| A | B |
|---|
| dexter | right handed |
| sinister | left handed |
| levorotary | an optical isomer that rotates a plane of polarized light to the left, counter-clockwise |
| dextrorotary | an optical isomer that rotates a plane of polarized light to the right, clockwise |
| cis-isomer | a stereo isomer with the substituted groups on the same side of the plane of the molecule |
| trans-isomer | a stereo isomer with the substituted on opposite sides of the molecular plane |
| methyl group | a side branch containing only one carbon |
| ethyl group | a side branch containing a two carbon chain |
| 2-propanol | isopropyl alcohol, rubbing alcohol |
| propyl group | a side branch containing a three carbon chain |
| freon | a type of chlorofluorocarbon compound used as a refrigerant |
| structural isomers | isomers having different bonding patterns resulting in completely different molecules |
| isomers | compounds having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms within the molecular structure |
| racemic | a mixture having equal amounts of two different optical isomers |
| chirality | the structure of an isomer that makes it distinguishable from its mirror image or opposite |
| stereo isomers | isomers having the same molecular formula and the same order of attachment of atoms, but differing in their placement in space |
| optical isomers | isomers having the same molecular formula and the same order of attachment but because of an asymmetrical carbon atom rotate a plane of polarized light in opposite directions |
| thalidomide | a racemic mixture drug developed in the 1950's that had benefits in preventing morning sickness but caused severe birth defects |
| teratology | the branch of science studying birth defects |
| ibuprofen (Advil) | a common analgesic pain reliever that is a racemic mixture with only one isomer effective in pain relief, but the body will transform the non-effective isomer to the effective in about 20 minutes after ingesting |
| monomer | small molecule capable of being bonded repeated to others like it to make larger molecules |
| polymer | large molecule made up of many small molecules bonded to each other like links in a chain |
| cellulose | polymer of glucose bonded by a bond that humans do not have the ability to break |
| starch | polymer of glucose bonded by a bond which humans can digest |
| glycogen | polymer of glucose stored in your muscles |
| Nucleotide bases | monomers of DNA and RNA |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid, the gene molecule |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| amino acid | monomers of protein |
| gelatin | protein polymer of similar composition to your finger nails |
| extruded polystyrene | polymer formed by a chemical process that makes a good construction material |
| expanded polystyrene | "bead board" a polymer formed by heat and chemical process used to make cups, small coolers, etc. |
| Suffix for alcohols | "ol" |
| Suffix for ketones | "one" |
| Suffix for aldehydes | "al" |
| IUPAC name for embalming fluid | methanal |
| Common name for embalming fluid | formaldehyde |
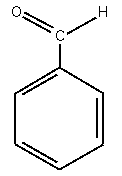 | benzaldehyde |
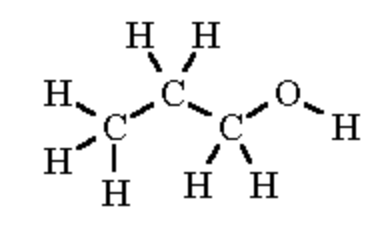 | 1-propanol |
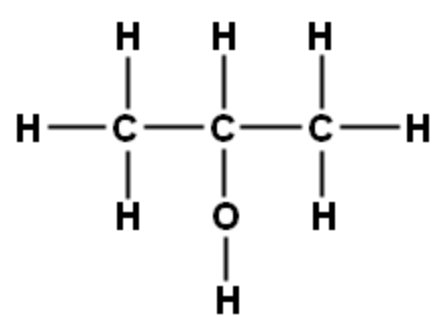 | 2-propanol |
