| A | B |
|---|
| Air moves from areas of _____ pressure toward areas of _____ pressure. | high, low, 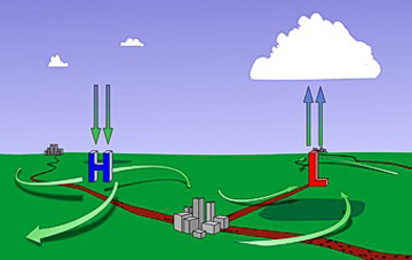 |
| Warm rising air causes ____ pressure at the surface. | low,  |
| Descending air causes ____ pressure at the surface. | high,  |
| Surface air generally moves from the _____ toward the ______. | poles, equator, 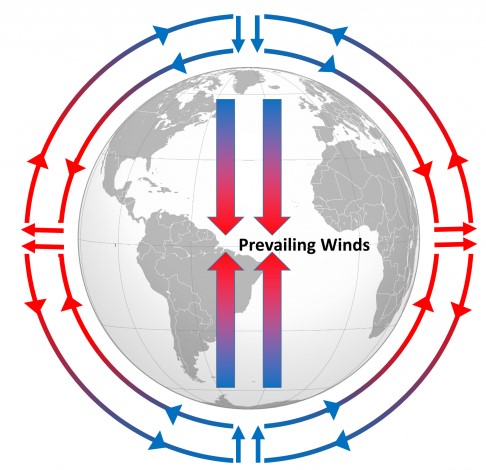 |
| Air at high altitudes generally moves from the _____ toward the ______. | equator, poles,  |
| Air travels in three rotating belts called ___________ cells in each hemisphere. | convection, 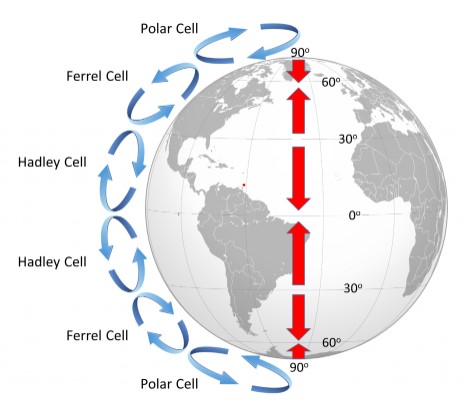 |
| Air rises at ___ and ____ degrees latitude. | 0, 60,  |
| Air descends at ___ and ____ degrees latitude. | 30, 90 |
| Latitudes where air is generally descending tend to have _____ climates. | dry |
| Latitudes where air is generally rising tend to have _____ climates. | wet |
| The convection cells are deflected by the __________ effect creating three ________ belts in each hemisphere. | Coriolis, wind, 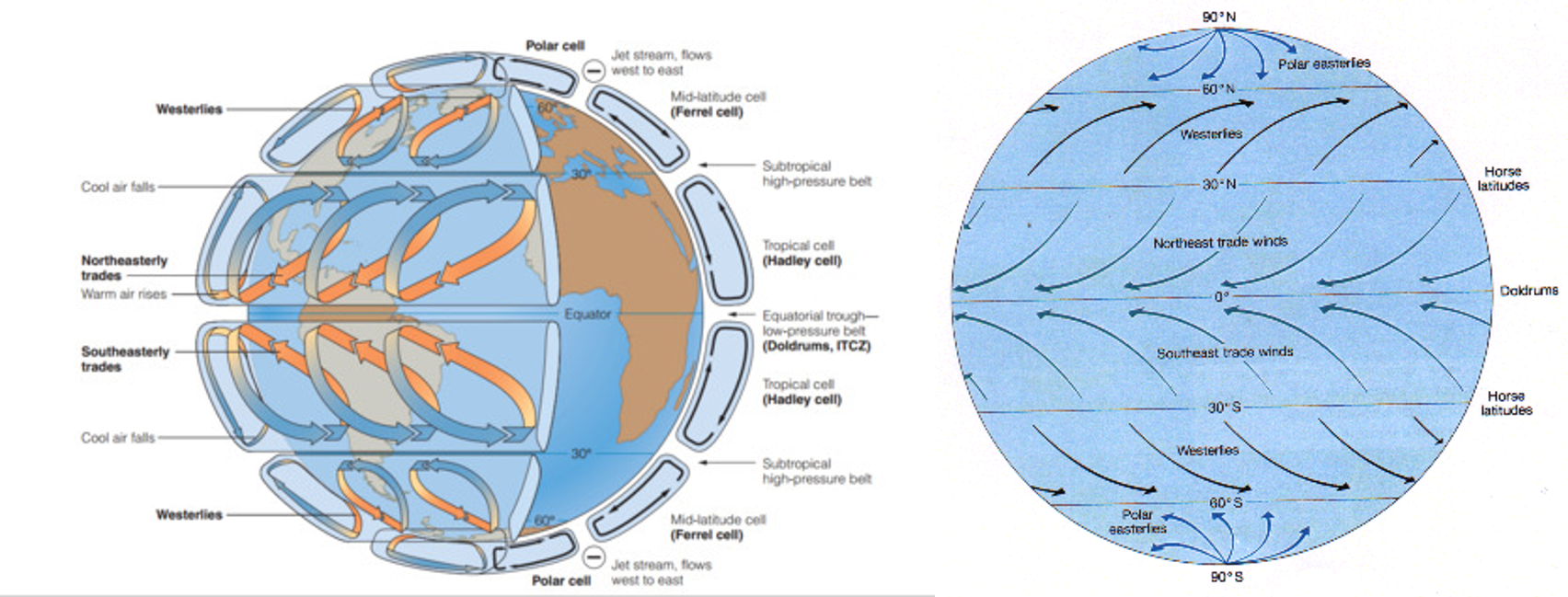 |
