| A | B |
|---|
| dexter | right handed |
| sinister | left handed |
| levorotary | an optical isomer that rotates a plane of polarized light to the left, counter-clockwise |
| dextrorotary | an optical isomer that rotates a plane of polarized light to the right, clockwise |
| cis-isomer | a stereo isomer with the substituted groups on the same side of the plane of the molecule |
| trans-isomer | a stereo isomer with the substituted on opposite sides of the molecular plane |
| methyl group | a side branch containing only one carbon |
| ethyl group | a side branch containing a two carbon chain |
| 2-propanol | isopropyl alcohol, rubbing alcohol |
| propyl group | a side branch containing a three carbon chain |
| freon | a type of chlorofluorocarbon compound used as a refrigerant |
| structural isomers | isomers having different bonding patterns resulting in completely different molecules |
| isomers | compounds having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms within the molecular structure |
| racemic | a mixture having equal amounts of two different optical isomers |
| chirality | the structure of an isomer that makes it distinguishable from its mirror image or opposite |
| stereo isomers | isomers having the same molecular formula and the same order of attachment of atoms, but differing in their placement in space |
| optical isomers | isomers having the same molecular formula and the same order of attachment but because of an asymmetrical carbon atom rotate a plane of polarized light in opposite directions |
| thalidomide | a racemic mixture drug developed in the 1950's that had benefits in preventing morning sickness but caused severe birth defects |
| teratology | the branch of science studying birth defects |
| ibuprofen (Advil) | a common analgesic pain reliever that is a racemic mixture with only one isomer effective in pain relief, but the body will transform the non-effective isomer to the effective in about 20 minutes after ingesting |
| Suffix for alcohols | "ol" |
| Suffix for ketones | "one" |
| Suffix for aldehydes | "al" |
| IUPAC name for embalming fluid | methanal |
| Common name for embalming fluid | formaldehyde |
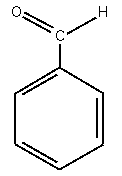 | benzaldehyde |
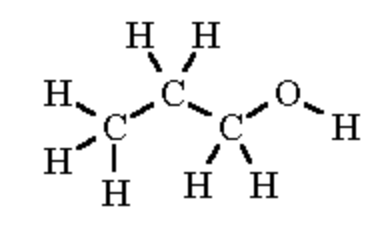 | 1-propanol |
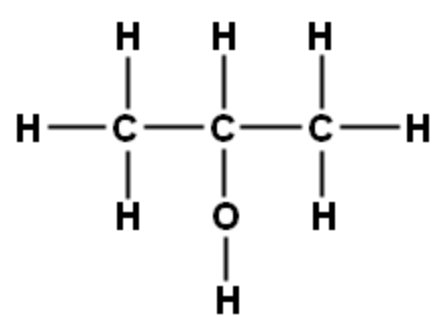 | 2-propanol |
| Common name for rubbing alcohol | isopropyl alcohol |
| IUPAC name for rubbing alcohol | 2-propanol |
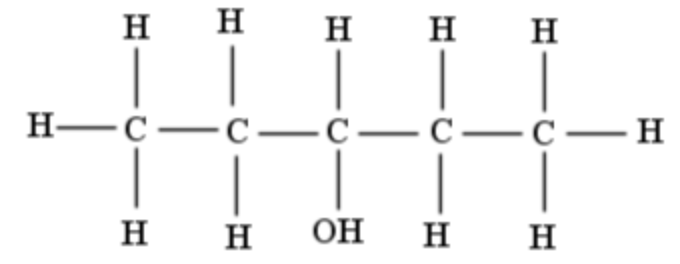 | 3-pentanol |
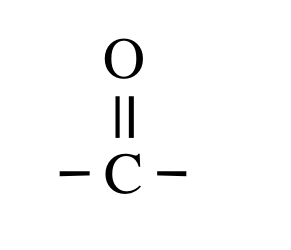 | carbonyl group |
 | hydroxyl group |
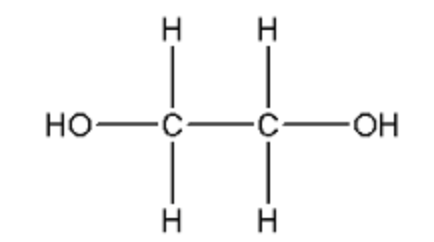 | ethylene glycol |
| common alcohol in antifreeze | ethylene glycol AKA 1,2-dihydroxylethanol |
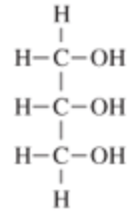 | glycerine AKA 1,2,3-trihydroxy1propanol |
| Aldehyde in maraschino cherries | benzaldehye |
| Ketone in fingernail polish remover | acetone AKA propanone |
| aldehyde in almond extract | benzaldehye |
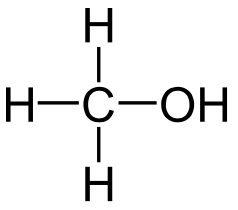 | Methanol |
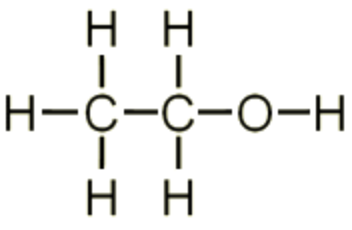 | ethanol |
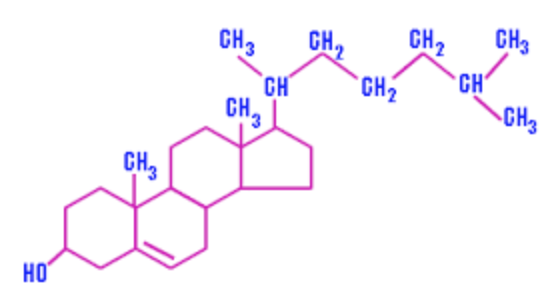 | cholesterol |
| diol | alcohol with two hydroxyl groups |
| miscible | mutually dissolvable in any ratio |
| grain alcohol (IUPAC) | ethanol |
| wood alcohol (IUPAC) | methanol |
| wood alcohol (common name) | methyl alcohol |
| grain alcohol (common name) | ethyl alcohol |
| complex waxy alcohol that clogs arteries | cholesterol |
| serotonin | primary chemical used in pharmaceutical treatment of depression |
| epinephrine | chemical similar to adrenaline causing "heart throb" sensation |
| pheromones | odorless chemical attractants detected by the vomeronasal organ |
