| A | B |
|---|
| A natural, usually inorganic solid that has a characteristic chemical composition, an orderly internal structure, and a characteristic set of physical properties is called a(n) _______. | mineral |
| Rubies, gold nuggets, and salt are examples of _____. | minerals |
| Although there are over 4000 known minerals, only about ____ of them are common. | 20 |
| Rocks are made up of ____. | minerals |
| TRUE or FALSE: One characteristic that most minerals share is that they are organic in their chemical composition. | FALSE (Minerals are inorganic, meaning they are not organic. Organic chemicals are chemicals that were made inside living things and have the element carbon as their backbone, like the picture of the glucose molecule below), 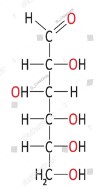 |
| TRUE or FALSE: One characteristic that most minerals share is that they are inorganic in their chemical composition. | TRUE (Most minerals are inorganic, meaning they are not organic. Organic chemicals are chemicals that were made inside living things and have the element carbon as their backbone, like the picture of the glucose molecule below. However, there are a small number of minerals that are organic),  |
| An organic molecule is a chemical compound that was originally made inside a _________ and has the element _____ as its backbone. | living thing, carbon (Minerals are inorganic, meaning they are not organic. Organic chemicals are chemicals that were made inside living things and have the element carbon as their backbone, like the picture of the glucose molecule below),  |
| TRUE or FALSE: All minerals occur naturally | TRUE |
| TRUE or FALSE: All minerals are solids | TRUE (But just because something is solid doesn't mean it's automatically a mineral. It must be a solid in at normal temperatures and have a crystalline structure. Ice has a crystalline structure but solid ice is not water's most common state. Glass is also a solid and it has the same chemical formula as the mineral quartz, but it does not have a crystalline structure. Ice and glass are not minerals.), 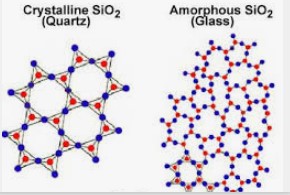 |
Substances that have a highly ordered repeating pattern are said to have a(n) _________ structure.,  | crystalline (Which mean's "crystal-like), 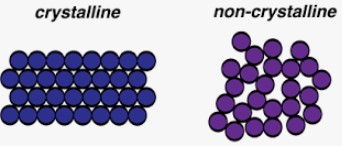 |
| TRUE or FALSE: Minerals must have a defined chemical composition with a consistent ratio of elements. | TRUE (For example, quartz is a mineral with a consistent ratio of 1 silicon atom for every two oxygen atoms. It's formula is SiO2. However, that is also the chemical formula for glass. Glass is not a mineral because it doesn't have all 4 of the characteristics of minerals. It doesn't have crystalline structure like quartz does.),  |
