| A | B |
|---|
| A ball of gas that is hot enough to sustain nuclear fusion reactions giving off tremendous amounts of electromagnetic energy is known as a(n) ____. | star |
| A ball of gas that condenses and heats up to the point where limited fusion reactions can occur, but not the sustained fusion of hydrogen-1, is called a(n) _____. | protostar |
| What is the ball of gas called when it can glow, but isn't a full fledged star yet? | A protostar |
| If a protostar never gets hot enough start fusing hydrogen-1 as fuel, it will become a _____ instead of a star. | brown dwarf |
| A protostar becomes a star when it becomes hot enough for nuclear _____ of hydrogen-1 to occur at a temperature of 10 million degrees Kelvin. | fusion |
| A protostar becomes a star when it becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion of ____ to occur at a temperature of 10 million degrees Kelvin. | hydrogen-1 |
| A protostar becomes a star when it becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion of hydrogen-1 to occur at a temperature of _____. | 10 million degrees Kelvin |
| The combining of smaller atomic nuclei into bigger atomic nuclei causing the release of huge amounts of energy is the definition of a process called _____. | nuclear fusion |
| All stars fuse _____ nuclei to create ____ nuclei as their fuel source during the main sequence part of their lifecycle. | hydrogen, helium |
| Clouds of gas and dust in space are called _____. | nebulae (a single one is called a nebula) |
| The most common gas in nebulae is _____ with the second most common being _____. | hydrogen, helium |
| Clouds of gas and dust clump together due to _____ to form protostars. | gravity |
| When pressure increases inside a protostar, this causes _____ to also increase. | temperature |
| As balls of gas start clumping together due to gravity, ______ increases which causes temperatures to increase. | pressure |
| Scientists can tell which elements are in a star by analyzing the _______ caused by elements in the surface atmosphere of stars absorbing specific wavelengths energy coming from the interior of the star. | absorption spectrum, 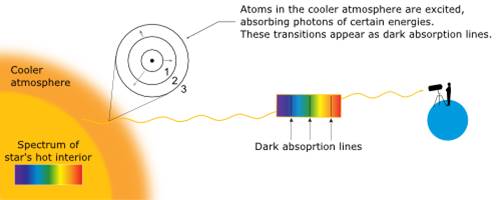 |
This picture shows the _______ for both hydrogen and helium., 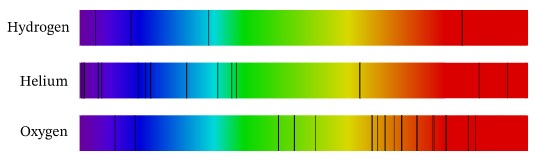 | absorption spectrum (since every element absorbs different wavelengths of energy, the absorption spectrum coming from a star can be used to identify which elements are in the gases surrounding the star),  |
The white dwarf star called Sirius B has an approximate surface temperature of _____ degrees Kelvin. (Give your answer to the nearest thousand by reading this diagram), 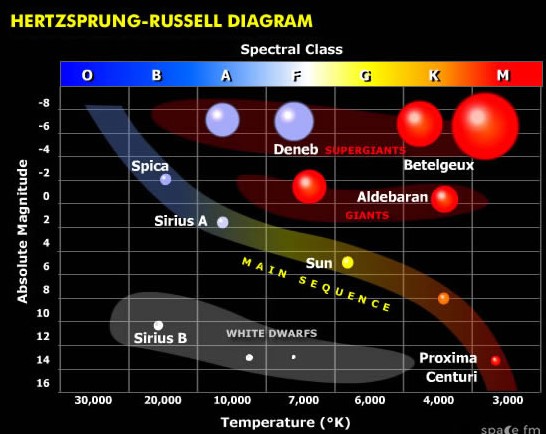 | 21,000,  |
| H-R Diagrams show the ______ of a star on the x-axis and the _____ of a star on the y-axis. | temperature, luminosity (luminosity can also be called "absolute magnitude"), 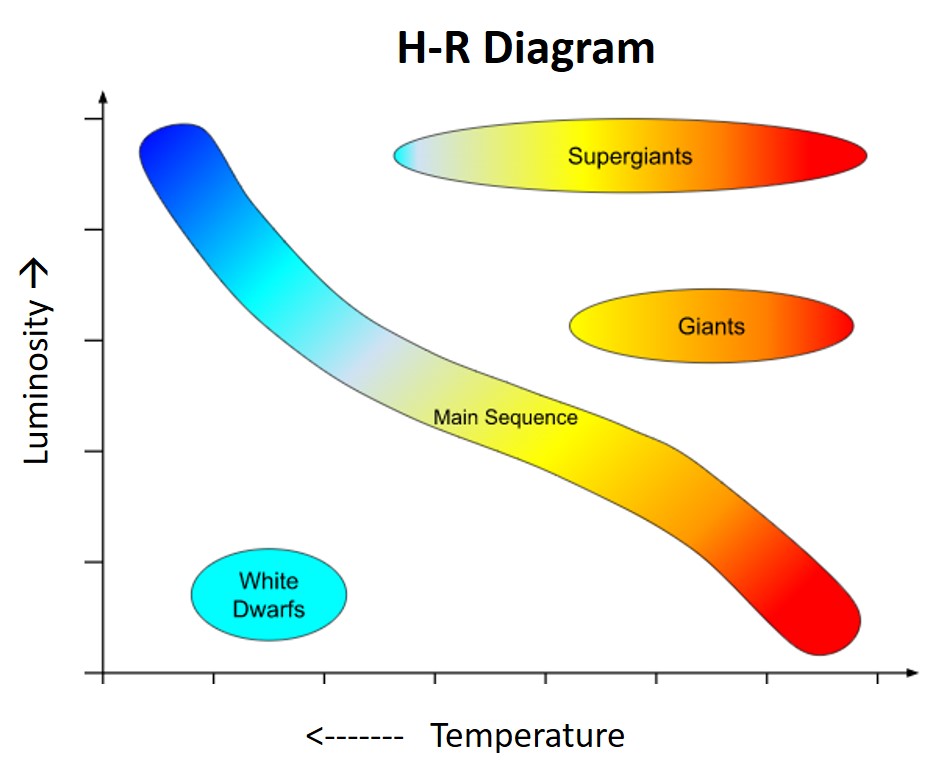 |