| dopamine | brain chemical associated with pleasant feelings, plays powerful role in all sorts of addictions |
| phenylethylamine | chemical produced by your body when you fall in love, also present in dark chocolate |
| Vitamin E | Nutrient that produces healthy skin, good general health, formation of sex hormones, asparagus is a good source |
| Zinc | Mineral nutrient that boosts immune system, oysters are a good source |
| FDA | Government agency that holds the position that there is no such thing as an aphrodisiac |
| capsaicin | chemical "heat" in chili peppers that causes your body to release endorphins |
| endorphins | chemicals produced in the brain that are natural pain killers and produce "runner's high" |
| dark chocolate | actually contains phenylethylamine, a chemical the produces that loving feeling |
| oxytocin | the "cuddling" chemical, plays important role in lactation |
| vasopressin | chemical shown to promote monogamy (at least in voles), suppresses both dopamine and norepinephrine |
| testosterone | sex hormone that is the primary cause of adolescent boys getting interested in girls |
| estrogen | chemical controller of a woman's fertility cycle |
| progesterone | this chemical increases to sustain a pregnancy |
| placebo | chemical with no demonstrable effect other than making you think something should happen |
| oxidation | loss of electrons |
| reduction | gain of electrons |
| electrolyte | substance with the capacity to transfer and electric current |
| volt | unit of electrical potential |
| ohm | unit of electrical resistance |
| ampere | unit of electrical current |
| anode | negative electrode in an electrochemical cell |
| cathode | positive electrode in an electrochemical cell |
| anode process in electrochemical cell | oxidation |
| cathode process in electrochemical cell | reduction |
| half cell | part of an electrochemical cell with an electrode and electrolyte and one end of the salt bridge |
| salt bridge | a hollow tube or gel containing an electrolyte different from the electrolytes of the half cells, allows the current to flow continuously through the wet cell |
| electrodes | metal strips, plates or bars in an electrochemical cell |
| dry cell | electrochemical cell in which the electrolyte is a paste |
| battery | two or more electrochemical cells joined together |
| series connection | + to - connected, increases voltage |
| parallel connection | + to +, - to - connection, amperage increases |
| fuel cells | cells with renewable electrodes |
| coulomb | unit measuring the size of an electrical charge |
| one coulomb of charge | 6.24 x 10^18 electrons |
| EMF | electromotive force, volts |
| Galvanometer | device for detecting small amounts of current |
| Ammeter | device that measures amount of electric current |
| Voltmeter | device for measuring the amount of electrical potential |
| Exergonic Reaction | Any reaction that has a net yield of energy of any kind |
| Exothermic Reaction | A reaction that gives of heat energy |
| Endergonic Reaction | Any reaction that absorbs a net amount of any energy |
| Endothermic Reaction | Any reaction that absorbs heat energy |
| Spontaneous Reaction | A reaction that requires not activation energy |
| Activation Energy | Energy required to start a reaction |
| Activated Complex | The reactants and the necessary activation energy |
| Active Site | The actual region of the reactant substance where the chemical bond will form |
| Enzyme | An organic catalyst |
| Catalyst | A chemical substance that alters the rate of a reaction |
| Inhibitor | A chemical substance that slows or stops a chemical reaction |
| Energy | The ability to do work |
| Enthalpy | The total energy content of a system |