| Air masses are large bodies of air throughout which ___________ and _________ are similar. | temperature and moisture |
| Air masses form when air moves ____________. | slowly or not at all (this gives the air mass time to take on the characteristic temperature and humidity characteristics of the region that they're hovering over) |
| Air masses that form over frozen polar regions tend to be _______ and ________. | cold and dry |
| Air masses that form over tropical oceans are _______ and ________ | warm and moist |
| Air masses that form over large areas of land are called ______ air masses. | continental |
| Continental air masses tend to have low _______. | humidity |
| Continental polar air masses are _____ and _____. | cold, dry |
| Continental tropical air masses are _____ and _____. | warm, dry |
| Maritime polar air masses are _____ and _____. | cold, moist |
| Maritime tropical air masses are _____ and _____ | warm, moist |
| The boundary between 2 different types of air masses is called a | front |
| ________ differences between 2 different types of air masses prevent the air masses from mixing much. | Density |
| Warm air is ______ dense than cold air. | less |
| Cold air is ______ dense than warm air. | more |
| Moist air is ______ dense than dry air. | less |
| Dry air is ______ dense than moist air. | more |
| _____ dense air masses slide under ________ dense air masses. | More, less |
| Changes in _________ usually occur along a front. | weather |
| What kind of weather can you usually expect along a front line? | rainy, 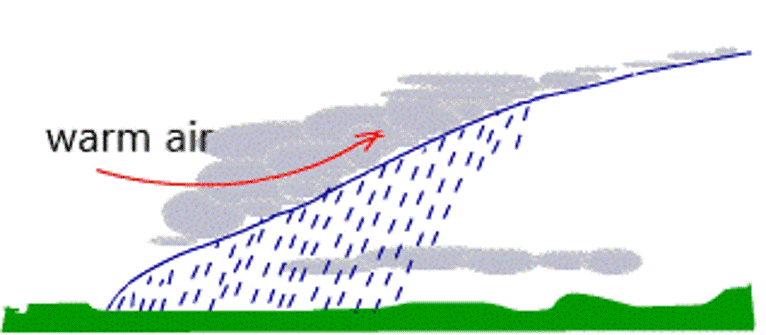 |
| A _________front is one in which air masses either move very slowly or not at all. | stationary |
| A(n) ________ front occurs when a fast moving cold air mass overtakes a warm air mass and lifts it up completely | occluded, 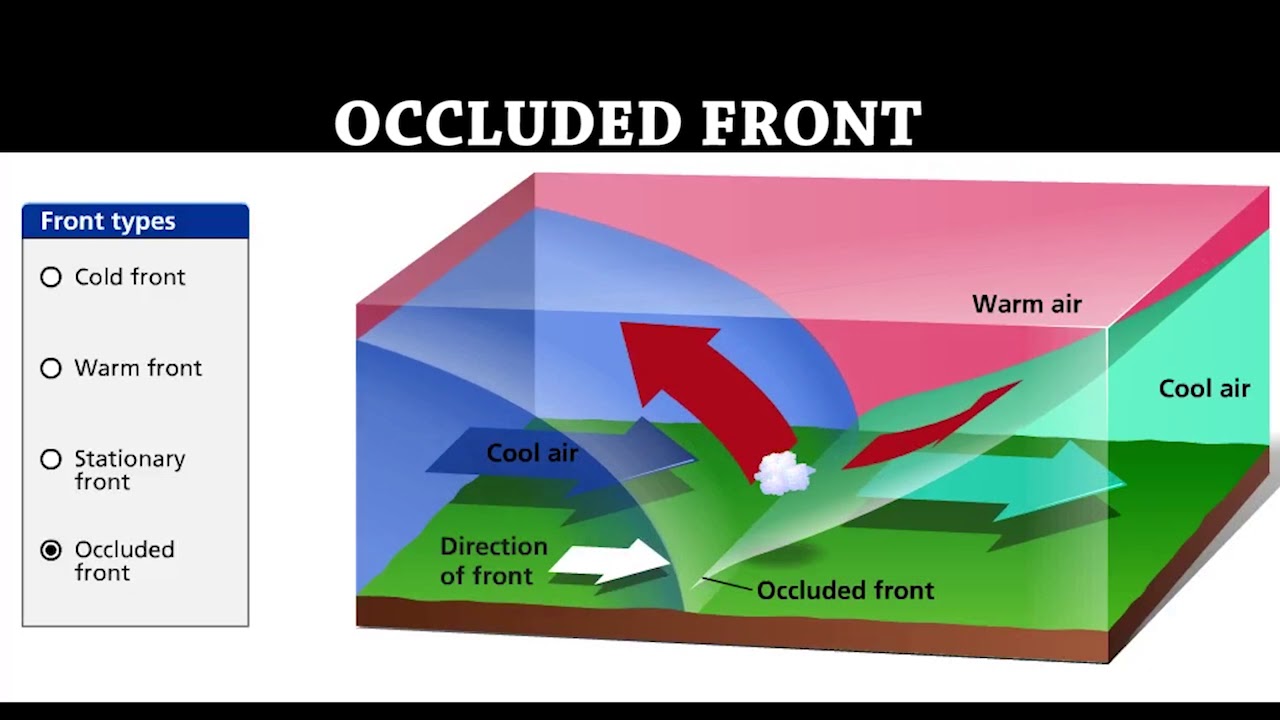 |
| ____ fronts tend to be the fastest moving of all the types of fronts. | Cold |
| ____ fronts tend to produce the most violent of storms of any of the types of fronts. | Cold |
| Rapid changes in ____________ and ________ occur as a front passes by an area. | temperature, pressure |
