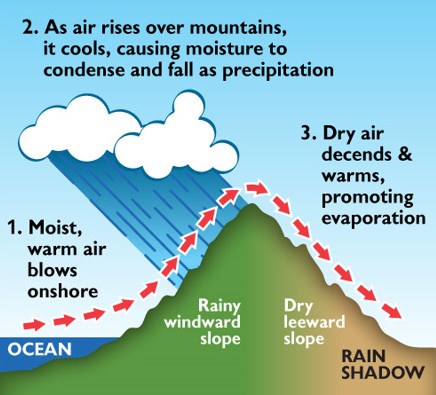 |
| The leeward side of a mountain range has a _____ climate than the windward side of the mountain range. | drier,  |
| _______ biomes can be found on the lee side of a tall mountain range because of the rain shadow effect. | Desert,  |
| Desert biomes can be found on the lee side of a tall mountain range because of the ____ effect. | rain shadow,  |
| ______ cooling is the process by which the temperature of an air mass decreases as the air mass moves over a colder surface, like snow or a cold ocean current coming down from the north along the coast. | Advective cooling, 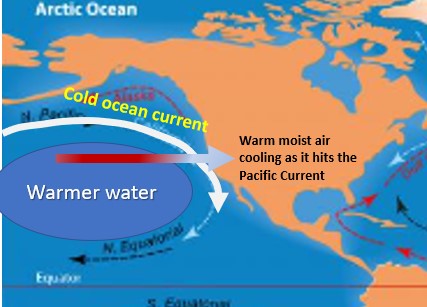 |
Look at the image below. As the warm moist air blowing in from the middle of the Pacific hits the cold ocean current coming down from Alaska along the coast, what will often times form in the air as it blows inland?,  | Fog,  |
| Clouds are classified by their ____ and _____. | shape, altitude |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled A?, 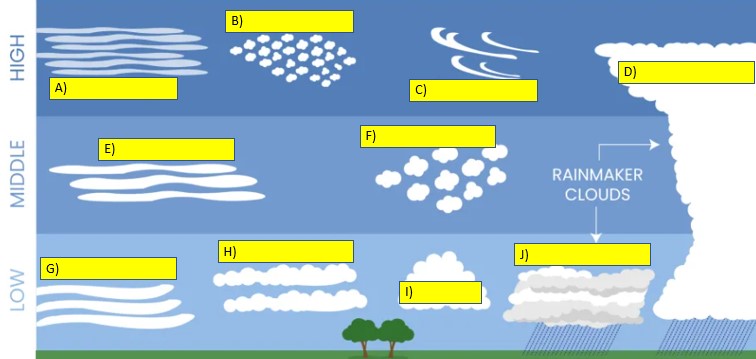 | Cirrostratus, 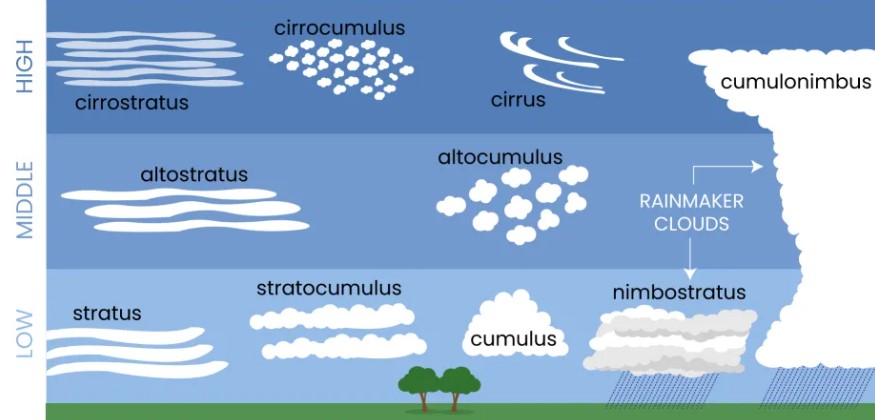 |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled B?,  | Cirrocumulus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled C?,  | Cirrus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled D?,  | Cumulonimbus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled E?,  | Altostratus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled F?,  | Altocumulus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled G?,  | Stratus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled H?,  | Stratocumulus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled I?,  | Cumulus,  |
Look at the cloud-type illustration below. What is the name of the cloud type labelled J?,  | Nimbostratus,  |
Cumulonimbus clouds can rise to great altitudes once warm moist air starts to condense because of further expansion due to the release of ________.,  | latent heat (when water vapor starts to condense, it releases a lot of heat which causes the cumulonimbus clouds to expand further and rise),  |
| What is the scientific name of the type of cloud that is most likely to produce violent thunderstorms, hail, and even tornadoes? | Cumulonimbus cloud,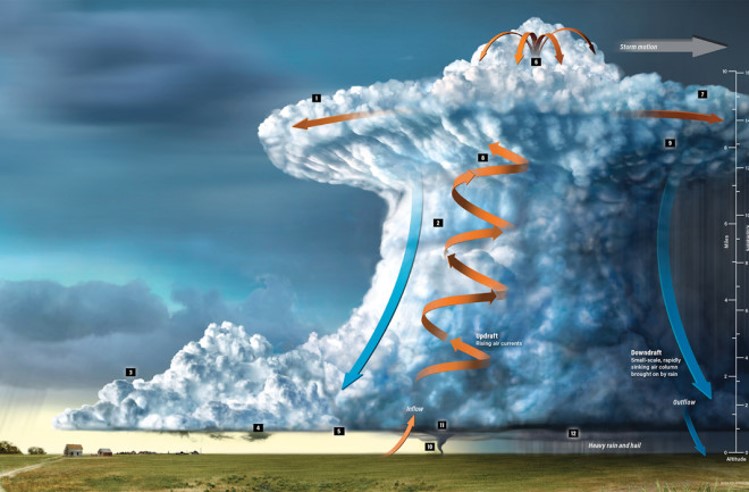  |
| Which type of clouds are made of tiny frozen ice crystals? | Any type of cirrus cloud,  |
_______ fog is fog that is caused at night when the ground cools off due to radiational cooling and drops the temperature of air that comes in contact with it below the air’s dew point.,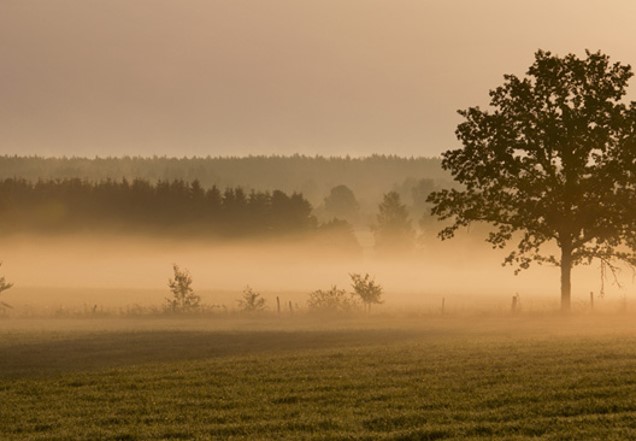  | Radiation fog, 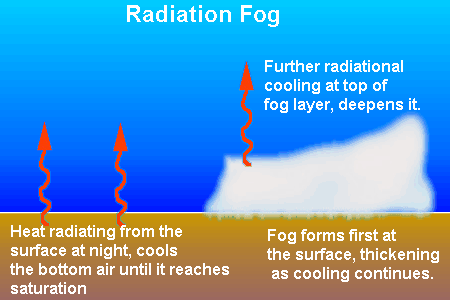 |
____ fog is fog caused by warm moist air moving across a colder