| Entropy | Energy that is not in usable form, creates disorder in the system |
 | Exothermic Reaction Graph |
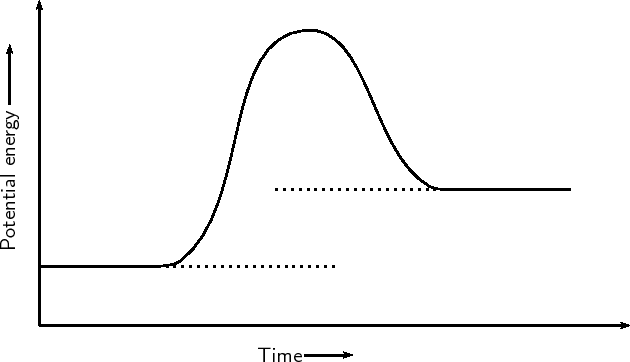 | Endothermic Reaction Graph |
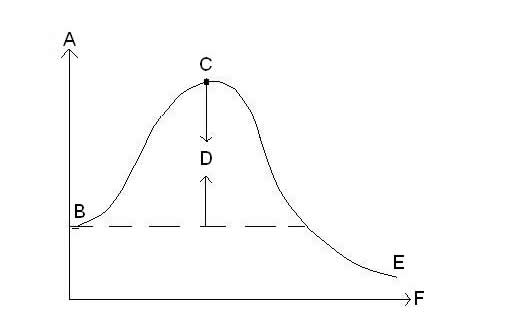
| x-axis on reaction energy graph | represents time |
| y-axis on reaction energy graph | represents energy |
| monomer | small molecule capable of being bonded repeated to others like it to make larger molecules |
| polymer | large molecule made up of many small molecules bonded to each other like links in a chain |
| cellulose | polymer of glucose bonded by a bond that humans do not have the ability to break |
| starch | polymer of glucose bonded by a bond which humans can digest |
| glycogen | polymer of glucose stored in your muscles |
| Nucleotide bases | monomers of DNA and RNA |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid, the gene molecule |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| amino acid | monomers of protein |
| gelatin | protein polymer of similar composition to your finger nails |
| extruded polystyrene | polymer formed by a chemical process that makes a good construction material |
| expanded polystyrene | "bead board" a polymer formed by heat and chemical process used to make cups, small coolers, etc. |
| reactant | compounds on the left of the reaction arrow |
| product | compounds on the right of the reaction arrow |
| precipitate | a product settling out of a solution |
| effervescence | bubbling off of a product |
| catalyst | a substance that changes the rate of the reaction without being either a reactant or product |
| activation energy | energy required to start a reaction |
| exothermic reaction | a reaction that gives off energy to the surrounding |
| endothermic reaction | a reaction that absorbs energy from the surroundings |
| conservation of mass | a chemical law stating that the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants |
| conservation of atoms | a chemical law stating that the number of each kind of atom must be the same on the product side of the reaction arrow as on the reactant side of the reaction arrow |
| activated complex | the reactants and the energy necessary for the reaction to begin |
| spectator ions | ions in solution both at the beginning and the end of a reaction |
| decomposition reaction | reaction in which a large complex substance breaks down into smaller substances |
| synthesis reaction | reaction in which small substances are combined into a more complex substance |
| combustion | reaction involving a flammable substance and oxygen |
| ----> | yields |
| ∆H | add heat |
| <=> | a reversible reaction |
| heptodecafluoro-1-octane sulfonic acid | Scotchguard |
| dichlorodifluoromethane | Freon-12 |
| polymer of 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane | Teflon |
| 1,2-dichloro-1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane | Freon-114 |
| tetrachloromethane | dry cleaning fluid IUPAC name |
| carbon tetrachloride | dry cleaning fluid common name |
| trichloromethane | chloroform IUPAC name |
| polyamide used in ladies stockings and other clothing | nylon |
| Lysergic acid diethylamide | LSD |
| amino acids | building blocks of proteins |
| Kevlar | bullet proof aramid fiber |
| IUPAC name for vinegar | ethanoic acid |
| common lab name for vinegar | acetic acid |
| acetone | active ingredient in fingernail polish remover |
| penicillin | antibiotic amide |
| aminobenzene | aniline |
| Formic acid | common name for active ingredient in red ant bites and other insect stings |
| Methanoic acid | IUPAC name for active ingredient in red ant bite and other insect stings |