Which type of front is pictured below?, 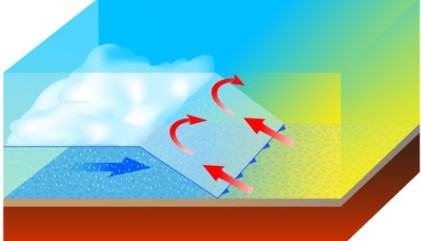 | cold front,  |
Which type of front is pictured below?, 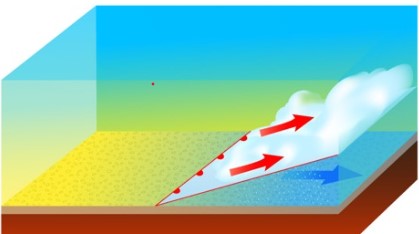 | warm front,  |
| Which type of front (warm or cold) is associated with the most violent weather? | cold front |
Which type of front is pictured below?, 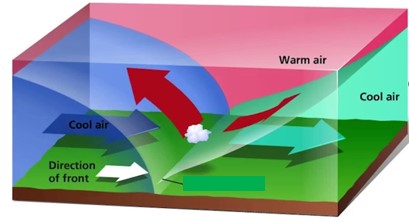 | occluded front (notice that the warm air mass is completely off the ground),  |
The weather map symbol below shows a(n) ______ front.,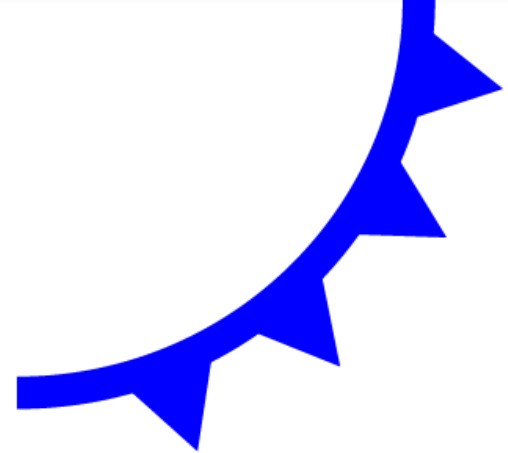  | cold, 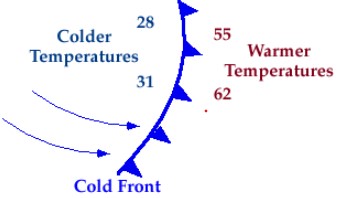 |
The weather map symbol below shows a(n) ______ front.,  | warm, 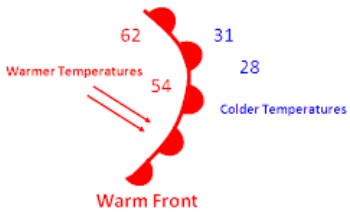 |
The weather map symbol below shows a(n) ______ front., 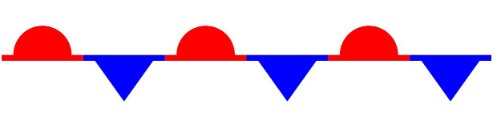 | stationary, 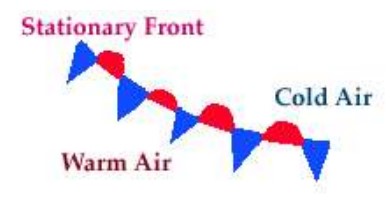 |
The warm air mass would be found ______ the stationary front line in the diagram below (your choices are "above" or "below."),  | below (the red nubs show the direction that the warm air mass is trying to move. If it's trying to move up, that means it is below the front line),  |