| TRUE or FALSE: As long as a substance has at least 3 of the 4 characteristics of minerals, it is a mineral. | FALSE (It needs all 4. Technically there is an exception. There actually are a small percentage of minerals that are organic, but you can't have any 3 to be a mineral. You would need to have the other 3 than the condition of being organic. You couldn't for instance be organic, be a solid, and have a consistent chemical composition, but not occur naturally and still be a mineral)) |
| What are the two basic types of minerals? | silicate and non-silicate |
| 96% of the minerals on Earth are classified as ______ minerals. | silicate (which means they have the elements silicon and oxygen in them) |
| The two most common silicate minerals, ______ and ______, make up 50% of the Earth's crust. | Feldspars, quartz |
| Silicate minerals have the elements ______ and ______ in them. | silicon, oxygen |
| TRUE or FALSE: Pure gold would be considered to be a mineral. | TRUE (All pure metal elements are considered to be minerals except for mercury because it is not a solid at normal temperatures) |
| What are the three basic types of rocks? | igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary, 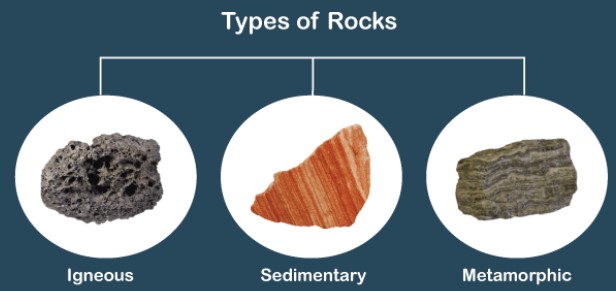 |
| Another word for molten rock underneath the Earth's surface is ______._. | magma (it is usually called "lava" once it appears on the surface of the Earth) |
| Magma that solidifies below the Earth’s surface forms ______ igneous rock | intrusive,  |
| Magma that solidifies above the Earth’s surface forms _______ igneous rock | extrusive,  |
| Magma that cools slowly tends to have _______ mineral crystals. | bigger (The slow cooling time gives the crystals a longer time to grow. For example, granite is an intrusive igneous rock that cools slowly below ground. Notice the large crystals which give granite its course structure.),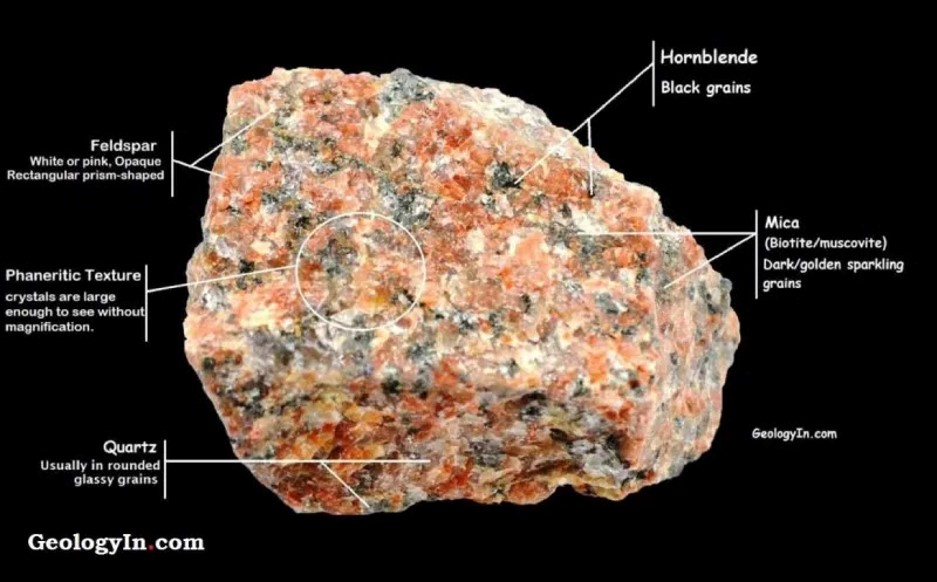  |
| Magma that cools quickly tends to have _______ mineral crystals. | smaller (The fast cooling time doesn't give the magma as much time to grow crystals, so it has a smoother texture) |
| Magma that has a lot of gases in it and cools quickly enough to trap them can form a very light type of igneous rock called ______ that can actually float on water. | pumice,  |
This black glassy looking rock formed from lava that cooled quickly with minimal crystal growth and is called _____.,  | obsidian,  |
This intrusive igneous rock had time to form big crystals as it slowly cooled below the surface of the Earth. It is called ______.,  | granite (This huge rock structure is a granite dome formed from slowly cooling magma inside a volcano. As it hardened, it formed a plug that only came to the surface after the rest of the volcano eroded away starting about 22 million years ago), ) |
| The type of rock that forms when molten rock cools and hardens is called _____ rock. | igneous,  |
| The type of rock that is made of tiny pieces of many other rocks from many other places is called _____ rock. These tiny fragments get washed or blown into an area then get buried, compressed, and cemented into layers of rock. | sedimentary (Notice how sedimentary rock gets layed down in layers),  |