| Lactic acid | builds up in muscles during anaerobic exercise |
| methylsalicylate | oil of wintergreen |
| reactant | compounds on the left of the reaction arrow |
| product | compounds on the right of the reaction arrow |
| precipitate | a product settling out of a solution |
| effervescence | bubbling off of a product |
| catalyst | a substance that changes the rate of the reaction without being either a reactant or product |
| activation energy | energy required to start a reaction |
| exothermic reaction | a reaction that gives off energy to the surrounding |
| endothermic reaction | a reaction that absorbs energy from the surroundings |
| conservation of mass | a chemical law stating that the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants |
| conservation of atoms | a chemical law stating that the number of each kind of atom must be the same on the product side of the reaction arrow as on the reactant side of the reaction arrow |
| activated complex | the reactants and the energy necessary for the reaction to begin |
| spectator ions | ions in solution both at the beginning and the end of a reaction |
| decomposition reaction | reaction in which a large complex substance breaks down into smaller substances |
| synthesis reaction | reaction in which small substances are combined into a more complex substance |
| combustion | reaction involving a flammable substance and oxygen |
| ----> | yields |
| ∆H | add heat |
| <=> | a reversible reaction |
| Thermodynamics | the science of energy as it flows through a system |
| First Law of Thermodynamics | Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can change form. |
| Second Law of Thermodynamics | When energy changes from one form to another, some energy becomes entropy. |
| entropy | Energy that "escapes" the system in an unusable form. It contributes to the randomness or breakdown of the system. |
| enthalpy | the total energy of a system |
| Gibbs Free Energy | the usable energy produced in a system |
| catalyst | a substance that alters the rate of a reaction without itself being a reactant |
| enzyme | an organic catalyst |
| active site | actual position on a molecule where the new bond may be formed |
| activation energy | amount of required energy to get a reaction started |
| exothermic | a reaction yielding more energy that what it absorbed |
| endothermic | a reaction that absorbs more energy that it gives off |
| spontaneous reaction | a reaction that does not require activation energy |
| kinetic theory of matter | all matter is made of particles that are in motion |
| temperature rule for reaction rate | A ten degree Celsius temperature increase will double the reaction rate. |
| collision theory | Particles must strike each other with sufficient force at specific locations on their surfaces if new bonds are to be made. |
| activated complex | All reactants with sufficient energy to start a reaction |
| Joule | energy unit equal to one newton of force acting through a distance of one meter |
| calorie | energy unit equal to raising one gram of water one degree Celsius |
| Heat equivalent of work | One calorie = 4.2 joules |
| energy | the ability to do work |
| temperature | the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance |
| Exergonic Reaction | Any reaction that has a net yield of energy of any kind |
| Exothermic Reaction | A reaction that gives of heat energy |
| Endergonic Reaction | Any reaction that absorbs a net amount of any energy |
| Endothermic Reaction | Any reaction that absorbs heat energy |
| Spontaneous Reaction | A reaction that requires not activation energy |
| Activation Energy | Energy required to start a reaction |