The cold air mass would be found ______ the stationary front line in the diagram below (your choices are "above" or "below."),  | above (the blue arrows are pointing in the direction that cold air mass is trying to go. Since they are pointing down, the cold air mass must be above the stationary front line),  |
| TRUE or FALSE: Rain would be expected just after a warm front passes through an area. | False (Rain occurs before a warm front passes through an area. Notice the "front" line in the diagram below and where the rain is located., 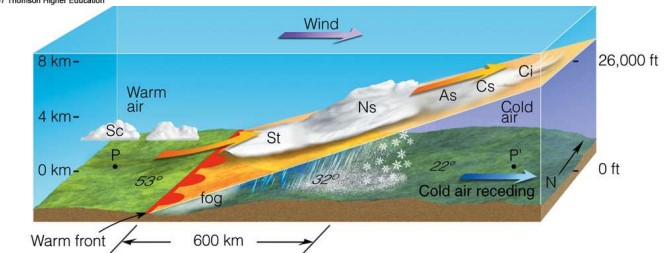 |
| TRUE or FALSE: Rain would be expected just after a cold front passes through an area. | TRUE (Notice where the rain is occuring in relationship to the cold front line and the direction that the cold air is moving), 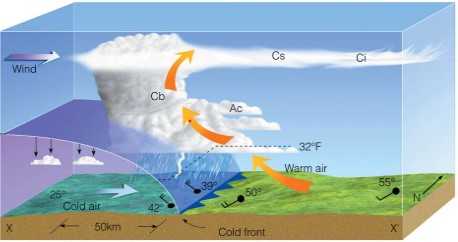 |
The weather map symbol below shows a(n) ______ front., 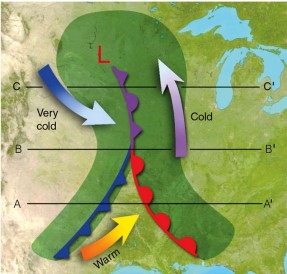 | occluded,  |
