| A | B |
|---|
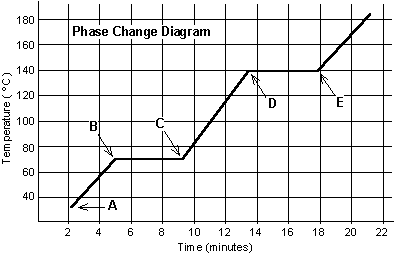 | Phase Change Diagram |
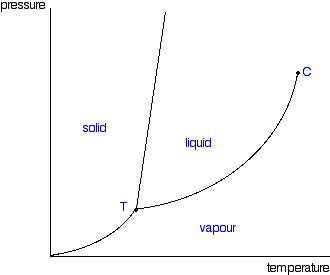 | Phase Diagram |
 | Carbon Dioxide Phase Diagram |
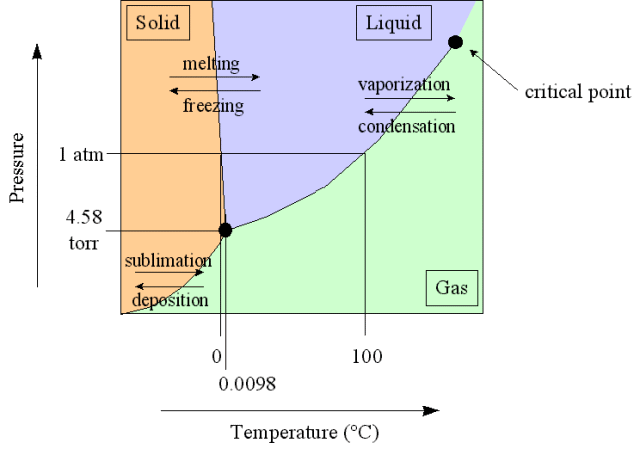 | Water Phase Diagram |
| Specific Heat | The heat capacity of a substance |
| Heat of Fusion | The amount of heat involved in a change from solid to liquid |
| Heat of Vaporization | The amount of heat involved in a change from liquid to vapor |
| Bose-Einstein Condensate | State of matter in the extreme cold of deep space |
| Plasma (state of matter) | State of matter at extremely high temperatures such as lightning bolts and nuclear fusion |
| solid | state of matter with definite shape and volume |
| vapor | state of matter without definite shape or volume |
| liquid | state of matter with definite volume but not definite shape |
| Boson | representative particle of the Bose-Einstein condensate |
| BTU | heat unit still in use for rating furnaces and air conditioners |
| Specific heat of liquid water | 1 calorie per gram degree Celsius |
| Heat of fusion of water | 80 calories per gram |
| Heat of vaporization of water | 540 calories per gram |
| calorie | amount of heat required to change the temperature of one gram of water one degree Celsius |
| 4.2 Joules | Heat equivalent to one calorie |
| Dietary Calorie | One kilocalorie (1000 calories) energy unit used to rate food energy content |
| Joule | Energy unit equal to a force of one Newton moving a distance of one meter |
| Triple point | a combination of temperature and pressure conditions at which a substance can exist in all three phases |
| critical temperature | highest temperature at which a substance can be liquified by high pressure |
| critical pressure | pressure required to liquify a substance at its critical temperature |
| sublimation | changing directly from solid to vapor phase |
| melting | changing from solid to liquid phase |
| freezing | changing from liquid to solid phase |
| evaporation | changing from liquid to vapor phase |
| boiling point | conbination of temperature and pressure conditions at which all the liquid particles will change to vapor |
| 0 Kelvin | Absolute zero, all motion stops |