| Activated Complex | The reactants and the necessary activation energy |
| Active Site | The actual region of the reactant substance where the chemical bond will form |
| Enzyme | An organic catalyst |
| Catalyst | A chemical substance that alters the rate of a reaction |
| Inhibitor | A chemical substance that slows or stops a chemical reaction |
| Energy | The ability to do work |
| Enthalpy | The total energy content of a system |
| Entropy | Energy that is not in usable form, creates disorder in the system |
| x-axis on reaction energy graph | represents time |
| y-axis on reaction energy graph | represents energy |
| In this reaction energy graph, what does B represent? | Energy level of reactants |
| In this reaction energy graph, what does C represent? | activated complex |
| In this reaction energy graph, what does D represent? | activation energy |
| In this reaction energy graph, what does E represent? | energy level of products |
| Of these four graphs, which reaction has the greatest amount of activation energy? | Reaction C |
| Of these four graphs, which reaction has the lowest amount of activation energy? | Reaction B |
| Of these four graphs, which reaction is endothermic? | Reaction C |
| dexter | right handed |
| sinister | left handed |
| levorotary | an optical isomer that rotates a plane of polarized light to the left, counter-clockwise |
| dextrorotary | an optical isomer that rotates a plane of polarized light to the right, clockwise |
| cis-isomer | a stereo isomer with the substituted groups on the same side of the plane of the molecule |
| trans-isomer | a stereo isomer with the substituted on opposite sides of the molecular plane |
| methyl group | a side branch containing only one carbon |
| ethyl group | a side branch containing a two carbon chain |
| 2-propanol | isopropyl alcohol, rubbing alcohol |
| propyl group | a side branch containing a three carbon chain |
| freon | a type of chlorofluorocarbon compound used as a refrigerant |
| structural isomers | isomers having different bonding patterns resulting in completely different molecules |
| isomers | compounds having the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms within the molecular structure |
| racemic | a mixture having equal amounts of two different optical isomers |
| chirality | the structure of an isomer that makes it distinguishable from its mirror image or opposite |
| stereo isomers | isomers having the same molecular formula and the same order of attachment of atoms, but differing in their placement in space |
| optical isomers | isomers having the same molecular formula and the same order of attachment but because of an asymmetrical carbon atom rotate a plane of polarized light in opposite directions |
| thalidomide | a racemic mixture drug developed in the 1950's that had benefits in preventing morning sickness but caused severe birth defects |
| teratology | the branch of science studying birth defects |
| ibuprofen (Advil) | a common analgesic pain reliever that is a racemic mixture with only one isomer effective in pain relief, but the body will transform the non-effective isomer to the effective in about 20 minutes after ingesting |
| monomer | small molecule capable of being bonded repeated to others like it to make larger molecules |
| polymer | large molecule made up of many small molecules bonded to each other like links in a chain |
| cellulose | polymer of glucose bonded by a bond that humans do not have the ability to break |
| starch | polymer of glucose bonded by a bond which humans can digest |
| glycogen | polymer of glucose stored in your muscles |