A long row of violent thunderstorms along a cold front line is called a _______ line, 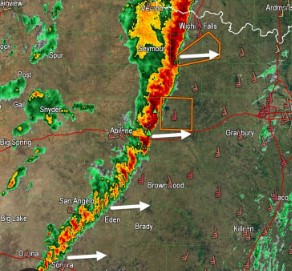 | squall (The red areas indicate areas of heavy thunderstorm action in this radar image),  |
Based on the rotation of this cyclone, it would be found in the ______ hemisphere., 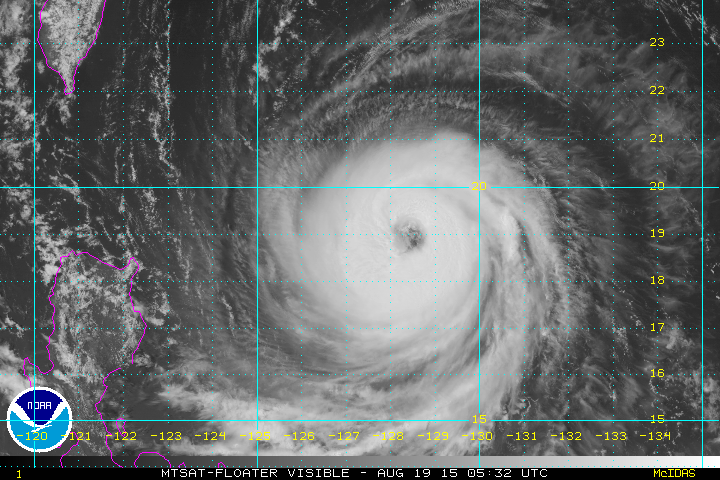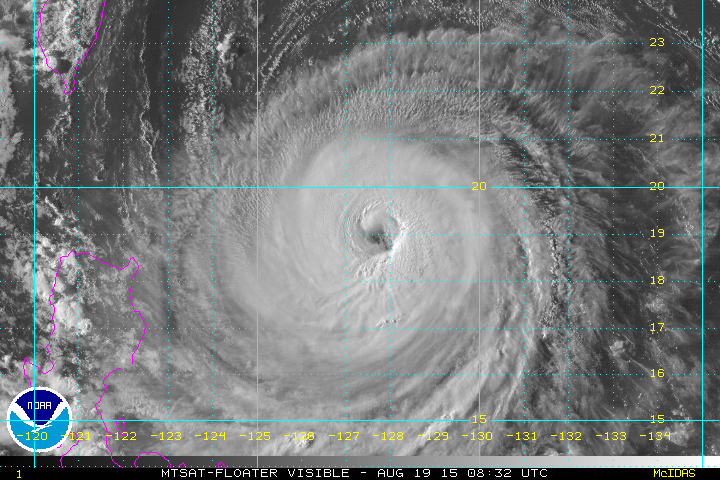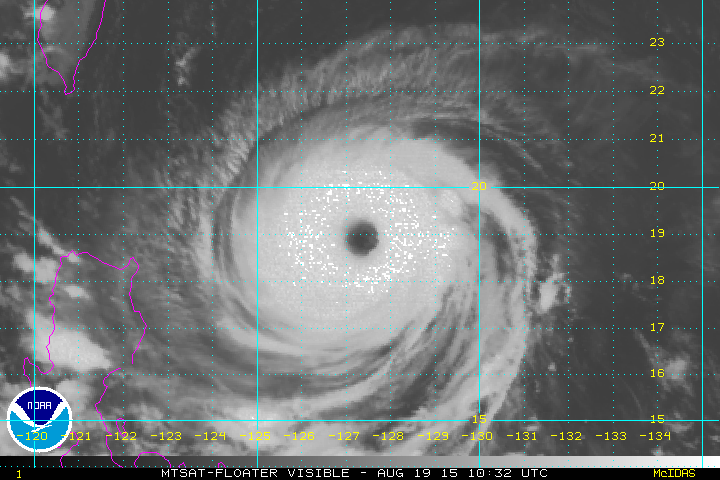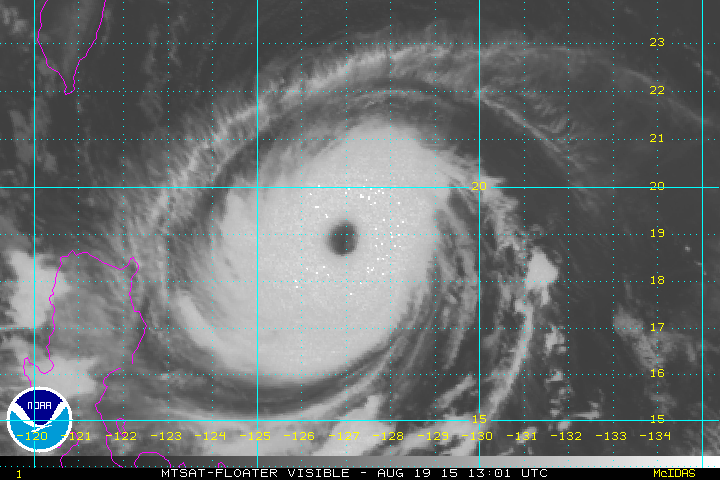 | northern (notice that it is spinning in the counterclockwise directions, which is what large-scale cyclones do in the northern hemisphere),  |
Based on the rotation of this cyclone, it would be found in the ______ hemisphere., 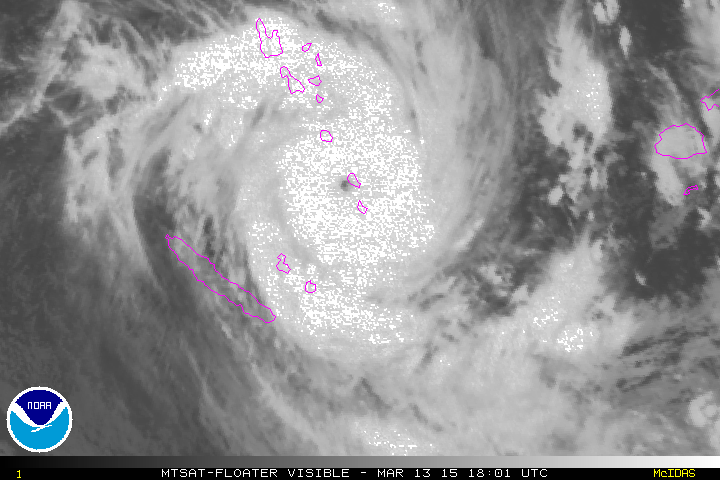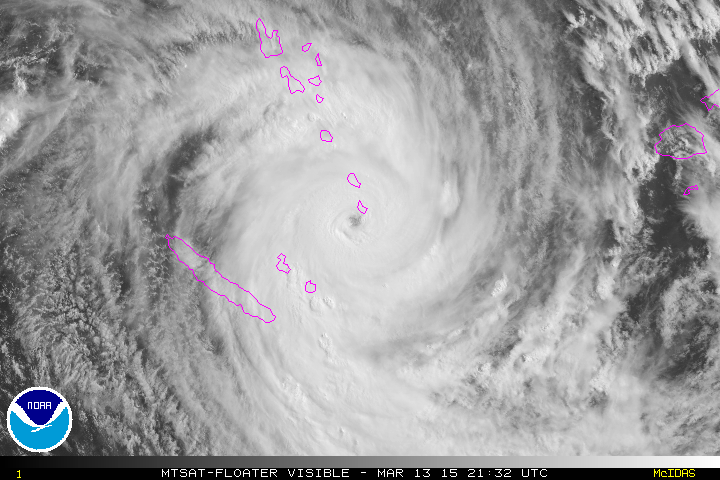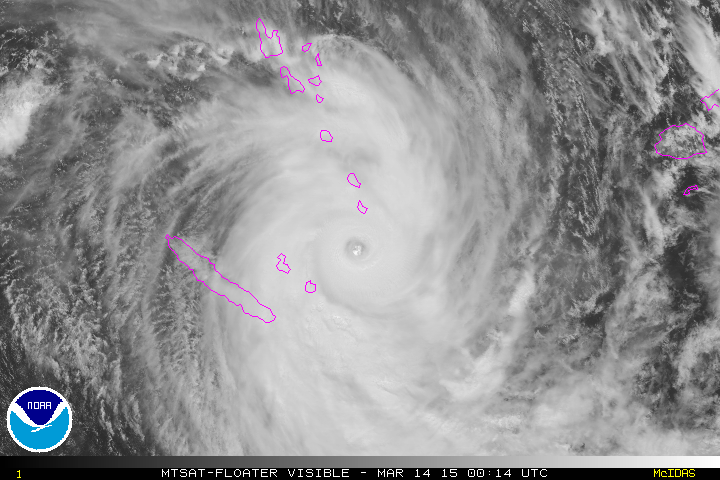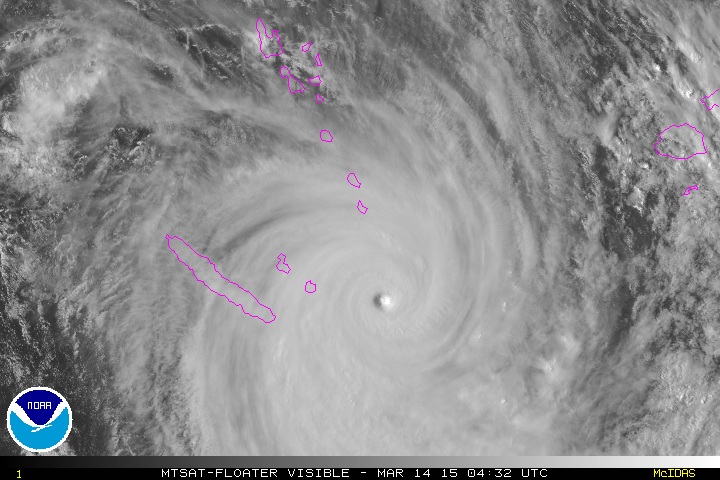 | southern (notice that it is spinning in the clockwise directions, which is what large-scale cyclones do in the southern hemisphere),  |