| Common name for rubbing alcohol | isopropyl alcohol |
| IUPAC name for rubbing alcohol | 2-propanol |
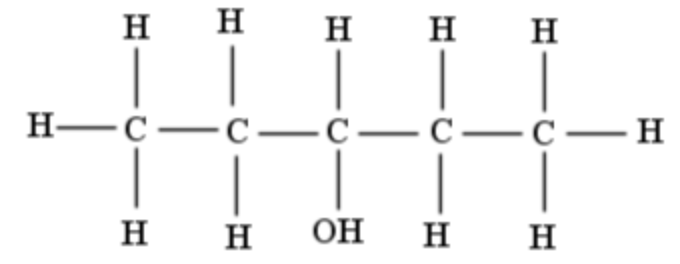 | 3-pentanol |
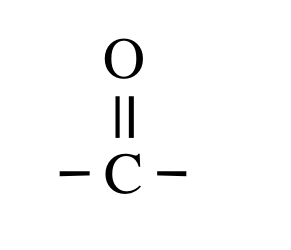 | carbonyl group |
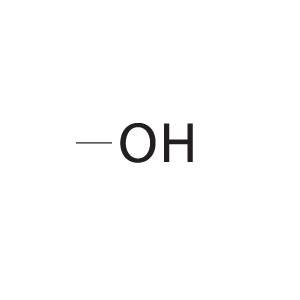 | hydroxyl group |
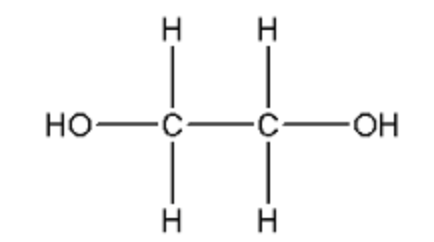 | ethylene glycol |
| common alcohol in antifreeze | ethylene glycol AKA 1,2-dihydroxylethanol |
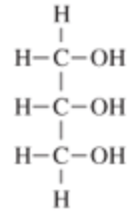 | glycerine AKA 1,2,3-trihydroxy1propanol |
| Aldehyde in maraschino cherries | benzaldehye |
| Ketone in fingernail polish remover | acetone AKA propanone |
| aldehyde in almond extract | benzaldehye |
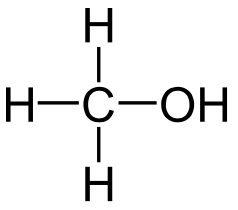 | Methanol |
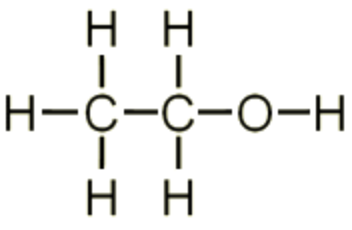 | ethanol |
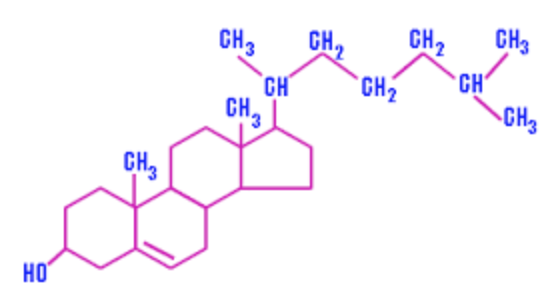 | cholesterol |
| diol | alcohol with two hydroxyl groups |
| miscible | mutually dissolvable in any ratio |
| grain alcohol (IUPAC) | ethanol |
| wood alcohol (IUPAC) | methanol |
| wood alcohol (common name) | methyl alcohol |
| grain alcohol (common name) | ethyl alcohol |
| complex waxy alcohol that clogs arteries | cholesterol |
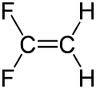 | 1,1difluoroethene |
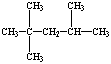 | 2,2,4-trimethylpentane |
 | 2,3dimethylpentane |
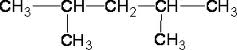 | 2,4dimethylpentane |
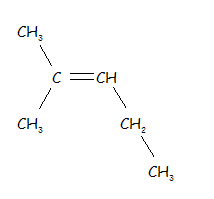 | 2-methyl-2-pentene |
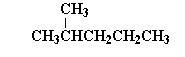 | 2-methylpentane |
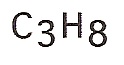 | propane |
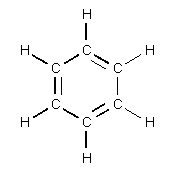 | benzene |
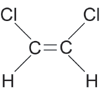 | cis-1,2-dichloroethene |
| Germany | Leading nation in organic chemistry |
| Vitalism | Theory that only living things could synthesize organic compounds. |
| Whale oil | Primary fuel of the first half of the 19th century. |
| Nicholas Otto | Inventor of first practical four stroke engine. |
| Wohler | German scientist who first synthesized an organic compound. |
| Kolbe | Germany scientist and student of Wohler who greatly advanced organic synthesis. |
| Spanish Armada | Pivotal event in 1588 that led to English outlawing use of wood for fuel and turning to fossil fuels (coal). |
| Aniline dyes | Synthetic dyes of yellow, oranges, and reds |
| Kevlar | Bullet proof aramid polymer |
| testosterone | primarily a male hormone responsible for male secondary traits and sex drive |
| estrogen | primarily a female hormone that regulates female fertility cycle |
| progesterone | female hormone which increases during pregnancy |
| oxytocin | hormone causing emotional bonding between individuals such as mother and child or couples, cuddling causes body to produce |
| phenylethylamine | compound in dark chocolate that causes increased sex drive |
| serotonin | chemical in moderate to high levels causes peaceful feeling, in low levels caused OCD |
| endorphins | natural pain killers secreted by the body |
| norepinephrine | adrenaline, causes heightened level of excitement |
| vasopressin | increased levels of this hormone are linked to monogamous behavior |
| dopamine | substance secreted in brain during pleasurable experiences, plays role in addiction |
| IUPAC name for vinegar | ethanoic acid |