| Nucleotide bases | monomers of DNA and RNA |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid, the gene molecule |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| amino acid | monomers of protein |
| gelatin | protein polymer of similar composition to your finger nails |
| extruded polystyrene | polymer formed by a chemical process that makes a good construction material |
| expanded polystyrene | "bead board" a polymer formed by heat and chemical process used to make cups, small coolers, etc. |
| Suffix for alcohols | "ol" |
| Suffix for ketones | "one" |
| Suffix for aldehydes | "al" |
| IUPAC name for embalming fluid | methanal |
| Common name for embalming fluid | formaldehyde |
| Common name for rubbing alcohol | isopropyl alcohol |
| IUPAC name for rubbing alcohol | 2-propanol |
| common alcohol in antifreeze | ethylene glycol AKA 1,2-dihydroxylethanol |
| Aldehyde in maraschino cherries | benzaldehye |
| Ketone in fingernail polish remover | acetone AKA propanone |
| aldehyde in almond extract | benzaldehye |
| diol | alcohol with two hydroxyl groups |
| miscible | mutually dissolvable in any ratio |
| grain alcohol (IUPAC) | ethanol |
| wood alcohol (IUPAC) | methanol |
| wood alcohol (common name) | methyl alcohol |
| grain alcohol (common name) | ethyl alcohol |
| complex waxy alcohol that clogs arteries | cholesterol |
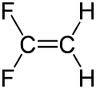 | 1,1difluoroethene |
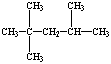 | 2,2,4-trimethylpentane |
 | 2,3dimethylpentane |
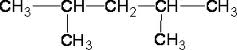 | 2,4dimethylpentane |
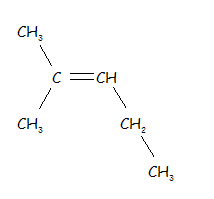 | 2-methyl-2-pentene |
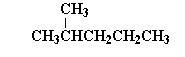 | 2-methylpentane |
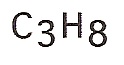 | propane |
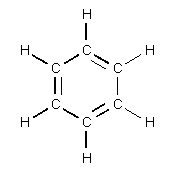 | benzene |
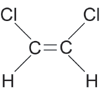 | cis-1,2-dichloroethene |
| reactants | substances to the left of the reaction symbol |
| products | substances to the right of the reaction symbol |
| ---> | "yields" |
| <=> | reaction symbol indicating a reaction is reversible |
| catalyst | a substance that alters the rate of the reaction but is not a reactant |
| enzyme | an organic catalyst |
| ∆ | Greek letter "delta" used to indicate change |
| ∆H | indicates change in heat |
| endothermic | reaction that absorbs heat, results in colder temperature |
| exothermic | reaction giving off heat, causing temperature increase |
| ↓ | indicates substance precipitates as a solid |
| ꜛ | indicates substance bubbles off as a gas |
| precipitate | a product that forms as an insoluble solid substance |
| effervescence | bubbling off of a gaseous product |
| coefficients | numbers written in front of chemical formula to indicate the number of units of that substance required to balance the reaction equation |
| subscripts | numbers written to behind and slightly below the element's symbol in a compound formula indicating the number of atoms in a molecule |
| Conservation of Atoms | fundamental concept that the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the reaction arrow |
| (s) | symbol written after a substance formula to indicate it is a solid |
| (l) | symbol written after a substance to indicate is is a liquid |
| (aq) | symbol written after a substance to indicate it is in a water solution, "aqueous" |
| (g) | symbol written after a substance to indicate it is a gas |
| Gas explodes with a small pop and clean flame | Standard lab test for Hydrogen |
| Gas causes glowing splint to burst into bright flame | Standard lab test for Oxygen |
| Gas extinguishes burning splint | Standard lab test for Carbon dioxide |
| Gas ignites into a slow burning orange flame with black smoke | Standard lab test for Ethyne (Acetylene) |
| Hot glass looks just like --- | Cold glass |