The type of rotating weather systems that greatly affect weather patterns in the United States are called _____.,  | midlatitude cyclones,  |
Large scale weather patterns, like the midlatitude cyclone shown below, move from ____ to ____ across the continental U.S.,  | west to east,  |
| TRUE or FALSE: A midlatitude cyclone is caused uneven interactions between cold polar air masses and warm tropical air masses. | TRUE,  |
| TRUE or FALSE: A tropical cyclone (like a hurricane) is caused by uneven interactions between cold polar air masses and warm tropical air masses. | FALSE (Tropical cyclones get their energy from warm tropical ocean waters creating rapidly rising moist warm air), 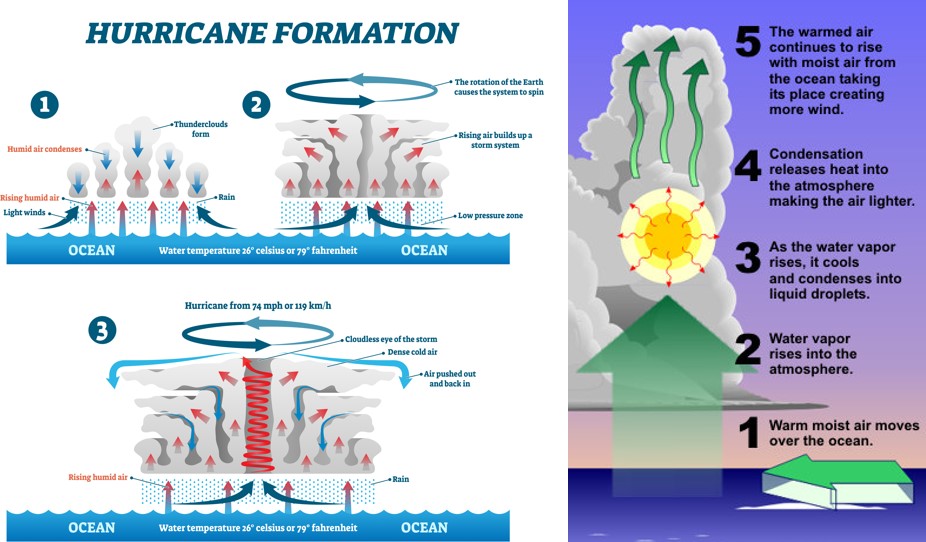 |
| Hurricanes and Typhoons are just very strong types of _________ with sustained wind speeds of at least ____ mph. | Tropical cyclones, 74mph (What it's called depends on what part of the world the tropical cyclone is in. Off the coast of North or Central America, they're called hurricanes. Off the coast of East Asia in the Pacific, they're called typhoons. Everywhere else, regardless of wind speed, they're just called cyclones) |