surface. Often happens near coasts where warm air crosses a cold current, or blows inland across cold ground. Can also happen when warm moist air blows over snow or ice.,  | Advective fog,  |
| ____ fog is fog that forms by the lifting and cooling of air as the air rises along land slopes. | Upslope fog,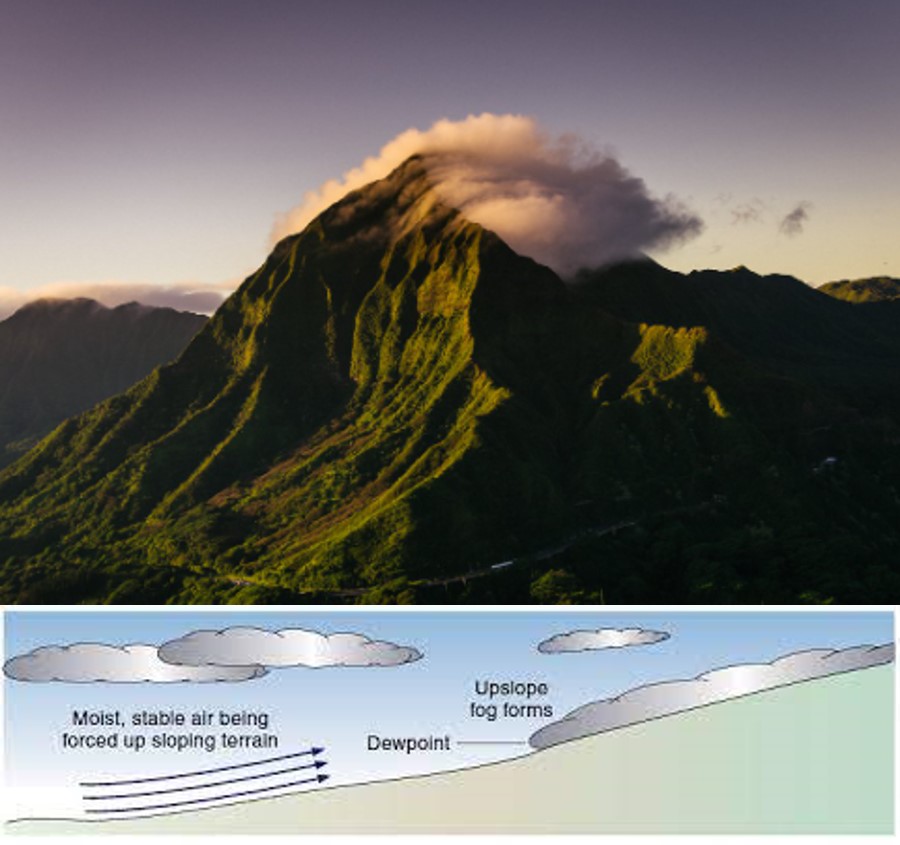  |
___ fog is a shallow layer of fog that that forms when cold air moves over an inland warm body of water, like a river.,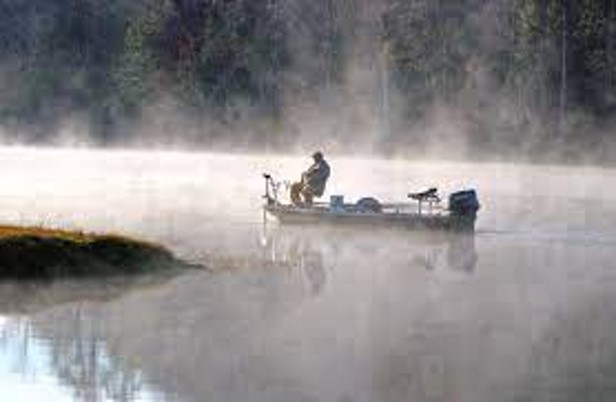  | Steam fog,  |
| ______ is any form of water that falls from the air toward the ground. | Precipitation |
| ____ is liquid water that forms into falling droplets between 0.5 and 5mm in diameter. If it’s smaller than 0.5mm, it’s called ________. | Rain, drizzle |
| ____ is made up of frozen pellets or crystals of water. | Snow |
| _____ is caused by rain falling through a freezing layer of air closer to the ground and freezing into clear ice pellets. | Sleet |
| _____ is caused by rain that doesn’t freeze until it hits the ground. | glaze ice (can also be called "freezing rain") |
| ______ is made of large chunks of ice formed inside cumulonimbus clouds through uplifting. | Hail |
| The process of human induced precipitation in which tiny particles are dropped into clouds (usually by airplanes) to act as condensation or freezing nuclei is called _____. | cloud seeding |