What type of rock are almost all fossils (like the ones below) found in?,  | sedimentary,  |
| Fossils found in deeper layers (strata) of sedimentary rock are ______ than fossils found closer to the surface. | older, 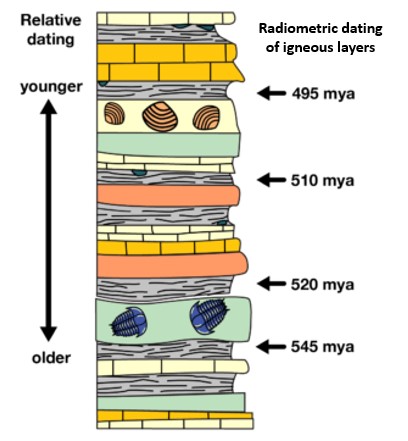 |
TRUE or FALSE: Most living things leave fossil evidence behind that can last for millions of years.,  | FALSE (Most living things leave no long-lasting fossil evidence. It takes a special set of circumstances to leave a fossil imprint in sedimentary rock. The organism needs to get buried quickly by sediments and decompose slowly enough to leave an imprint that will remain long after the actual bones and/or tissues of the organism have completely decomposed, leaving nothing but the imprint.),  |
| The age of igneous rock can be determined using knowledge of the steady __________ decay rate of radioactive elements within the rock. | half-life (The half life of a radioactive form of an element is the amount of time it takes for half of that element to change into a different element through radioactive decay. Since every type of radioactive element decays at a different but steady rate. This knowledge allows scientists to determine the age of the igneous rock and can help give an age-range for fossils trapped within sedimentary between two layers of igneous rock.),  |
| TRUE or FALSE: You can determine the age of sedimentry rock by using the knowledge of the half-life decay rate of radioactive elements within the rock. | FALSE (Since sedimentary rock is made up of many small grains of many other rocks or many different ages coming from many different places, the age of sedimentary rock can't be determined using this method. You would have to get a date range based on determining the age of igneous rock above and below the sedimentary layers)),  |
| Metamormphic rock is rock that is formed when existing rock is altered by high _________, _________, or chemical processes. | temperature, pressure,  |
| ________ rock is rock that is formed when existing rock is altered by high temperature, pressure, or chemical processes. | Metamorphic,  |
The picture is showing the _____., 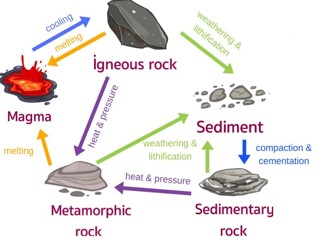 | rock cycle,  |
Using your knowledge of how the 3 different types of rock form, the type of rock that go behind the question mark would be ___ rock., 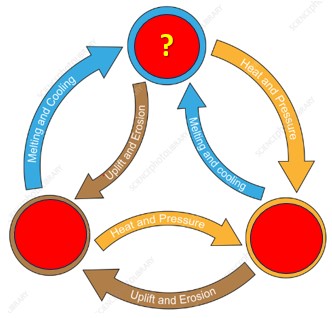 | igneous, 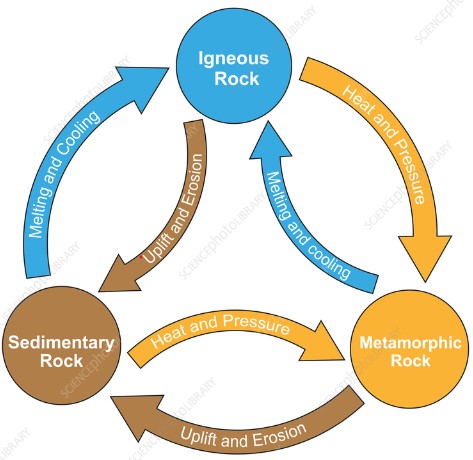 |
Using your knowledge of how the 3 different types of rock form, the type of rock that go behind the question mark would be ___ rock., 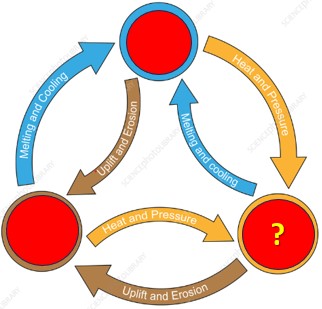 | metamorphic,  |
Using your knowledge of how the 3 different types of rock form, the type of rock that go behind the question mark would be ___ rock., 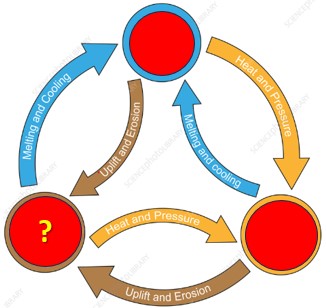 | sedimentary,  |