| Where are the calmest winds in a hurricane found? (Give the technical name) | The eye (which is the clear center region) |
| Where are the strongest winds in a hurricane found? (Give the technical name) | The eyewall (the clouds that are closest the eye of the hurricane) |
| TRUE or FALSE: Tropical Cyclones, like hurricanes, occur over larger areas than midlatitude cyclones | FALSE (While they are usually stronger than midlatitude cyclones, they don't usually cover as much area) |
| TRUE or FALSE: Tropical Cyclones, like hurricanes, occur over larger areas than tornadoes | TRUE (Tornadoes are much smaller in size than hurricanes, but can have even stronger more destructive winds) |
| Thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes all form from ________. | cumulonimbus,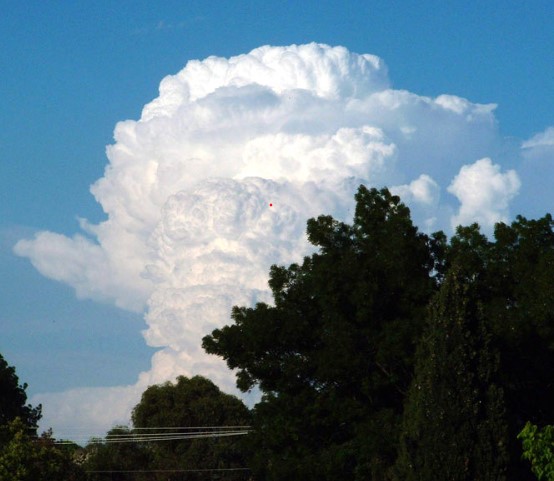  |
| The strongest winds on Earth are found in ______. | tornadoes,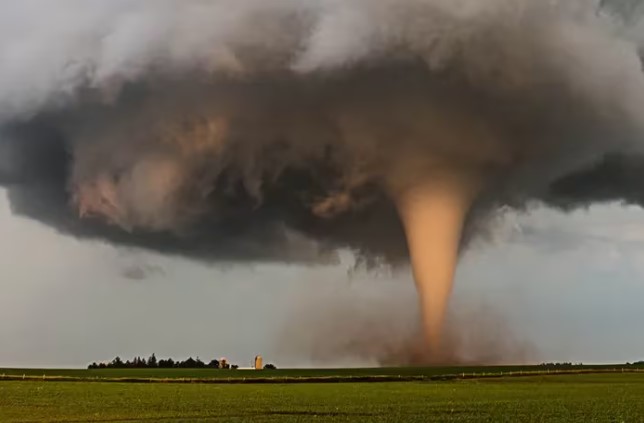  |
The extension of a tornado that reaches toward the ground is called the _____.,  | funnel,  |