| A | B |
|---|
| Exergonic Reaction | Any reaction that has a net yield of energy of any kind |
| Exothermic Reaction | A reaction that gives of heat energy |
| Endergonic Reaction | Any reaction that absorbs a net amount of any energy |
| Endothermic Reaction | Any reaction that absorbs heat energy |
| Spontaneous Reaction | A reaction that requires not activation energy |
| Activation Energy | Energy required to start a reaction |
| Activated Complex | The reactants and the necessary activation energy |
| Active Site | The actual region of the reactant substance where the chemical bond will form |
| Enzyme | An organic catalyst |
| Catalyst | A chemical substance that alters the rate of a reaction |
| Inhibitor | A chemical substance that slows or stops a chemical reaction |
| Energy | The ability to do work |
| Enthalpy | The total energy content of a system |
| Entropy | Energy that is not in usable form, creates disorder in the system |
 | Exothermic Reaction Graph |
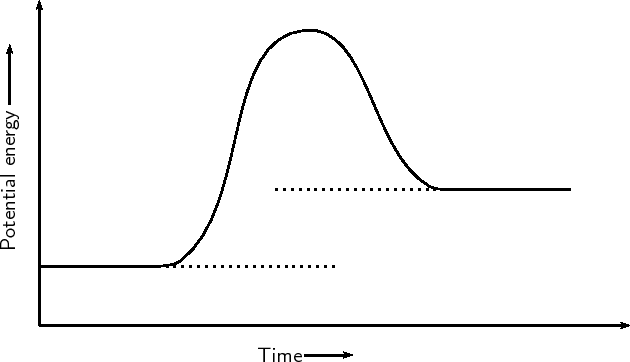 | Endothermic Reaction Graph |
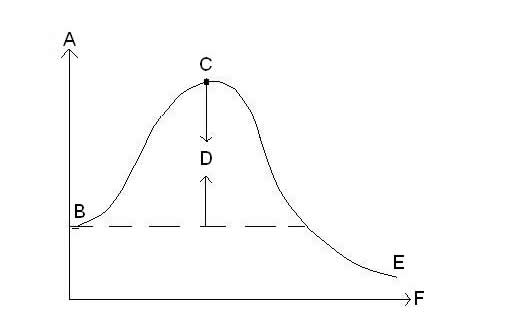
| x-axis on reaction energy graph | represents time |
| y-axis on reaction energy graph | represents energy |
In this reaction energy graph, what does B represent?, 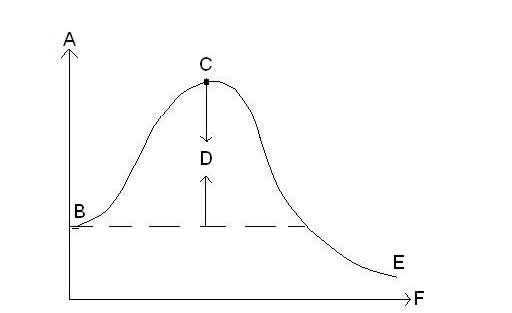 | Energy level of reactants |
In this reaction energy graph, what does C represent?,  | activated complex |
In this reaction energy graph, what does D represent?,  | activation energy |
In this reaction energy graph, what does E represent?,  | energy level of products |
Of these four graphs, which reaction has the greatest amount of activation energy?, 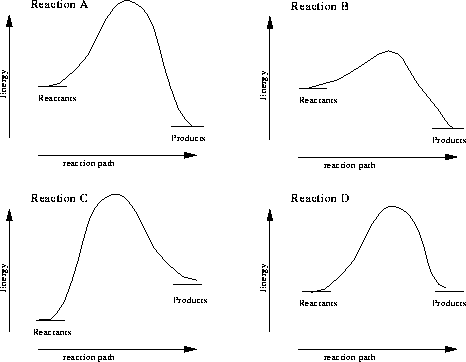 | Reaction C |
Of these four graphs, which reaction has the lowest amount of activation energy?,  | Reaction B |
Of these four graphs, which reaction is endothermic?,  | Reaction C |